MyBatis
MyBatis
Mybatis概念
* MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,用于简化 JDBC 开发
* MyBatis 本是 Apache 的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis 。2013年11月迁移到Github
* 官网:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
持久层:
* 负责将数据到保存到数据库的那一层代码。以后开发我们会将操作数据库的Java代码作为持久层。而Mybatis就是对jdbc代码进行了封装。
* JavaEE三层架构:表现层、业务层、持久层
框架:
* 框架就是一个半成品软件,是一套可重用的、通用的、软件基础代码模型
* 在框架的基础之上构建软件编写更加高效、规范、通用、可扩展
Mybatis快速入门
需求:查询user表中所有的数据
- 创建user表,添加数据
create database mybatis;
use mybatis;
drop table if exists tb_user;
create table tb_user(
id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(20),
password varchar(20),
gender char(1),
addr varchar(30)
);
INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES (1, 'zhangsan', '123', '男', '北京');
INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES (2, '李四', '234', '女', '天津');
INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES (3, '王五', '11', '男', '西安');
- 创建模块,导入坐标(在创建好的模块中的 pom.xml 配置文件中添加依赖的坐标)
<dependencies>
<!--mybatis 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql 驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.46</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit 单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加slf4j日志api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.20</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加logback-classic依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加logback-core依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
注意:需要在项目的 resources 目录下创建logback的配置文件
- 编写 MyBatis 核心配置文件 -- > 替换连接信息 解决硬编码问题
在模块下的 resources 目录下创建mybatis的配置文件mybatis-config.xml,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 类型别名,给pojo包下所有的类起了别名(别名就是类名,不区分大小写) -->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--environments:配置数据库连接环境信息。可以配置多个environment,通过default属性切换不同的environment-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--数据库连接信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="tt951008"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="test">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--数据库连接信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="tt951008"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!--加载sql映射文件-->
<!--<mapper resource="com\itheima\mapper\UserMapper.xml"/>-->
<!--Mapper代理方式-->
<package name="com.itheima.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 编写 SQL 映射文件 --> 统一管理sql语句,解决硬编码问题
