二叉树
二叉树
94.二叉树的中序遍历


方案一:递归算法
中序遍历顺序左根右
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void inorder(TreeNode *d,vector<int>&a){//d是当前根节点,a是答案返回数组
if(!d){#d为空节点
return;
}
inorder(d->left,a);//左
a.push_back(d->val);//根
inorder(d->right,a);//右
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>ans;
inorder(root,ans);
return ans;
}
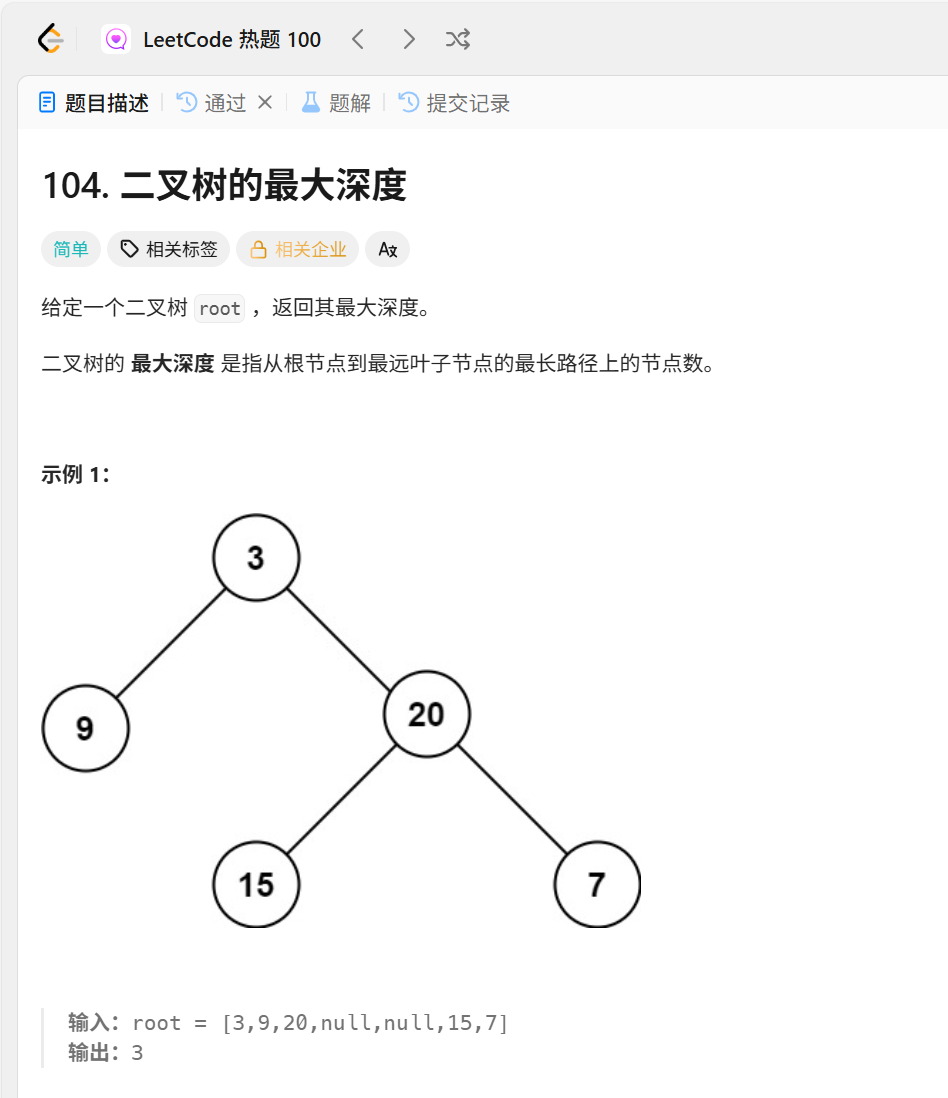
};104.二叉树的最大深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int calculate_height(TreeNode*a){
if(!a){//空节点
return 0;
}
return 1+max(calculate_height(a->left),calculate_height(a->right));//递归
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return calculate_height(root);
}
};226.翻转二叉树
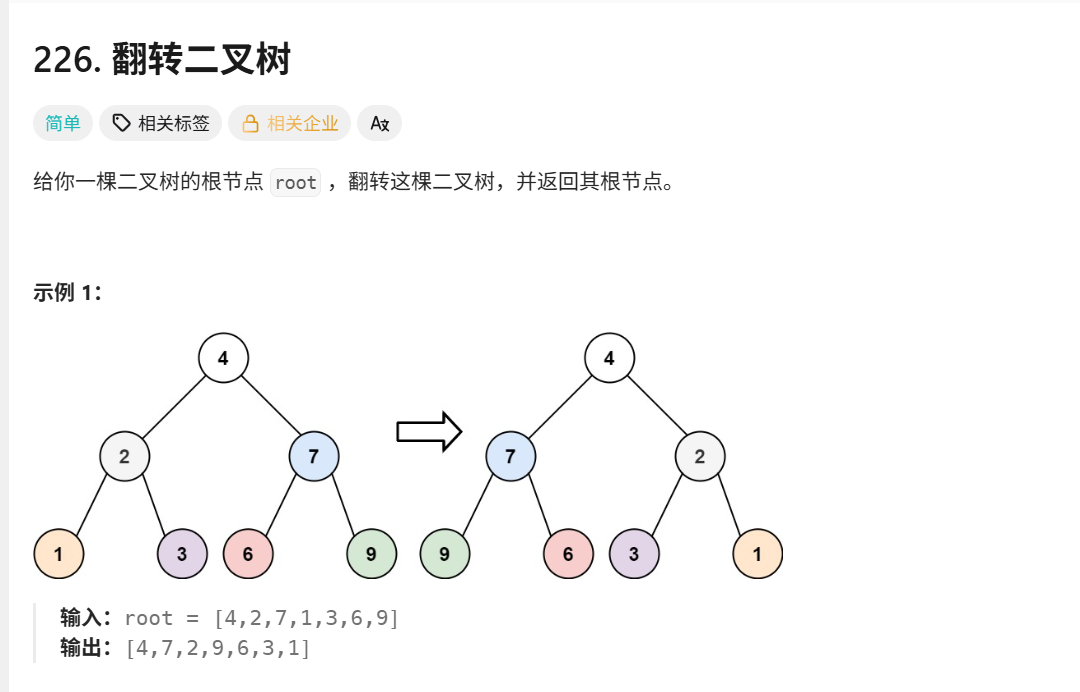
递归思想:先递归翻转左右子树,再交换左右子树,记得保存左右指针副本防止被覆盖(交换时左右指针不变)。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root){
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode*l=root->left;
TreeNode*r=root->right;
root->left=invertTree(r);
root->right=invertTree(l);
return root;
}
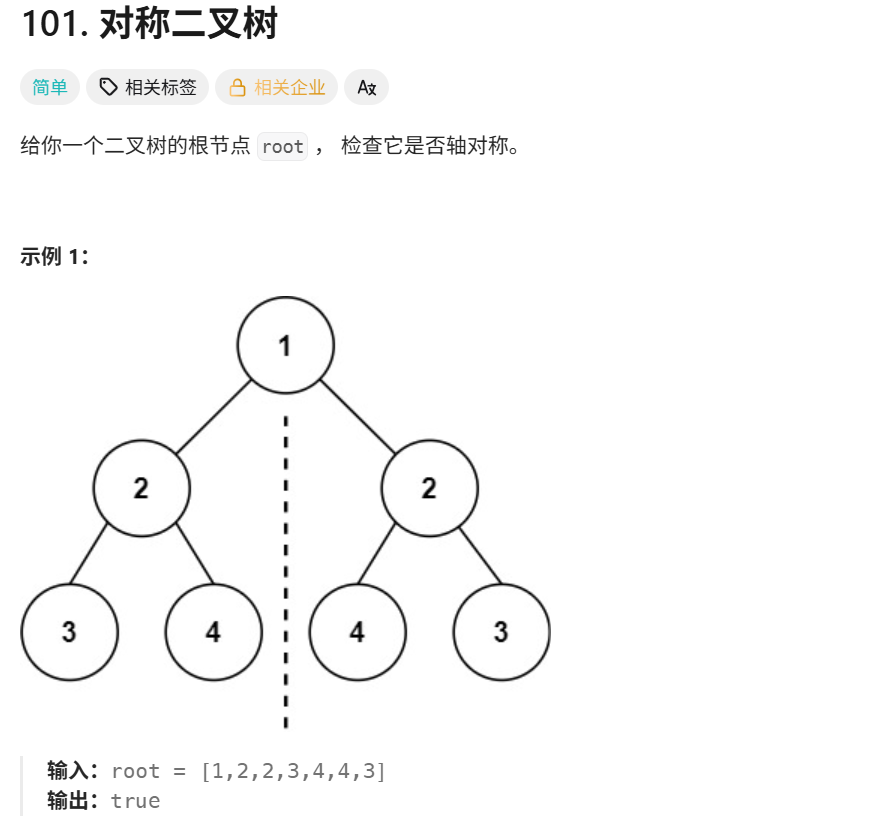
};101.对称二叉树
递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool ismirror(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b) { // 判断a和b两个子树是否对称
