一. system_server进程和Zygote进程
system_server进程:是用于管理整个Java framework层,包含ActivityManager,PowerManager等各种系统服务;Zygote进程:是Android系统的首个Java进程,Zygote是所有Java进程的父进程,包括system_server进程以及所有的App进程都是Zygote的子进程。
进程创建图
对于大多数的应用开发者来说创建线程比较熟悉,而对于创建进程并没有太多的概念。对于系统工程师或者高级开发者,还是有很必要了解Android系统是如何一步步地创建出一个进程的。先来看一张进程创建过程的简要图:
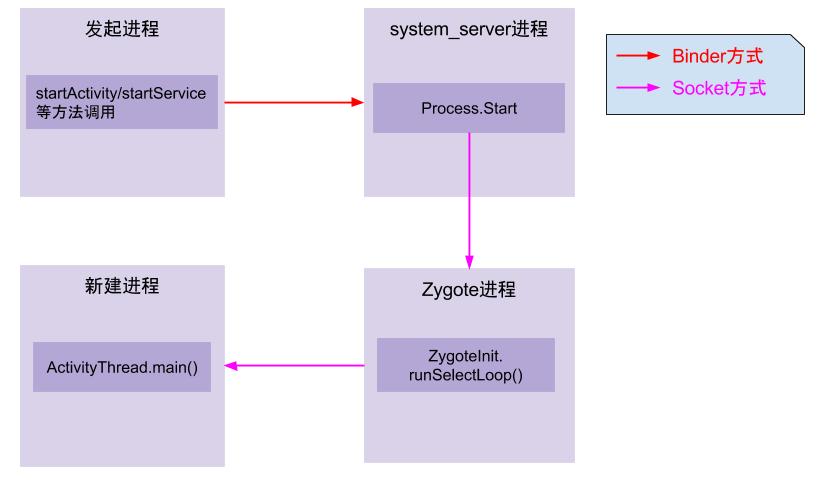
图解:
- App发起进程:当从桌面启动应用,则发起进程便是Launcher所在进程;当从某App内启动远程进程,则发送进程便是该App所在进程。发起进程先通过binder发送消息给system_server进程;
- system_server进程:调用Process.start()方法,通过socket向zygote进程发送创建新进程的请求;
- zygote进程:在执行
ZygoteInit.main()后便进入runSelectLoop()循环体内,当有客户端连接时便会执行ZygoteConnection.runOnce()方法,再经过层层调用后fork出新的应用进程; - 新进程:执行handleChildProc方法,最后调用ActivityThread.main()方法。
接下来,依次从system_server进程发起请求到Zygote创建进程,再到新进程的运行这3大块展开讲解进程创建是一个怎样的过程。
二. system_server发起请求
ActivityManagerService.java
private boolean startProcessLocked(String hostingType, String hostingNameStr, String entryPoint, ProcessRecord app, int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet, String invokeWith, long startTime) {
......... startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith,new String[] {PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq}); ........ }
AMS通过调用startProcessLocked方法向Zygote进程发送请求
1.获取要创建的应用程序进程的用户id
2.创建用户组id并赋值
3.若字符串entryPoint为null,则将其赋值为”android.app.ActivityThread”, 该值为应用程序进程主线程的类名
1. Process.start
[-> Process.java]
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass, final String niceName, int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int debugFlags, int mountExternal, int targetSdkVersion, String seInfo, String abi, String instructionSet, String appDataDir, String[] zygoteArgs) { try { return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo, abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, zygoteArgs); } catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) { throw new RuntimeException(""); } }
2. startViaZygote
[-> Process.java]
private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass, final String niceName, final int uid, final int gid, final int[] gids, int debugFlags, int mountExternal, int targetSdkVersion, String seInfo, String abi, String instructionSet, String appDataDir, String[] extraArgs) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx { synchronized(Process.class) { ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>(); argsForZygote.add("--runtime-args"); argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid); argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid); argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion); if (niceName != null) { argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName); } if (appDataDir != null) { argsForZygote.add("--app-data-dir=" + appDataDir); } argsForZygote.add(processClass); if (extraArgs != null) { for (String arg : extraArgs) { argsForZygote.add(arg); } } return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote); } }
1.创建ArrayList对象,保存应用进程的启动参数
2.调用openZygoteSocketIfNeeded方法获取ZygoteSocket对象
1).调用ZygoteState的connect方法与Zygote进程建立主模式的Socket连接,返回ZygoteState对象。mSocket=”zygote”
2).判断主模式返回的ZygoteState对象是否与启动应用程序进程所需的ABI匹配,若匹配,则返回
3).若不匹配,调用ZygoteState的connect方法与Zygote进程建立辅模式的Socket连接,返回ZygoteState对象。mSecondarySocket=”zygote_secondary”
4). 判断辅模式返回的ZygoteState对象是否与启动应用程序进程所需的ABI匹配,若匹配,则返回。若不匹配,则抛出ZygoteStartFailedEx异常
3.调用zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法,传入ArrayList对象和ZygoteSocket对象作为参数
该过程主要工作是生成argsForZygote数组,该数组保存了进程的uid、gid、groups、target-sdk、nice-name等一系列的参数。
3. zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult
[-> Process.java]
private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult( ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList<String> args) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx { try { //将保存在ArrayList中的启动参数写入ZygoteState对象中。
