LeetCode 01-10题
# 第一个
if target - num in hash_mapping.keys():
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
# 第二个,排序
for i in range(len(nums)):
nums[i] = [i, nums[i]]
nums.sort(key=lambda num : num[1])
# 第三个
# 倘若 cur = ListNode(t % 10, None),他指向的是一个新的存储单元,原本标签数据并不会修改
# 非常的坑爹,这是灵活的使用头结点!
cur.next = ListNode(t % 10, None)
# 第四个
python Class 函数中 第一个参数 self 一定要记得写
# 第五个
info = [0 for i in range(N)]
s = '@#' + '#'.join([ch for ch in s]) + '#$'
info[i] = min(info[2 * id - i], mx - i) if mx > i else 1
# 第六个
res = [[] for i in range(numRows)]
ret += ''.join(res[i])
res = [""] * numRows # 等价于 res = ["" for i in range(numRows)]
''.join(res)
# 第七个
str_res = str(x)[::-1] if x >= 0 else '-' + str(x)[1:][::-1] # 使用了切片大法
str_x = str_x[::-1]
str_x = ''.join(reversed(str_x))
print('0 011112'.lstrip(' 01')) # 可以将前面的 0 空格 1 全部去掉,并没有要求他们连着
if -2 ** 31 <= str_x <= 2 ** 31 - 1:
return 1
# 第十个
# 使用 python 写Dp
class Solution:
def isMatch(self, s: str, p: str) -> bool:
s, p = ' ' + s, ' ' + p
n, m = len(s), len(p)
f = [[False] * m for i in range(n)]
f[0][0] = True
for i in range(n):
for j in range(1, m):
if p[j] != '*':
f[i][j] = i > 0 and f[i-1][j-1] and (s[i] == p[j] or p[j] == '.')
else:
f[i][j] = f[i][j-2] or i > 0 and f[i-1][j] and (s[i] == p[j-1] or p[j-1] == '.')
return f[n-1][m-1]
string y = to_string(x);
return y == string(y.rbegin(), y.rend());
vector<vector<bool> > f(n + 1, vector<bool>(m + 1));
0.找到的超级精简的代码
第一题
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
dic = {}
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
rest = target - num
if rest in dic:
return [i, dic[rest]]
dic[num] = i
作者:为什么这么多题哭
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/333354/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
第二题
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
head = ListNode()
cur = head
t = 0
while l1 is not None or l2 is not None or t != 0:
if l1 is not None:
t += l1.val
l1 = l1.next
if l2 is not None:
t += l2.val
l2 = l2.next
cur.next = ListNode(t % 10, None)
cur = cur.next
t = t // 10
return head.next
第三题
第三题找的代码比较多,也是各有特色
- 使用精简的 while 循环一个顶俩,使用 set 维护当前的子字符串
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
myset = set()
i, j, n = 0, 0, len(s)
max_length = 0
while i < n:
if s[i] not in myset:
myset.add(s[i])
