Kubernetes进阶实战读书笔记:管理Pod资源对象(资源对象和容器)
一、容器与pod资源对象
绝大对数场景中都应该于一个容器中仅运行一个进程、它将日志信息直接输出至容器的标准输出、支持用户直接使用命令(kubectl logs)获取、这也是Docker及Kubernetes使用容器的标准方式
需要特别强调的是:一个pod对象中的多个容器必须运行于同一工作节点之上
1、Sidercar pattern(边车模型或跨都模型)
容器中的日志使用agent收集至日志服务器中时,可以将agent运行为辅助应用容器、为主应用容器中的database server启动本地缓存
2、Ambassador pattern(大使模型)
一主多从模型的远程redis应用时,可在当前pod容器中为redis服务创建一个Ambassador container
主应用容器中的进程直接通过localhost接口访问Ambassador container即可。即便是redis主从集群架构发生变动时,也仅需要将Ambassador container、加以修改即可,主应用容器无需对此做任何反应
3、adapter pattern(适配器模型)
将主应用容器中的内容进行标准输出
1、日志数据或指标数据的输出
2、某应用滚动升级后的版本不兼容旧版本时,其报告信息的格式也存在不兼容的可能性,使用adapter pattern有助于避免那些调用此报告数据的应用发生错误
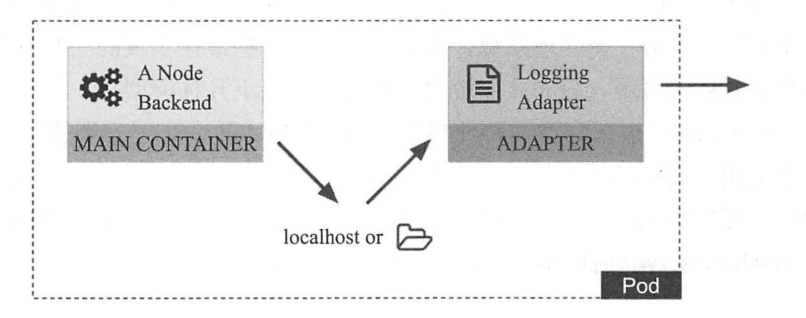
kubernetes系统的pod资源对象用于运行单个容器化应用、此应用成为pod对象的主容器,同时pod也容纳多个容器、不过额外的容器一般工作为sidecar模型,用于辅助主容器完成工作职能
二、镜像及获取策略
1、定义一个容器的基础框架
name:CONTAINER_NAME images:IMAGE_FILE_NAME
2、镜像及获取策略
1、资源清单
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: private-image-test-1
spec:
containers:
- name: uses-private-image
image: $PRIVATE_IMAGE_NAME
imagePullPolicy: Always
command: [ "echo", "SUCCESS" ]
2、官方手册
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.imagePullPolicy
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
FIELD: imagePullPolicy <string>
DESCRIPTION:
Image pull policy. One of Always, Never, IfNotPresent. Defaults to Always
if :latest tag is specified, or IfNotPresent otherwise. Cannot be updated.
More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#updating-images
首先将于本地查找指定的镜像文件,不存在的镜像则需要从指定的镜像仓库下载至本地
1、imagePullPolicy: 网络资源较为紧张时可以 禁止从仓库中获取镜像文件
2、always: 镜像标签为 "latest" 或镜像不存在是 总是从指定的仓库中获取镜像
3、ifNotPresent: 仅当本地镜像缺失时才从目标仓库下载镜像 默认策略
4、Never: 禁止从仓库下载镜像,即使用本地镜像
三、暴露端口
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.ports
RESOURCE: ports <[]Object>
DESCRIPTION:
List of ports to expose from the container. Exposing a port here gives the
system additional information about the network connections a container
uses, but is primarily informational. Not specifying a port here DOES NOT
prevent that port from being exposed. Any port which is listening on the
default "0.0.0.0" address inside a container will be accessible from the
network. Cannot be updated.
ContainerPort represents a network port in a single container.
FIELDS:
hostIP <string> #主机端口要绑定的主机IP
#默认为0.0.0.0,即主机之上所有可用的ip地址
What host IP to bind the external port to.