ZygoteState是ZygoteProcess的静态内部类,用于表示Zygote进程的通信状态。 final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer; final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream; writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size())); writer.newLine(); int sz = args.size(); for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) { String arg = args.get(i); if (arg.indexOf('\n') >= 0) { throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx( "embedded newlines not allowed"); } writer.write(arg); writer.newLine(); } writer.flush(); ProcessStartResult result = new ProcessStartResult(); //等待socket服务端(即zygote)返回新创建的进程pid; //对于等待时长问题,Google正在考虑此处是否应该有一个timeout,但目前是没有的。 result.pid = inputStream.readInt(); if (result.pid < 0) { throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed"); } result.usingWrapper = inputStream.readBoolean(); return result; } catch (IOException ex) { zygoteState.close(); throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex); } }
这个方法的主要功能是通过socket通道向Zygote进程发送一个参数列表,然后进入阻塞等待状态,直到远端的socket服务端发送回来新创建的进程pid才返回。
在Zygote进程启动后,会调用ZygoteServer对象的runSelectLoop方法,循环等待AMS的请求。此时,通过zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法,将保存在ArrayList中的启动参数写入ZygoteState对象中。Zygote进程会收到创建新的应用程序的请求。当Zygote进程收到创建新的应用程序的请求时,在runSelectLoop方法中会调用对应ZygoteConnection对象的runOnce方法。
4. openZygoteSocketIfNeeded
private static ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx { if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) { try { //向主zygote发起connect()操作 primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(ZYGOTE_SOCKET); } catch (IOException ioe) { ... } } if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) { return primaryZygoteState; } if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed()) { //当主zygote没能匹配成功,则采用第二个zygote,发起connect()操作 secondaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_SOCKET); } if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) { return secondaryZygoteState; } ... }
openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi)方法是根据当前的abi来选择与zygote还是zygote64来进行通信。
三. Zygote创建进程
既然system_server进程的zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult()方法通过socket向Zygote进程发送消息,这是便会唤醒Zygote进程,来响应socket客户端的请求(即system_server端),接下来的操作便是在Zygote来创建进程。Zygote进程是由由init进程而创建的,进程启动之后调用ZygoteInit.main()方法,经过创建socket管道,预加载资源后,便进程runSelectLoop()方法。
5. ZygoteInit.main
[–>ZygoteInit.java]
public static void main(String argv[]) { try { runSelectLoop(abiList); .... } catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) { caller.run(); } catch (RuntimeException ex) { closeServerSocket(); throw ex; } }
之后runSelectLoop()方法会抛出异常MethodAndArgsCaller,从而进入caller.run()方法。
6. runSelectLoop
[-> ZygoteInit.java]
private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller { ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>(); ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>(); //sServerSocket是socket通信中的服务端,即zygote进程。保存到fds[0] fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor()); peers.add(null); while (true) { StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) { pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd(); pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i); pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN; } try { //处理轮询状态,当pollFds有事件到来则往下执行,否则阻塞在这里 Os.poll(pollFds, -1); } catch (ErrnoException ex) { ... } for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) { //采用I/O多路复用机制,当接收到客户端发出连接请求 或者数据处理请求到来,则往下执行; // 否则进入continue,跳出本次循环。 if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) { continue; } if (i == 0) { //即fds[0],代表的是sServerSocket,则意味着有客户端连接请求; // 则创建ZygoteConnection对象,并添加到fds。 ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList); peers.add(newPeer); fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor()); //添加到fds. } else { //i>0,则代表通过socket接收来自对端的数据,并执行相应操作 boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce(); if (done) { peers.remove(i); fds.remove(i); //处理完则从fds中移除该文件描述符 } } } } }
