链表
链表
160.相交链表
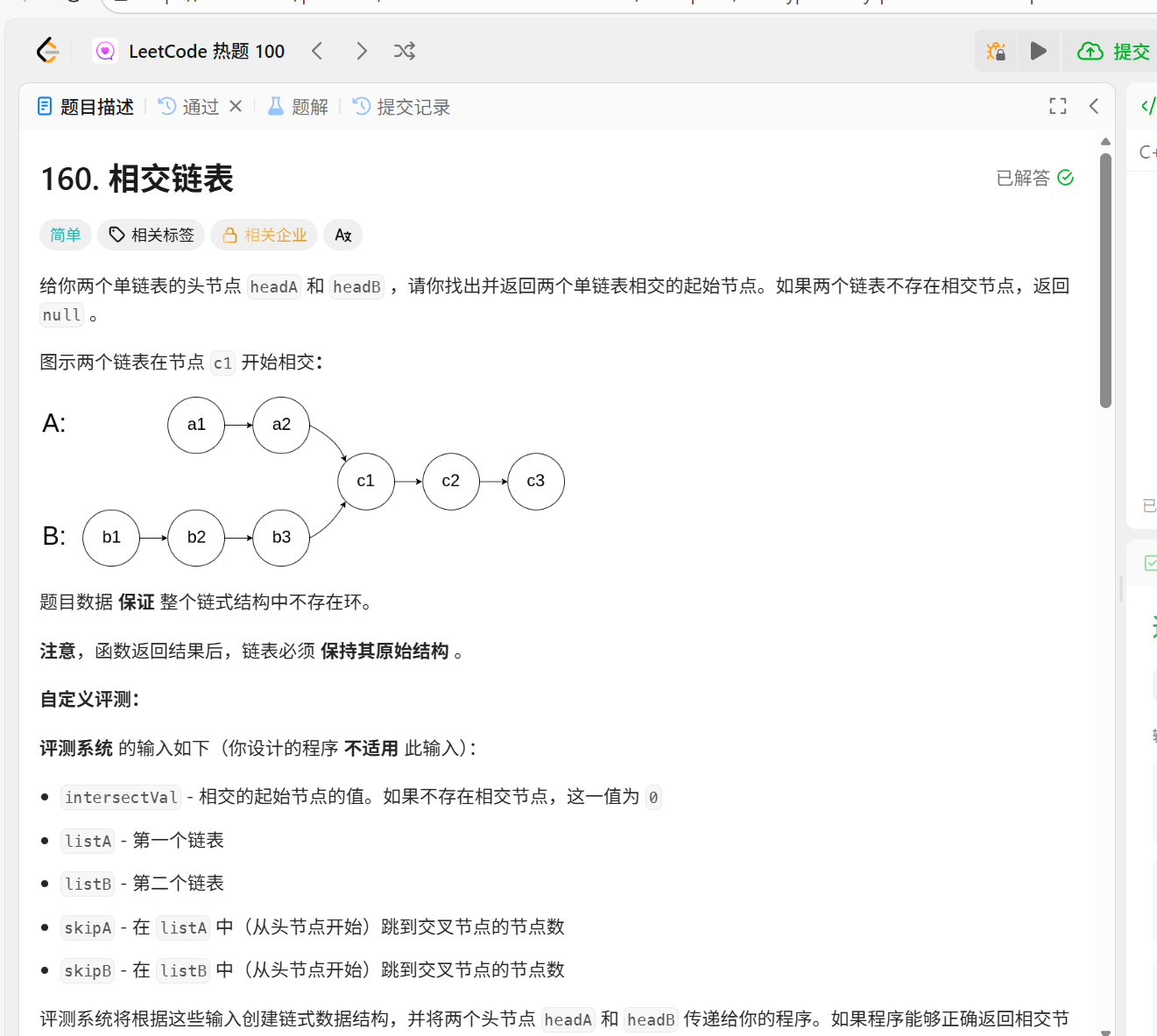

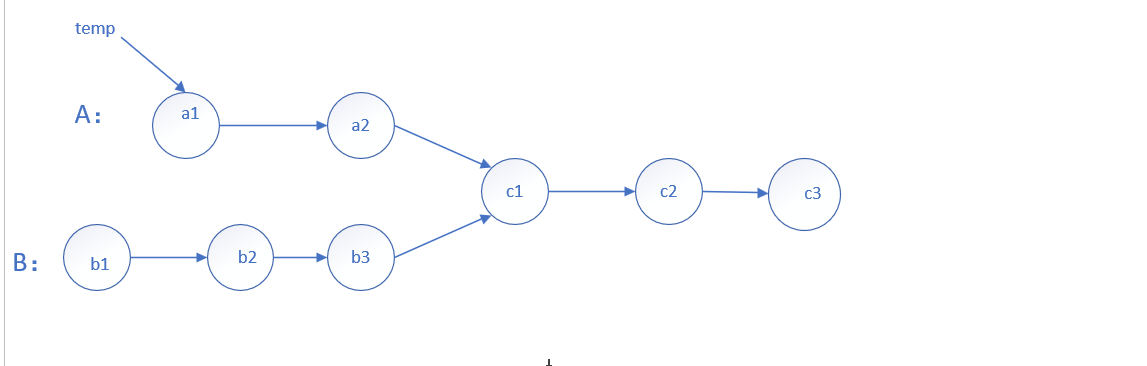
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
unordered_set<ListNode *>visited;
ListNode *temp=headA;
while(temp!=nullptr){
visited.insert(temp);
temp=temp->next;
}
temp=headB;
while(temp!=nullptr){
if(visited.count(temp)){
return temp;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};用一个指针指向链表A的表头然后遍历链表并放入哈希表,然后再遍历链表B看链表B里的点是否有在哈希表内的,如果有就返回。没有就返回空
206.反转链表
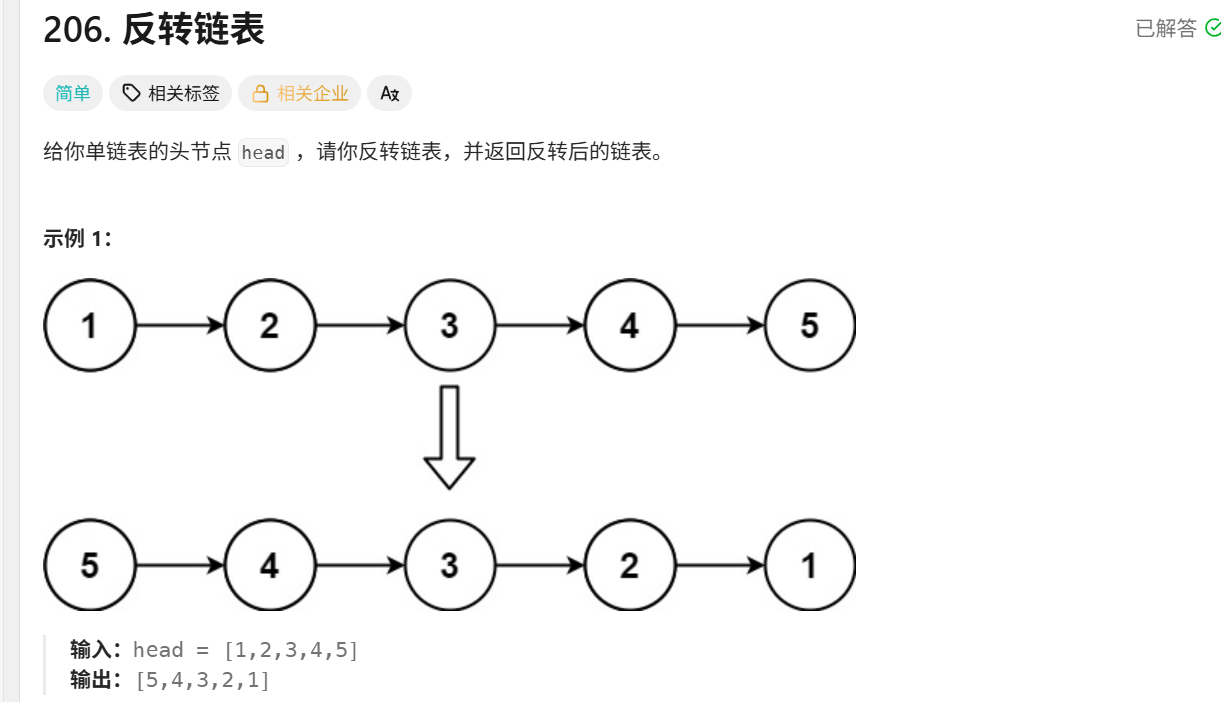
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *curr=head;#指向当前结点
ListNode *prev=nullptr;#指向当前结点的前一个点
while(curr){#退出的时候curr为nullptr
ListNode *next=curr->next;
curr->next=prev;
prev=curr;
curr=next;
