/*
* main.c
*
* Created on: Oct 9, 2018
* Author: lgh
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "nlopt.h"
#define INF 1e10
int i = 0;
double step = 1;
//目标函数;
double utility(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{
if (grad) {
grad[0] = (-1.0 + x[0])*step;
grad[1] = (-2.0 + x[2])*step;
}
printf("迭代次数 i= %d, x[0]=%f, x[1]= %f,f(x1,x2)=%f\n",
i++, x[0], x[1], -x[0] - 2 * x[1] + 0.5*x[0] * x[0] + 0.5*x[1] * x[1]);
return (-x[0] - 2 * x[1] + 0.5*x[0] * x[0] + 0.5*x[1] * x[1]);
}
//不等式限制条件;
double inconstraint_1(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{
if (grad) {
grad[0] = 2.0*step;
grad[1] = 3.0*step;
}
return (2 * x[0] + 3 * x[1] - 6);
}
//不等式限制条件;
double inconstraint_2(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{
if (grad) {
grad[0] = 1.0*step;
grad[1] = 4.0*step;
}
return (x[0] + 4 * x[1] - 5);
}
//不等式限制条件;
double inconstraint_3(unsigned n, const double *x, double *grad, void *data)
{
if (grad) {
grad[0] = 2.0*step;
grad[1] = 6.0*x[1] * step;
}
return (2 * x[0] + 3 * x[1] * x[1] - 6);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
double tol = 1e-4;
double lb[2] = { 0,0 }; //x1、x2的下边界;
double ub[2] = { INF,INF };
double x[2] = { 1, 1 }; //给x1、x2赋予初始值;
double f_min;
nlopt_opt opter = nlopt_create(NLOPT_LD_SLSQP/*NLOPT_LD_MMA*/, 2);
//设置自变量下限;
nlopt_set_lower_bounds(opter, lb);
// 目标函数;
nlopt_set_min_objective(opter, utility, NULL);
// 不等式约束;
nlopt_add_inequality_constraint(opter, inconstraint_1, NULL, tol);
nlopt_add_inequality_constraint(opter, inconstraint_2, NULL, tol);
nlopt_add_inequality_constraint(opter, inconstraint_3, NULL, tol);
// 停止时需要的条件;
nlopt_set_xtol_rel(opter, tol);
// 开始优化;
nlopt_result result = nlopt_optimize(opter, x, &f_min);
if (result)
{
printf("极小值=%g, x=(%g,%g)\n", f_min, x[0], x[1]);
}
//free
nlopt_destroy(opter);
getchar();
return 0;
}
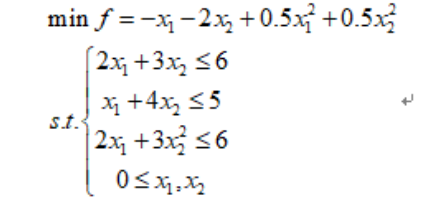


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号