if (!a && !b) { // a和b两个都是空节点->一定对称
return true;
}
if (!a || !b) { // a和b之间有一个是空节点
return false;
}
//a与b都是非空结点
return (a->val==b->val)&&ismirror(a->left,b->right)&&ismirror(a->right,b->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
return ismirror(root->left,root->right);//看左右子树是否镜像对称
}
};迭代:
用一个队列存放
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool check(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b) {
//迭代
queue<TreeNode*>q;
q.push(a);
q.push(b);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode*x=q.front();q.pop();
TreeNode*y=q.front();q.pop();
if(!x&&!y)continue;//都是空节点也相等可以跳下一步
if((!x||!y)||(x->val!=y->val))return false;//不相等的情况:1.一个空一个非空 2.如果是都非空则值不相等时不相等
//对称:左枝左和右枝右,左枝右和右枝左
q.push(x->left);
q.push(y->right);
q.push(x->right);
q.push(y->left);
}
return true;//只用当循环结束时才知道完全对称
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return check(root,root);
}
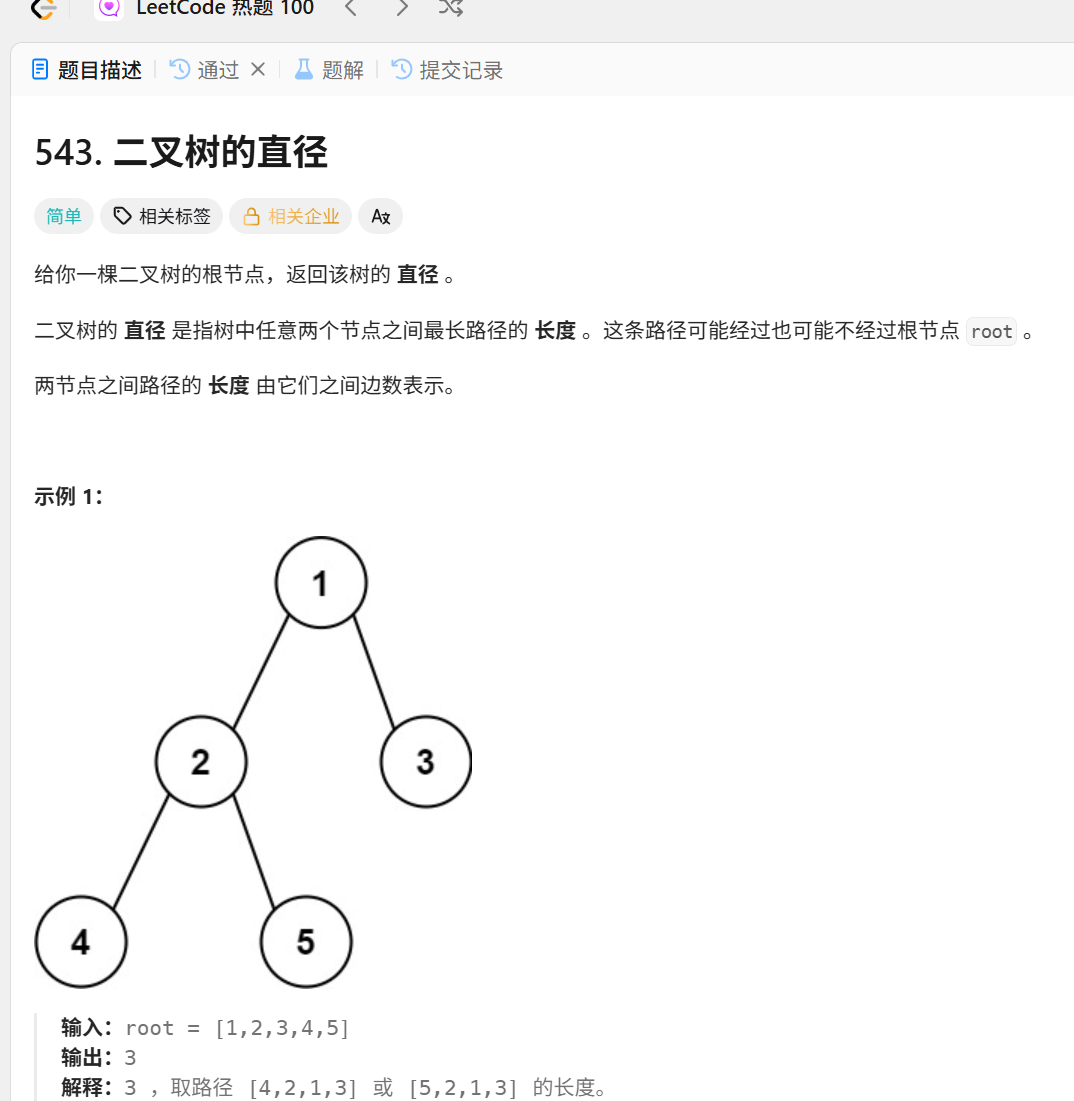
};543.二叉树的直径
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int ans;
int depth(TreeNode*root){
//从下往上计算深度,空节点的深度0
if(root==nullptr)return 0;
int l=depth(root->left);
int r=depth(root->right);
ans=max(ans,l+r+1);//一个节点跨两边算以这个节点为根的的边的总和。