在模块的resources目录下创建映射配置文件UserMapper.xml,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="test">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User"> resultType: 查询返回结果类型
select * from tb_user;
</select>
</mapper>
- 编码
- 在
com.itheima.pojo包下创建 User类
- 在
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String gender;
private String addr;
//省略了 setter 和 getter
}
- 在
com.itheima包下编写 MybatisDemo 测试类
public class MyBatisDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象,用它来执行sql
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 执行sql
List<User> users = sqlSession.selectList("test.selectAll"); //参数是一个字符串,该字符串必须是映射配置文件的namespace.id
System.out.println(users);
//4. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}
Mapper代理开发
Mapper代理开发概述
之前我们写的代码是基本使用方式,它也存在硬编码的问题,如下:

这里调用 selectList() 方法传递的参数是映射配置文件中的 namespace.id值。这样写也不便于后期的维护。如果使用 Mapper 代理方式(如下图)则不存在硬编码问题。

通过上面的描述可以看出 Mapper 代理方式的目的::
* 解决原生方式中的硬编码
* 简化后期执行SQL
Mybatis 官网也是推荐使用 Mapper 代理的方式。下图是截止官网的图片
使用Mapper代理要求
使用Mapper代理方式,必须满足以下要求:
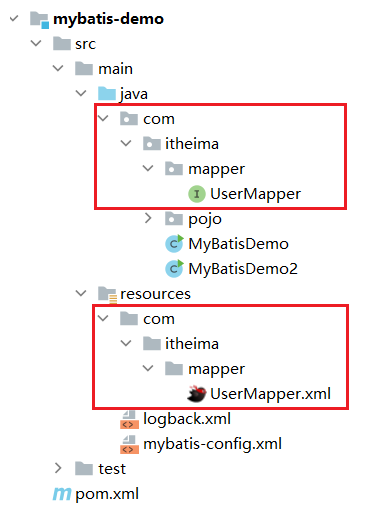
- 定义与SQL映射文件同名的Mapper接口,并且将Mapper接口和SQL映射文件放置在同一目录下。如下图:
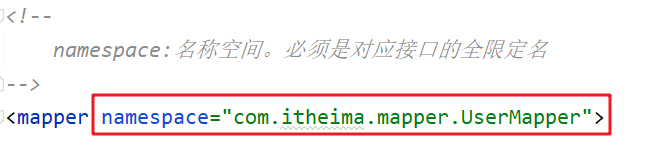
- 设置SQL映射文件的namespace属性为Mapper接口全限定名
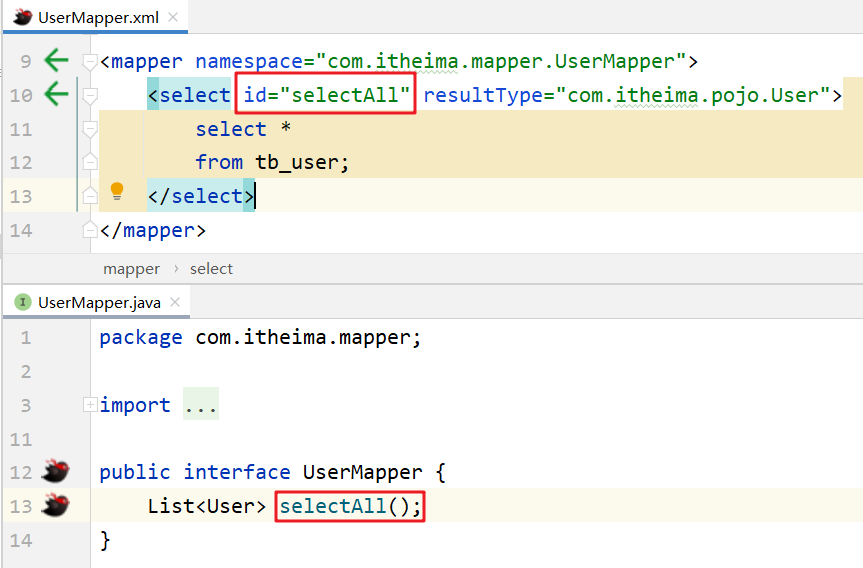
- 在 Mapper 接口中定义方法,方法名就是SQL映射文件中sql语句的id,并保持参数类型和返回值类型一致
案例代码实现
- 在
com.itheima.mapper包下创建 UserMapper接口,代码如下:
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> selectAll();
}
- 在
resources下创建com/itheima/mapper目录,并在该目录下创建 UserMapper.xml 映射配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace:名称空间。必须是对应接口的全限定名-->
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
select * from tb_user;
</select>
</mapper>
- 在
com.itheima包下创建 MybatisDemo2 测试类,代码如下:
/**
* Mybatis 代理开发
*/
public class MyBatisDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2. 获取SqlSession对象,用它来执行sql
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 执行sql
//3.1 获取UserMapper接口的代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(users);
//4. 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}
如果Mapper接口名称和SQL映射文件名称相同,并在同一目录下,则可以使用包扫描的方式简化SQL映射文件的加载。也就是将核心配置文件的加载映射配置文件的配置修改为
<mappers>
<!--加载sql映射文件-->
<!-- <mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>-->
<!--Mapper代理方式-->
<package name="com.itheima.mapper"/>
</mappers>
SqlSessionFactory工具类抽取
在写Servlet的时候,因为需要使用Mybatis来完成数据库的操作,所以对于Mybatis的基础操作就出现了些重复代码,如下
// 1. 加载mybatis的核心配置文件,获取 SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
有了这些重复代码就会造成一些问题:
* 重复代码不利于后期的维护
* SqlSessionFactory工厂类进行重复创建
* 就相当于每次买手机都需要重新创建一个手机生产工厂来给你制造一个手机一样,资源消耗非常大但性能却非常低。所以这么做是不允许的。
那如何来优化呢?