#考虑到托管的pod对象时由调度器调度运行的,工作节点的IP地址难以明确指定,因此此字段通常使用默认值
hostPort <integer> #主机端口
#它将接受到的请求通过NAT机制转发至由containersport字段指定的容器端口
Number of port to expose on the host. If specified, this must be a valid
port number, 0 < x < 65536. If HostNetwork is specified, this must match
ContainerPort. Most containers do not need this.
name <string> #当前端口的名称,
#必须符合IANA_SVC_BANE规范且在当前pod内必须唯一的;此端口可被service资源调用
If specified, this must be an IANA_SVC_NAME and unique within the pod. Each
named port in a pod must have a unique name. Name for the port that can be
referred to by services.
protocol <string> #端口相关的协议,其值金可为TCP或UDP,默认TCP
Protocol for port. Must be UDP or TCP. Defaults to "TCP".
containerPort <integer> -required- #必须字段
#指定在pod对象的ip地址上暴露的容器端口
Number of port to expose on the pod's IP address. This must be a valid port
number, 0 < x < 65536. #有效范围为:(0,65536) #应该总是指定容器应用正常监听着的端口
通过其所在的工作节点的IP地址和端口将其暴露到集群外部
需要注意的是:hostPort与nodePort对象暴露端口的方式不同,nodePort是通过所有节点暴露容器服务的、而hostPort则是经由pod对象所在节点的IP地址来进行
四、自定义运行的容器化应用
1、args
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.args
FIELD: args <[]string>
DESCRIPTION:
'''
自定义args,也是向容器中的应用程序传递配置信息的常用方式之一,对于非原生的应用程序
这几乎也是最简单的配置方式,领一个常用方式是使用环境变量
'''
Arguments to the entrypoint. The docker image's CMD is used if this is not
provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the container's
environment. If a variable cannot be resolved, the reference in the input
string will be unchanged. The $(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a
double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME). Escaped references will never be expanded,
regardless of whether the variable exists or not. Cannot be updated. More
info:
http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/containers#containers-and-commands
2、command
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.command
FIELD: command <[]string>
'''
容器的command字段能够指定不同奖项默认运行的应用程序、同时使用args字段进行参数传递,他们将覆盖镜像中的默认定义
只定义args字段:将作为参数传递给镜像中默认指定运行的应用程序
只定义了command字段:会覆盖镜像中定义的程序及参数、并以无参数方式运行用用程序
'''
DESCRIPTION:
Entrypoint array. Not executed within a shell. The docker image's
ENTRYPOINT is used if this is not provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME)
are expanded using the container's environment. If a variable cannot be
resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. The
$(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME).
Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless of whether the
variable exists or not. Cannot be updated. More info:
http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/containers#containers-and-commands
3、模板文件
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: command-demo
labels:
purpose: demonstrate-command
spec:
containers:
- name: command-demo-container
image: debian
command: ["printenv"]
args: ["HOSTNAME", "KUBERNETES_PORT"]
restartPolicy: OnFailur
五、环境变量
1、解决了什么问题
1、非容器化的传统管理方式中、复杂应用的配置信息多数由配置文件进行制定、用户可借助与简单的文本编辑器完成配置管理
2、然而对容器隔离出的环境中的应用程序、用户就不得不穿透容器边界在容器内进行配置编辑并进行重载、这种方式复杂且低效
3、于是、由环境变量在容器启动时传递配置信息就成为一种受青睐的方式
这种方式依赖于应用程序支持通过环境变量进行配置的能力、否则、用户在制作Dorker镜像时需要通过enrypoint脚本完成环境变量到程序配置文件的同步
2、官方手册
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pods.spec.containers.env
RESOURCE: env <[]Object>
DESCRIPTION:
List of environment variables to set in the container. Cannot be updated.
EnvVar represents an environment variable present in a Container.
FIELDS:
name <string> -required- #环境变量的名称,必选字段
Name of the environment variable. Must be a C_IDENTIFIER.
value <string> #传递环境变量的值,通过$(VAR_NAME)引用、默认值为空
Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the previous defined
environment variables in the container and any service environment
variables. If a variable cannot be resolved, the reference in the input
string will be unchanged. The $(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a
double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME). Escaped references will never be expanded,
regardless of whether the variable exists or not. Defaults to "".
valueFrom <Object>
Source for the environment variable's value. Cannot be used if value is not
empty.