该方法主要功能:
- 客户端通过openZygoteSocketIfNeeded()来跟zygote进程建立连接。zygote进程收到客户端连接请求后执行accept();然后再创建ZygoteConnection对象,并添加到fds数组列表;
- 建立连接之后,可以跟客户端通信,进入runOnce()方法来接收客户端数据,并执行进程创建工作。
7. acceptCommandPeer
[-> ZygoteInit.java]
private static ZygoteConnection acceptCommandPeer(String abiList) { try { return new ZygoteConnection(sServerSocket.accept(), abiList); } catch (IOException ex) { ... } }
接收客户端发送过来的connect()操作,Zygote作为服务端执行accept()操作。 再后面客户端调用write()写数据,Zygote进程调用read()读数据。
没有连接请求时会进入休眠状态,当有创建新进程的连接请求时,唤醒Zygote进程,创建Socket通道ZygoteConnection,然后执行ZygoteConnection的runOnce()方法。
8. runOnce
[-> ZygoteConnection.java]
boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller { String args[]; Arguments parsedArgs = null; FileDescriptor[] descriptors; try { //读取socket客户端发送过来的参数列表 args = readArgumentList(); descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors(); } catch (IOException ex) { closeSocket(); return true; } PrintStream newStderr = null; if (descriptors != null && descriptors.length >= 3) { newStderr = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(descriptors[2])); } int pid = -1; FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null; FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null; try { //将binder客户端传递过来的参数,解析成Arguments对象格式 parsedArgs = new Arguments(args); ... int [] fdsToClose = { -1, -1 }; FileDescriptor fd = mSocket.getFileDescriptor(); if (fd != null) { fdsToClose[0] = fd.getInt$(); } fd = ZygoteInit.getServerSocketFileDescriptor(); if (fd != null) { fdsToClose[1] = fd.getInt$(); } fd = null; pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids, parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo, parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, parsedArgs.instructionSet, parsedArgs.appDataDir); } catch (Exception e) { ... } try { if (pid == 0) { //子进程执行 IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd); serverPipeFd = null; handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr); //子进程预期的是抛出异常ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller或者执行exec(). return true; } else { //父进程执行 IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd); childPipeFd = null; return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs); } } finally { IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd); IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd); } }
runOnce方法的执行过程
1.调用readArgumentList方法获取String[]类型的启动参数
2.将String[]类型的启动参数封装成Arguments类型的对象
3.调用Zygote的forkAndSpecialize方法,传入Arguments对象作为参数创建应用程序进程。返回值为pid
4.由于当前代码逻辑运行在新建的子进程中,所以pid为0。 由于pid为0,会调用handleChildProc方法对应用程序进程进行处理
9. forkAndSpecialize
[-> Zygote.java]
public static int forkAndSpecialize(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int debugFlags, int[][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName, int[] fdsToClose, String instructionSet, String appDataDir) { VM_HOOKS.preFork(); int pid = nativeForkAndSpecialize( uid, gid, gids, debugFlags, rlimits, mountExternal, seInfo, niceName, fdsToClose, instructionSet, appDataDir); ... VM_HOOKS.postForkCommon(); return pid; }
四. 新进程运行
在前面[流程6]runOnce()过程中调用forkAndSpecialize()创建完新进程后,返回值pid=0(即运行在子进程)继续开始执行handleChildProc()方法。
10. handleChildProc
[-> ZygoteConnection.java]
