软工作业-WC程序(java实现)
WC个人项目博客
github项目传送门:https://github.com/LuozhanH/WcProject
一、项目相关要求
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:
- wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
- wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
- wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
扩展功能:
- -s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。
- -a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。
二、PSP开发耗时
PSP2.1
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
40 | 60 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
40 | 60 |
|
Development |
开发 |
710 | 600 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 | 150 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
60 | 40 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 | 30 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
30 | 30 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
120 | 60 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
210 | 200 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
40 | 30 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
100 | 60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
100 | 80 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
40 | 40 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 | 30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 | 30 |
|
合计 |
850 | 740 |
三、设计程序流程
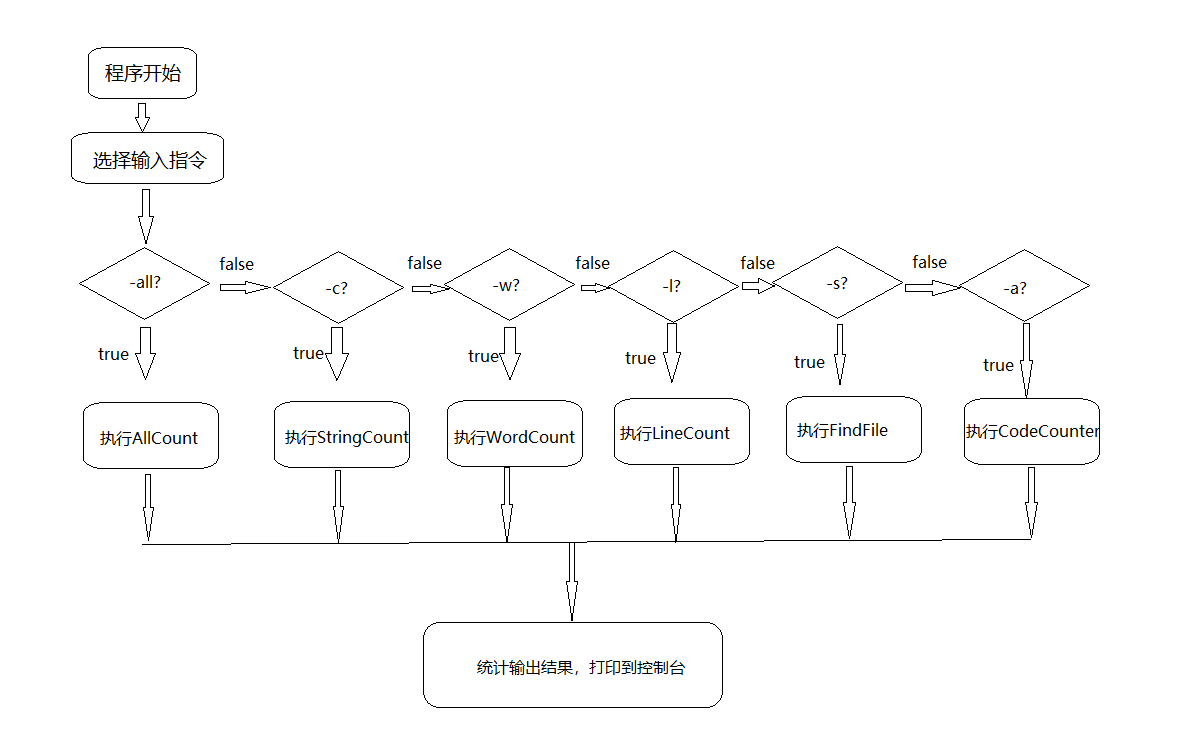
四、关键代码
项目目录:

主类代码:(启动程序)main.java