1、REDIS_HOST:定义了filebeat手机的日志信息要发往的redis主机地址,
2、LOG_LEVEL:则定义了filebeat的日志级别
这些环境变量可直接注入容器的shell环境中,无论他们是否真正被用到,使用printenv一类的命令都能在容器中获取所有环境变量的列表
3、生产用例
[root@master chapter5]# cat filebeat-ds.yaml
.....
spec:
selector:
.....
spec:
containers:
- name: filebeat
image: ikubernetes/filebeat:5.6.5-alpine
env:
- name: REDIS_HOST
value: db.ikubernetes.io:6379
- name: LOG_LEVEL
value: info
六、共享节点的网络名称空间
也有一些特殊的pod对象需要运行于所在节点的名称空间中,执行系统级的管理任务、例如查看和操作节点的网络资源甚至是网络设备等
kube-apiserver kube-controller-manager kube-scheduler kube-proxy kube-flannel
1、pod对象网络名称空间
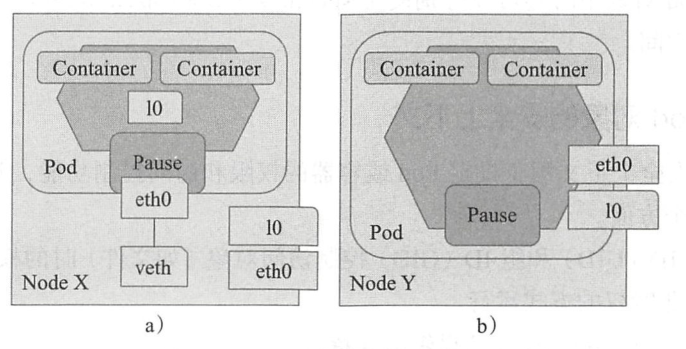
2、官方手册
spec.hostNetwork的属性为true即可创建共享节点网络名称空间的pod对象
[root@master ~]# kubectl explain pod.spec.hostNetwork
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
FIELD: hostNetwork <boolean>
DESCRIPTION:
Host networking requested for this pod. Use the host's network namespace.
If this option is set, the ports that will be used must be specified.
Default to false.
3、测试用例
1、资源清单
[root@master pod]# cat pod-use-hostnetwrk.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-user-hostnetwork
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp
image: ikubernetes/myapp:v1
hostNetwork: true
2、创建验证
[root@master pod]# kubectl apply -f pod-use-hostnetwrk.yaml
pod "pod-user-hostnetwork" created
[root@master pod]# kubectl apply -f pod-use-hostnetwrk.yaml
pod "pod-user-hostnetwork" configured
[root@master pod]# kubectl exec -it pod-use-hostnetwork --sh
/ #ifconfig
root@master pod]# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 52:54:00:52:4A:B1
inet addr:192.168.118.19 Bcast:192.168.118.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::5054:ff:fe52:4ab1/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:4792773 errors:0 dropped:10180 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:2124456 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:3485493892 (3.2 GiB) TX bytes:282501368 (269.4 MiB)
3、查看pod-use-hostnetwork运行的结点
[root@master pod]# kubectl get all -o wide pod/pod-use-hostnetwork 1/1 Running 0 2m29s 192.168.118.19 node1 <none> <none>
通过向node1结点发起请求来验证
[root@node1 ~]# hostname node1 [root@node1 ~]# curl node1 Hello MyApp | Version: v1 | <a href="hostname.html">Pod Name</a>
另外,在pod对象中时还可以分别使用spec.hostPID和spec.hostIPC来共享工作节点的PID和IPC名称空间
七、设置pod对象的安全上下文
1、设置pod对象安全上文常用属性
Pod对象的安全上下文用于设定Pod或容器的权限和访问控制功能、其支持设置的常用属性包括一下几个方面
- 基于用户ID和组ID控制访问对象时的权限
- 以特权或非特权的方式运行
- 通过Linux Capabilities为其提供部分特权
- 基于Seccomp过滤进行的系统调用
- 基于seLinux的安全标签
- 是否能够进行权限升级
2、测试用例
pod对象的安全上下文定在pod.spec.securityContext字段中 而容器的安全上下文则定义在字段pod.spec.containers.securityContext中、且二者可嵌套使用的字段还有所不同
1、配置清单
[root@master chapter4]# cat pod-with-seccontext.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-with-securitycontext
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","sleep 86400"]
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 1000
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
2、运行验证
[root@master chapter4]# kubectl apply -f pod-with-seccontext.yaml
pod/pod-with-securitycontext created
[root@master chapter4]# kubectl exec pod-with-securitycontext -- ps aux
PID USER TIME COMMAND
1 1000 0:00 sleep 86400
6 1000 0:00 ps aux


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号