}
return prev;
}
};234.回文链表
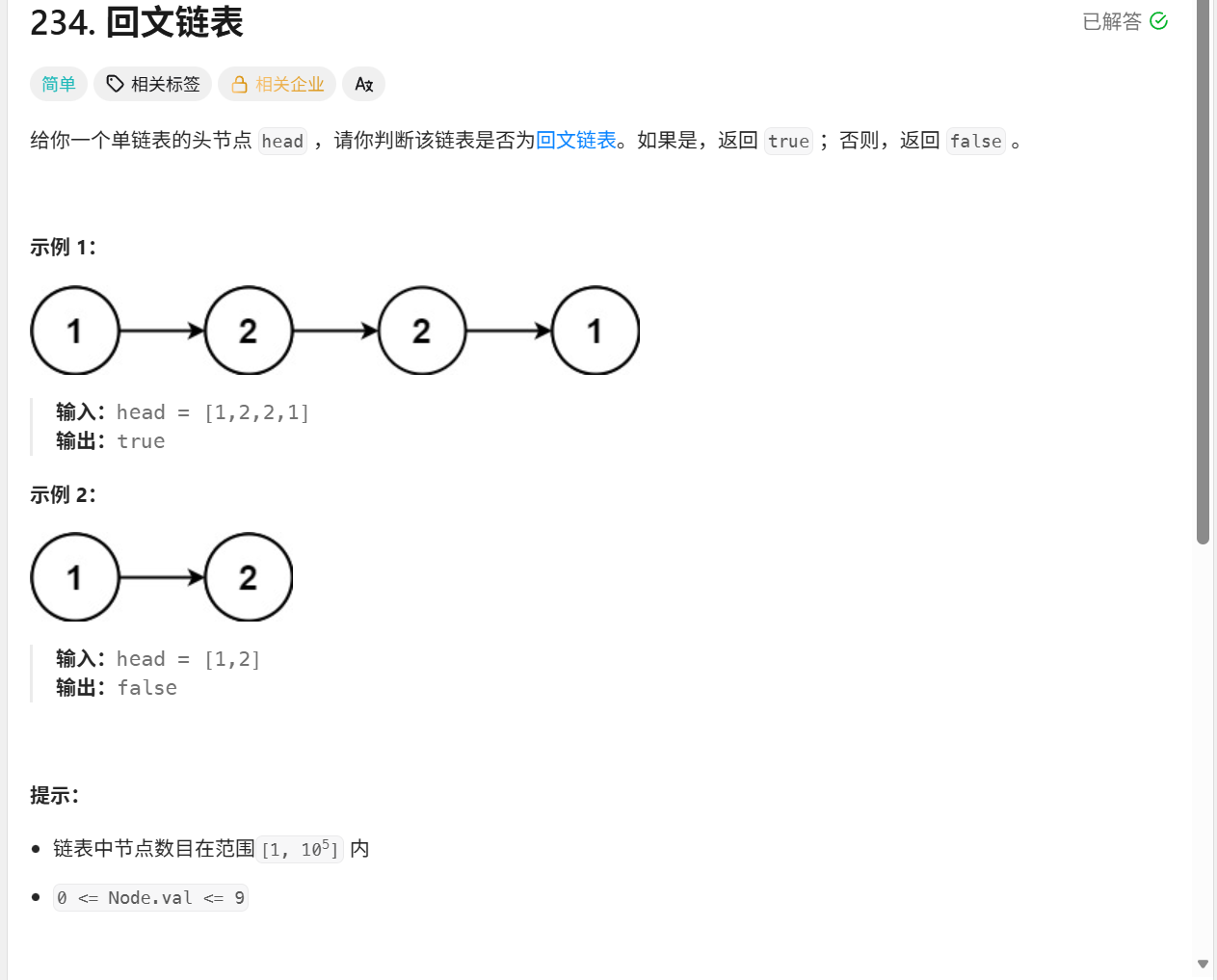
思想:
回文链表就是对称
方法是先将链表内的数按序放入一个数组中,然后左右指针向中间靠拢,检查一下是否左右对应相等呢
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
vector<int>nums;
ListNode *t=head;
while(t){
nums.push_back(t->val);
t=t->next;
}
int n=nums.size();
int i=0;
int j=n-1;
while(i<j){
if(nums[i]!=nums[j]){
return false;
}
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
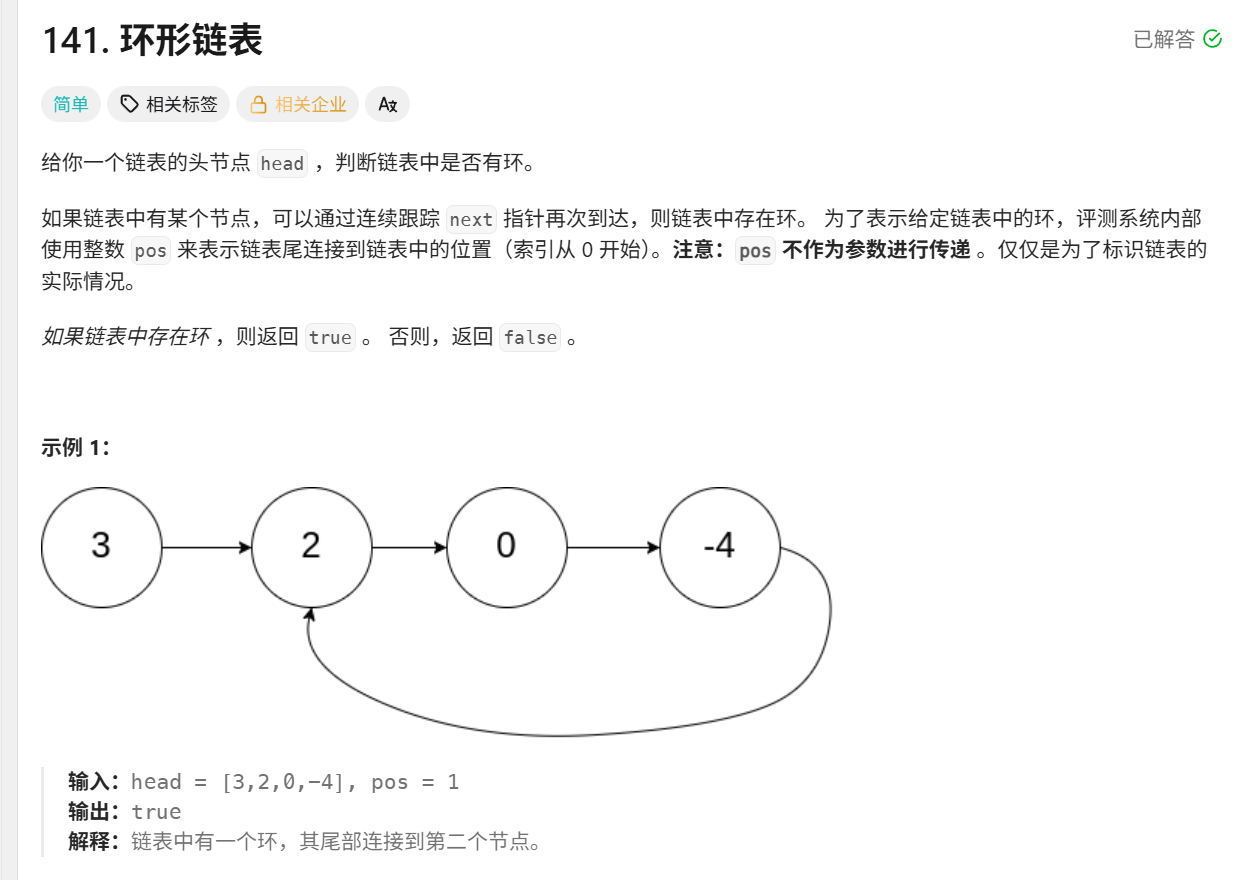
};141 环形链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode* head) {
unordered_set<ListNode*> visit;
ListNode* t = head;
while (t) {
if (visit.count(t))
return true;
visit.insert(t);
t=t->next;
}
return false;
}
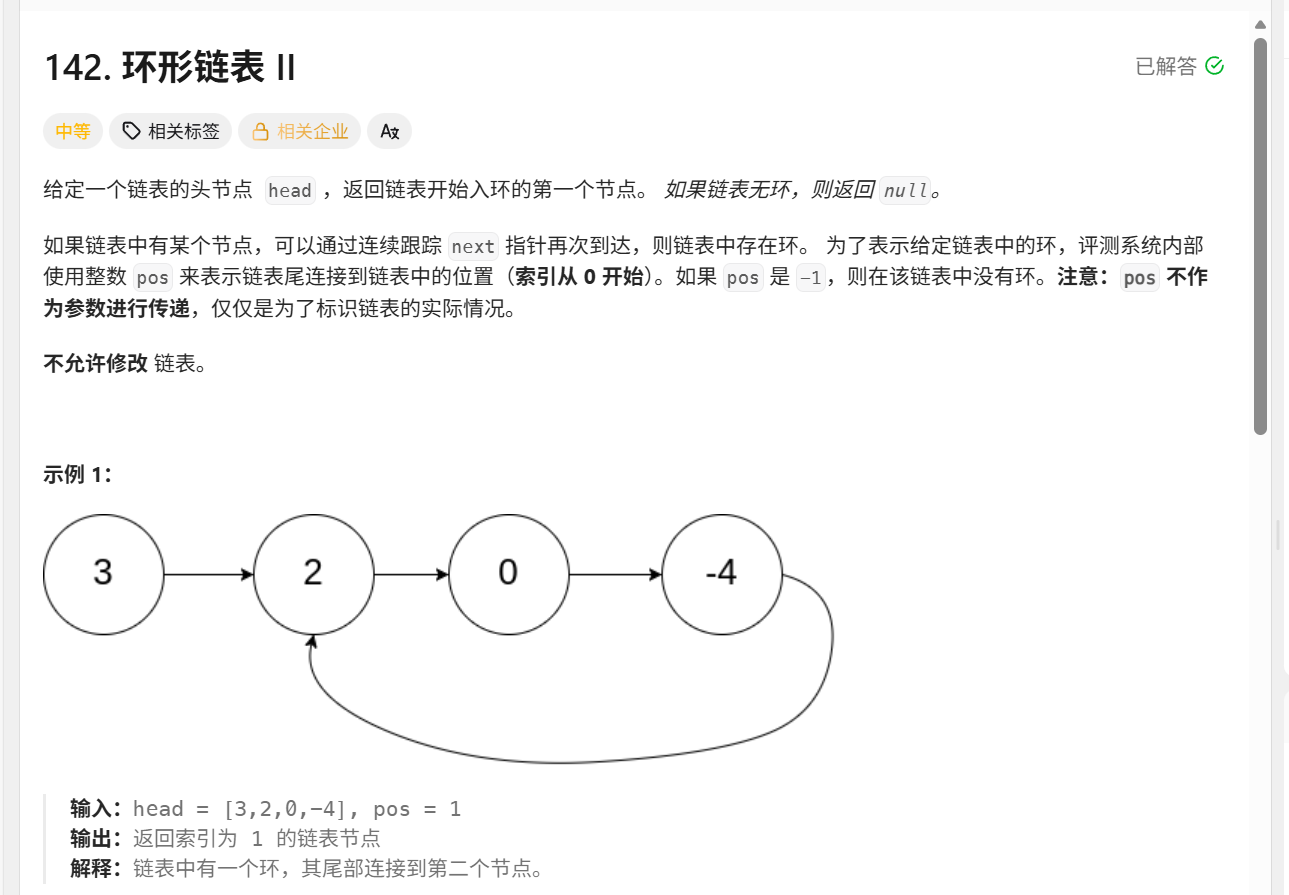