return max(l,r)+1;//当前的结点高度
}
public:
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
ans=1;
depth(root);
return ans-1;
}
};102.二叉树的层序遍历
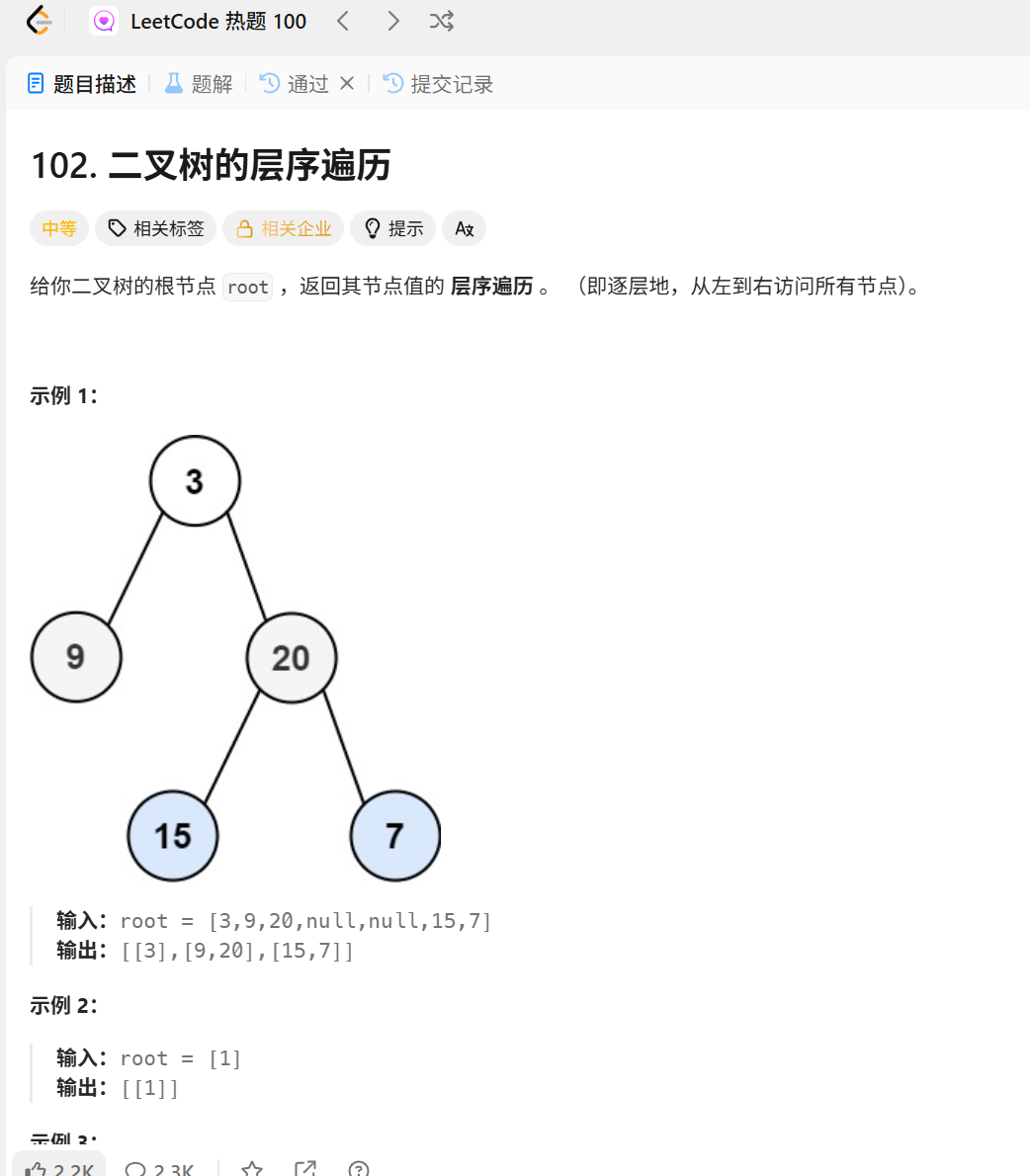
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) {
return ans;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int s = q.size();
ans.push_back(vector<int>()); // 先在二维数组内放入一个一维数组
for (int i = 1; i <= s; i++) {//当前层
TreeNode* a = q.front();
q.pop();
ans.back().push_back(a->val);
if (a->left)
q.push(a->left);
if (a->right)
q.push(a->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public: // 因为本身有序所以可以用二分法
TreeNode*
sorttree(vector<int>& nums, int low,
int high) { // 对数组下标low->high的元素进行二叉搜索树转换
if (low > high) {
return nullptr;
}
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]); // 二叉树根节点
//根节点左右
root->left = sorttree(nums, low, mid - 1);
root->right = sorttree(nums, mid+1, high);
return root;
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
return sorttree(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};98.验证二叉搜索树

下面这个方法错误的原因是:
例如左儿子<根且左边是二叉搜索树并不能保证左子树上点全小于根。
root->left->val < root->val && isValidBST(root->left)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
