node 的模块运行机制
2020-01-02 11:02 罗小二 阅读(866) 评论(0) 收藏 举报node 的模块运行机制简单了解。 涉及大概流程,略过的底层系统区别。
- CommonJS 的规范
- node 模块加载过程
- 小结
1.CommonJS 的规范
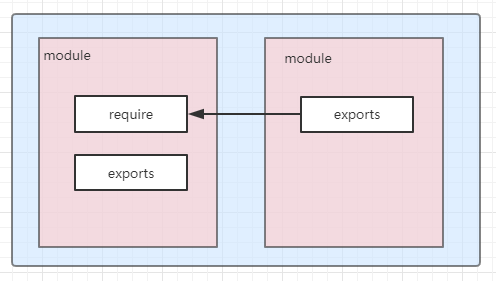
CommonJS 的规范,包括模块引用,模块定义,模块标识,3个部分
模块引用: 模块通过require方法来同步加载所依赖的模块
模块定义: 在node中一个文件就是一个模块,提供exports对象导出当前模块的方法或变量
模块标识: 模块标识传递给require()方法的参数,可以是按小驼峰(camelCase)命名的字符串,也可以是文件路径。
1.1.node 模块中CommonJS 的应用
模块内容导出两种方式:
a.js的内容如下,
方式一:可将需要导出的变量或函数挂载到 exports 对象的属性上
// node.js 每一个文件都是一个单独模块 // Node对获取的Javascript文件的内容进行了包装,以传入如下变量 console.log(exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname); // 可将需要导出的变量或函数挂载到 exports 对象的属性上, exports.name = 'luoxiaobu'; exports.age = '18'
方式二:使用 module.exports 对象整体导出一个变量对象或者函数
// node.js 每一个文件都是一个单独模块 // Node对获取的Javascript文件的内容进行了包装,以传入如下变量 console.log(exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname); let name = 'luoxiaobu'; let age = '18' // 使用 module.exports 对象整体导出一个变量对象或者函数, module.exports = {name,age};
模块的引用的方式: 按照引用模块的来源来分
// 核心模块的引入 node自己的模块 let crypto = require('crypto') // 用户自己编写的模块引入 let aModule = require('./a.js') // 第三方,别人实现发布的模块(其实也是其他用户编写) let proxy = require('http-proxy');
2.node 模块加载过程
// 非 node NativeModule function Module(id = '', parent) { this.id = id; this.path = path.dirname(id); this.exports = {}; this.parent = parent; updateChildren(parent, this, false); this.filename = null; this.loaded = false; this.children = []; }