};142环形链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* detectCycle(ListNode* head) {
unordered_set<ListNode*> visit;
ListNode* t = head;
while (t) {
if (visit.count(t)) {
return t;
}
visit.insert(t);
t = t->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
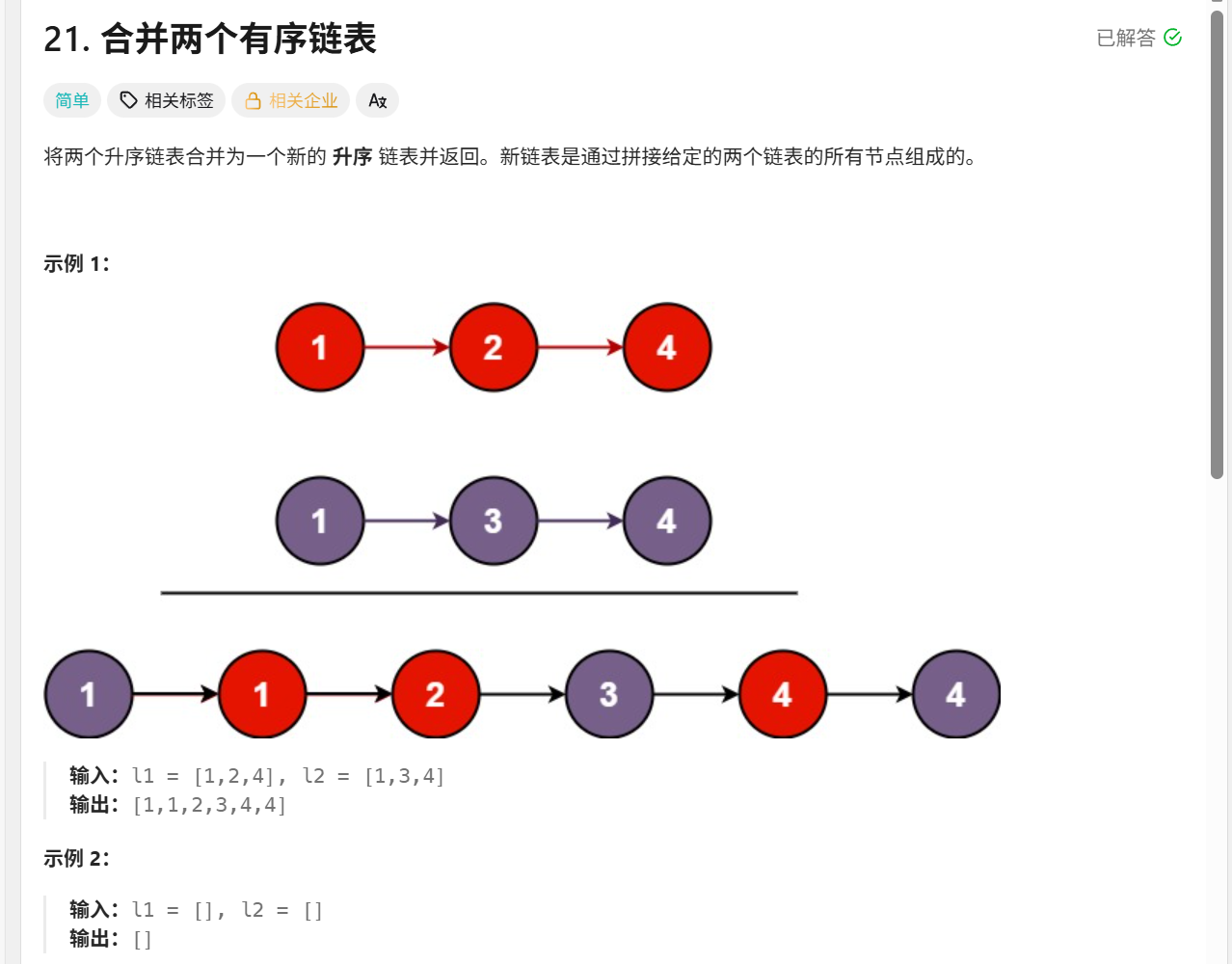
21合并两个有序链表

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if(!list1&&!list2)return nullptr;
ListNode* head;
if(!list1){
head=list2;
}
else if(!list2){
head=list1;
}
else{
ListNode* a = list1;
ListNode* b = list2;
ListNode* t;
if ((a->val) <= (b->val)) {
head = a;
t = a;
a = a->next;
} else {
t = b;
head = b;
b = b->next;
}
while (a && b) {
if (a->val <= b->val) {
t->next = a;
t=a;
a = a->next;
