第二章 感知机
感知器模型数学理论
感知器(Perceptron)是一种二分类的线性分类模型,其输入为实例的特征向量,输出为实例的类别(取 +1 和 -1)。
模型定义
给定一个输入向量 \(\mathbf{x} = (x_1, x_2, \cdots, x_n)^T\),感知器模型的输出 \(y\) 由以下公式计算:
\[y = \text{sign}(\mathbf{w}^T\mathbf{x} + b)
\]
其中,\(\mathbf{w} = (w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_n)^T\) 是权重向量,\(b\) 是偏置,\(\text{sign}\) 是符号函数,定义为:
\[\text{sign}(z) =
\begin{cases}
+1, & \text{if } z \geq 0 \\
-1, & \text{if } z < 0
\end{cases}
\]
学习策略
感知器的学习目标是找到一组权重 \(\mathbf{w}\) 和偏置 \(b\),使得对于所有的训练样本 \((\mathbf{x}_i, y_i)\),都有 \(y_i(\mathbf{w}^T\mathbf{x}_i + b) > 0\)。感知器使用误分类驱动的损失函数,定义为:
\[L(\mathbf{w}, b) = -\sum_{\mathbf{x}_i \in M} y_i(\mathbf{w}^T\mathbf{x}_i + b)
\]
其中,\(M\) 是误分类样本的集合。
学习算法
感知器使用随机梯度下降法来更新权重和偏置。具体更新规则如下:
\[\mathbf{w} \leftarrow \mathbf{w} + \eta y_i \mathbf{x}_i
\]
\[b \leftarrow b + \eta y_i
\]
其中,\(\eta\) 是学习率,\((\mathbf{x}_i, y_i)\) 是一个误分类样本。
Python 实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 生成随机数据
def generate_data(num_samples):
X = np.random.randn(num_samples, 2)
y = np.sign(X[:, 0] + X[:, 1])
return X, y
# 感知器模型
class Perceptron:
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.1, max_iter=100):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.w = None
self.b = None
def fit(self, X, y):
num_samples, num_features = X.shape
self.w = np.zeros(num_features)
self.b = 0
for _ in range(self.max_iter):
misclassified = False
for i in range(num_samples):
if y[i] * (np.dot(self.w, X[i]) + self.b) <= 0:
self.w += self.learning_rate * y[i] * X[i]
self.b += self.learning_rate * y[i]
