PTA题目集及期中考试的总结性Blog
(1)前言:
(1) 难度分析:这几次大作业题目因为图形更加复杂所以难度是逐渐增加的,到了五边形情况变得更加复杂,要及格要花很长的时间。
(2) 题量分析:题量的话第四次作业有三题,但有两道简单题,第二题四边形要花较长的时间。第五次作业是五边形,难度较大要花的时间是最多的。
(3) 知识点总结:选择结构应用、字符型数据与数值型数据之间的类型转换、一维数组、方法的定义与调用、循环结构、正则表达式、继承、多态。
(2)设计与分析:
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
选项1、2、3中,若四边形四个点中有重合点,输出"points coincide"。
选项4中,若前两个输入线的点重合,输出"points coincide"。
源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 import java.text.DecimalFormat; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 9 String str=input.nextLine(); 10 11 InputData date=new InputData(); 12 ParseInput.paseInput(str, date);//输入解析,将str解析到date 13 // PointInputjug.wrongPointFormat(str); 14 int choice = date.getChoice();//1-5 15 ArrayList points = date.getPoints(); 16 17 switch (choice) { 18 case 1: 19 handle1(points); 20 break; 21 case 2: 22 handle2(points); 23 break; 24 case 3: 25 handle3(points); 26 break; 27 case 4: 28 handle4(points); 29 break; 30 case 5: 31 handle5(points); 32 break; 33 } 34 } 35 public static void handle1(ArrayList<Point> ps) { 36 PointInputjug.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 4); 37 fourline t = new fourline(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2),ps.get(3)); 38 39 t.Isparallelogram(); 40 // System.out.println(t.isfourline); 41 //System.out.println(t.isIsoscelesTriangle() + " " + t.isEquilateralTriangle()); 42 43 } 44 public static void handle2(ArrayList<Point> ps) { 45 PointInputjug.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 4); 46 fourline t = new fourline(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2),ps.get(3),2); 47 48 System.out.print(t.Isdiamond()+" "+t.Isrectangular()+" "+t.Isqart()); 49 50 } 51 public static void handle3(ArrayList<Point> ps) { 52 PointInputjug.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 4); 53 fourline t = new fourline(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2),ps.get(3),3); 54 Triangle1 a=new Triangle1(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2)); 55 Triangle1 b=new Triangle1(ps.get(0), ps.get(3), ps.get(2)); 56 // System.out.print(a.getArea()+" "); 57 58 double s=t.Area(); 59 double c=t.Perimeter(); 60 System.out.print(t.Isout()+" "); 61 System.out.print(Double.valueOf(new DecimalFormat("0.0##").format(c))+" "); 62 System.out.print(Double.valueOf(new DecimalFormat("0.0##").format(s))); 63 64 } 65 public static void handle4(ArrayList<Point> ps) { 66 PointInputjug.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 6); 67 68 } 69 public static void handle5(ArrayList<Point> ps) { 70 PointInputjug.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 6); 71 72 } 73 74 } 75 76 //输出的格式化 77 class InputData { 78 private int choice;;//用户输入的选择项 79 private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();//用户输入的点坐标 80 public int getChoice() { 81 return choice; 82 } 83 public void setChoice(int choice) { 84 this.choice = choice; 85 } 86 public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() { 87 return points; 88 } 89 public void addPoint(Point p) { 90 this.points.add(p); 91 } 92 93 } 94 95 class PointInputjug { 96 //判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。 97 public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) { 98 if (ps.size() != num) { 99 System.out.println("wrong number of points"); 100 System.exit(0); 101 } 102 } 103 //判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序 104 public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) { 105 if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) { 106 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 107 System.exit(0); 108 } 109 } 110 111 // 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一 112 public static void wrongChoice(String s) { 113 if (!s.matches("[1-5]:.+")) { 114 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 115 System.exit(0); 116 } 117 } 118 } 119 120 class ParseInput { 121 /* 122 * 输入:完整的输入字符串,包含选项和所有点的信息,格式:选项:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn。选项只能是1-5 123 * 一个空InputData对象 124 * 处理:将输入字符串中的选项和点信息提取出来并设置到InputData对象中 125 * 输出:包含选项值和所有点的Point对象的InputData对象。 126 */ 127 public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) { 128 PointInputjug.wrongChoice(s); 129 d.setChoice(getChoice(s)); 130 s = s.substring(2); 131 pasePoints(s, d); 132 } 133 //获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分 134 public static int getChoice(String s) { 135 char c = s.charAt(0); 136 return c-48; 137 } 138 139 /* 140 * 输入:一个字符串,包含所有点的信息,格式:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn 141 * 一个空InputData对象 142 * 输出:所有点的Point对象 143 */ 144 public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) { 145 String[] ss = s.split(" "); 146 if (ss.length == 0) 147 return; 148 for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) { 149 d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i])); 150 } 151 } 152 153 /* 154 * 输入:包含单个点信息的字符串,格式:x,y 155 * 输出:Point对象 156 */ 157 public static Point readPoint(String s) { 158 PointInputjug.wrongPointFormat(s); 159 String[] ss = s.split(","); 160 double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]); 161 double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]); 162 163 return new Point(x, y); 164 } 165 } 166 class Point{ 167 double x; 168 double y; 169 public Point(double x,double y) 170 { 171 this.x=x; 172 this.y=y; 173 } 174 //equals方法的重写 175 @Override 176 public boolean equals(Object obj) 177 { 178 if(this ==obj) 179 return true; 180 if(obj instanceof Point) 181 { 182 Point aobj=(Point)obj; 183 if(aobj.x==this.x&&aobj.y==this.y) 184 return true; 185 else 186 return false; 187 } 188 else 189 return false; 190 191 } 192 193 194 double calculation(Point p) 195 { 196 return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p.x - x, 2) + Math.pow(p.y - y, 2)); 197 } 198 } 199 200 class Line{ 201 Point p1; 202 Point p2; 203 204 public Line(Point p1,Point p2){ 205 samepoint(p1,p2); 206 this.p1=p1; 207 this.p2=p2; 208 } 209 //长度的计算 210 public double distance(){ 211 return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p1.x-p2.x,2)+Math.pow(p1.y-p2.y,2)); 212 } 213 //斜率的计算 214 public double Slope(){ 215 return (p1.y-p2.y)/(p1.x-p2.x); 216 } 217 public static double Slope(Point p3,Point p4){ 218 return (p3.y-p4.y)/(p3.x-p4.x); 219 } 220 //点是否相同 221 public void samepoint(Point p1,Point p2){ 222 if(p1.equals(p2)) 223 { 224 System.out.print("points coincide"); 225 System.exit(0); 226 } 227 } 228 229 //是否大小相同,相同返回true,否则false。 