} else {
t->next = b;
t=b;
b = b->next;
}
}
if(a){
t->next=a;
}
if(b){
t->next=b;
}}
return head;
}
};
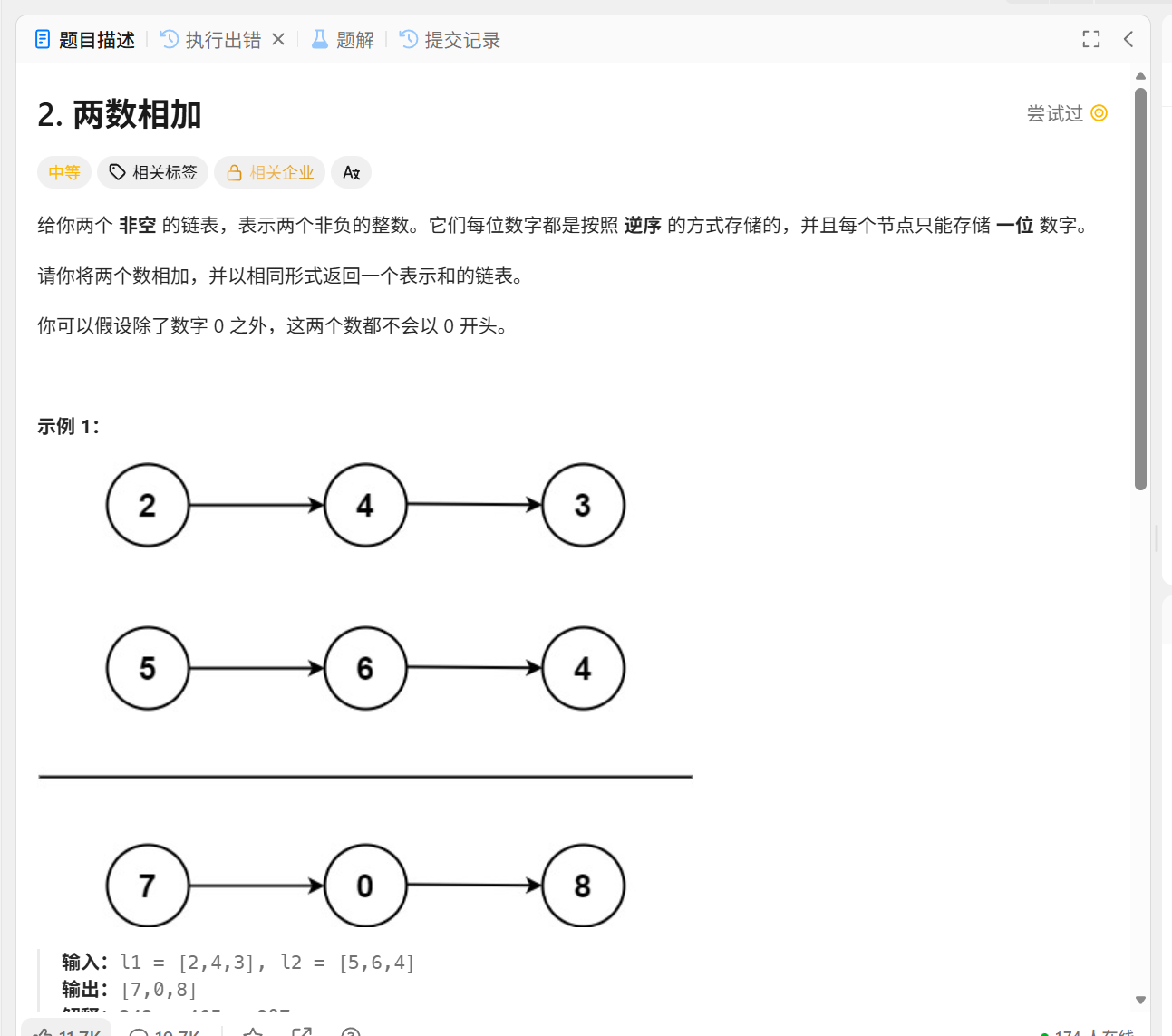
2两数相加

超时方法因为节点数过多用int存不了!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *t=l1;
int sum1=0;
int sum2=0;
int k=1;
while(t){
sum1+=(t->val)*k;
k*=10;
t=t->next;
}
k=1;
t=l2;
while(t){
sum2+=(t->val)*k;
k*=10;
t=t->next;
}
int sum=sum1+sum2;//807
ListNode *head;
ListNode* a=new ListNode(sum%10);
head=a;
t=a;
sum/=10;
while(sum){
int y=sum%10;
sum/=10;
a=new ListNode(y);
t->next=a;
t=t->next;
}
return head;
}
};正确解:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
//考点:对于初始定义指针得指向空的指针。
ListNode* head=nullptr;//答案返回的头指针。
ListNode* tail=nullptr;//用于遍历的尾指针!