public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub while (true) { // 输出面板 System.out.println("\n---------------------3116005151 WC程序---------------------"); System.out.println("| |"); System.out.println("| -all [文件路径] 返回字符数、单词数、行数 |"); System.out.println("| -c [文件路径] 返回文件字符数 |"); System.out.println("| -w [文件路径] 返回文件词的数目 |"); System.out.println("| -l [文件路径] 返回文件行数 |"); System.out.println("| -s [文件夹路径/文件路径] 搜索文件名 |"); System.out.println("| -a [文件路径] 统计代码行/空行/注释行 |"); System.out.println("| |"); System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------"); // 获取输入指令 System.out.print("[Please...] 请输入命令:"); Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); String m = s.nextLine(); String arr[]= m.split("\\s"); // 根据获取指令来执行函数 try { switch (arr[0]){ case "-all": AllCount.wc(arr[1]);break; //返回字符数、单词数、行数 case "-c": StringCount.wc(arr[1]);break; //返回文件字符数 case "-w": WordCount.wc(arr[1]);break; //返回文件单词数目 case "-l": LineCount.wc(arr[1]);break; //返回文件行数 case "-s": FindFile.findFile(arr[1]);break; //搜索文件名 case "-a": CodeCounter.code(arr[1]);break; //统计代码行 / 空行 / 注释行 default: System.out.println("\n******** 不存在该功能指令哟(^U^)ノ~YO!!! **********");break; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("\n******** 发生错误:输入路径文件找不到!!! **********"); } catch (IOException e){ System.out.println("\n******** 发生错误:文件读入发生异常!!! **********"); } } }
逻辑函数代码:
(基本功能整合)
public class AllCount { public static int words = 1; public static int lines = 1; public static int chars = 0; // 算法实现函数 public static void wc(String p) throws IOException { // 二进制读取 FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream(p); int c = 0; // 用来判断是否为一个单词 前后空格 boolean lastNoWhite = false; String whiteSpaceFlag = " \t\n\r"; while ((c = f.read()) != -1) { chars++; if(c == '\n') { lines++; } if(whiteSpaceFlag.indexOf(c) != -1) { if(lastNoWhite) { words++; } lastNoWhite = false; } else { lastNoWhite = true; } } System.out.println("[result] 输出的结果为:"); System.out.println("[print] 行数:" + lines); System.out.println("[print] 单词数:" + words); System.out.println("[print] 字符数:" + (chars - (lines-1)*2)); } }