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs, FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr) throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller { //关闭Zygote的socket两端的连接 closeSocket(); ZygoteInit.closeServerSocket(); if (descriptors != null) { try { Os.dup2(descriptors[0], STDIN_FILENO); Os.dup2(descriptors[1], STDOUT_FILENO); Os.dup2(descriptors[2], STDERR_FILENO); for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors) { IoUtils.closeQuietly(fd); } newStderr = System.err; } catch (ErrnoException ex) { Log.e(TAG, "Error reopening stdio", ex); } } if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) { //设置进程名 Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName); } if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) { //据说这是用于检测进程内存泄露或溢出时场景而设计,后续还需要进一步分析。 WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith, parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs); } else { //执行目标类的main()方法 RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, null); } }
11. zygoteInit
[–>RuntimeInit.java]
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller { redirectLogStreams(); //重定向log输出 commonInit(); // 通用的一些初始化 nativeZygoteInit(); // zygote初始化 applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader); // 应用初始化 }
12.applicationInit
[–>RuntimeInit.java]
private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller { //true代表应用程序退出时不调用AppRuntime.onExit(),否则会在退出前调用 nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true); //设置虚拟机的内存利用率参数值为0.75 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f); VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion); final Arguments args; try { args = new Arguments(argv); //解析参数 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { return; } Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); //调用startClass的static方法 main() invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader); }
此处args.startClass为”android.app.ActivityThread”。
13. invokeStaticMain
[–>RuntimeInit.java]
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller { Class<?> cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader); Method m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class }); int modifiers = m.getModifiers(); ... //通过抛出异常,回到ZygoteInit.main()。这样做好处是能清空栈帧,提高栈帧利用率。 throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv); }
invokeStaticMain()方法中抛出的异常MethodAndArgsCaller caller,该方法的参数m是指main()方法, argv是指ActivityThread. 根据前面可知,下一步进入caller.run()方法,也就是MethodAndArgsCaller.run()。
14. MethodAndArgsCaller
[–>ZygoteInit.java]
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception implements Runnable { public void run() { try { //根据传递过来的参数,此处反射调用ActivityThread.main()方法 mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs }); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new RuntimeException(ex); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { Throwable cause = ex.getCause(); if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) cause; } else if (cause instanceof Error) { throw (Error) cause; } throw new RuntimeException(ex); } } }
进入到了ActivityThread类的main()方法。
15. ActivityThread.main
[–> ActivityThread.java]
public static void main(String[] args) { ... Environment.initForCurrentUser(); ... Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>"); //创建主线程looper Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); //attach到系统进程 thread.attach(false); if (sMainThreadHandler == null) { sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler(); } //主线程进入循环状态 Looper.loop(); throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); }
1.调用Looper的prepareMainLooper方法创建主线程Looper
2.创建ActivityThread对象
3.通过调用ActivityThread对象的getHandler方法获取主线程H类对象,H类继承了Handler类,是ActivityThread的内部类,用于处理线程的消息循环
4.调用Looper的loop方法开启消息循环
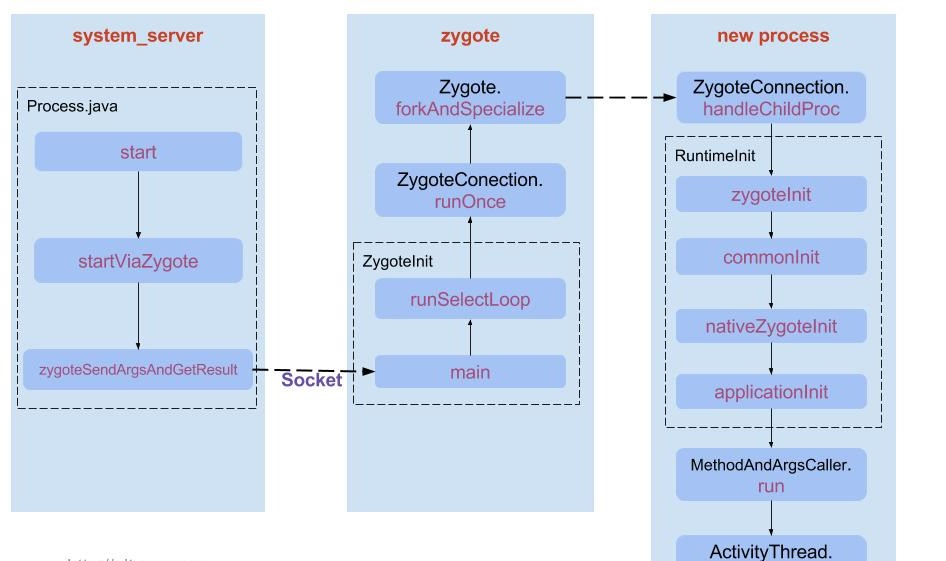
五. 总结



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号