// Set up NativeModule. function NativeModule(id) { this.filename = `${id}.js`; this.id = id; this.exports = {}; this.module = undefined; this.exportKeys = undefined; this.loaded = false; this.loading = false; this.canBeRequiredByUsers = !id.startsWith('internal/'); }
2.1 node 模块加载简述
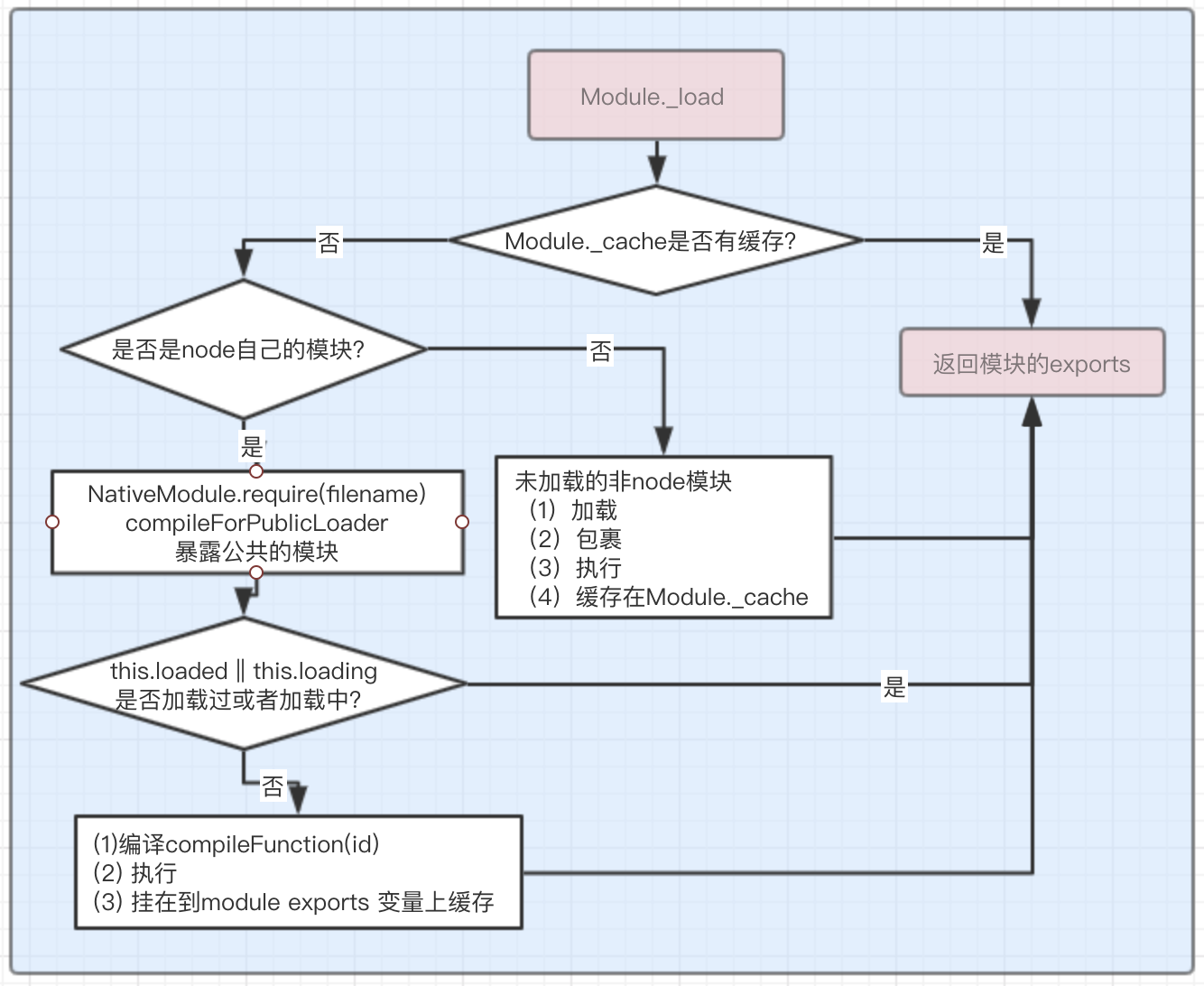
// Check the cache for the requested file. // 1. If a module already exists in the cache: return its exports object. // 2. If the module is native: call // `NativeModule.prototype.compileForPublicLoader()` and return the exports. // 3. Otherwise, create a new module for the file and save it to the cache. // Then have it load the file contents before returning its exports // object. Module._load = function(request, parent, isMain) { let relResolveCacheIdentifier; if (parent) { debug('Module._load REQUEST %s parent: %s', request, parent.id); ... } // 查找文件具体位置 const filename = Module._resolveFilename(request, parent, isMain); // 存在缓存,则不需要再次执行 返回缓存 const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename]; if (cachedModule !== undefined) { updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true); if (!cachedModule.loaded) return getExportsForCircularRequire(cachedModule); return cachedModule.exports; } // 加载node原生模块,原生模块loadNativeModule // 如果有 且能被用户引用 返回 mod.exports(这包括node模块的编译创建module对象,将模块运行结果保存在module对象上) const mod = loadNativeModule(filename, request); if (mod && mod.canBeRequiredByUsers) return mod.exports; // 创建一个模块 // Don't call updateChildren(), Module constructor already does. const module = new Module(filename, parent); if (isMain) { process.mainModule = module; module.id = '.'; } // 缓存模块 Module._cache[filename] = module; if (parent !== undefined) { relativeResolveCache[relResolveCacheIdentifier] = filename; } // 加载执行新的模块 module.load(filename); return module.exports; };