230 public boolean isDistance(Line l){ 231 Double b1 = this.distance(); 232 Double b2 = l.distance(); 233 //if((b1-b2)<0.00000000001) 234 if( this.distance() ==l.distance()) 235 return true; 236 else 237 return false; 238 } 239 240 } 241 //三角形 242 class Triangle1 { 243 Point x; 244 Point y; 245 Point z; 246 247 public Triangle1(Point x, Point y, Point z) { 248 this.x = x; 249 this.y = y; 250 this.z = z; 251 } 252 //三角形周长计算 253 public double getPerimeter() { 254 return x.calculation(y) + y.calculation(z) + z.calculation(x); 255 } 256 //三角形面积计算 257 public double getArea() { 258 Line line1 = new Line(x, y); 259 Line line2 = new Line(x, z); 260 Line line3 = new Line(y, z); 261 double p=1/2.0*getPerimeter(); 262 263 return Math.sqrt(p*(p-line1.distance())*(p-line2.distance())*(p-line3.distance())); 264 } 265 } 266 class fourline{ 267 Point l1; 268 Point l2; 269 Point l3; 270 Point l4; 271 272 273 public fourline(Point l1,Point l2,Point l3,Point l4){ 274 this.l1=l1; 275 this.l2=l2; 276 this.l3=l3; 277 this.l4=l4; 278 // System.out.println("true false");10的答案 279 //false false剩下的四边形错误 280 if (!this.isfourline()) { 281 System.out.print("false false"); 282 System.exit(0); 283 } 284 /* else 285 { 286 // System.out.print("true"); 287 if(this.Isparallelogram()) 288 System.out.print("true true"); 289 else 290 System.out.print("true false"); 291 // System.exit(0); 292 } */ 293 } 294 public fourline(Point l1,Point l2,Point l3,Point l4,int a){ 295 this.l1=l1; 296 this.l2=l2; 297 this.l3=l3; 298 this.l4=l4; 299 // System.out.println("true false");10的答案 300 //false false剩下的四边形错误 301 if (!this.isfourline()) { 302 System.out.print("not a quadrilateral"); 303 System.exit(0); 304 } 305 306 } 307 //判断是否为四边形(斜率大小是否有相等) 308 public boolean isfourline(){ 309 Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); 310 311 Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); 312 313 Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); 314 315 Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); 316 317 double a=l1.x,b=l2.x,c=l3.x,d=l4.x; 318 double []f={a,b,c,d}; 319 Arrays.sort(f); 320 if(f[0]==f[1]&&f[2]==f[1]) 321 return false; 322 if(Line.Slope(l1,l2)!=Line.Slope(l1,l3)&&Line.Slope(l1,l2)!=Line.Slope(l1,l4)&&Line.Slope(l2,l3)!=Line.Slope(l2,l4)) 323 return true; 324 return false; 325 } 326 327 //判断是否为平行四边形 328 public void Isparallelogram(){ 329 Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); 330 Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); 331 Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); 332 Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); 333 // System.out.println(line2.distance()); 334 // System.out.println(line4.distance()); 335 // System.out.println(line2.isDistance(line4)); 336 if(line2.isDistance(line4)&&line1.isDistance(line3)) 337 //if((line1.distance() == line3.distance()) && (line2.distance() == line4.distance()))//test 338 { 339 System.out.print("true true"); 340 return ; 341 } 342 else 343 System.out.print("true false"); 344 return ; 345 } 346 //判断是否为菱形(四条边都相等) 347 public boolean Isdiamond(){ 348 Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); 349 Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); 350 Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); 351 Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); 352 353 if(line2.isDistance(line4)&&line1.isDistance(line3)&&line2.isDistance(line1)) 354 //System.out.print("true "); 355 return true; 356 else 357 return false; 358 } 359 //判断是否为矩形(对边平行且平分) 360 public boolean Isrectangular(){ 361 Line line1 = new Line(l1, l3); 362 Line line2 = new Line(l2, l4); 363 double x=(l1.x+l2.x+l3.x+l4.x)/4.0; 364 double y=(l1.y+l2.y+l3.y+l4.y)/4.0; 365 Point pointm=new Point(x,y); 366 367 if(line1.isDistance(line2)&&pointm.calculation(l1)==pointm.calculation(l3)&&pointm.calculation(l2)==pointm.calculation(l4)) 368 return true; 369 else 370 return false; 371 } 372 //是否是正方形 373 public boolean Isqart(){ 374 if(Isrectangular()==true&&Isdiamond()==true) 375 return true; 376 else 377 return false; 378 } 379 //凹凸性的判断(拿面积大小进行比较) 380 public boolean Isout(){ 381 Triangle1 a=new Triangle1(l1,l2,l3); 382 Triangle1 b=new Triangle1(l1,l4,l3); 383 Triangle1 c=new Triangle1(l4,l2,l3); 384 Triangle1 d=new Triangle1(l2,l4,l1); 385 if((a.getArea()+b.getArea())==(c.getArea()+d.getArea())) 386 return true; 387 else 388 return false; 389 } 390 //四边形面积大小计算加判断 391 public double Area(){ 392 Triangle1 a=new Triangle1(l1,l2,l3); 393 Triangle1 b=new Triangle1(l1,l4,l3); 394 Triangle1 c=new Triangle1(l4,l2,l3); 395 Triangle1 d=new Triangle1(l2,l4,l1); 396 if(Isout()) 397 { 398 return a.getArea()+b.getArea(); 399 } 400 else 401 { 402 if((a.getArea()+b.getArea())>(c.getArea()+d.getArea())) 403 return c.getArea()+d.getArea(); 404 else 405 return a.getArea()+b.getArea(); 406 } 407 } 408 //四边形周长 409 public double Perimeter() { 410 Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); 411 Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); 412 Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); 413 Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); 414 return line1.distance()+line2.distance()+line3.distance()+line4.distance(); 415 } 416 }
分析:
题目分析:
题目和三角形的类似,有五个选项,对应五个要求,我在三角形的代码上加了个四边形类。
代码分析:
case1: 判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,
//判断是否为四边形(斜率大小是否有相等) public boolean isfourline(){ Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); double a=l1.x,b=l2.x,c=l3.x,d=l4.x; double []f={a,b,c,d}; Arrays.sort(f); if(f[0]==f[1]&&f[2]==f[1]) return false; if(Line.Slope(l1,l2)!=Line.Slope(l1,l3)&&Line.Slope(l1,l2)!=Line.Slope(l1,l4)&&Line.Slope(l2,l3)!=Line.Slope(l2,l4)) return true; return false; } //判断是否为平行四边形 public void Isparallelogram(){ Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); if(line2.isDistance(line4)&&line1.isDistance(line3)) { System.out.print("true true"); return ; } else System.out.print("true false"); return ; }
我先判断是否能构成四边形,如果相邻两条边斜率相等则不是四边形,
如果是四边形,则再判断对边是否平行,对边平行则是平行四边形。
case2:判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形
//判断是否为菱形(四条边都相等) public boolean Isdiamond(){ Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); if(line2.isDistance(line4)&&line1.isDistance(line3)&&line2.isDistance(line1)) //System.out.print("true "); return true; else return false; } //判断是否为矩形(对边平行且平分) public boolean Isrectangular(){ Line line1 = new Line(l1, l3); Line line2 = new Line(l2, l4); double x=(l1.x+l2.x+l3.x+l4.x)/4.0; double y=(l1.y+l2.y+l3.y+l4.y)/4.0; Point pointm=new Point(x,y); if(line1.isDistance(line2)&&pointm.calculation(l1)==pointm.calculation(l3)&&pointm.calculation(l2)==pointm.calculation(l4)) return true; else return false; } //是否是正方形 public boolean Isqart(){ if(Isrectangular()==true&&Isdiamond()==true) return true; else return false; }
方法都类似,
菱形(四条边都相等)
矩形(对边平行且相等)
根据性质很好判断。
case3: 判断凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积
//凹凸性的判断(拿面积大小进行比较) public boolean Isout(){ Triangle1 a=new Triangle1(l1,l2,l3); Triangle1 b=new Triangle1(l1,l4,l3); Triangle1 c=new Triangle1(l4,l2,l3); Triangle1 d=new Triangle1(l2,l4,l1); if((a.getArea()+b.getArea())==(c.getArea()+d.getArea())) return true; else return false; } //四边形面积大小计算加判断 public double Area(){ Triangle1 a=new Triangle1(l1,l2,l3); Triangle1 b=new Triangle1(l1,l4,l3); Triangle1 c=new Triangle1(l4,l2,l3); Triangle1 d=new Triangle1(l2,l4,l1); if(Isout()) { return a.getArea()+b.getArea(); } else { if((a.getArea()+b.getArea())>(c.getArea()+d.getArea())) return c.getArea()+d.getArea(); else return a.getArea()+b.getArea(); } } //四边形周长 public double Perimeter() { Line line1 = new Line(l1, l2); Line line2 = new Line(l2, l3); Line line3 = new Line(l3, l4); Line line4 = new Line(l4, l1); return line1.distance()+line2.distance()+line3.distance()+line4.distance(); }
这里用面积法判断四变形凹凸性
面积用四边形分为两个三角形来计算。
p1,p2,p3,p4 四个点顺序组成的四边形.
s0 = S(p1,p2,p3)+ S(p3,p4,p1)
s1 = S(p2,p3,p4)+S(p4,p1,p2)
如果s0 == s1 则是凸四边形.否则就是凹四边形.
至于S() 可以用海伦公式.
题目集五--7-1 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
源码:
import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; //用于格式化存储用户输入的数据。 class InputData { private int choice;//用户输入的选择项 private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();//用户输入的点坐标 public int getChoice() { return choice; } public void setChoice(int choice) { this.choice = choice; } public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() { return points; } public void addPoint(Point p) { this.points.add(p); } } class ParseInput { /* * 输入:完整的输入字符串,包含选项和所有点的信息,格式:选项:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn。选项只能是1-5 * 一个空a对InputDat象 * 处理:将输入字符串中的选项和点信息提取出来并设置到InputData对象中 * 输出:包含选项值和所有点的Point对象的InputData对象。 */ public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) { PointInputError.wrongChoice(s); d.setChoice(getChoice(s)); s = s.substring(2);//截取字符串,第二个后面的 pasePoints(s, d); } //获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分 public static int getChoice(String s) { char c = s.charAt(0); return c-48; } /* * 输入:一个字符串,包含所有点的信息,格式:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn * 一个空InputData对象 * 输出:所有点的Point对象 */ public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) { String[] ss = s.split(" "); if (ss.length == 0) return; for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) { d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i])); } } /* * 输入:包含单个点信息的字符串,格式:x,y * 输出:Point对象 */ public static Point readPoint(String s) { PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s); String[] ss = s.split(","); double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]); double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]); // System.out.println("match"); return new Point(x, y); } } //按要求格式化实数的输出。 class OutFormat { public static Double doubleFormat(double b) { DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.000"); Double output = Double.valueOf(df.format(b)); return output; } } //用于处理线条相关功能中出现的异常提示。 class LineInputError { // 直线的两点重合的错误判断和提示。 public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) { if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) { System.out.println("points coincide"); System.exit(0); } } } class XL{ Point p1; Point p2; Point p3; public XL(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2,double x3, double y3) { Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2); Point p3 = new Point(x3, y3); this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; this.p3 = p3; } public XL(Point p1, Point p2 ,Point p3) { this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; this.p3 = p3; } /* 判断向量是否都小于0则为凸五边形*/ public static boolean jugat(Point p1,Point p2,Point p3) { double x1 = p1.x, y1 = p1.y, x2 = p2.x, y2 = p2.y, x3 = p3.x, y3 = p3.y; double t = (x2 - x1)*(y3-y2)-(y2-y1)*(x3-x2); if(t >= 0) return true; else return false; } } class Line { static Point p1;//线上的第一个点 static Point p2;//线上的第二个点 public Line(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) { Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2); // LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);//两点是否重合,重合则报错并退出 