42接雨水--双指针/动态规划/单调栈
42接雨水--双指针/动态规划/单调栈
题目:

分析
法一:动态规划
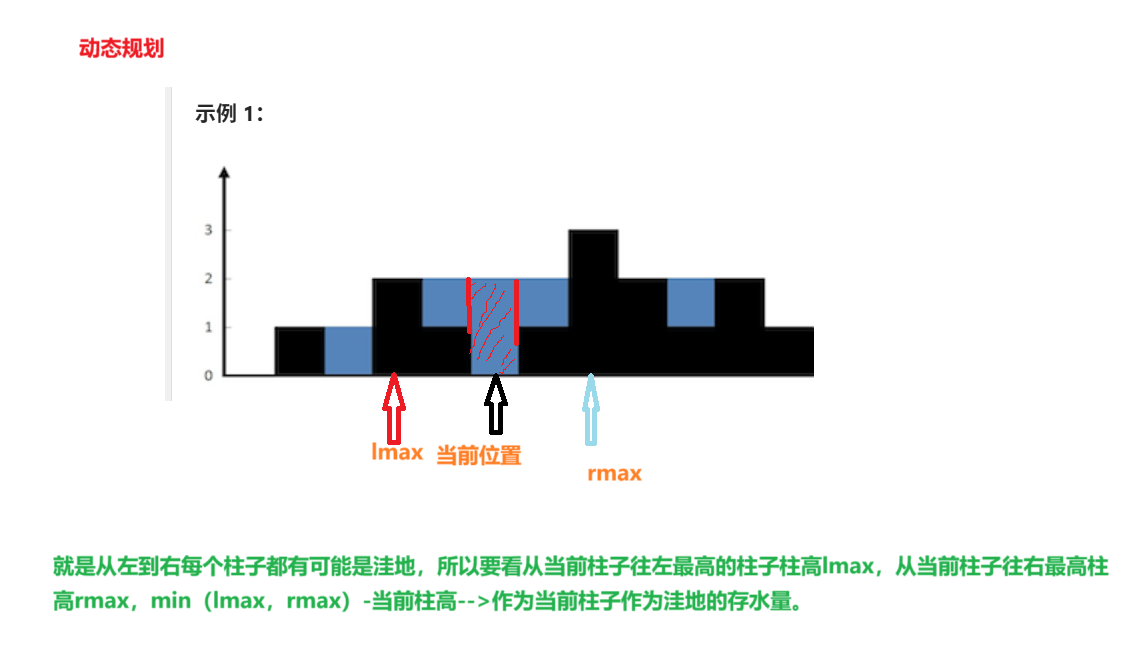
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
int ans=0;
int dlmax[20006];//从左往右到当前的柱子最高柱高
int drmax[20006];//从右往左到当前的柱子最高柱高
dlmax[0]=height[0];
drmax[height.size()-1]=height[height.size()-1];
//体现动态规划的思想
for(int i=1;i<height.size();i++){
dlmax[i]=max(height[i],dlmax[i-1]);
}
for(int i=height.size()-2;i>=0;i--){
drmax[i]=max(height[i],drmax[i+1]);
}
for(int i=0;i<height.size();i++){
ans=ans+min(dlmax[i],drmax[i])-height[i];
}
return ans;
}
};法二:双指针
左右指针,从两边向中间走
左右柱最终决定水深的是低的柱子
需要记录左柱最高高度和右柱最高高度
左指针l=0
右指针r=size-1
左柱最高高度lmax
右柱最高高度rmax
初始lmax=0,rmax=0
从左往右如果h[l]>lmax更新lmax=h[l],否则左柱最高大于目前柱所以是个洼地能存水
这个洼地存水=lmax-h[l]
从右往左如果h[r]>rmax更新rmax=h[r],否则右柱最高大于目前柱所以是个洼地能存水
这个洼地存水=rmax-h[r]
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
int l=0;
int r=height.size()-1;
int lmax=0;
int rmax=0;
int ans=0;
while(l<r){
if(height[l]<height[r]){
//左柱低
if(height[l]>lmax){
lmax=height[l];
}
else{
//洼地
ans=ans+lmax-height[l];
}
l++;
}
else{
if(height[r]>rmax){
rmax=height[r];
}
else{
//洼地
ans=ans+rmax-height[r];
}
r--;
}
}
return ans;
}
};法三:单调栈
本题为:栈顶到栈底单调递减栈,栈顶最小
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
/*
单调栈:本题目把比栈顶小的柱子高度对应的下标压栈
碰到比栈顶高的柱子:就弹出栈顶说明栈顶位置为低洼,栈顶下面那个元素柱的高度大于栈顶柱子高
所以他下面的元素和当前元素就是栈顶左右边
栈顶洼地:宽度=当前位置-栈顶下面元素下标-1
高度=min(当前位置柱高,栈顶下面元素对应柱高)-栈顶柱高
ans=ans+宽度*高度
*/
int i = 0;
int ans = 0;
stack<int> a;//注意:栈内存柱子下标
while (i < height.size()) { // 从左往右遍历所有的柱子
while (!a.empty() && height[i] >height[ a.top()]) {
int b = a.top();
a.pop();
if(a.empty()){//当栈为空的时候要退出循环因为没法a.top()
break;
}
int wid = i - a.top() - 1;
int h = min(height[i], height[a.top()]) - height[b];
ans = ans + wid * h;
}
a.push(i);
i++;
}
return ans;
}
};




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号