generator 到 async 的简单理解。
2019-10-25 00:14 罗小二 阅读(2338) 评论(0) 收藏 举报generator 到 async 的简单理解。觉得实现方式很有意思。
1. generator
generator 函数返回一个遍历器对象
遍历器对象 每次调用next 方法 返回 有着value 和done 两个属性的对象
generator 函数 yield 后面的表达式即为 返回对象 value属性的值
举个简单例子:

generator 函数返回一个遍历器
遍历器对象每执行一次next() 都只执行了generator 函数内部部分代码,遇到yield本次执行就结束了。
借助工具查看generator 经过转换后的代码,来了解一下generator 的大概实现
源码
1 function *gen() { 2 console.log('开始') 3 let a = yield '第一步' 4 console.log(a) 5 let b = yield '第二步' 6 console.log(b) 7 let c = yield '第三步' 8 console.log(c) 9 } 10 11 var it = gen() 12 console.log(it.next('')) 13 console.log(it.next()) 14 console.log(it.next()) 15 console.log(it.next())
转换后的代码如图(有图可见,原来的gen函数代码被转换成switch case的函数了,这个函数,就像状态机,状态不同,跳转执行的结果不同)

如图,查看源码,左边函数,被准换成右边带有状态的switch 片段
执行it.next() 的时候,内部就会调用左边的while 包裹的函数,默认_context_next = 0 (_context是内部用来存储 状态 ,next传入参数,等值得)
将_context_next 的值付给_context_prev,_context_prev就是当前传入switch的值,执行对应的case片段,修改 _context_next的值 ,return 跳出while循环
下一次调用it.next() 的时候,内部又调用左边的while 包裹的函数,将_context_next 的值付给_context_prev,_
context_prev就是当前传入switch的值,执行对应的case片段,修改 _context_next的值,return 跳出while循环
如此重复上面片段 直到 执行第四个 it.next的时候 ,执行对应的case片段,没有return 接着会执行 case: end
执行 _context_stop() 函数,得到 第四个 it.next()的返回值,{value:undefined, done: true} 迭代结束。
借助查看babel,regenerator的实现 查找上图的几个函数,来看看以下细节
-
regeneratorRuntime.mark (包裹函数,返回新函数,新函数能生成迭代器)
-
_context (保留函数执行的上下文状态)
-
新的$gen,由gen数中的每个 yield 表达式分割的片段都重写为 switch case的函数,每个 case 中使用 _context 来保存函数当前的上下文状态。
- regeneratorRuntime.wrap (设置调用函数,这个地方设计的特别好,暴露接口,由makeInvokeMehtod来设置具体的invoke方法)