int carry = 0; // 进位
int sum = 0;
int n1, n2;
while (l1 || l2) {
if (!l1) {
n1 = 0;
} else {
n1 = l1->val;
}
if (!l2) {
n2 = 0;
} else {
n2 = l2->val;
}
sum = n1 + n2 + carry;
if (!head) {
// 头指针为空
head = new ListNode(sum % 10);
tail = head;
} else {
tail->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
tail = tail->next;
}
carry = sum / 10; // 进位
if (l1) {
l1 = l1->next;
}
if (l2) {
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) {
tail->next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return head;
}
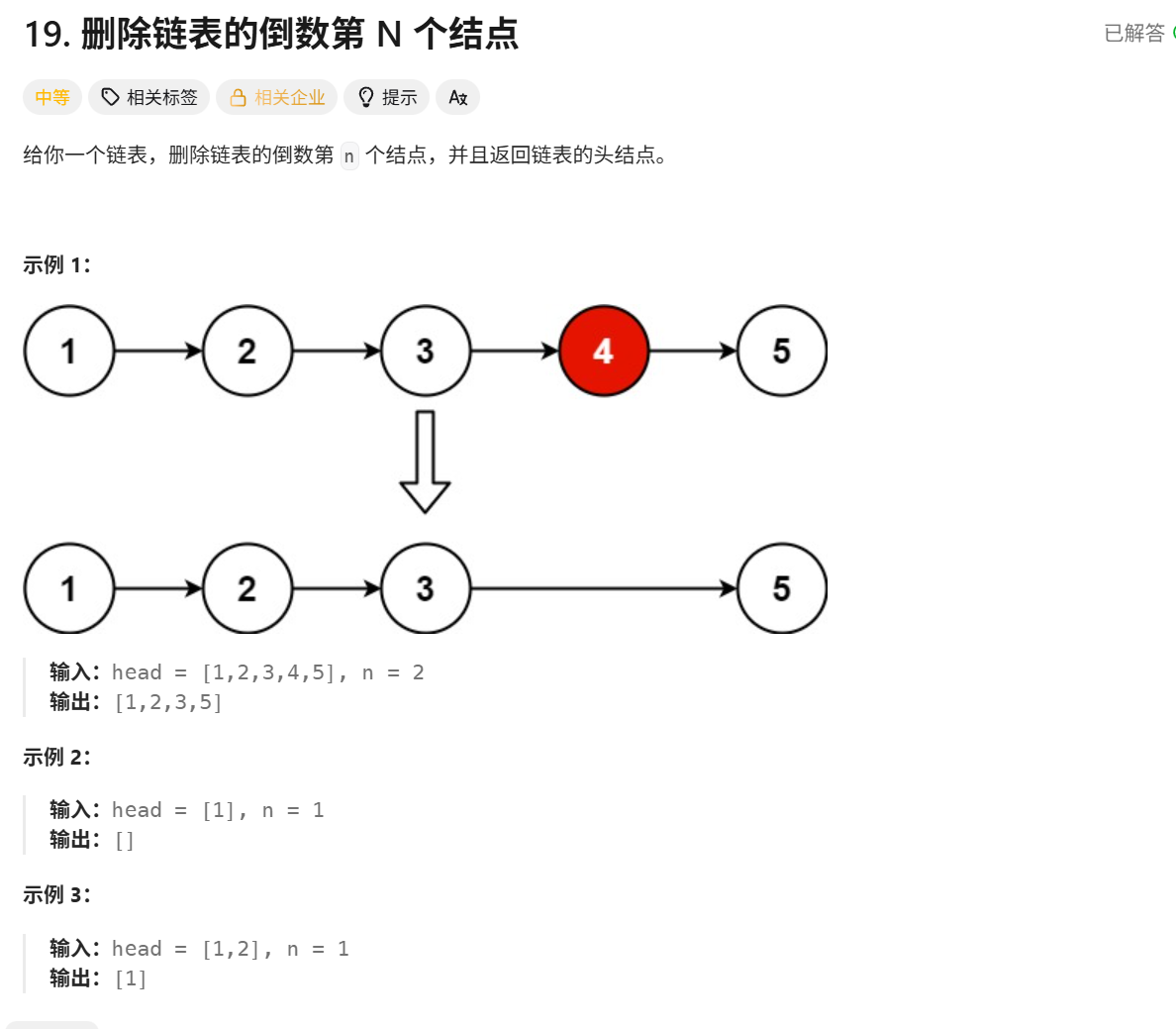
};19.删除链表的倒数第N个结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode *runner=head;//快
ListNode *chaser=head;//慢
if(!head)return nullptr;
while(n>0){
runner=runner->next;
n--;
}
if(runner==nullptr)head=head->next;
else{
while(runner->next){
runner=runner->next;
chaser=chaser->next;
}
chaser->next=chaser->next->next;
}
return head;
}
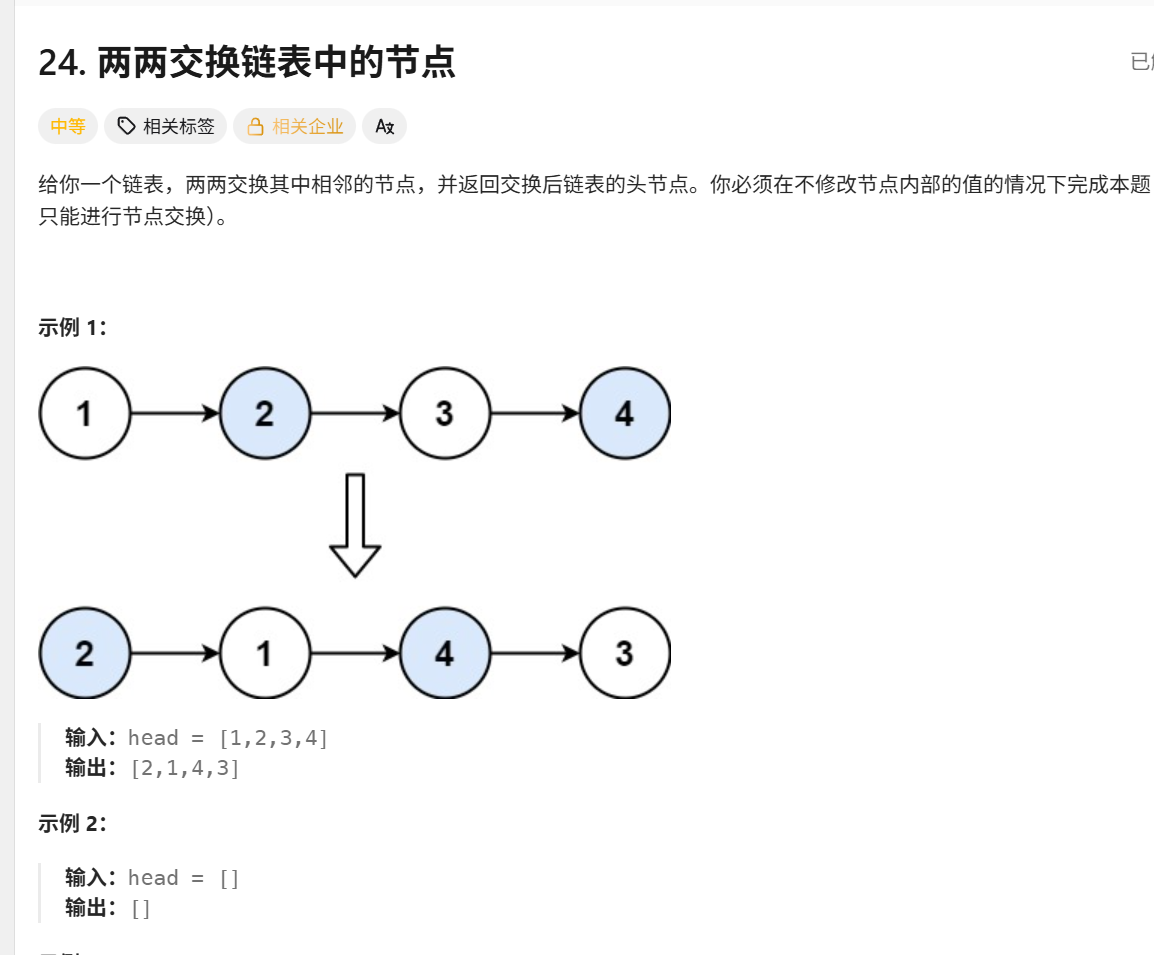
};24.两两交换链表中的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {//1234
//1.如果链表里没有结点及头指针为空或链表里只有一个结点即头指针的next是空指针
if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr)return head;
ListNode *newhead=head->next;
