Insertion Sort List
Source
Sort a linked list using insertion sort. A graphical example of insertion sort. The partial sorted list (black) initially contains only the first element in the list. With each iteration one element (red) is removed from the input data and inserted in-place into the sorted list Algorithm of Insertion Sort: Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and growing a sorted output list. At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list, and inserts it there. It repeats until no input elements remain. Example 1: **Input:** 4->2->1->3 **Output:** 1->2->3->4 Example 2: **Input:** -1->5->3->4->0 **Output:** -1->0->3->4->5
题解1 - 从首到尾遍历
插入排序常见的实现是针对数组的,但这道题中的排序的数据结构为单向链表,故无法再从后往前遍历比较值的大小了。好在天无绝人之路,我们还可以从前往后依次遍历比较和交换。
由于排序后头节点不一定,故需要引入 dummy 大法,并以此节点的 next 作为最后返回结果的头节点,返回的链表从 dummy->next 这里开始构建。首先我们每次都从 dummy->next 开始遍历,依次和上一轮处理到的节点的值进行比较,直至找到不小于上一轮节点值的节点为止,随后将上一轮节点插入到当前遍历的节点之前,依此类推。
C++
/** * Definition of ListNode * class ListNode { * public: * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->next = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /** * @param head: The first node of linked list. * @return: The head of linked list. */ ListNode *insertionSortList(ListNode *head) { ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
// 这里不能直接连接head,保证已经排序好的节点与未排序好的节点是断开的 ListNode *cur = head; while (cur != NULL) { ListNode *pre = dummy; while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val < cur->val) { pre = pre->next; } ListNode *temp = cur->next; cur->next = pre->next; pre->next = cur; cur = temp; } return dummy->next; } };
Java
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
// 这里不能直接连接head,保证已经排序好的节点与未排序好的节点是断开的 ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null) { ListNode pre = dummy; while (pre.next != null && pre.next.val < cur.val) { pre = pre.next; } ListNode temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre.next; pre.next = cur; cur = temp; } return dummy.next; } }
源码分析
- 新建 dummy 节点,用以处理最终返回结果中头节点不定的情况。
- 以 cur 表示当前正在处理的节点,在从 dummy 开始遍历前保存 cur 的下一个节点作为下一轮的 cur.
- 以 pre 作为遍历节点,直到找到不小于 cur 值的节点为止。
- 将 pre 的下一个节点 pre->next 链接到 cur->next 上,cur 链接到 pre->next, 最后将 cur 指向下一个节点。
- 返回 dummy->next 最为最终头节点。
复杂度分析
最好情况:原链表已经逆序,每得到一个新节点仅需要一次比较, 时间复杂度为 O(n), 使用了 dummy 和 pre, 空间复杂度近似为 O(1).
最坏情况:原链表正好升序,由于是单向链表只能从前往后依次遍历,交换和比较次数均为 1/2 O(n^2), 总的时间复杂度近似为 O(n^2), 空间复杂度同上,近似为 O(1).
题解2 - 优化有序链表
从题解1的复杂度分析可以看出其在最好情况下时间复杂度都为 O(n^2),这显然是需要优化的。 仔细观察可发现最好情况下的比较次数是可以优化到 O(n) 的。思路自然就是先判断链表是否有序,仅对降序的部分进行处理。优化之后的代码就没题解1那么容易写对了,建议画个图自行纸上分析下。
C++
/** * Definition of ListNode * class ListNode { * public: * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->next = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /** * @param head: The first node of linked list. * @return: The head of linked list. */ ListNode *insertionSortList(ListNode *head) { ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy->next = head; ListNode *cur = head; while (cur != NULL) { if (cur->next != NULL && cur->next->val < cur->val) { ListNode *pre = dummy; // find insert position for smaller(cur->next) while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val <= cur->next->val) { pre = pre->next; } // insert cur->next after pre ListNode *temp = pre->next; pre->next = cur->next; cur->next = cur->next->next; pre->next->next = temp; } else { cur = cur->next; } } return dummy->next; } };
Java
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy.next = head; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null) { if (cur.next != null && cur.next.val < cur.val) { // find insert position for smaller(cur->next) ListNode pre = dummy; while (pre.next != null && pre.next.val < cur.next.val) { pre = pre.next; } // insert cur->next after pre ListNode temp = pre.next; pre.next = cur.next; cur.next = cur.next.next; pre.next.next = temp; } else { cur = cur.next; } } return dummy.next; } }
源码分析
- 新建 dummy 节点并将其next 指向head
- 分情况讨论,仅需要处理逆序部分。
- 由于已经确认链表逆序,故仅需将较小值(cur->next而不是cur)的节点插入到链表的合适位置。
- 将cur->next插入到pre之后,这里需要四个步骤,需要特别小心!
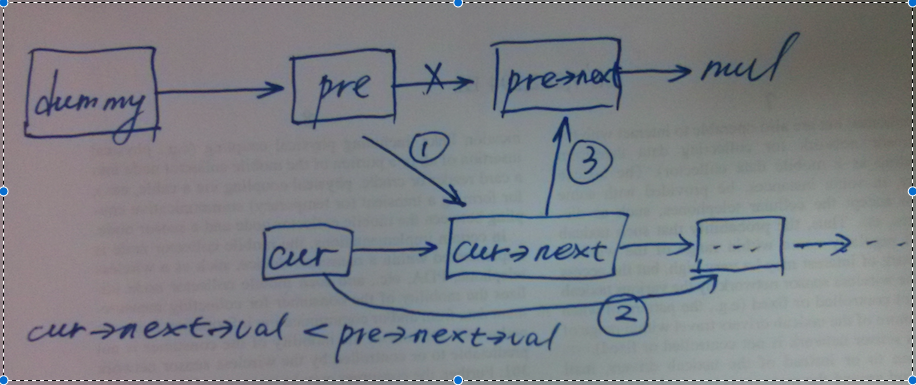
如上图所示,将cur->next插入到pre节点后大致分为3个步骤。
复杂度分析
最好情况下时间复杂度降至 O(n), 其他同题解1.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号