TreeNode* l;
TreeNode* r;
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
return true;
} else if (!root->right) {
if (root->left->val < root->val && isValidBST(root->left)) {
return true;
}
return false;
} else if (!root->left) {
if (root->right->val > root->val && isValidBST(root->right)) {
return true;
}
return false;
} else {
if (root->right->val > root->val && isValidBST(root->right) &&
root->left->val < root->val && isValidBST(root->left)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
};正确方法与第108题一样,二分
按照取值二分:最小~最大
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool checker(TreeNode*root,long long lower,long long upper){//lower下界,upper上界
if(!root){
return true;//空节点
}
if(lower>=root->val||upper<=root->val){
return false;
}
return checker(root->left,lower,root->val)&&checker(root->right,root->val,upper);
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return checker(root,LONG_MIN,LONG_MAX);//系统默认最大最小值LONG_MIN,LONG_MAX
}
};230.二叉搜索树中第k小的元素
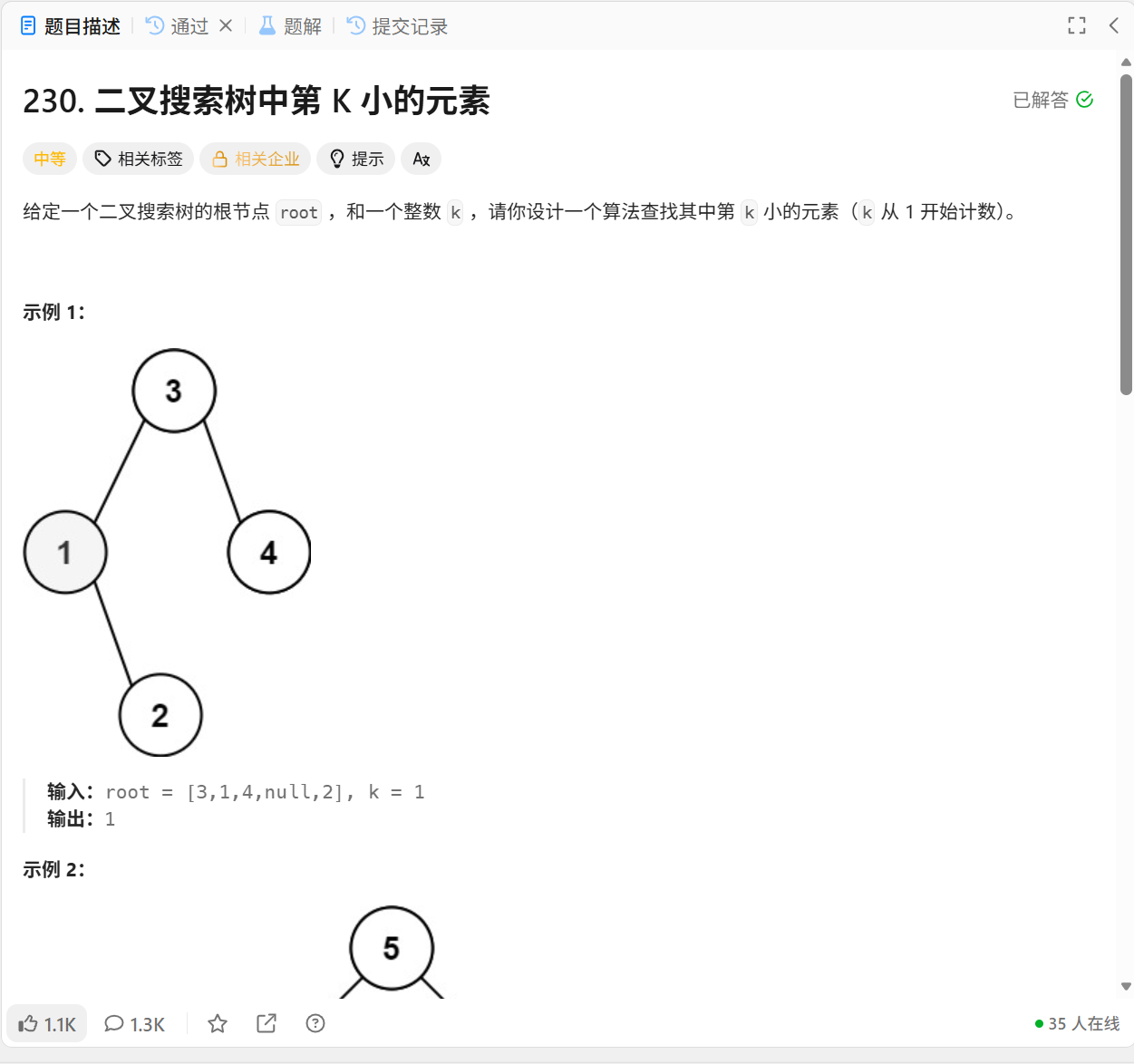
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void zx(TreeNode*root,vector<int>&v){
if(!root){
return ;
}
zx(root->left,v);
v.push_back(root->val);