max_length = max(max_length, i - j + 1)
i += 1
else:
myset.remove(s[j])
j += 1
return max_length
- 使用了字典来记录当前重复字符的位置
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
max_ch_pos = {}
i, j, n = 0, 0, len(s)
max_length = 0
while i < n:
if s[i] not in max_ch_pos: # max ch pos 记录的是当前 char 对应的 position
max_ch_pos[s[i]] = i
max_length = max(max_length, i - j + 1)
i += 1
else:
j = max(max_ch_pos[s[i]] + 1, j)
max_ch_pos[s[i]] = i
max_length = max(max_length, i - j + 1)
i += 1
return max_length
1. Two Sum
题目链接
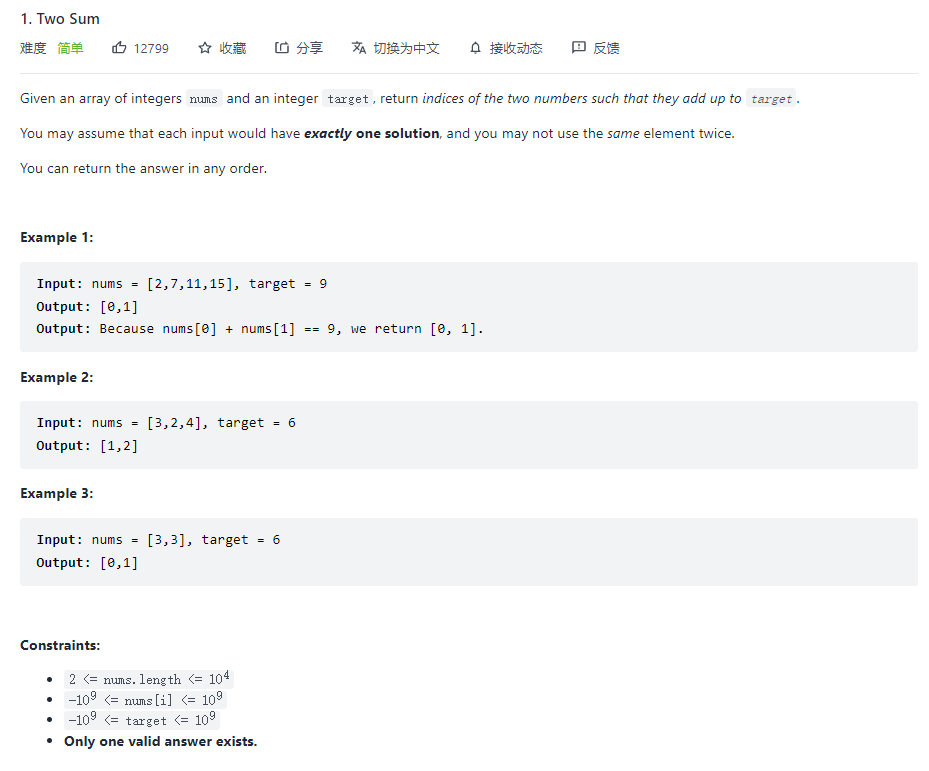
本题大致有三个思路,
第一个是直接暴力,使用指针遍历列表,\(O(N^2)\)做法,
第二种是只用 Hash表,python库函数做法,
第三种是双指针做法,
下面为三种方法的代码:
- 暴力求解办法
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i in range(0, len(nums)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j];
return [-1, -1];
- 使用字典 hash
倘若是 C++ 使用 map 或者是 unordered_map
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> heap;
int r;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i ++ ) {
r = target - nums[i];
if (heap.count(r)) {
return {i, heap[r]};
} else {
heap[nums[i]] = i;
}
}
return {}; // 这个是为了防止语法报错
}
};
首先字典预先存储 values -> indices 的映射,然后我们对每一个数字 num,查找 target - nums 是否在字典中存在,以及是不是他自己
不过,因为涉及到可能存在多个 value,这里存在bug,所以说我直接是 一个 value 对应一个 indices 列表
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
hash_mapping = {}
# 进行 hash 字典,他是一个 int -> list[int] 的映射
for i in range(0, len(nums)):
if nums[i] in hash_mapping.keys():
hash_mapping[nums[i]].append(i)
else:
hash_mapping[nums[i]] = [i]
for i in range(len(nums)):
num = nums[i]
if target - num in hash_mapping.keys():
cur_list = hash_mapping[target - num]
flag = False
for indice in cur_list:
if indice != i:
return [i, indice]
但是仔细想来,没必要使用列表,因为题目保证了唯一解,倘若有多个数字相同,而且他还与答案相关,情况一,为他是答案的一个数,另一个数和他不同,那么 list 为 int->int 的映射没有问题。 情况二,答案的两个数字都是她,那也不怕也能得到正确结果
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
heap = {}
for i in range(len(nums)):
if target - nums[i] in heap.keys():
return [i, heap[target-nums[i]]]
else:
heap[nums[i]] = i
return []
- 双指针算法
算法竞赛中采用的做法,因为要保留原地址的indice ,所以说list需要扩展一下在进行排序。
那么排序之后是如何做的呢?
使用i, j 指针分别指向排序后的数组a, 然后比较 a[i].val + a[j].val 与 target 的大小,如果 a[i].val + a[j].val > target,那么我们应该 j -- ,保证运算后的 a[i].val + a[j].val 变小,已达到向 target 贴近的目的,否则 i ++, 使得a[i].val + a[j].val变大。
至于为什么可以知道最终的唯一解呢?