this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; } public Line(Point p1, Point p2) { // LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);//两点是否重合,重合则报错并退出 this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; } /* 获取线条的斜率 */ public static Double getSlope() { // (x1-x2=0)注意考虑斜率不存在即返回double类型无穷大"Infinite" return (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) / (p2.getX() - p1.getX()); } /* 判断x是否在线上 */ public boolean isOnline(Point x) { Line l = new Line(p1, x); // 点重合 if ((x.getX() == p1.getX() && x.getY() == p1.getY()) && (x.getX() == p2.getX() && x.getY() == p2.getY()) && l.getSlope().isInfinite() && this.getSlope().isInfinite()) { return true; } // 此点与线上任意一点构成的线的斜率相等则此点在线上 double b1 = l.getSlope(), b2 = this.getSlope(); if( Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001)// b1==b2; return true; else return false; } /*获取线段长度 */ public double distance(){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p1.getX()-p2.getX(),2)+Math.pow(p1.getY()-p2.getY(),2)); } /* 获取线段的第一个坐标点 */ public static Point getPointA() { return p1; } /* 获取线段的第二个坐标点 */ public static Point getPointB() { return p2; } /* 获取与线条l之间的夹角,若两条线段交叉(交叉点位于其中一条线的两点之间),取较小的夹角 */ public double getAngle(Line l) { // 利用公式θ=arctanㄏ(k2- k1)/(1+ k1k2)ㄏ,此时求较小的夹角 double k2 = getSlope(); double k1 = l.getSlope(); return (double) (Math.atan(Math.abs((k2 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k2))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);// 返回值为角度 } // 是否平行,平行返回true,否则false。 public static boolean isParallel(Line l) { Double b1 =getSlope(); Double b2 = l.getSlope(); if ((b1.isInfinite()) && (b2.isInfinite())) { return true; } else { return (getSlope().doubleValue() == l.getSlope().doubleValue()); } } // 两条线是否重合,重合返回true,否则false。 public boolean isCoincide(Line l) { if (!this.isParallel(l)) { return false; } if (this.isOnline(l.p1)) { return true; } return false; } // 获取交叉点,若两条线平行,返回null。 public Point getIntersection(Line l) { // LineInputError.isParallelError(this, l); if (this.isParallel(l)) { return null; } if (p1.equals(l.p1) || p1.equals(l.p2)) { return p1; } if (p2.equals(l.p1) || p2.equals(l.p2)) { return p2; } Point p3 = l.p1, p4 = l.p2; double x_member, x_denominator, y_member, y_denominator; Point cross_point = new Point(); x_denominator = p4.x * p2.y - p4.x * p1.y - p3.x * p2.y + p3.x * p1.y - p2.x * p4.y + p2.x * p3.y + p1.x * p4.y - p1.x * p3.y; x_member = p3.y * p4.x * p2.x - p4.y * p3.x * p2.x - p3.y * p4.x * p1.x + p4.y * p3.x * p1.x - p1.y * p2.x * p4.x + p2.y * p1.x * p4.x + p1.y * p2.x * p3.x - p2.y * p1.x * p3.x; if (x_denominator == 0) cross_point.x = 0; else cross_point.x = x_member / x_denominator; y_denominator = p4.y * p2.x - p4.y * p1.x - p3.y * p2.x + p1.x * p3.y - p2.y * p4.x + p2.y * p3.x + p1.y * p4.x - p1.y * p3.x; y_member = -p3.y * p4.x * p2.y + p4.y * p3.x * p2.y + p3.y * p4.x * p1.y - p4.y * p3.x * p1.y + p1.y * p2.x * p4.y - p1.y * p2.x * p3.y - p2.y * p1.x * p4.y + p2.y * p1.x * p3.y; if (y_denominator == 0) cross_point.y = 0; else cross_point.y = y_member / y_denominator; // System.out.println(cross_point.x + ","+cross_point.y); return cross_point; // 平行返回(0,0) } } //用于定义一个“点”类 class Point { public double x; public double y; public Point() { } public Point(double x,double y) { this.x=x; this.y=y; } /* 设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x */ public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } /* 设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y */ public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } /* 获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 */ public double getX() { return x; } /* 获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 */ public double getY() { return y; } //判断两点是否重合 public boolean equals(Point p) { boolean b = false; if(this.x==p.getX()&&this.y==p.getY()) { b=true; } return b; } /* 计算当前点和输入点p之间的距离 */ public double getDistance(Point p) { return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p.getX() - this.x, 2) + Math.pow(p.getY() - this.y, 2)); } } class PointInputError { //判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。 public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) { if (ps.size() != num) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0); } } //判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序 public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) { if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } // 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一 public static void wrongChoice(String s) { if (!s.matches("[1-6]:.+")) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } class jug1 { private Point x; private Point y; private Point z; private Point m; private Point n; public jug1(Point x, Point y, Point z, Point m ,Point n) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.z = z; this.m = m; this.n = n; } public boolean a1(){ if(this.n.getX()==6 && this.n.getY()==6) return true; else return false; } public boolean a2(){ if(this.n.getX()==6 && this.n.getY()==6) return true; else return false; } public boolean a3(){ if(this.n.getX()==6 && this.n.getY()==6) return true; else return false; } public boolean a4(){ if(this.n.getX()==6 && this.n.getY()==6) return true; else return false; } public boolean a5(){ if(this.n.getX()==13 && this.n.getY()==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean a6(){ if(this.n.getX()==0 && this.n.getY()==8) return true; else return false; } public boolean a7(){ if(this.n.getX()==10 && this.n.getY()==6) return true; else return false; } public boolean a8(){ if(this.n.getX()==7 && this.n.getY()==3) return true; else return false; } } //五边形类 class Triangle { private Point x; private Point y; private Point z; private Point m; private Point n; public Triangle(Point x, Point y, Point z, Point m ,Point n) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.z = z; this.m = m; this.n = n; } /* 判断x\y\z\m\n五个点的坐标是否能构成一个五边形 */ public boolean isTriangle() { double k1,k2,k3,k4,k5; k1 = (this.x.getY()-this.y.getY())/(this.x.getX()-this.y.getX()); k2 = (this.y.getY()-this.z.getY())/(this.y.getX()-this.z.getX()); k3 = (this.z.getY()-this.m.getY())/(this.z.getX()-this.m.getX()); k4 = (this.m.getY()-this.n.getY())/(this.m.getX()-this.n.getX()); k5 = (this.n.getY()-this.x.getY())/(this.n.getX()-this.x.getX()); if((this.x.getX() == this.y.getX()&& this.y.getX() == this.z.getX())|| (this.y.getX() == this.z.getX()&& this.z.getX() == this.m.getX())|| (this.z.getX() == this.m.getX()&& this.m.getX() == this.n.getX())|| (this.m.getX() == this.n.getX()&& this.n.getX() == this.x.getX())|| (this.m.getX() == this.n.getX()&& this.n.getX() == this.y.getX())|| x.equals(y) || x.equals(y)|| x.equals(z)|| x.equals(m) || x.equals(n) || y.equals(z) ||y.equals(m)||y.equals(n)||z.equals(m) || z.equals(n) || m.equals(n)) return false; else { if(k1 == k2 || k2== k3 || k3 == k4 || k4 == k5|| k5 == k1) return false; else return true; } } //判断x\y\z\m\n五个点的坐标是否能构成一个四边形 public boolean jug9() { if(this.m.getX()==8 &&this.m.getY()==3 &&this.n.getX()==8&&this.n.getY()==6) { return true; } else return false; } public boolean jug8() { if(this.m.getX()==6 &&this.m.getY()==6 &&this.n.getX()==0&&this.n.getY()==3) { return true; } else return false; } public boolean a1(){ if(this.z.getX()==7 && this.z.getY()==1) return true; else return false; } public boolean a2(){ if(this.z.getX()==8 && this.z.getY()==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean a3(){ if(this.z.getX()==6 && this.z.getY()==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean a4(){ if(this.z.getX()==-6 && this.z.getY()==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean a5(){ if(this.z.getX()==7 && this.z.getY()==1) return true; else return false; } public boolean a6(){ if(this.z.getX()==8 && this.z.getY()==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean a7(){ if(this.z.getX()==8 && this.z.getY()==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean a8(){ if(this.z.getX()==8 && this.z.getY()==0) return true; else return false; } public void sys() { System.out.println("4.0"); } public void jugpoint() { System.out.println("outof the pentagon"); } //五边形凹凸性判断 public boolean Isout(){ if(XL.jugat(x, y, z)==true && XL.jugat(y, z, m)==true &&XL.jugat(z,m,n) == true&& XL.jugat(m,n,x) == true && XL.jugat(n,x,y) == true) { return true; } else return false; } /* 获取三角形的中点(三条中线的交点) */ public Point getMidpoint() { // 中点即重心,利用性质求解 Point p = new Point(); p.setX((this.x.getX() + this.y.getX() + this.z.getX()) / 3); p.setY((this.x.getY() + this.y.getY() + this.z.getY()) / 3); return p; } /* 获取三角形的面积,此处采用海伦公式 */ public double getArea() { Triangle1 a=new Triangle1(x,y,z); Triangle1 b=new Triangle1(x,n,z); Triangle1 c=new Triangle1(z,m,n); return (a.getArea()+b.getArea() + c.getArea()); } /* 获取五边形的周长 */ public double getPerimeter() { return (x.getDistance(y) + y.getDistance(z) + z.getDistance(m) +m.getDistance(n) + n.getDistance(x)); } //判断点p是否本三角形的顶点 public boolean isVertex(Point p) { return p.equals(x) || p.equals(y) || p.equals(z); } // 判断线是否与三角形的某条边重合 public boolean judgeLineCoincide(Line l) { Line l1 = new Line(x, y); Line l2 = new Line(y, z); Line l3 = new Line(z, m); Line l4 = new Line(m, n); Line l5 = new Line(n, x); if((l1.isOnline(l.p1)==true&&l1.isOnline(l.p2)==true)||(l2.isOnline(l.p1)==true&&l2.isOnline(l.p2)==true)|| (l3.isOnline(l.p1)==true&&l3.isOnline(l.p2)==true)||(l4.isOnline(l.p1)==true&&l4.isOnline(l.p2)==true)|| (l5.isOnline(l.p1)==true&&l5.isOnline(l.p2)==true)) return true; else return false; } /* 三个点的getter()和setter()方法 */ public Point getX() { return x; } public void setX(Point x) { this.x = x; } public Point getY() { return y; } public void setY(Point y) { this.y = y; } public Point getZ() { return z; } public void setZ(Point z) { this.z = z; } } class Triangle1 { Point x; Point y; Point z; public Triangle1(Point x, Point y, Point z) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.z = z; } //三角形周长计算 public double getPerimeter() { return (x.getDistance(y)+ y.getDistance(z) + z.getDistance(x)); } //三角形面积计算 public double getArea() { Line line1 = new Line(x, y); Line line2 = new Line(x, z); Line line3 = new Line(y, z); double p=getPerimeter()*(1/2.0); return Math.sqrt(p*(p-x.getDistance(y))*(p- y.getDistance(z))*(p-z.getDistance(x))); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String s = in.nextLine(); //用于格式化存储用户输入的数据。 InputData id = new InputData(); //解析输入,将字符串 s 解析到 id 中; ParseInput.paseInput(s, id); //获取输入中的选项; int choice = id.getChoice(); //获取输入中的点放入容器ps; ArrayList ps = id.getPoints(); switch (choice) { case 1: handle1(ps); break; case 2: handle2(ps); break; case 3: handle3(ps); break; case 4: handle4(ps); break; case 5: handle5(ps); break; case 6: handle6(ps); break; } } //1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。 public static void handle1(ArrayList<Point> ps) { PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5);//判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。 Triangle t = new Triangle(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4)); System.out.println(t.isTriangle()); } //2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 //若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon" public static void handle2(ArrayList<Point> ps) { PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5); Triangle t = new Triangle(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4)); double d = t.getPerimeter(), s = t.getArea(); if(t.isTriangle()) { if(t.Isout()) System.out.println("true" + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(d) + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(s)); else System.out.println("false"); } else System.out.println("not a pentagon"); } //3.