zx(root->right,v);
}
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<int>v;
zx(root,v);
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
return v[k-1];
}
};利用中序遍历,将所有点放入数组,再排序
199.二叉树的右视图
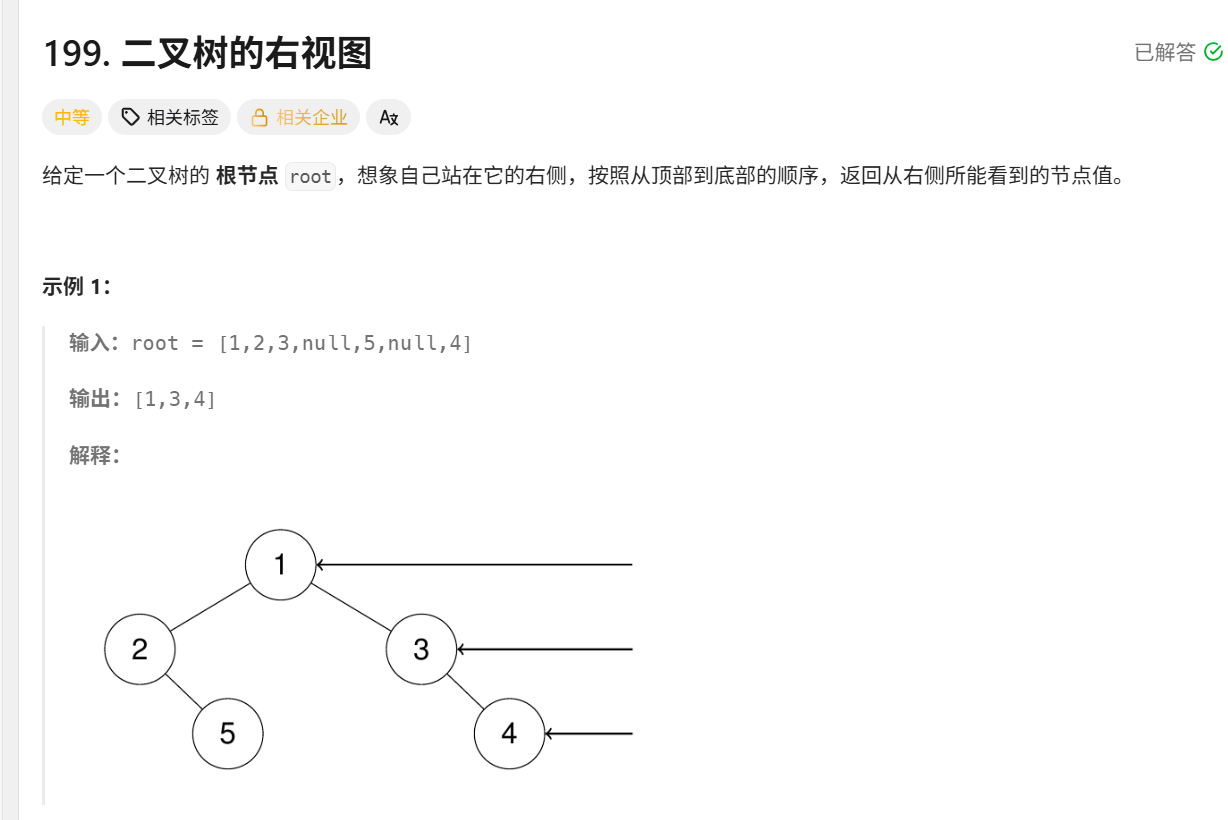
思路:层序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
int maxdepth = -1;
// 思路:利用层序遍历每一层遍历的最后一个是右视图内的点。
unordered_map<int, int> mp; // 层高和本层最后的一个元素
queue<TreeNode*> qt; // 树结点
queue<int> qd; // 树深
qt.push(root);
qd.push(0);
while (!qt.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = qt.front();
int depth = qd.front();//弹出一个点需要弹出他的对应高度
qt.pop();
qd.pop();
if (node) {
mp[depth] = node->val;
maxdepth = max(maxdepth, depth);
qt.push(node->left);
qt.push(node->right);
qd.push(depth + 1); // 左子树深
qd.push(depth + 1); // 右子树深
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= maxdepth; i++) {
ans.push_back(mp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};114.二叉树展开为链表
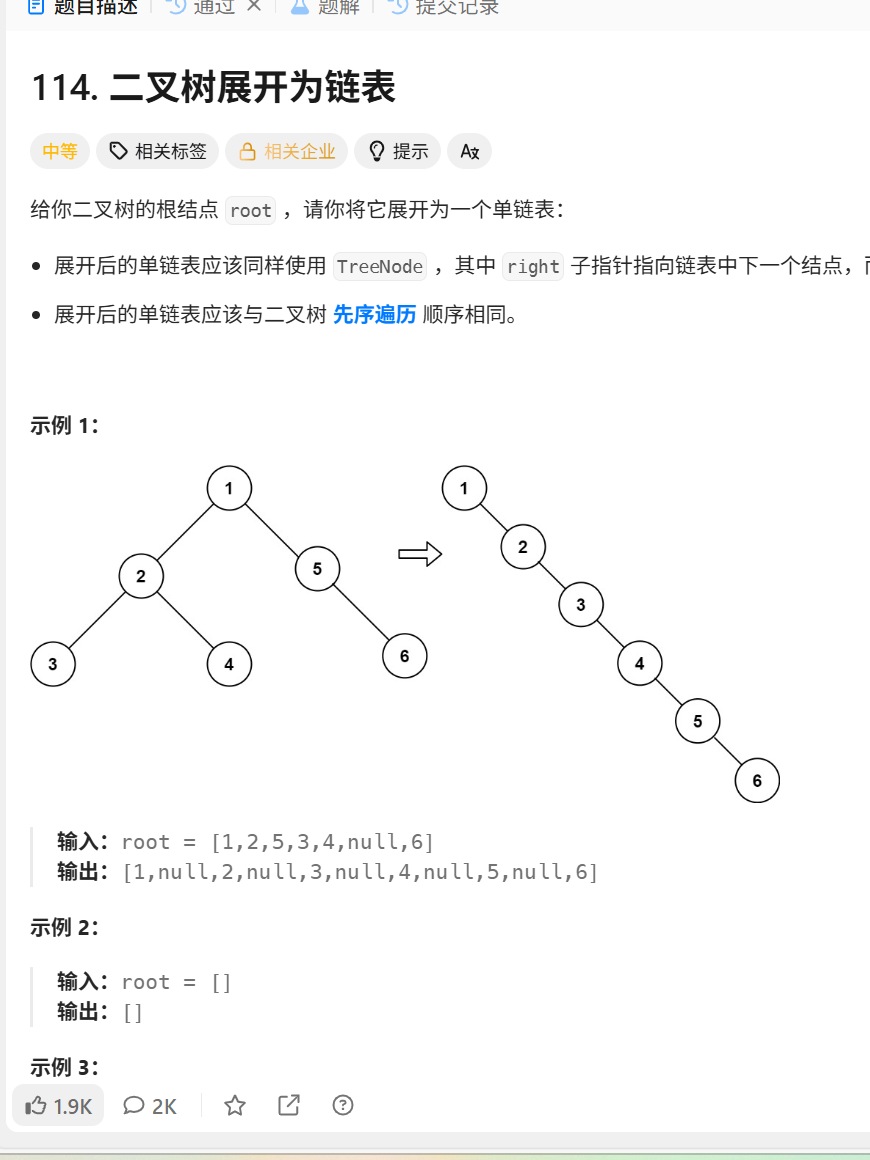
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
queue<TreeNode*> q;
public:
void xx(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root)
return;
q.push(root); // 先序遍历:根
xx(root->left); // 先序遍历:左