对于此时的 a[i].val + a[j].val < target, 说明 i 对于所有的 j 都无法组成 target,因为此时保证有解的最大的a[j].val都小于 target,同理 > target 也是一样的道理。
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: list, target: int) -> list[int]:
# 首先,我们需要对 nums 扩展数组进行排序
for i in range(len(nums)):
nums[i] = [i, nums[i]]
nums.sort(key=lambda num: num[1]) # 按照第二关键字进行排序
i, j = 0, len(nums) - 1
while i < j:
if nums[i][1] + nums[j][1] == target:
return [nums[i][0], nums[j][0]]
elif nums[i][1] + nums[j][1] > target:
j -= 1
else:
i += 1
return []
Add Two Number
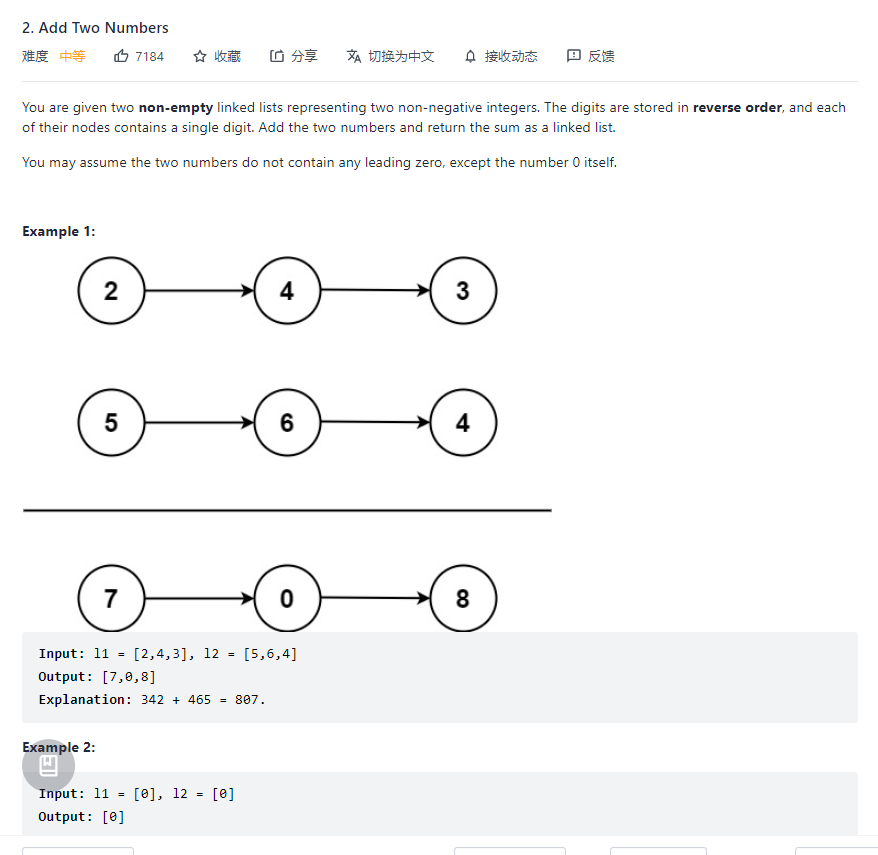
如果大伙之前接触过大整数相加的话,这就是一个链表的模拟办法,不过是和C/C++不同,C/C++的参数传递很是方便,引用、值传递、指针;使用 python 的时候,就会有一些注意事项
正常按位相加,进一处理就可以了
这里我先写一个 C++代码找找感觉:注意使用一个头结点,使得我们不需要处理空节点等等特殊的情况,非常的方便。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
// 首先我们定义一个虚拟头结点,直接帮助我们处理了为空,等等特别难搞的问题
ListNode *head = new ListNode();
ListNode *cur = head;
int t = 0;
while (l1 || l2 || t) {
if (l1) t += l1->val, l1 = l1->next;
if (l2) t += l2->val, l2 = l2->next;
cur->next = new ListNode(t % 10, nullptr);
cur = cur->next;
t /= 10;
}
return head->next;
}
};
Python的代码:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
head = ListNode()
cur = head
t = 0
while l1 is not None or l2 is not None or t != 0:
if l1 is not None:
t += l1.val
l1 = l1.next
if l2 is not None:
t += l2.val
l2 = l2.next
cur.next = ListNode(t % 10, None)
cur = cur.next
t = t // 10
return head.next
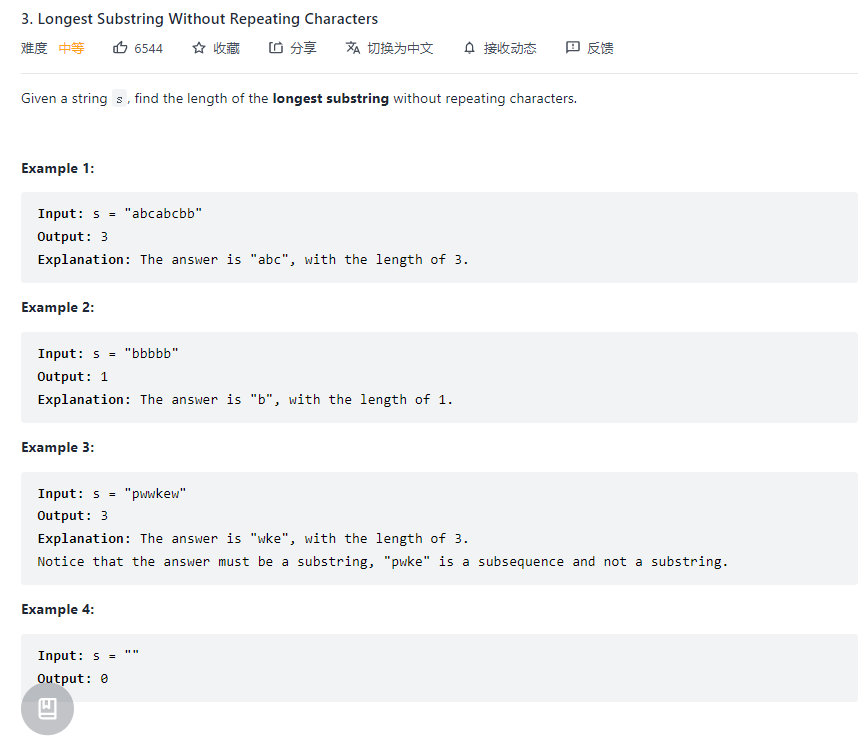
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
本题就是一个双指针的题目,然后加上一个字典存储每个字符出现的次数
不过从本质上来说,这个题目的解题思路是,首先将这个 \(N^2\)个字符串进行了分类,分为了 \(N\) 个类别,主要是以 0,1,.. n 为结尾的类别。
然后发现这 n 个类别之间在不重复字符上进行递进的关系
C++代码
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> heap;
int j = 0;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ) {
heap[s[i]] ++;
while (heap[s[i]] > 1) {
heap[s[j]] --;
j ++;
}