head->next =swapPairs(newhead->next);//1->4
newhead->next=head;//2->1
//2变成为头指针
return newhead;
}
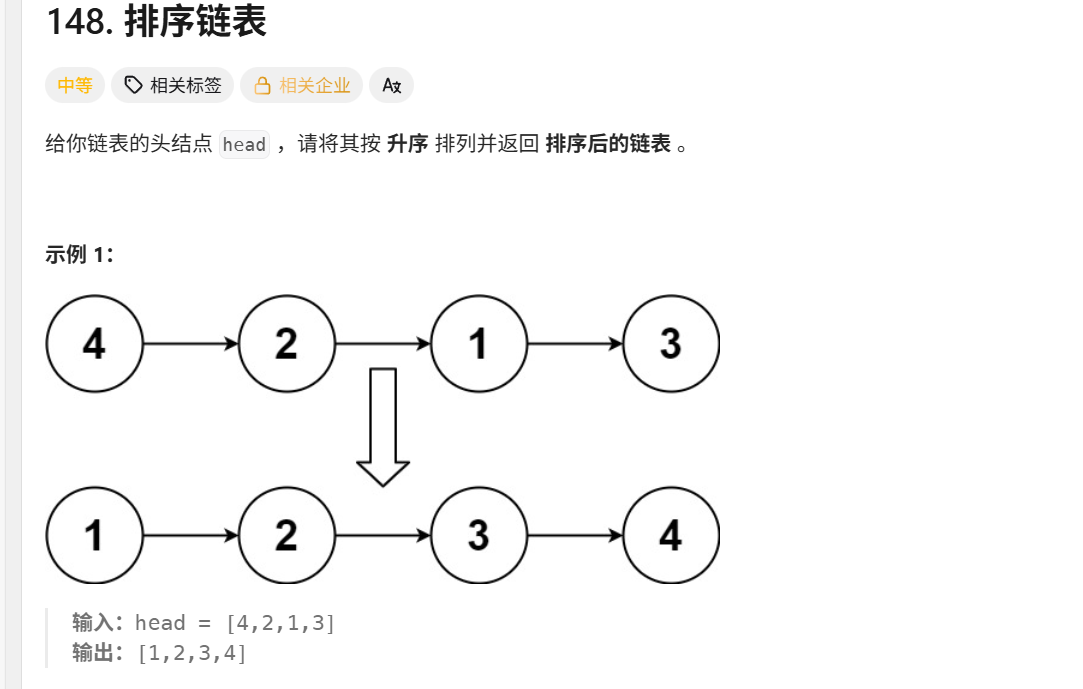
};148.排序链表
因为时间复杂度的要求是(nlogn),所以采用归并(二分)即快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode *head1,ListNode*head2){//合并两个内部是有序的链表
ListNode*dumpyhead=new ListNode(0);//哑头,用于统一方法,当做头结点(其实是个空白结点值为0)
ListNode *temp1=head1;
ListNode *temp2=head2;
ListNode *temp=dumpyhead;
while(temp1&&temp2){
if(temp1->val<=temp2->val){
temp->next=temp1;
temp1=temp1->next;
}
else{
temp->next=temp2;
temp2=temp2->next;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
if(temp1){
temp->next=temp1;
}
if(temp2){
temp->next=temp2;
}
return dumpyhead->next;
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) { // 当前区间头尾
// 1.没有结点
if (head == nullptr) {
return head;
}
// 2.只有一个结点
else if (head->next == tail) {
head->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
//快慢指针
ListNode* faster = head;
ListNode* slower = head;
// 二分
while (faster != tail) {
faster = faster->next;
slower = slower->next;
if (faster != tail) {
faster = faster->next;
}
}
ListNode* mid = slower;
ListNode* list1 = sortList(head, mid);