(拓展功能)
public class FindFile { public static void findFile(String p) { File dir = new File(p); selectFiles(dir); } public static void selectFiles(File file) { if(file.isDirectory()) { System.out.println("[result] 这是一个文件夹:" + file.getPath()); // 递归输出里面的文件 File[] files = file.listFiles(); for(File f : files) { selectFiles(f); } } else { if (file.exists()) { System.out.println("\n[result] 输出的结果为:"); System.out.println("[print] FileName:" + file.getName()); System.out.println("[print] FilePath:" + file.getPath()); System.out.println("[print] 文件可读性:" + file.canRead()); System.out.println("[print] 文件可写性:" + file.canWrite()); } else { if (!file.isFile()) { System.out.println("[error] 这不是个正确或完整的文件名!!!"); } else { System.out.println("[error] 找不到文件!!!"); } } } } }
public class CodeCounter { // 初始化变量:代码行、注释行、空行 private static Integer code = 0; private static Integer codeComments = 0; private static Integer codeBlank = 0; public static void code(String src) { File file = new File(src); factFiles(file); System.out.println("[result] 输出的结果为:"); System.out.println("[print] 代码行数:" + code); System.out.println("[print] 空白行数:" + codeBlank); System.out.println("[print] 注释行数:" + codeComments); } public static void factFiles(File file) { BufferedReader br = null; String s = null; // 如果是一个目录 则递归寻找底下符合的文件 if(file.isDirectory()) { File[] files = file.listFiles(); for(File f : files) { factFiles(f); } } else { try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); boolean comm = false; while((s = br.readLine()) != null) { // 判断是否为注释行(开始) if(s.startsWith("/*") && s.endsWith("*/")) { codeComments++; } else if(s.trim().startsWith("//")) { codeComments++; } else if(s.startsWith("/*") && !s.endsWith("*/")) { codeComments++; comm = true; } else if(!s.startsWith("/*") && s.endsWith("*/")) { codeComments++; comm = false; } else if(comm) { codeComments++; // 判断是否为注释行(结束) } else if(s.trim().length() < 1) { // 判断去掉空格之后剩余的字符数如果小于1,则为空行 codeBlank++; } else { // 除空白行和注释行外,其余皆为代码行 code++; } } br.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
五、测试运行
程序启动:
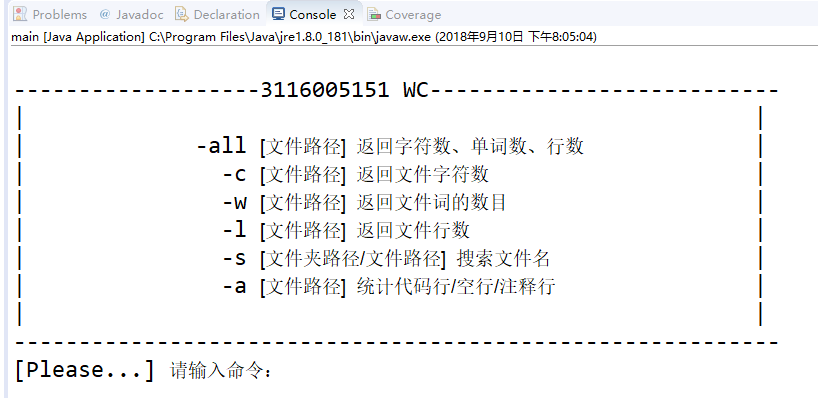
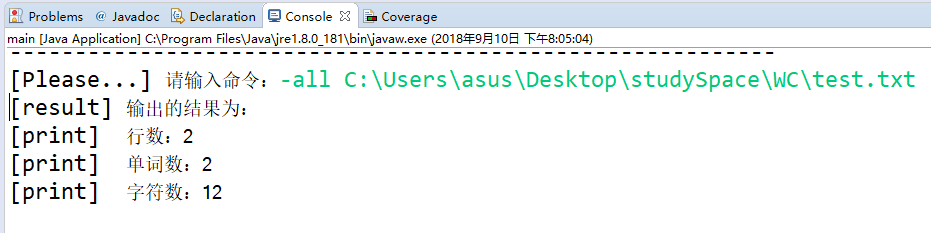
基本功能:
测试文件

测试结果
递归查询文件
测试目录
测试结果
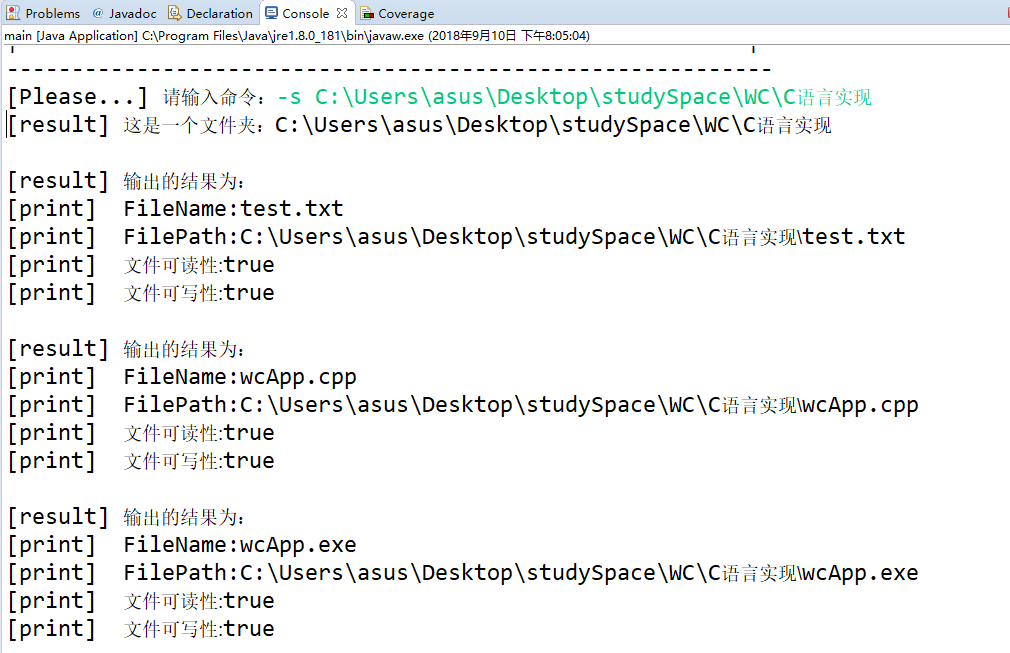
统计代码行、注释行、空行
测试文件及结果
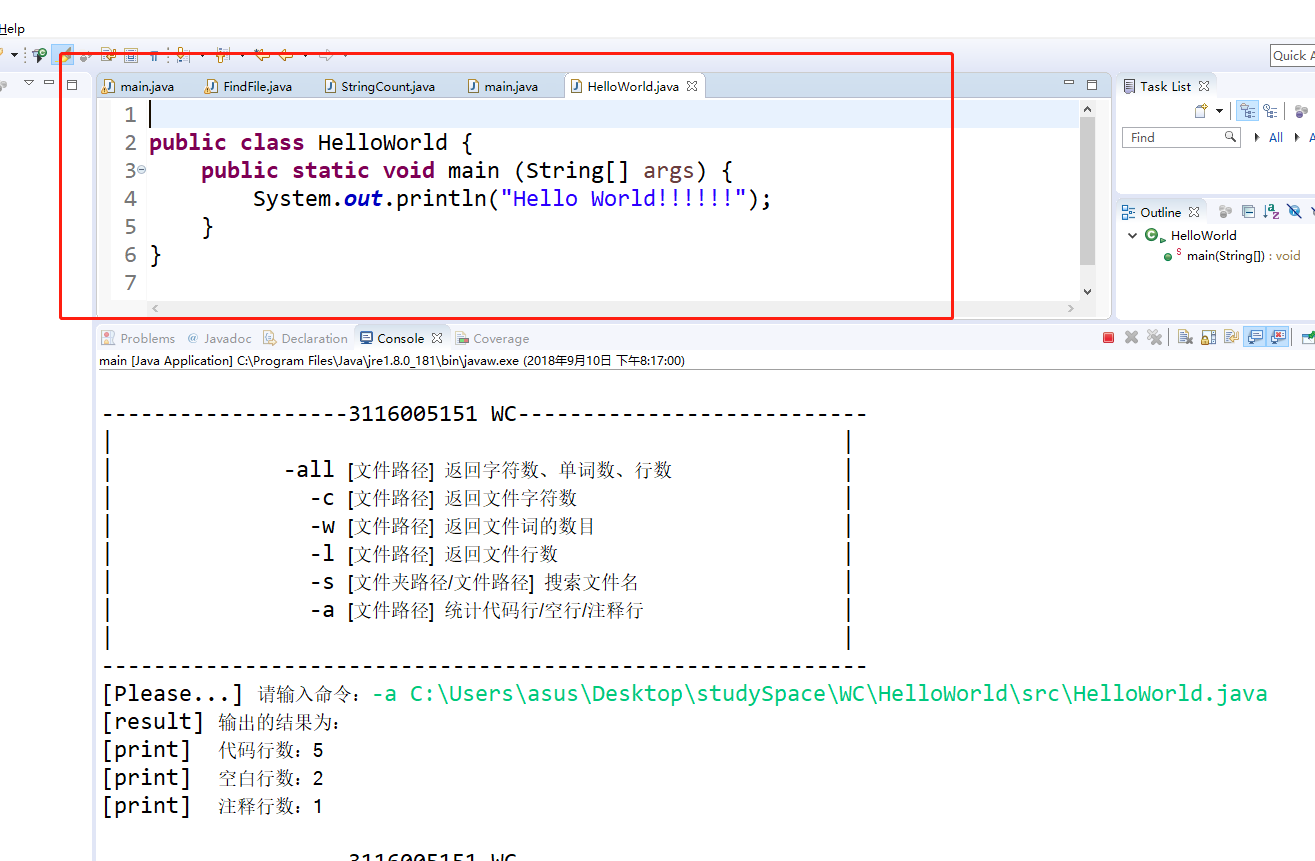
六、遇到的困难及解决方法
# 选择实现语言的困难:
由于自己在计算机学习方向是前端和美工,所以自己当初看到这个作业的时候,需要实现一个命令行程序,当时就十分纠结到底要用什么语言去实现。因为脚本语言和超文本语言都无法实现这样的功能,所以必须要另作打算。
# 编程语言不熟悉的困难:
由于太久没要写java,在编程的过程当中需要边查边写逻辑,导致写得有点慢。
# 功能实现的困难:
开始编写读取文件的时候,选择的buffer读取文件流,来实现基础的功能,发现由于个人的问题,导致字符统计的bug一直存在无法找到原因在哪。后来选择使用read()函数来进行对文件的读取操作,通过二进制流来操作。这样对于基础的判断行数、单词书、字符数功能,比buffer要实现得稍微简单一点。
# 做过的尝试:
最初,选择使用node.js来实现这个功能程序,后来选择的是c语言,但是后来又觉得习惯了面向对象编程,就想起来了大二学习的一门选修java,所以最终选择了 java 这门语言实现。
在功能实现方面,基础功能使用了read(),拓展功能时,则尝试使用了buffer来处理,直接操作内容。并在逻辑方面,有疑问的地方通过搜索一些博客参照,自己重写理念方法。
# 解决:
最后,简单地实现了基础功能以及两个拓展功能。
# 有所收获:
在这次的编程当中,深刻理解到了条条道路通罗马的道理。在一条路实现一个功能难以实现或者比较复杂的时候,应当自己要寻找另外的实现方法来实现。同时,在遇到困难的时候,一定要经过自己的思考之后,再去了解是如何实现的。这样才能够更好地理解和实现这个功能。
七、项目小结
通过这次作业,重新回顾了一下Java的知识,同时也学会了从0到1实现一个程序,从预估、设计、编码、开发、测试、文档等流程中锻炼自己。
并且,在作业当中使用了博客的方法来提交作业。第一锻炼了养成做电子笔记的习惯,第二也有了写博客的概念,同时也增强了自己代码能力外的其他学习能力。
(完)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号