res = max(res, i - j + 1);
}
return res;
}
};
Python 代码
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
dic = {}
j, res = 0, 0
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i] in dic:
dic[s[i]] += 1
else:
dic[s[i]] = 1
while dic[s[i]] > 1:
dic[s[j]] -= 1
j += 1
res = max(res, i - j + 1)
return res
4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays
暴力解法
倘若是使用暴力的方法来写,就是 \(O(N+M)\)
class Solution:
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1: list, nums2: list) -> float:
m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2)
if (m + n) % 2 == 0: # find two number
ret = self.getKey(nums1, nums2, (m + n) // 2 - 1, True) # 1, 1, --> 0, 1
else: # find one number
ret = self.getKey(nums1, nums2, (m + n) // 2, False) # 1, 0, --> 0
return ret
def getKey(self, nums1: list, nums2: list, k: int, flag: bool):
i, j = 0, 0
drop_num = -1;
for tmp in range(0, k + 1):
if i >= len(nums1):
drop_num = nums2[j]
j += 1
elif j >= len(nums2):
drop_num = nums1[i]
i += 1
else:
if nums1[i] <= nums2[j]:
drop_num = nums1[i]
i += 1
else:
drop_num = nums2[j]
j += 1
if not flag:
return drop_num
else:
if i == len(nums1):
drop_num += nums2[j]
elif j == len(nums2):
drop_num += nums1[i]
else:
drop_num += min(nums1[i], nums2[j])
return drop_num / 2
if __name__ == "__main__":
solution = Solution()
nums1 = [1, 3]
nums2 = [2]
print(solution.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2))
nums1 = [1, 2]
nums2 = [3, 4]
print(solution.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2))
nums1 = [0, 0]
nums2 = [0, 0]
print(solution.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2))
nums1 = []
nums2 = [1]
print(solution.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2))
nums1 = [2]
nums2 = []
print(solution.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2))
那么如何达到他所规定的 \(O(log(M+N))\)呢?