xx(root->right); // 先序遍历:右
}
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root){
return;
}
xx(root);
root = q.front();
q.pop();
TreeNode* curr = root;
while (!q.empty()) {
curr->left = nullptr;
curr->right = q.front();
q.pop();
curr = curr->right;
}
}
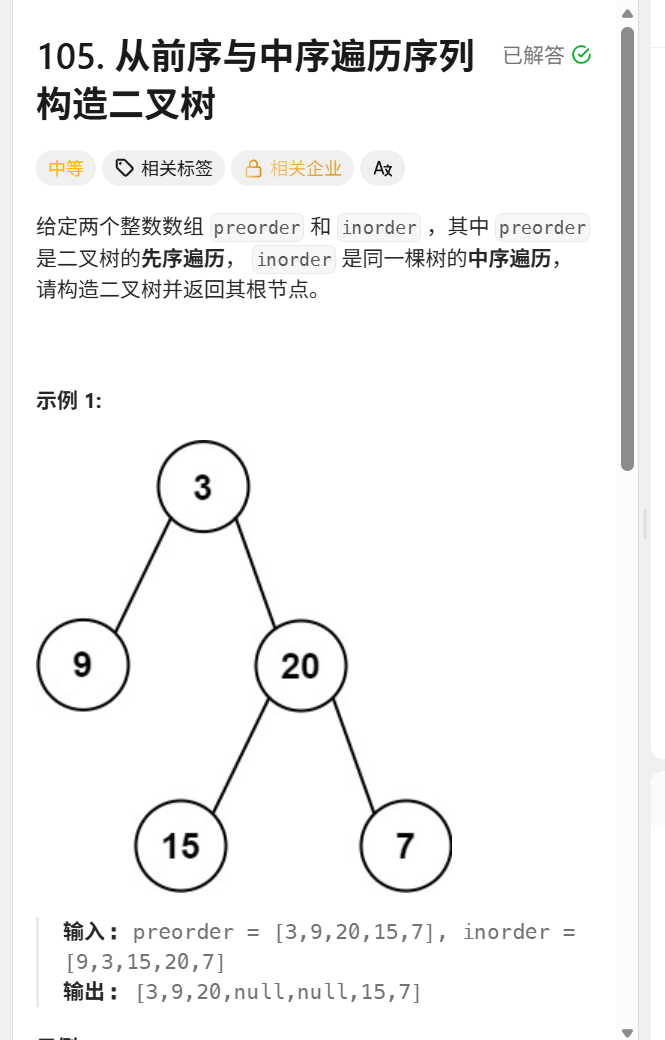
};105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:unordered_map<int,int>index;//因为要根据中序遍历定位,高效定位用哈希表,index[元素值]=中序遍历的位置的下标
public:
TreeNode*mybuildtree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int preleft,int preright,int inorderleft,int inorderright){
//vector<int>& preorder前序遍历, vector<int>& inorder中序遍历,int preleft前序的左端点,int preright前序的右端点,int inorderleft中序左端点,int inorderright中序右端点
if(preleft>preright){
return nullptr;
}
int treeroot=preorder[preleft];//前序遍历中第一个点是根,该变量存根值
TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(treeroot);
int p=index[treeroot];//中序遍历,找到根节点在中序遍历中位置由此确定左右子树大小
int ltree=p-inorderleft;//左子树大小(由中序遍历确定,左根右)
//递归左子树,在前序遍历中排除根后左子树从preleft+1到preleft+ltree,在中序遍历中左子树从inorderleft到左子树中最后一个点(中序遍历中根的前一个点p-1)
root->left=mybuildtree(preorder,inorder,preleft+1,preleft+ltree,inorderleft,p-1);//递归构建左子树