* 代码重复可以抽取工具类
* 对指定代码只需要执行一次可以使用静态代码块
优化后代码
public class SqlSessionFactoryUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
//静态代码块会随着类的加载而自动执行,且只执行一次
try {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory(){
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
}
工具类抽取以后,以后在对Mybatis的SqlSession进行操作的时候,就可以直接使用,这样就可以很好的解决上面所说的代码重复和重复创建工厂导致性能低的问题了。
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSessionFactory();
核心配置文件

多环境配置
在核心配置文件的 environments 标签中其实是可以配置多个 environment ,使用 id 给每段环境起名,在 environments 中使用 default='环境id' 来指定使用哪儿段配置。我们一般就配置一个 environment 即可。
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--数据库连接信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="1234"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="test">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--数据库连接信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatis?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="1234"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
类型别名
映射配置文件中的 resultType 属性需要配置数据封装的类型(类的全限定名)。而每次这样写是特别麻烦的,Mybatis 提供了 类型别名(typeAliases) 可以简化这部分的书写。
首先需要现在核心配置文件中配置类型别名,也就意味着给pojo包下所有的类起了别名(别名就是类名),不区分大小写。内容如下:
<typeAliases>
<!--name属性的值是实体类所在包-->
<package name="com.itheima.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
通过上述的配置,我们就可以简化映射配置文件中 resultType 属性值的编写
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="user">
select * from tb_user;
</select>
</mapper>
配置各个标签时,需要遵守前后顺序
配置文件实现CRUD
实体属性名和数据库字段名不一致如何封装
实体类属性名 和 数据库表列名 不一致,不能自动封装数据
解决方式一: 在写sql语句时给这两个字段起别名,将别名定义成和属性名一致即可
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
from tb_brand;
</select>
缺点: SQL语句中的字段列表书写麻烦,如果表中还有更多的字段,同时其他的功能也需要查询这些字段时就显得我们的代码不够精炼
解决方式二: 定义SQL片段(将需要复用的SQL片段抽取到 `sql` 标签中,在原`sql`语句中进行引用)
<sql id="brand_column"> id属性值是唯一标识,引用时也是通过该值进行引用。
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
</sql>
在原sql语句中进行引用
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select
<include refid="brand_column" /> 使用 `include` 标签引用上述的 SQL 片段,而 `refid` 指定上述 SQL 片段的id值。
from tb_brand;
</select>
缺点: 如果还有功能只需要查询部分字段,而不是查询所有字段,那么我们就需要再定义一个 SQL 片段,这就显得不是那么灵活。
解决方案三: 在映射配置文件中使用resultMap定义 字段 和 属性 的映射关系(常用)
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="brand">
<!--
id:完成主键字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名
result:完成一般字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名
-->
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"/>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"/>
</resultMap>
注意:在上面只需要定义 字段名 和 属性名 不一样的映射,而一样的则不需要专门定义出来。
SQL语句正常编写
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap"> 在<select>标签中,使用resultMap属性,替换 resultType属性
select *
from tb_brand;
</select>
参数占位符
* #{} :执行SQL时,会将 #{} 占位符替换为?,将来自动设置参数值。从上述例子可以看出使用#{} 底层使用的是 `PreparedStatement`
* ${} :拼接SQL。底层使用的是 `Statement`,会存在SQL注入问题。
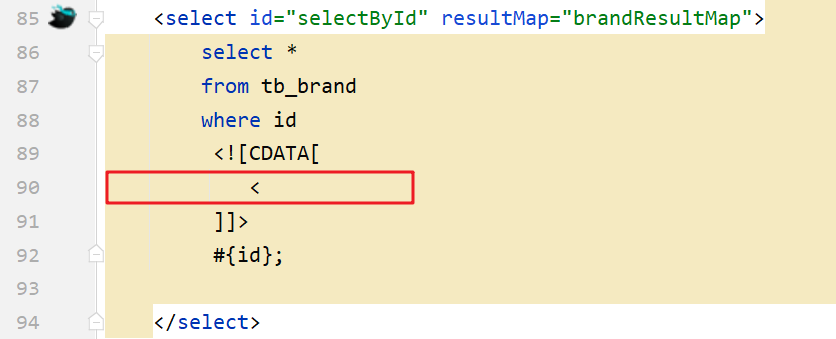
SQL语句中特殊字段处理
转义字符,下图的 `<` 就是 `<` 的转义字符。

<![CDATA[内容]]>
用法: idea中输入大写的CD回车即可
多条件查询参数封装方法
- 散装参数: 需要使用
@Param("参数名称")标记每一个参数,在映射配置文件中就需要使用#{参数名称}进行占位
List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status") int status, @Param("companyName") String companyName,@Param("brandName") String brandName);
- 实体类封装参数: 要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和实体类属性名保持一致。
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Brand brand);
- map集合: 要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和map集合中键的名称一致。
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);