2.2 node 源码目录
大概源码结构:(只标注了部分感兴趣的)
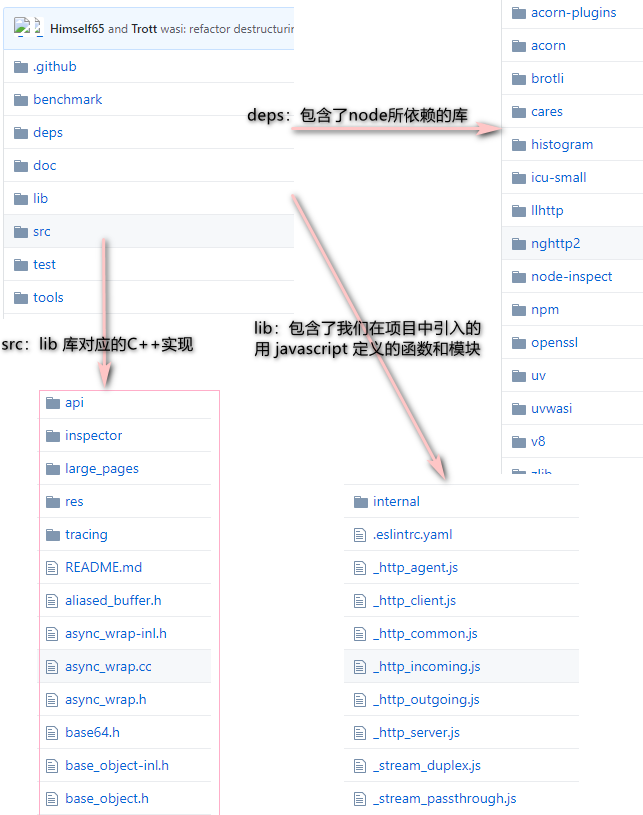
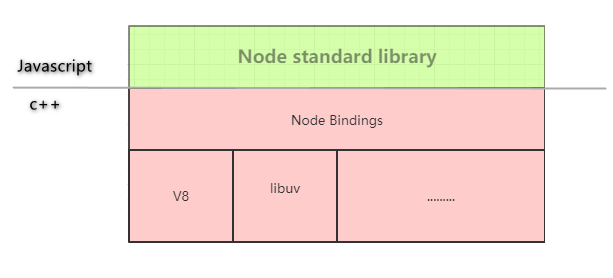
Node Bindings: 是沟通JS 和 C++的桥梁,将V8 引擎暴露的c++ 接口转换成JS API
V8: JavaScript的引擎,提供JavaScript运行环境
c++ 模块的引用大概流程
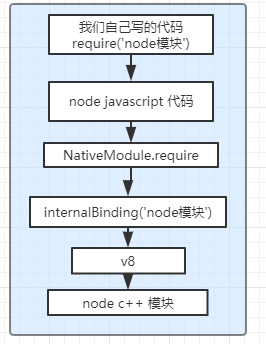
2.3 node 模块分类
// This file creates the internal module & binding loaders used by built-in// modules. In contrast, user land modules are loaded using// lib/internal/modules/cjs/loader.js (CommonJS Modules) or// lib/internal/modules/esm/* (ES Modules).//// This file is compiled and run by node.cc before bootstrap/node.js// was called, therefore the loaders are bootstraped before we start to// actually bootstrap Node.js. It creates the following objects:
- node的核心模块
- node的核心模块js实现
- node核心模块c++实现,js包裹调用c++模块
- 第三方模块,或者用户自己编写模块
-
JavaScript 模块,我们开发写的JavaScript 模
- JSON 模块,一个 JSON 文件
- C/C++ 扩展模块,使用 C/C++ 编写,编译后后缀名为 .node(感兴趣可以了解动态链接库)
-
2.3.1 node的核心模块
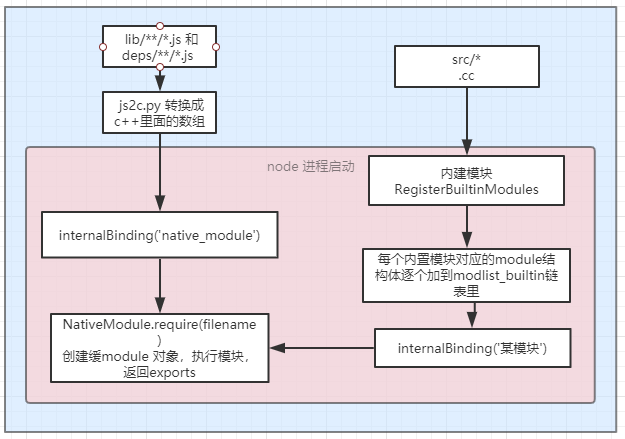
Process.binding / InternalBinding 实际上是C++函数,是用于将Node标准库中C++端和Javascript端连接起来的桥梁。
2.3.2 node的非 核心模块
- JavaScript 模块,我们开发写的JavaScript 模(或着第三方模块)
- JSON 模块,一个 JSON 文件
- C/C++ 扩展模块,使用 C/C++ 编写,编译后后缀名为 .node(感兴趣可以了解动态链接库)
此类模块的大概加载流程:
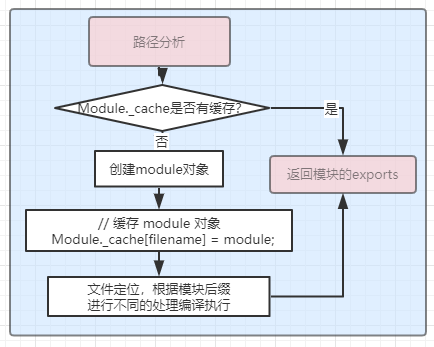
路径分析
const filename = Module._resolveFilename(request, parent, isMain);
是否有缓存