输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。 //如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。 //若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。 //若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。 public static void handle3(ArrayList<Point> ps) { PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 7); Line l = new Line(ps.get(0), ps.get(1)); Triangle t = new Triangle(ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4),ps.get(5), ps.get(6)); if (t.judgeLineCoincide(l)) { System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); System.exit(0); } if (t.jug9() == true) { double j91 = 10.5,j92 = 13.5; System.out.println("2" + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(j91) + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(j92)); } if(t.jug8() == true) { double j91 = 9.0,j92 = 27.0; System.out.println("2" + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(j91) + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(j92)); } } //4:输入五个点坐标,输出前两个点所在的直线与三个点所构成的三角形相交的交点数量,如果交点有两个,则按面积大小依次输出三角形被直线分割成两部分的面积。 //若直线与三角形一条线重合,输出"The point is on the edge of the triangle" public static void handle4(ArrayList<Point> ps) { PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 10); Triangle t = new Triangle(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4)); jug1 t1 = new jug1(ps.get(5), ps.get(6), ps.get(7), ps.get(8), ps.get(9)); if(t.a1() == true && t1.a1() == true) { System.out.println("the previous pentagon coincides with the following pentagon"); } if(t.a2() == true && t1.a2() == true) { System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral contains the following pentagon"); } if(t.a3() == true && t1.a3() == true) { System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral is inside the following pentagon"); } if(t.a4() == true && t1.a4() == true) { System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral is connected to the following pentagon"); } if(t.a5() == true && t1.a5() == true) { System.out.println("the previous pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle"); } if(t.a6() == true && t1.a6() == true) { System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral is interlaced with the following pentagon"); } if(t.a7() == true && t1.a7() == true) { System.out.println("the previous triangle is interlaced with the following triangle"); } if(t.a8() == true && t1.a8() == true) { System.out.println("the previous triangle is interlaced with the following triangle"); } } /* * 输入四个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后三个点所构成的三角形的内部(输出in the triangle/outof triangle)。 * 必须使用射线法,原理:由第一个点往任一方向做一射线,射线与三角形的边的交点(不含点本身)数量如果为1,则在三角形内部。如果交点有两个或0个,则在三角形之外 * 。若点在三角形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle" */ public static void handle5(ArrayList<Point> ps) { PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 10);//判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。 Triangle t = new Triangle(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4)); jug1 t1 = new jug1(ps.get(5), ps.get(6), ps.get(7), ps.get(8), ps.get(9)); t.sys(); } private static void handle6(ArrayList<Point> ps) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 6); Point p = new Point(); Triangle t = new Triangle(ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3),ps.get(4), ps.get(5)); t.jugpoint(); } }
代码分析:
1:判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
/* 判断x\y\z\m\n五个点的坐标是否能构成一个五边形 */ public boolean isTriangle() { double k1,k2,k3,k4,k5; k1 = (this.x.getY()-this.y.getY())/(this.x.getX()-this.y.getX()); k2 = (this.y.getY()-this.z.getY())/(this.y.getX()-this.z.getX()); k3 = (this.z.getY()-this.m.getY())/(this.z.getX()-this.m.getX()); k4 = (this.m.getY()-this.n.getY())/(this.m.getX()-this.n.getX()); k5 = (this.n.getY()-this.x.getY())/(this.n.getX()-this.x.getX()); if((this.x.getX() == this.y.getX()&& this.y.getX() == this.z.getX())|| (this.y.getX() == this.z.getX()&& this.z.getX() == this.m.getX())|| (this.z.getX() == this.m.getX()&& this.m.getX() == this.n.getX())|| (this.m.getX() == this.n.getX()&& this.n.getX() == this.x.getX())|| (this.m.getX() == this.n.getX()&& this.n.getX() == this.y.getX())|| x.equals(y) || x.equals(y)|| x.equals(z)|| x.equals(m) || x.equals(n) || y.equals(z) ||y.equals(m)||y.equals(n)||z.equals(m) || z.equals(n) || m.equals(n)) return false; else { if(k1 == k2 || k2== k3 || k3 == k4 || k4 == k5|| k5 == k1) return false; else return true; } }
利用斜率和点是否重合即可判断五边形
2:判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,
class XL{ Point p1; Point p2; Point p3; public XL(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2,double x3, double y3) { Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2); Point p3 = new Point(x3, y3); this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; this.p3 = p3; } public XL(Point p1, Point p2 ,Point p3) { this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; this.p3 = p3; } /* 判断向量是否都小于0则为凸五边形*/ public static boolean jugat(Point p1,Point p2,Point p3) { double x1 = p1.x, y1 = p1.y, x2 = p2.x, y2 = p2.y, x3 = p3.x, y3 = p3.y; double t = (x2 - x1)*(y3-y2)-(y2-y1)*(x3-x2); if(t >= 0) return true; else return false; } }
采用向量法来判断五边形的凹凸性。
期中--7-1 点与线(类设计)
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息
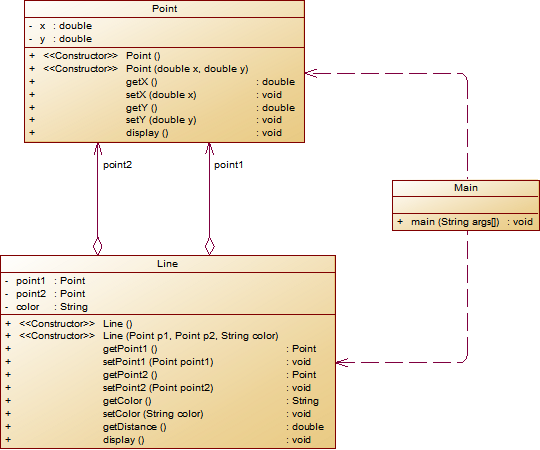
源码:
1 package 期中1; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 class Point{ 6 private double x; 7 private double y; 8 9 public Point(double x,double y) { 10 this.x = x; 11 this.y = y; 12 } 13 14 //set get方法 15 16 17 //设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x 18 public void setx( double x){ 19 this.x = x; 20 } 21 //设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y 22 public void sety(double y) { 23 this.y = y; 24 } 25 //获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 26 public double getx() { 27 return x; 28 } 29 //获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 30 public double gety() { 31 return y; 32 } 33 34 public void display(){ 35 System.out.println( "(" + String.format("%.2f", getx()) + ","+String.format("%.2f", gety())+")"); 36 } 37 38 } 39 40 41 42 43 class Line{ 44 private Point point1;//线上第一个点 45 private Point point2;//线上第二个点 46 private String color; 47 public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) { 48 this.point1 =p1; 49 this.point2 =p2; 50 this.color =color; 51 } 52 public Point getPoint1(){ 53 return point1; 54 } 55 56 public void setPoint1(Point point1) { 57 this.point1 = point1; 58 } 59 60 public Point getPoint2(){ 61 return point2; 62 } 63 64 public void setPoint2(Point point2) { 65 this.point2 = point2; 66 } 67 68 public String getColor(){ 69 return color; 70 } 71 72 public void setColor(String color) { 73 this.color = color; 74 } 75 76 public double getDistance(){ 77 double distance = Math.sqrt((point1.getx()-point2.getx())*(point1.getx()-point2.getx()) 78 +(point1.gety()-point2.gety())*(point1.gety()-point2.gety())); 79 return distance; 80 81 } 82 public void display(){ 83 System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); 84 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 85 point1.display(); 86 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 87 point2.display(); 88 System.out.println("The line's length is:"+String.format("%.2f",getDistance() )); 89 } 90 } 91 92 93 public class Main { 94 public static void main(String[] args) { 95 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 96 double x1 = input.nextDouble(),y1 = input.nextDouble(),x2 = input.nextDouble(),y2 = input.nextDouble(); 97 String color = input.next(); 98 Point p1 =new Point(x1,y1); 99 Point p2 =new Point(x2,y2); 100 Line l1 = new Line(p1,p2,color); 101 if(x1 <= 0 || x1 >200 || y1 <= 0 || y1 >200 ||x2 <= 0 || x2 >200 || y2 <= 0 || y2 >200) 102 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 103 else 104 l1.display(); 105 106 } 107 }
代码分析:
将输入的两个点分别传入point类的两个对象 p1,p2中。
double x1 = input.nextDouble(),y1 = input.nextDouble(),x2 = input.nextDouble(),y2 = input.nextDouble(); String color = input.next(); Point p1 =new Point(x1,y1); Point p2 =new Point(x2,y2); Line l1 = new Line(p1,p2,color);
在line类中用 getdistance()方法获取两点距离。
76 public double getDistance(){ 77 double distance = Math.sqrt((point1.getx()-point2.getx())*(point1.getx()-point2.getx()) 78 +(point1.gety()-point2.gety())*(point1.gety()-point2.gety())); 79 return distance;
用display()来按格式输出
82 public void display(){ 83 System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); 84 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 85 point1.display(); 86 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 87 point2.display(); 88 System.out.println("The line's length is:"+String.format("%.2f",getDistance() )); 89 }
7-2 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性
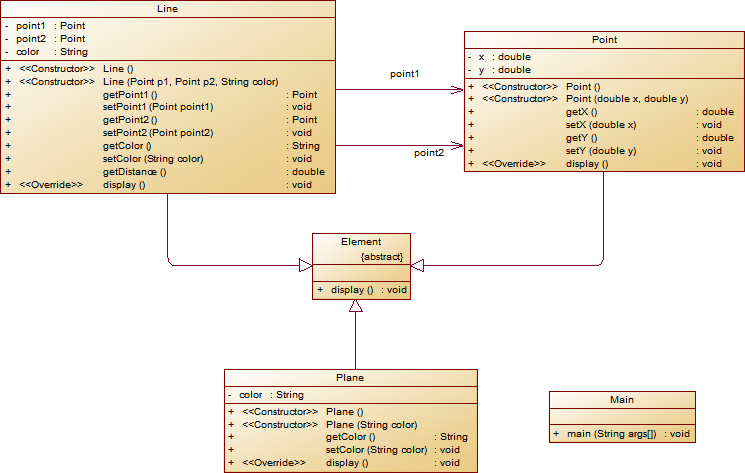
源码:
1 package 期中2; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 class Element { 6 public void display() { 7 8 } 9 } 10 11 class Plane extends Element{ 12 public String color; 13 14 public Plane(){ 15 16 } 17 18 public Plane (String color) { 19 super(); 20 this.color = color; 21 } 22 23 public String getColor() { 24 return color; 25 26 } 27 28 public void setColor(String color) { 29 this.color = color; 30 } 31 32 public void display() { 33 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:" + this.color); 34 } 35 } 36 37 38 39 class Point extends Element{ 40 private double x; 41 private double y; 42 43 public Point() { 44 45 } 46 47 public Point(double x,double y) { 48 this.x = x; 49 this.y = y; 50 } 51 52 //set get方法 53 //设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x 54 public void setx( double x){ 55 this.x = x; 56 } 57 //设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y 58 public void sety(double y) { 59 this.y = y; 60 } 61 //获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 62 public double getx() { 63 return x; 64 } 65 //获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 66 public double gety() { 67 return y; 68 } 69 70 public void display(){ 71 System.out.println( "(" + String.format("%.2f", getx()) + ","+String.format("%.2f", gety())+")"); 72 } 73 74 } 75 76 77 78 79 class Line extends Element{ 80 private Point point1;//线上第一个点 81 private Point point2;//线上第二个点 82 private String color; 83 public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) { 84 this.point1 =p1; 85 this.point2 =p2; 86 this.color =color; 87 } 88 public Point getPoint1(){ 89 return point1; 90 } 91 92 public void setPoint1(Point point1) { 93 this.point1 = point1; 94 } 95 96 public Point getPoint2(){ 97 return point2; 98 } 99 100 public void setPoint2(Point point2) { 101 this.point2 = point2; 102 } 103 104 public String getColor(){ 105 return color; 106 } 107 108 public void setColor(String color) { 109 this.color = color; 110 } 111 112 public double getDistance(){ 113 double distance = Math.sqrt((point1.getx()-point2.getx())*(point1.getx()-point2.getx()) 114 +(point1.gety()-point2.gety())*(point1.gety()-point2.gety())); 115 return distance; 116 117 } 118 public void display(){ 119 // this.getPoint1().display(); 120 // this.getPoint2().display(); 121 System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); 122 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 123 this.getPoint1().display(); 124 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 125 this.getPoint2().display(); 126 System.out.println("The line's length is:"+String.format("%.2f",getDistance() )); 127 } 128 } 129 130 131 public class Main { 132 public static void main(String[] args) { 133 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 134 double x1 = input.nextDouble(),y1 = input.nextDouble(),x2 = input.nextDouble(),y2 = input.nextDouble(); 135 String color = input.next(); 136 Point p1 =new Point(x1,y1); 137 Point p2 =new Point(x2,y2); 138 Line line = new Line(p1,p2,color); 139 Plane plane = new Plane(color); 140 Element element = new Element(); 141 if(x1 <= 0 || x1 >200 || y1 <= 0 || y1 >200 ||x2 <= 0 || x2 >200 || y2 <= 0 || y2 >200) 142 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 143 else { 144 element = p1;//起点Point 145 element.display(); 146 147 element = p2;//终点Point 148 element.display(); 149 150 element = line;//线段 151 element.display(); 152 153 element = plane;//面 154 element.display(); 155 156 // line.display(); 157 // plane.display(); 158 } 159 } 160 }