看看 makeInvokeMethod 返回的 invoke 方法

从上面分析可以看出 不断调用next方法 就是不断调用 switch case($gen函数) , _context做记录
再次调用next方法 方法 因为标记状态变了,执行的case 就变了。
2. generator 简单实现
generator 函数返回一个遍历器对象,对象有next方法。
遍历器对象每次调用next 方法 返回 有着value 和done 两个属性的对象
generator 函数 yield 后面的表达式即为 返回对象 value属性的值
1 // 第一步通过将原函数简单转换 (babel 编译过程中的节点修改可以了解一下) 2 // function genSourceCode() { 3 // console.log('开始') 4 // let a = yield '第一步' 5 // console.log(a) 6 // let b = yield '第二步' 7 // console.log(b) 8 // let c = yield '第三步' 9 // console.log(c) 10 // } 11 // 原函数变成由gen数中的每个 yield 表达式分割的片段都重写为 switch case的新函数 12 function gen$(_context) { 13 while (1) { 14 switch (_context.prev = _context.next) { 15 case 0: 16 console.log('开始'); 17 _context.next = 3; 18 return '第一步'; 19 20 case 3: 21 a = _context.sent; 22 console.log(a); 23 _context.next = 7; 24 return '第二步'; 25 26 case 7: 27 b = _context.sent; 28 console.log(b); 29 _context.next = 11; 30 return '第三步'; 31 32 case 11: 33 c = _context.sent; 34 console.log(c); 35 36 case 13: 37 case "end": 38 return _context.stop(); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 // context 43 var context = { 44 next:0, 45 prev: 0, 46 sent: undefined, // 这个值是用来记住每次调用next函数传递的参数 47 done: false, 48 stop: function stop () { 49 this.done = true 50 } 51 } 52 53 let gen = function() { 54 return { 55 next: function() { 56 value = context.done ? undefined: gen$(context) 57 done = context.done 58 return { 59 value, 60 done 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 var it = gen() 66 console.log(it.next()) 67 console.log(it.next()) 68 console.log(it.next()) 69 console.log(it.next())
3. generator产生的迭代器对象 ,迭代自执行
手动麻烦,产生了自执行的需求:
1 function* gen() { 2 console.log('开始') 3 let a = yield '第一步' 4 console.log(a) 5 let b = yield '第二步' 6 console.log(b) 7 let c = yield '第三步' 8 console.log(c) 9 } 10 11 var it = gen() 12 console.log(it.next('')) 13 console.log(it.next()) 14 console.log(it.next()) 15 console.log(it.next()) 16 17 function co(gen) { 18 let it = gen() 19 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { 20 !(function next(lastValue) { 21 let { value, done } = it.next(lastValue) 22 console.log({ value, done }) 23 if (done) { 24 resolve(value) 25 } else { 26 Promise.resolve(value).then(next,reason => reject(reason)) 27 } 28 })() 29 }) 30 } 31 co(gen)
自执行函数,会将上一次it.next()得到的value值传递到下一个it.next()输出中 下面这行代码值得思考
Promise.resolve(value).then(next,reason => reject(reason))
4. async的简单实现
async函数,实现 基于 generator 函数和自动执行器。