动态SQL
- if 标签
if:用于判断参数是否有值,使用test属性进行条件判断
存在的问题:第一个条件不需要逻辑运算符
*解决方案:
1)使用恒等式让所有条件格式都一样
2)<where>:标签替换where关键字
- where 标签
作用:
* 替换where关键字
* 会动态的去掉第一个条件前的 and
* 如果所有的参数没有值则不加where关键字
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</where>
</select>
- choose(when,otherwise)标签
<select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<choose><!--相当于switch-->
<when test="status != null"><!--相当于case-->
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName != null and companyName != '' "><!--相当于case-->
company_name like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName != null and brandName != ''"><!--相当于case-->
brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
- set标签,动态更新数据时使用
<update id="update">
update tb_brand
<set>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != ''">
brand_name = #{brandName},
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != ''">
company_name = #{companyName},
</if>
<if test="ordered != null">
ordered = #{ordered},
</if>
<if test="description != null and description != ''">
description = #{description},
</if>
<if test="status != null">
status = #{status}
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id};
</update>
- foreach 标签,如批量删除时需要遍历
foreach 标签
用来迭代任何可迭代的对象(如数组,集合)。
* collection 属性:
* mybatis会将数组参数,封装为一个Map集合。
* 默认:array = 数组
* 使用@Param注解改变map集合的默认key的名称
* item 属性:本次迭代获取到的元素。
* separator 属性:集合项迭代之间的分隔符。`foreach` 标签不会错误地添加多余的分隔符。也就是最后一次迭代不会加分隔符。
* open 属性:该属性值是在拼接SQL语句之前拼接的语句,只会拼接一次
* close 属性:该属性值是在拼接SQL语句拼接后拼接的语句,只会拼接一次
<delete id="deleteByIds">
delete from tb_brand where id
in
<foreach collection="array" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
;
</delete>
MyBatis事务
openSession0:默认开启事务,进行增删改操作后需要使用sqlSession.commit(); 手动提交事务
openSession(true):可以设置为自动提交事务(关闭事务)
添加-主键返回
在数据添加成功后,有时候需要获取插入数据库数据的主键(主键是自增长)。比如:添加订单和订单项
在 insert 标签上添加如下属性:
* useGeneratedKeys:是够获取自动增长的主键值。true表示获取
* keyProperty :指定将获取到的主键值封装到哪儿个属性里
<insert id="add" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values (#{brandName}, #{companyName}, #{ordered}, #{description}, #{status});
</insert>
Mybatis参数传递
MyBatis提供了ParamNameResolver类来进行参数封装,在getNamedParams( )方法中有封装的具体步骤
MyBatis 参数封装:
* 单个参数:
1. POJO类型:直接使用,属性名 和 参数占位符名称 一致
2. Map集合:直接使用,键名 和 参数占位符名称 一致
3. Collection:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",collection集合);
map.put("collection",collection集合);
4. List:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",list集合);
map.put("collection",list集合);
map.put("list",list集合);
5. Array:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",数组);
map.put("array",数组);
6. 其他类型:直接使用
比如int类型,`参数占位符名称` 叫什么都可以。尽量做到见名知意
* 多个参数:封装为Map集合,可以使用@Param注解,替换Map集合中默认的arg键名
map.put("arg0",参数值1)
map.put("param1",参数值1)
map.put("param2",参数值2)
map.put("agr1",参数值2)
---------------@Param("username")
map.put("username",参数值1)
map.put("param1",参数值1)
map.put("param2",参数值2)
map.put("agr1",参数值2)
注解实现CRUD
使用注解开发会比配置文件开发更加方便。如下就是使用注解进行开发
@Select(value = "select * from tb_user where id = #{id}")
public User select(int id);
注解是用来替换映射配置文件方式配置的,所以使用了注解,就不需要再映射配置文件中书写对应的 `statement`
Mybatis 针对 CURD 操作都提供了对应的注解,已经做到见名知意。如下:
* 查询 :@Select
* 添加 :@Insert
* 修改 :@Update
* 删除 :@Delete
注解完成简单功能,配置文件完成复杂功能。


 MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,用于简化 JDBC 开发
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,用于简化 JDBC 开发

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号