重学c++(三)
一、二进制文件操作
例子:
#include<string> #include<fstream> #include<istream> using namespace std; static const int bufferLen = 2048; bool CopyFile(const string &src, const string & dst) { ifstream in(src.c_str(), ios::in | ios::binary); ofstream out(dst.c_str(), ios::out | ios::binary); if (!in | !out) { return false; } char temp[bufferLen]; while (!in.eof()) { in.read(temp, bufferLen); streamsize count = in.gcount(); out.write(temp, bufferLen); } in.close(); out.close(); }
二、其他运算符重载
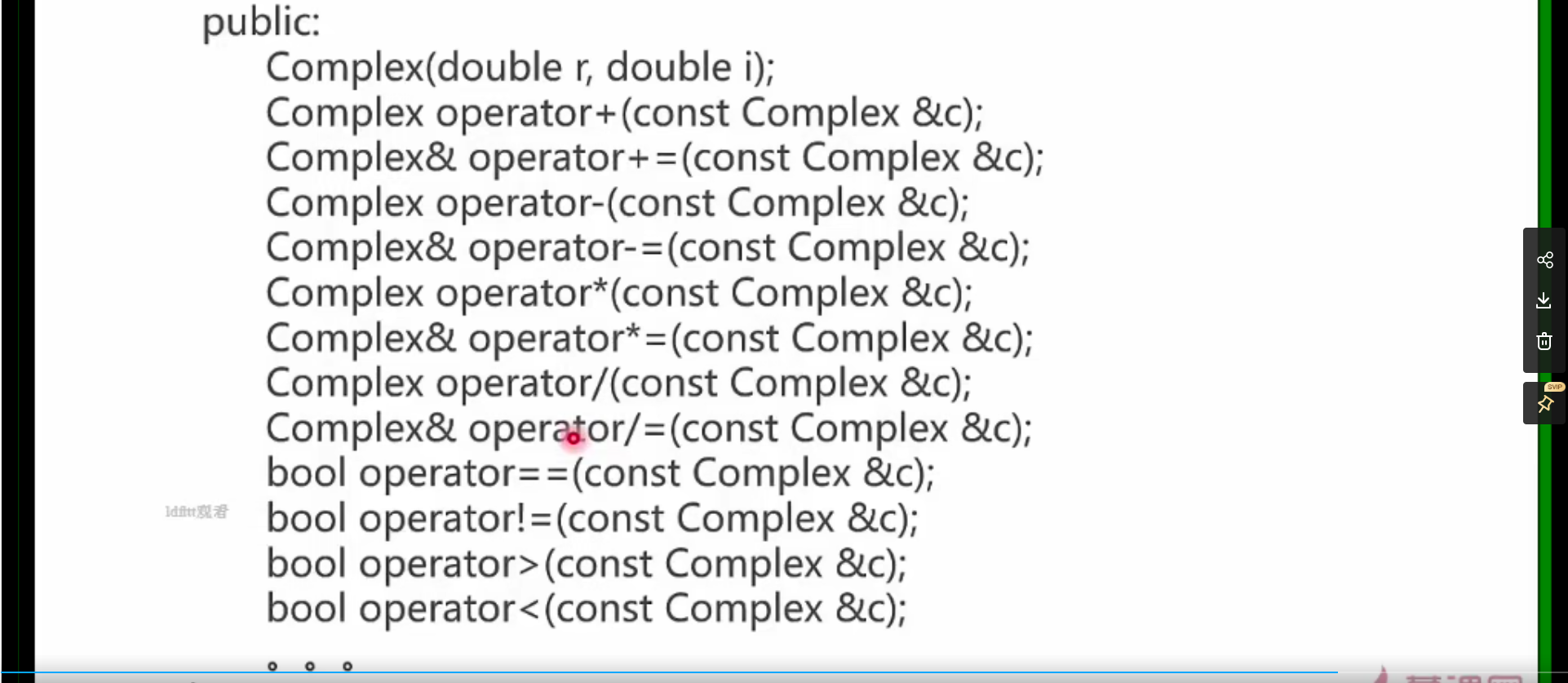
三、头文件重复问题
1、使用宏防止同一个文件被多次包含
#ifndef _SOMETHONG_H_
#define _SOMETHONG_H_
...
#endif
优:移植性好;缺:无法防止宏名重复,难以排错
2、使用编译器来防止同一个文件被多次包含
#pragma once
优:防止宏名重复;缺:移植性不好
总结:只考虑windows系统选2,否则1
四、深拷贝、浅拷贝;move语义
1、深拷贝:重新分配堆内存,拷贝指针指向内容(浪费空间但不会导致多次释放)
浅拷贝:只拷贝指针地址,c++默认拷贝构造和赋值运算符重载都是浅拷贝(节省空间,但容易引发多次释放)
2、解决深拷贝浅拷贝方法之一:move语义
类:
class String { public: String(const char* str = NULL); //普通拷贝构造函数 String(const String& other); //拷贝构造函数 String(String&& other); //移动构造函数 ~String(void); //析构函数 String& operator=(const String& other); //赋值函数 String& operator=(String&& rhs)noexcept; //移动赋值运算符(不抛出异常) friend ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const String& c);//cout输出 private: char* m_data;//用于保存字符串 };
类函数定义:
//普通拷贝构造函数 String::String(const char* str) { if (str == nullptr) { m_data = new char[1]; if (m_data != nullptr) *m_data = '\0'; else exit(-1); } else { int len = strlen(str);//_CRT_SECURE_NO_WRNNINGS m_data = new char[len+1];//结尾的\0 if (m_data != nullptr) { strcpy(m_data, str); } else exit(-1); } } //拷贝构造函数 String::String(const String& other) { int len = strlen(other.m_data);//_CRT_SECURE_NO_WRNNINGS m_data = new char[len + 1];//结尾的\0 if (m_data != nullptr) { strcpy(m_data, other.m_data); } else exit(-1); } //移动构造函数 String::String(String&& other) { if (other.m_data != nullptr) { m_data = other.m_data; other.m_data = nullptr; } } //赋值函数 String& String::operator=(const String& other) { if (this == &other) { return *this; } //释放原有内容 delete[] m_data; //重新分配资源并赋值 int len = strlen(other.m_data);//_CRT_SECURE_NO_WRNNINGS m_data = new char[len+1]; if (m_data != nullptr) { strcpy(m_data, other.m_data); } else exit(-1); } //移动赋值运算符 String& String::operator=(String&& rhs) { if (this != &rhs) { delete[]m_data; m_data = rhs.m_data; rhs.m_data = nullptr; } return *this; } ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const String& c) { os << c.m_data << endl; return os; }
主函数
int main() { String s1("Hello"); //构造函数 cout << s1 << endl; String s2(s1); //拷贝构造函数 String s2A(std::move(s1)); //移动构造函数 String s3; s3 = s2; //赋值函数 String s3A; s3A = std::move(s2A); //移动赋值运算符 }
注意:delete[]用法


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号