1 function spawn(gen) { 2 return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { 3 const it = gen() 4 !function step(nextFn) { 5 try{ 6 var {value, done } = nextFn() 7 } catch(e) { 8 reject(e) 9 return 10 } 11 if (done) { 12 resolve(value) 13 } else { 14 Promise.resolve(value).then((value)=>{ 15 step((value)=>it.next(value)) 16 },()=>{ 17 step((value)=>it.throw(value)) 18 }) 19 } 20 }(()=>it.next(undefined)) 21 }) 22 } 23 function* gen() { 24 try { 25 var a = yield new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 26 setTimeout(()=>{ 27 reject(100) 28 },1000) 29 }) 30 } catch(e) { 31 } 32 let b = yield new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 33 setTimeout(()=>{ 34 resolve(102) 35 },1000) 36 }) 37 return a + b 38 } 39 40 async function asyncDemo() { 41 try { 42 var a = await new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 43 setTimeout(()=>{ 44 reject(100) 45 },1000) 46 }) 47 } catch(e) { 48 49 } 50 let b = await new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 51 setTimeout(()=>{ 52 resolve(102) 53 },1000) 54 }) 55 return a + b 56 } 57 58 spawn(gen).then((value)=>{ 59 console.log('spawn-->onfulfilled:',value) 60 },(value)=>{ 61 console.log('spawn-->onRejected:',value) 62 }) 63 asyncDemo().then((value)=>{ 64 console.log('asyncDemo-->onfulfilled:',value) 65 },(value)=>{ 66 console.log('asyncDemo-->onRejected:',value) 67 })
运行上面代码 对async理解就比较深刻了。async 的内部实现generator 函数和自执行函数 。
5.总结
函数转换成 switch case 组成的函数(代码有点似状态机模型)
async 的内部实现包括了generator 函数和自执行函数
1 try { 2 var a = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => { 3 setTimeout(() => { 4 reject(100) 5 }, 1000) 6 }) 7 } catch (e) { 8 console.log(e) 9 }
1 async function asyncDemo() { 2 console.log('asyncDemo') 3 let a = await new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 4 setTimeout(()=>{ 5 reject(100) 6 },1000) 7 }) 8 console.log('asyncDemo--->b') 9 //为何下面代码没有执行 10 let b = await new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 11 setTimeout(()=>{ 12 resolve(102) 13 },1000) 14 }) 15 return a + b 16 } 17 18 async function asyncDemo2() { 19 console.log('asyncDemo2') 20 try { 21 var a = await new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 22 setTimeout(()=>{ 23 reject(100) 24 },1000) 25 }) 26 } catch(e){ 27 console.log(e) 28 } 29 //为何下面代码执行了 自执行出错有try catch 时候会增加一步走catch节点。 30 console.log('asyncDemo2--->b') 31 let b = await new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{ 32 setTimeout(()=>{ 33 resolve(102) 34 },1000) 35 }) 36 return a + b 37 } 38 asyncDemo().then(null,(reason)=>{ 39 console.log('asyncDemo:',reason) 40 }) 41 asyncDemo2().then((reason)=>{ 42 console.log('asyncDemo:',reason) 43 })
工具查看转化的代码,自执行出错有try catch 时候会增加一步走catch节点。
当case的promise rejected 的时候context.next 会被改变成case 6,
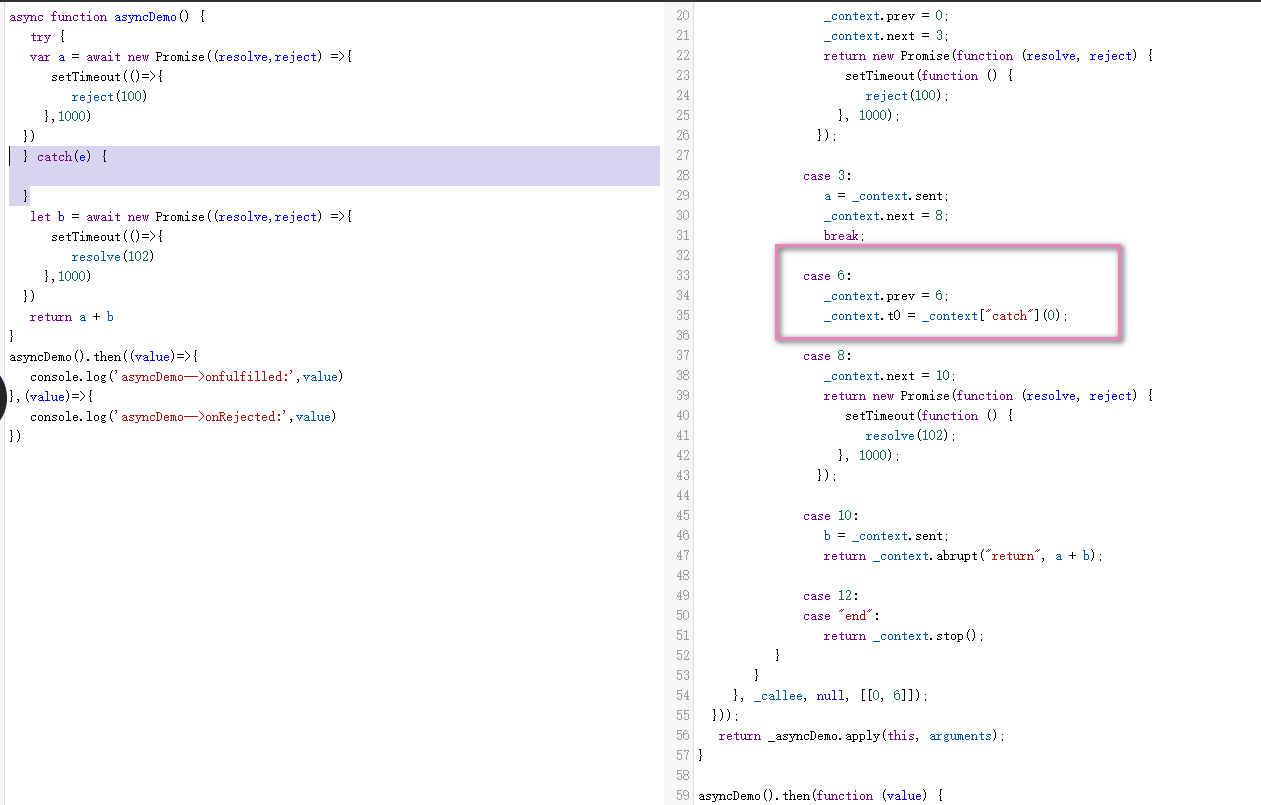
如图case 6:执行后没break 和return 则继续执行 case 8


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号