misclassified = True
if not misclassified:
break
def predict(self, X):
return np.sign(np.dot(X, self.w) + self.b)
def evaluate(self, X, y):
y_pred = self.predict(X)
accuracy = np.mean(y_pred == y)
return accuracy
# 生成数据
X, y = generate_data(100)
# 划分训练集、验证集和测试集
train_size = int(0.6 * len(X))
val_size = int(0.2 * len(X))
test_size = len(X) - train_size - val_size
X_train, X_val, X_test = X[:train_size], X[train_size:train_size+val_size], X[train_size+val_size:]
y_train, y_val, y_test = y[:train_size], y[train_size:train_size+val_size], y[train_size+val_size:]
# 训练感知器模型
perceptron = Perceptron(learning_rate=0.1, max_iter=100)
perceptron.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 验证模型
val_accuracy = perceptron.evaluate(X_val, y_val)
print(f"Validation accuracy: {val_accuracy}")
# 测试模型
test_accuracy = perceptron.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print(f"Test accuracy: {test_accuracy}")
# 可视化数据和决策边界
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='bwr')
x1 = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100)
x2 = -(perceptron.w[0] * x1 + perceptron.b) / perceptron.w[1]
plt.plot(x1, x2, 'k-')
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.title('Perceptron Classification')
plt.show()
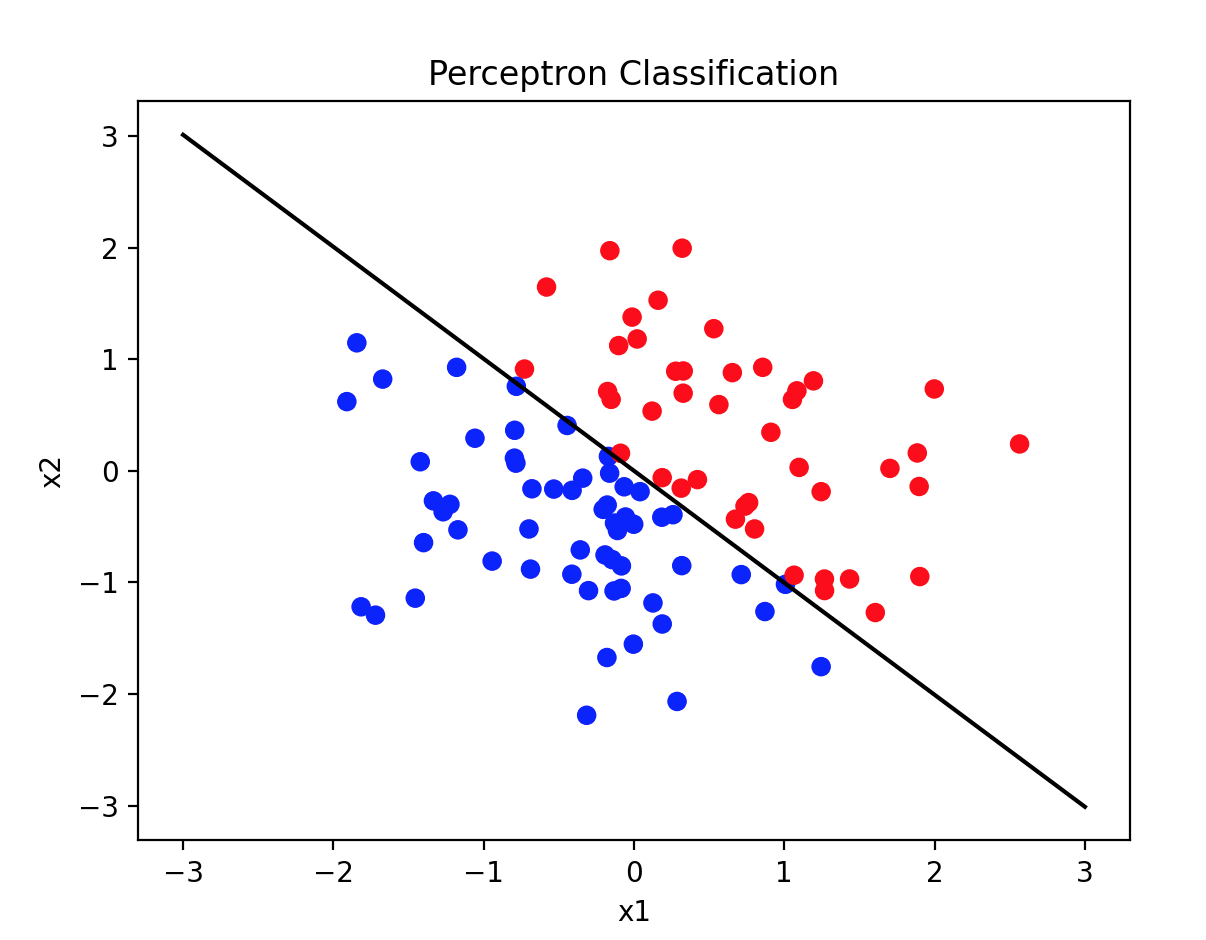
代码解释
- 数据生成:
generate_data函数生成随机的二维数据,并根据 \(x_1 + x_2\) 的符号来标记类别。 - 感知器模型:
Perceptron类实现了感知器模型的训练、预测和评估方法。 - 数据划分:将生成的数据划分为训练集、验证集和测试集。
- 模型训练:使用训练集对感知器模型进行训练。
- 模型验证和测试:使用验证集和测试集评估模型的准确率。
- 可视化:绘制数据点和决策边界。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号