const cachedModule = Module._cache[filename]; if (cachedModule !== undefined) { updateChildren(parent, cachedModule, true); return cachedModule.exports; }
创建module对象
const module = new Module(filename, parent); // 缓存 module 对象 Module._cache[filename] = module;
文件定位根据后缀编译执行
// Native extension for .js Module._extensions['.js'] = function(module, filename) { if (experimentalModules && filename.endsWith('.js')) { const pkg = readPackageScope(filename); if (pkg && pkg.type === 'module') { throw new ERR_REQUIRE_ESM(filename); } } const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf8'); module._compile(stripBOM(content), filename); }; // Native extension for .json Module._extensions['.json'] = function(module, filename) { const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf8'); if (manifest) { const moduleURL = pathToFileURL(filename); manifest.assertIntegrity(moduleURL, content); } try { module.exports = JSON.parse(stripBOM(content)); } catch (err) { err.message = filename + ': ' + err.message; throw err; } }; // Native extension for .node Module._extensions['.node'] = function(module, filename) { if (manifest) { const content = fs.readFileSync(filename); const moduleURL = pathToFileURL(filename); manifest.assertIntegrity(moduleURL, content); } // Be aware this doesn't use `content` return process.dlopen(module, path.toNamespacedPath(filename)); };
返回module.exports 对象。
3.总结
node 的模块运行机制简单了解。 涉及大概流程,略过的底层系统区别。
文章整理了相关资料,记录了部分实践和自己的理解,理解不准确之处,还请教正。欢迎一起讨论学习。
参考资料:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号