ListNode* list2 = sortList(mid, tail);
return merge(list1, list2);
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) { //答案函数
return sortList(head,nullptr);
}
};
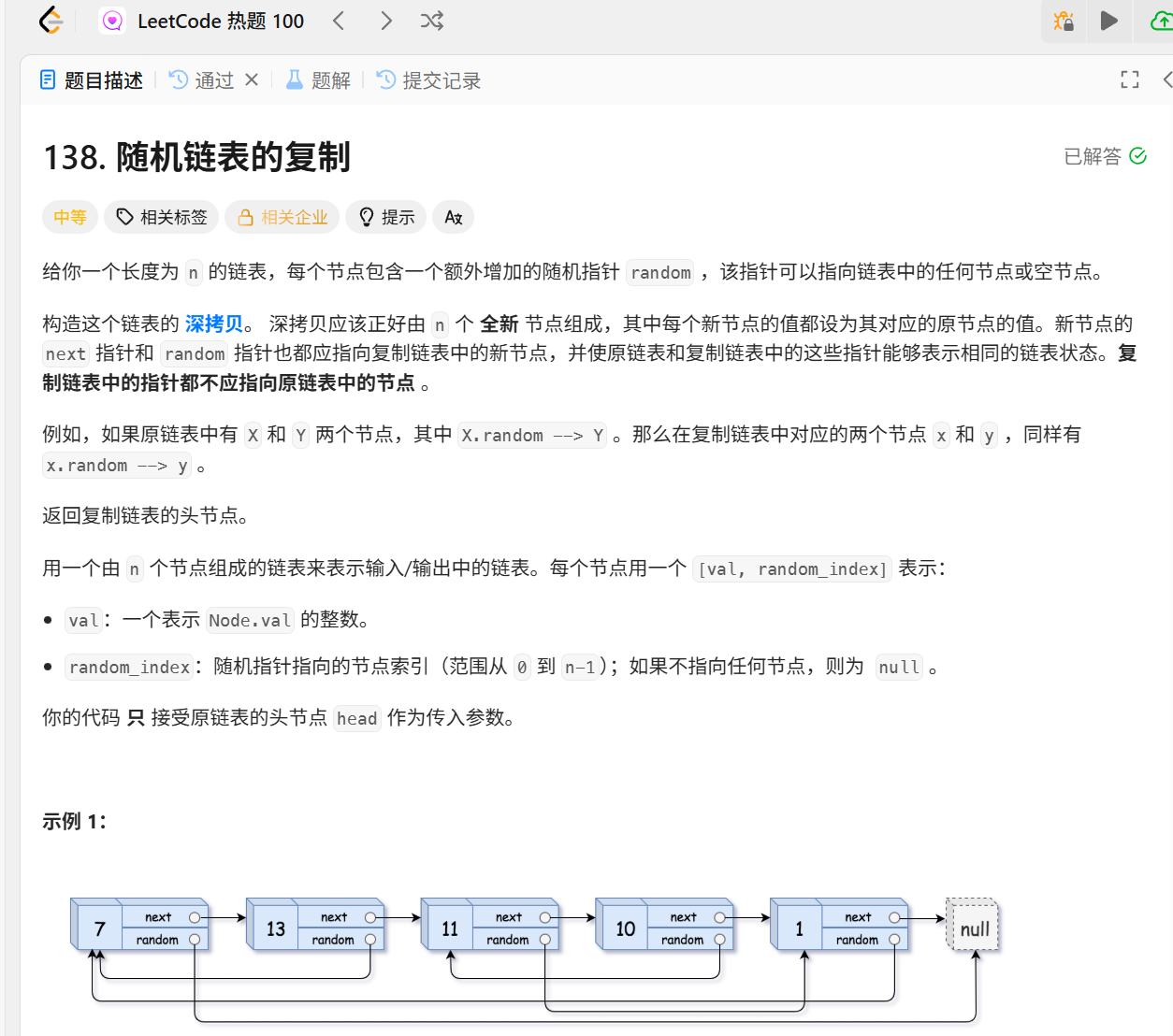
138.随机链表的复制
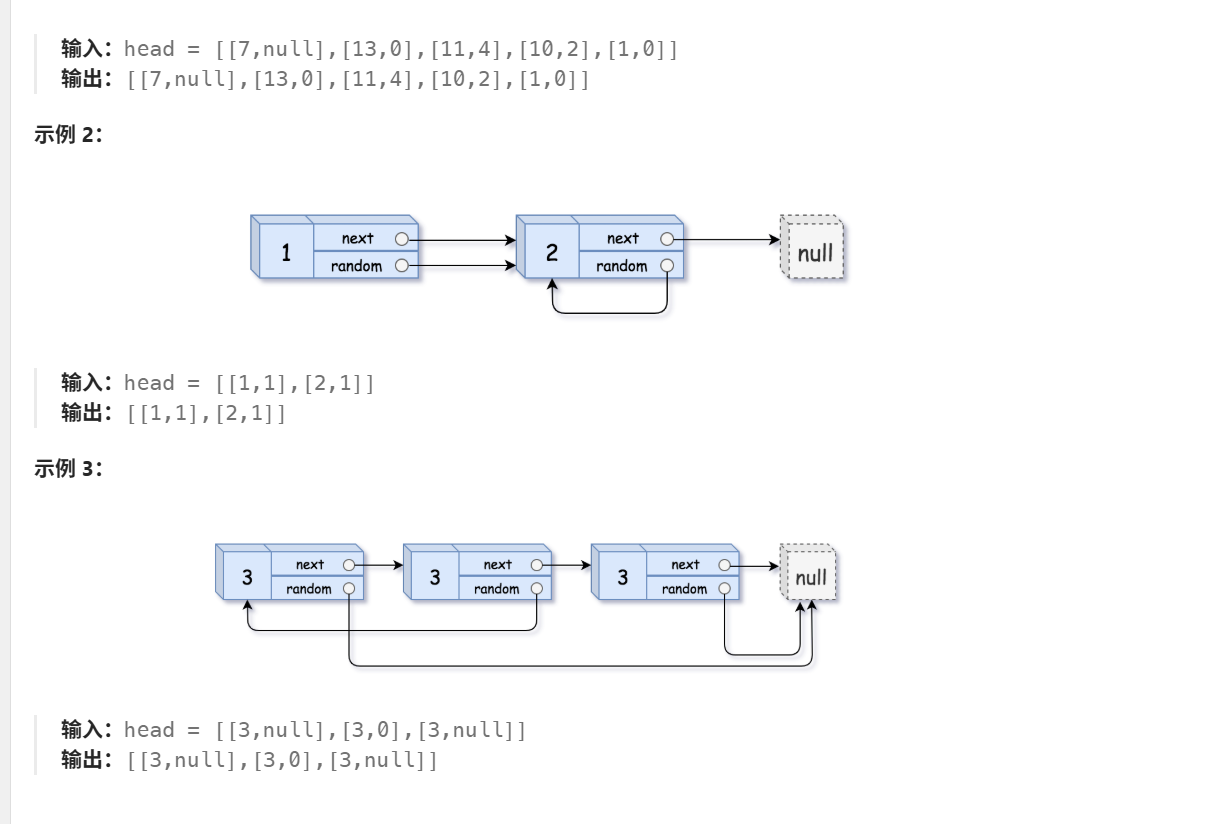
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<Node*,Node*>mp;//原链表映射到新链表
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head==nullptr)return nullptr;//没结点
//题意:复制链表
if(!mp.count(head)){//map里不存在head结点
Node *newhead=new Node(head->val);
//放入map
mp[head]=newhead;//head映射到新链表中的newhead结点!
//递归
newhead->next=copyRandomList(head->next);
newhead->random=copyRandomList(head->random);
}
return mp[head];
}
};23.合并k个升序链表

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
vector<int>a;
for(auto i:lists){//i为每个链表头指针
ListNode*t=i;
while(t){
a.push_back(t->val);
t=t->next;
}
}
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
ListNode*dp=new ListNode(0);
ListNode*temp=dp;
for(auto i:a){
temp->next=new ListNode(i);
temp=temp->next;
}
return dp->next;
}
};
25.K个一组翻转链表
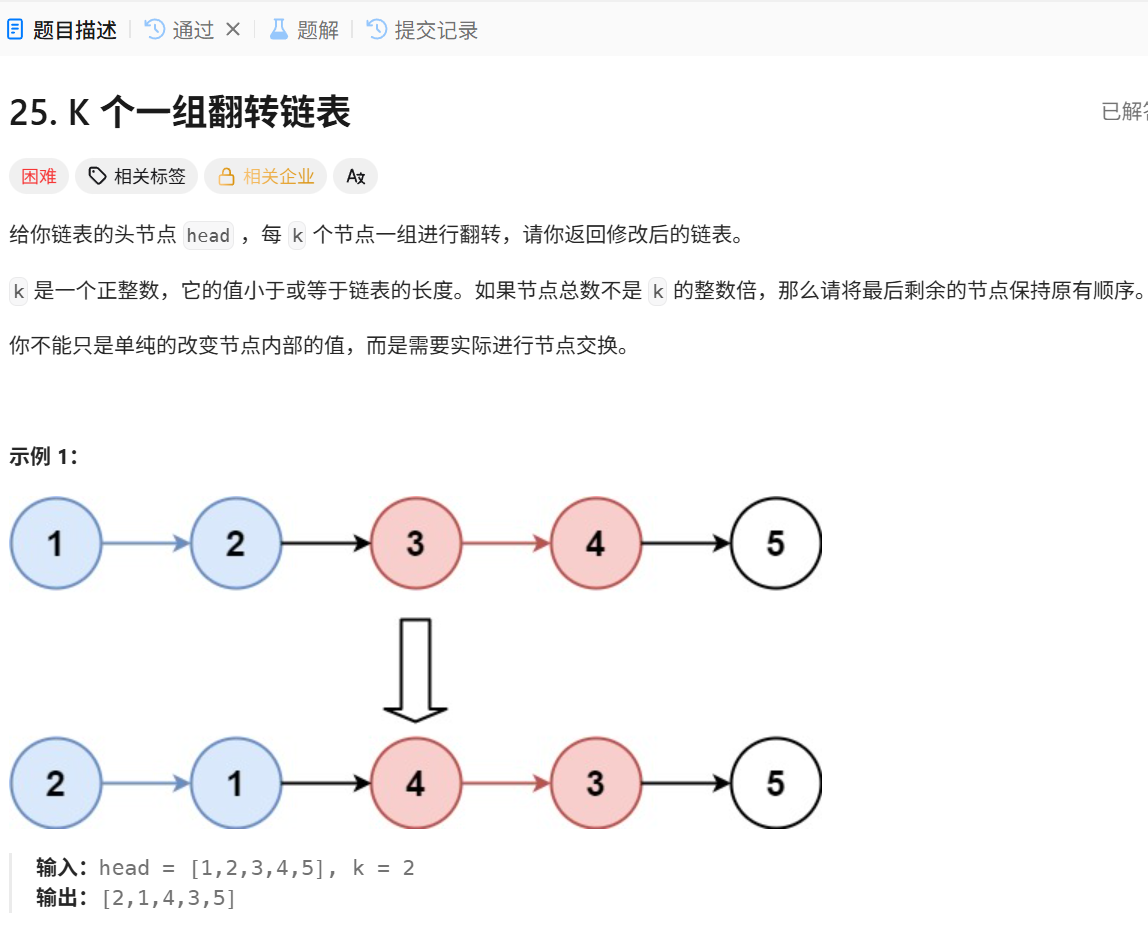
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = ListNode(0, head); // 头结点前面没有用的哑结点!