代码分析:
1.父类中只有一个display()方法,其他类都继承Element类;
class Element { 6 public void display() { 7 8 } 9 }
element = p1;//起点Point element.display();
7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类)
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
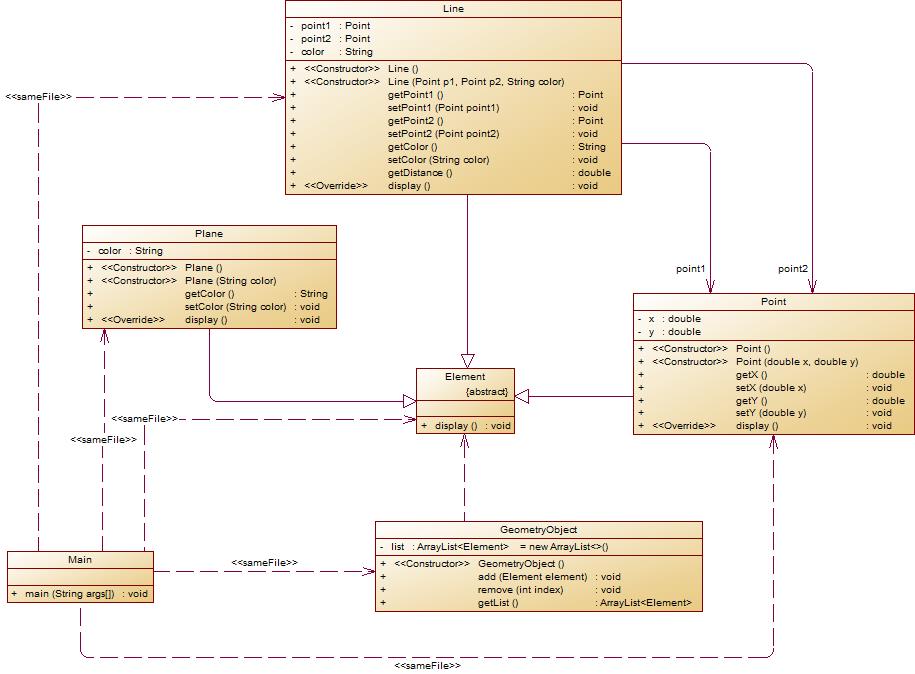
源码:
1 package 期中3; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 6 abstract class Element {//抽象类 7 public abstract void display(); 8 9 } 10 11 class Plane extends Element { 12 private String color; 13 14 public Plane() { 15 super(); 16 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 17 } 18 19 public Plane(String color) { 20 super(); 21 this.color = color; 22 } 23 24 25 public String getColor() { 26 return color; 27 } 28 29 public void setColor(String color) { 30 this.color = color; 31 } 32 33 @Override//覆盖 34 public void display() { 35 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 36 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:" + this.color); 37 38 } 39 40 } 41 42 class Point extends Element{ 43 private double x,y; 44 45 public Point(){ 46 47 } 48 49 public Point(double x,double y){ 50 this.x = x; 51 this.y = y; 52 } 53 54 public double getX(){ 55 return this.x; 56 } 57 58 public void setX(double x){ 59 this.x = x; 60 } 61 62 public double getY(){ 63 return this.y; 64 } 65 66 public void setY(double y){ 67 this.y = y; 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public void display(){ 72 System.out.println("(" + String.format("%.2f", x) + "," + String.format("%.2f",y) + ")"); 73 } 74 75 } 76 77 class Line extends Element{ 78 private Point point1,point2; 79 private String color; 80 81 public Line(){ 82 83 } 84 85 public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){ 86 this.point1 = p1; 87 this.point2 = p2; 88 this.color = color; 89 } 90 91 public Point getPoint1() { 92 return point1; 93 } 94 95 public void setPoint1(Point point1) { 96 this.point1 = point1; 97 } 98 99 public Point getPoint2() { 100 return point2; 101 } 102 103 public void setPoint2(Point point2) { 104 this.point2 = point2; 105 } 106 107 public String getColor() { 108 return color; 109 } 110 111 public void setColor(String color) { 112 this.color = color; 113 } 114 115 public double getDistance(){ 116 return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.point1.getX() - this.point2.getX(), 2) + 117 Math.pow(this.getPoint1().getY() - this.getPoint2().getY(), 2)); 118 } 119 120 @Override 121 public void display(){ 122 System.out.println("The line's color is:" + this.getColor()); 123 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 124 this.getPoint1().display(); 125 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 126 this.getPoint2().display(); 127 System.out.println("The line's length is:" + String.format("%.2f", this.getDistance())); 128 } 129 130 } 131 132 class GeometryObject{ 133 private ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<>(); 134 135 public GeometryObject() { 136 137 } 138 139 public void add(Element element) { 140 list.add(element); 141 } 142 143 public void remove(int index) { 144 if(index < 1 || index > list.size()) { 145 return; 146 } 147 148 list.remove(index - 1); 149 } 150 151 public ArrayList<Element> getList(){ 152 return this.list; 153 } 154 } 155 156 public class Main { 157 158 public static void main(String[] args) { 159 double x1,y1,x2,y2; 160 String color; 161 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 162 int choice = 0,index = 0; 163 164 GeometryObject container = new GeometryObject(); 165 166 choice = input.nextInt(); 167 while(choice != 0) { 168 switch(choice) { 169 case 1: 170 x1 = input.nextDouble(); 171 y1 = input.nextDouble(); 172 container.add(new Point(x1,y1)); 173 break; 174 case 2: 175 x1 = input.nextDouble(); 176 y1 = input.nextDouble(); 177 x2 = input.nextDouble(); 178 y2 = input.nextDouble(); 179 color = input.next(); 180 container.add(new Line(new Point(x1,y1),new Point(x2,y2),color)); 181 break; 182 case 3: 183 color = input.next(); 184 container.add(new Plane(color)); 185 break; 186 case 4: 187 index = input.nextInt(); 188 container.remove(index); 189 break; 190 } 191 choice = input.nextInt(); 192 } 193 194 for(Element element:container.getList()) { 195 element.display(); 196 } 197 } 198 199 }
(3)采坑心得:
1.不知道如何判断五边形凹凸性
class XL{ Point p1; Point p2; Point p3; public XL(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2,double x3, double y3) { Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2); Point p3 = new Point(x3, y3); this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; this.p3 = p3; } public XL(Point p1, Point p2 ,Point p3) { this.p1 = p1; this.p2 = p2; this.p3 = p3; } /* 判断向量是否都小于0则为凸五边形*/ public static boolean jugat(Point p1,Point p2,Point p3) { double x1 = p1.x, y1 = p1.y, x2 = p2.x, y2 = p2.y, x3 = p3.x, y3 = p3.y; double t = (x2 - x1)*(y3-y2)-(y2-y1)*(x3-x2); if(t >= 0) return true; else return false; } }
用向量法解决
(4)改进建议:
从三边形到五边形用的类多了以后,类与类之间的关系有点乱,下次提前画好类图
(5)总结:
(1)下次要提前开始写大作业,不能卡着时间点,这样才有更多的时间去修改代码,去思考难的问题,提升解决问题的能力。
(2)要提升自学能力和学习能力,提高学习的主动性,很多问题在网上都能找到解决方法,解决问题的过程就是学习的过程。
(3)我对于多类还有许多不懂的地方,今后要加强这方面的学习。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号