//递归构建右子树,排除根后右子树从preleft+1+ltree到preright,在中序遍历中右子树从p+1到右子树中最后一个点inorderright
root->right=mybuildtree(preorder,inorder,preleft+1+ltree,preright,p+1,inorderright);//递归去构建右子树
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int n=preorder.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
index[inorder[i]]=i;
}
return mybuildtree(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
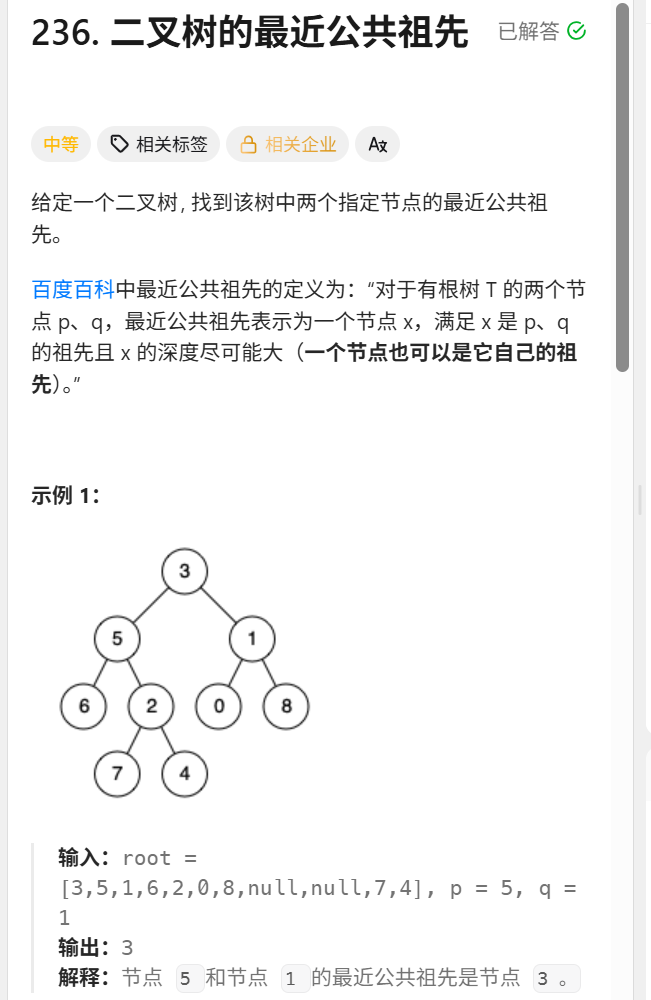
};236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
TreeNode*ans;
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode*root,TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q){//只有当root为根的树中同时包含p,q时才返回true
if(!root){//root是空的时候就不可能包含pq
return false;
}
bool lson=dfs(root->left,p,q);//左子树是否同时含p和q
bool rson=dfs(root->right,p,q);//右子树是否同时含有p与q
if((lson&&rson)||((lson||rson)&&((root->val==p->val)||(root->val==q->val)))){
//root可能是答案的情况:1.左右子树同时包含p与q 2.左右子树中有包含p与q的,且根恰好就是p与q中的一个
ans=root;
}
return lson||rson||(root->val==p->val)||(root->val==q->val);
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
dfs(root,p,q);
return ans;
}
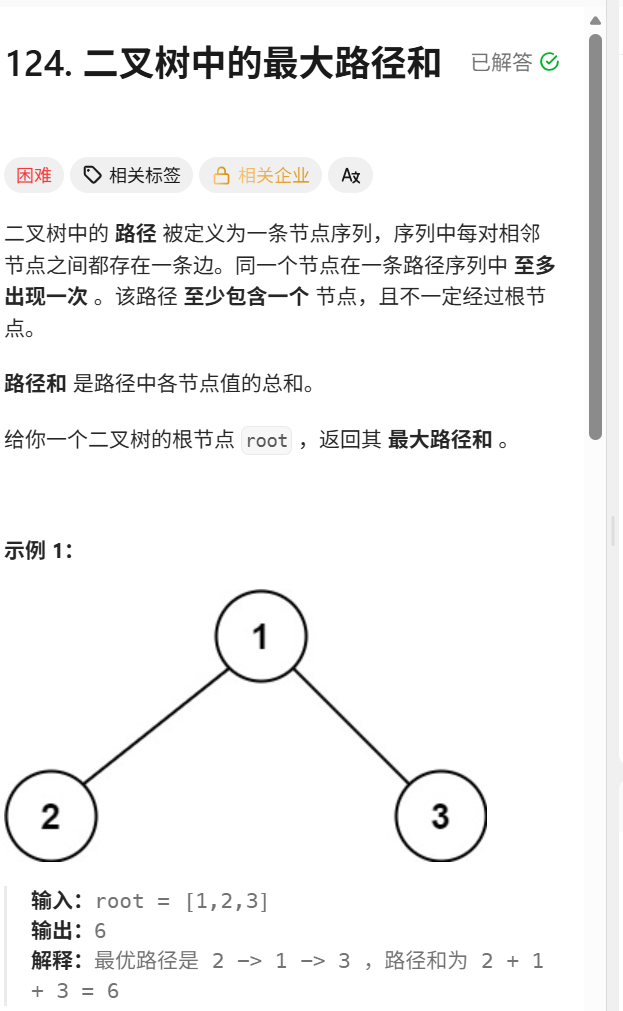
};124.二叉树中的最大路径和
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left),