int n = 0;
ListNode* t = head;
while (t) { // 统计节点数
n++;
t = t->next;
}
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* p0 = &dummy; // 指向每一组的开头
for (; n >= k; n -= k) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {//处理组内部
ListNode* nxt = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
//组间
ListNode* nxt = p0->next;
p0->next->next = cur;
p0->next = pre;
p0 = nxt;
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
/*
pre → 翻转后当前组的新头节点(比如原组是1→2,翻转后pre=2);
cur → 下一组的头节点(比如翻转完1→2后,cur=3);
p0 → 当前组的前驱节点(比如初始时p0=dummy);
p0->next → 翻转前当前组的旧头节点(翻转后变成当前组的新尾节点,比如p0->next=1)
*/146.LRU缓存
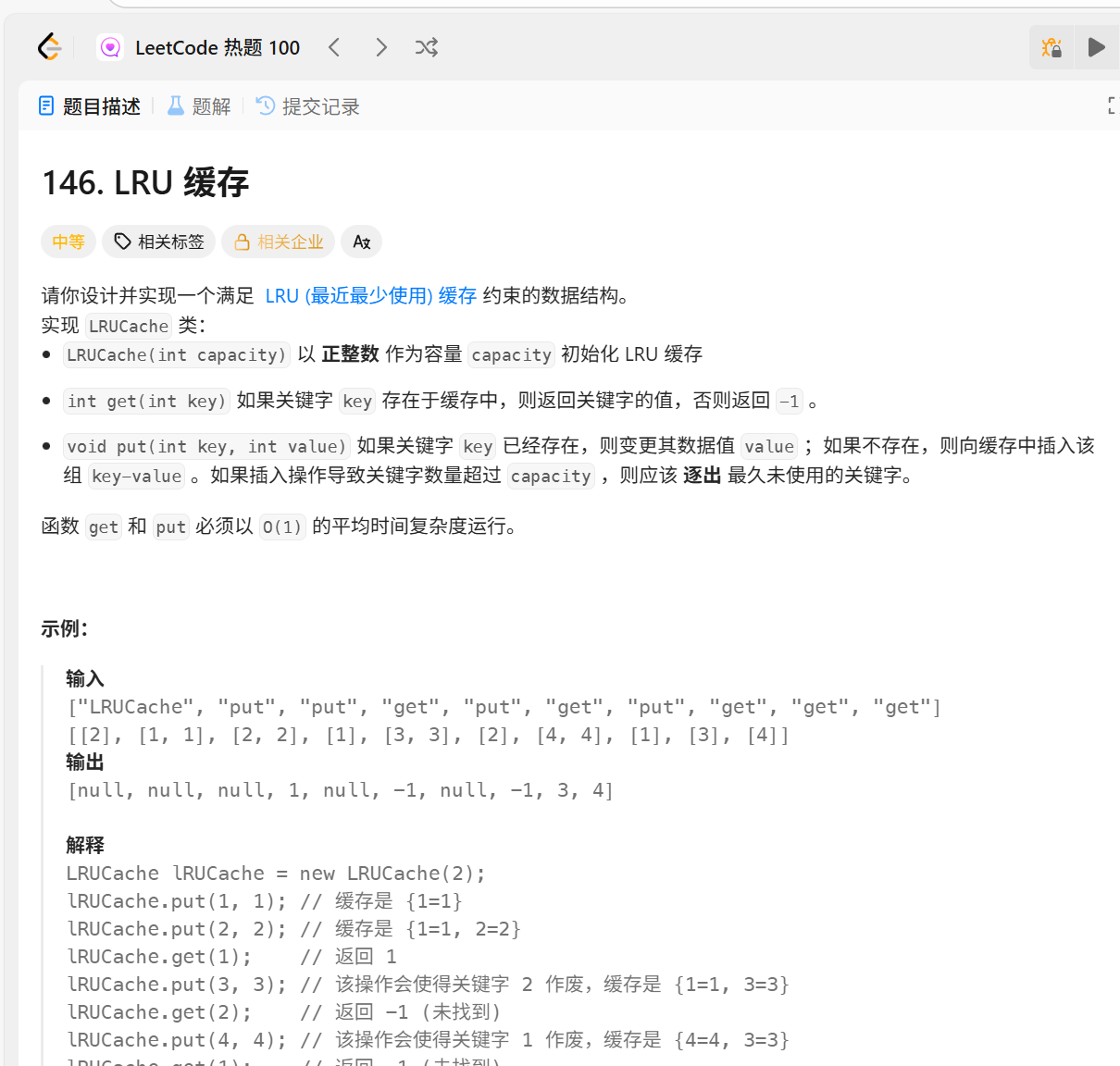
//在双向链表的实现中,使用一个伪头部(dummy head)和伪尾部(dummy tail)标记界限
struct doublelinklist { // 双向链表结点(存放键和值还有前指针和后指针)
int key;
int val;
doublelinklist* pre;
doublelinklist* next;
// 默认构造方法
doublelinklist() {
key = 0;
val = 0;
pre = nullptr;
next = nullptr;
}
// 有参数的构造方法
doublelinklist(int _key, int _val) {
key = _key;
val = _val;
pre = nullptr;
next = nullptr;
}
};
class LRUCache {
private:
unordered_map<int, doublelinklist*>mp; // 因为本题涉及了key、val所以用哈希表,key为int,val为链表的结点。
doublelinklist* head;
doublelinklist* tail;
int size; // 已存放多少结点
int capacity; // 最大存放的容量
public:
LRUCache(int _capacity) { // 缓存初始化
capacity = _capacity;
size = 0;
head = new doublelinklist();
tail = new doublelinklist();
head->next = tail;
tail->pre = head;
}
void addtohead(doublelinklist*t){
t->pre=head;
t->next=head->next;
head->next->pre=t;
head->next=t;
}
void removenode(doublelinklist*t){
t->pre->next=t->next;
t->next->pre=t->pre;
}
void movetohead(doublelinklist*t){//将当前结点移动至头结点
removenode(t);//删除结点
addtohead(t);//移动到链头
}
doublelinklist*deletetailnode(){//删除尾部的结点
doublelinklist*t=tail->pre;
removenode(t);
return t;
}
int get(int key) {
if (!mp.count(key)) { // 不存在这一个结点
return -1;
} else {
doublelinklist* node = mp[key];
movetohead(node);//因为是最近最少使用机制,所以最近最少使用的会被删除。所以一查询就移动到链表头
return node->val;
}
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(!mp.count(key)){//map里没有key
mp[key]=new doublelinklist(key,value);
size++;
addtohead(mp[key]);
if(size>capacity){//内存超过了,删除链表尾部元素
doublelinklist*a=deletetailnode();
size--;
mp.erase(a->key);//删除末尾结点,在哈希表内部删除用键删
delete a;
}
}
else{//map里有key
doublelinklist*b=mp[key];//用key找到结点位置
b->val=value;
movetohead(b);
}
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号