how an object looks like in memory applies to an array.
class A { int x; int y; } ... public void m1() { int i = 0; m2(); } public void m2() { A a = new A(); } ...
With the above declaration, let's invoke m1() and see what happens:
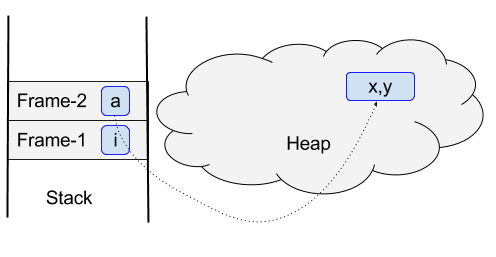
- When m1 is invoked, a new frame (Frame-1) is pushed into the stack, and local variable i is also created in Frame-1.
- Then m2 is invoked inside of m1, another new frame (Frame-2) is pushed into the stack. In m2, an object of class A is created in the heap and reference variable is put in Frame-2. Now, at this point, the stack and heap looks like the following:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号