* right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
int ans = INT_MIN;
int js(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int leftgain = max(0, js(root->left));//左子树最大权值和
int rightgain = max(0, js(root->right));//右子树最大权值和
int pathval = root->val + leftgain + rightgain;//经过root结点的路径中的最大权值和
ans = max(ans, pathval);
return root->val+max(leftgain,rightgain);//到当前结点时的最大权值和
}
public:
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
js(root);
return ans;
}
};
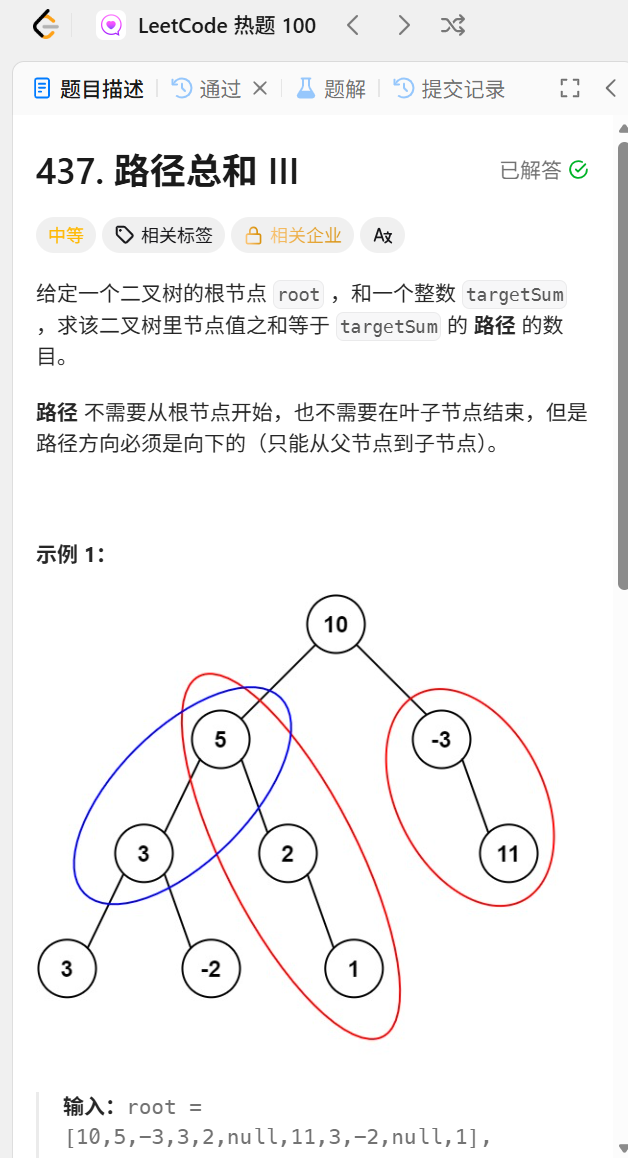
437.路径总和III

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int rootsum(TreeNode*root,long long targetSum){
if(!root){
return 0;
}
//利用ret来统计能凑到targetsum的路径数
int ret=0;
if(root->val==targetSum){//当前结点值是targetsum
ret++;
}
//包含根节点的左子树或右子树凑到targetsum
ret+=rootsum(root->left,targetSum-root->val);
ret+=rootsum(root->right,targetSum-root->val);
return ret;
}
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(!root){
return 0;
}
int ret=rootsum(root,targetSum);//计算包含root结点的路径和为targetsum的总路径数量。
ret+=pathSum(root->left,targetSum);//左子树凑到targetSum
ret+=pathSum(root->right,targetSum);//右子树凑到targetSum
return ret;
}
};




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号