本题难度较大,我就多说几句:
倘若是想要达到他的复杂度,最好想的办法就是使用 递归二分处理,思路如下:

c++代码
对应的 C++ 代码如下所示:
class Solution {
public:
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int n = nums1.size(), m = nums2.size(), t = n + m;
int x = t / 2;
if (t % 2 == 0) { // even 2 * x --> (x, x + 1)
// printf("even\n");
return (find(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, x) + find(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, x + 1)) / 2.0;
} else { // odd, 2 * x + 1 --> x
// printf("odd\n");
return find(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, x + 1);
}
}
void Show(vector<int> &v) {
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i ++ ) {
printf("%d ", v[i]);
}
cout << endl;
}
// 在有序数组 nums1[s1:] 和 nums2[s2:] 有序数组中查找第 k 大的数字
double find(vector<int> &nums1, int s1, vector<int> &nums2, int s2, int k) {
// printf("nums1:%d, nums2:%d, k:%d\n", s1, s2, k);
// Show(nums1);
// Show(nums2);
// 为了方便,我们这里假设的是 nums1 进行计算的长度小于 nums2 进行计算的长度
if (nums1.size() - s1 > nums2.size() - s2) {
return find(nums2, s2, nums1, s1, k);
}
// 倘若 nums1 已经被用光了
if (nums1.size() == s1) {
return nums2[s2 + k - 1];
}
// 倘若只要选择一个
if (k == 1) {
return min(nums1[s1], nums2[s2]);
}
int si = min(s1 + k / 2 - 1, (int)nums1.size() - 1);
int sj = (k - k / 2) + s2 - 1;
sj = k + s1 + s2 - 2 - si;
if (nums1[si] == nums2[sj]) {
return nums1[si];
} else if (nums1[si] < nums2[sj]) {
return find(nums1, si + 1, nums2, s2, k - (si + 1 - s1));
} else {
return find(nums1, s1, nums2, sj + 1, k - (sj + 1 - s2));
}
}
};
Python 代码
思路和 C++一样,不过是这个 self. 写的真的烦
class Solution:
def find(self, nums1: list, s1: int, nums2: list, s2: int, k: int):
if len(nums1) - s1 > len(nums2) - s2:
return self.find(nums2, s2, nums1, s1, k)
if len(nums1) == s1:
return nums2[s2 + k - 1]
if k == 1:
return min(nums1[s1], nums2[s2])
si = min(len(nums1) - 1, s1 + k // 2 - 1)
sj = k + s1 + s2 - 2 - si
if nums1[si] == nums2[sj]:
return nums1[si]
elif nums1[si] < nums2[sj]:
return self.find(nums1, si + 1, nums2, s2, k - (si + 1 - s1))
else:
return self.find(nums1, s1, nums2, sj + 1, k - (sj + 1 - s2))
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1: list, nums2: list) -> float:
n, m = len(nums1), len(nums2)
t = n + m
x = t // 2
if t % 2 == 0: # even
return (self.find(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, x) + self.find(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, x + 1)) / 2
else:
return self.find(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, x + 1)
5. 最长回文子串
本题主要考虑三种做法,第一种是暴力写法,第二种是字符串Hash + 二分查找,第三种是马拉车算法,下面我就这三种写法一一给出代码和思路:
暴力解法
暴力做法的思路就是我们枚举回文的中心点,然后不断的向外扩散,不断枚举,查看以某字符为中心点的最大回文半径。该问题具体书写代码时,需要分别计算回文串的长度奇偶的问题。
c++
class Solution {
public:
string str;
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
str = s;
return get_answer_violence();
}
string get_answer_violence() {
// odd
if (str.size() == 0) {
return "";
}
string ret_str = "";
int ret = 0, tmp_ret = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i ++ ) {
tmp_ret = 1;
for (int j = 1; true; j ++ ) {
if (i - j >= 0 && i + j < str.size() && str[i - j] == str[i + j]) {
tmp_ret += 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (tmp_ret > ret) {
ret = tmp_ret;
ret_str = str.substr(i - tmp_ret / 2, tmp_ret);
}
}
// even
for (int i = 0; i < str.size() - 1; i ++ ) {
tmp_ret = 0;
for (int j = 1; true; j ++ ) {
if (i - j + 1 >= 0 && i + j < str.size() && str[i - j + 1] == str[i + j]) {
tmp_ret += 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (tmp_ret > ret) {
ret = tmp_ret;
ret_str = str.substr(i - tmp_ret / 2 + 1, tmp_ret);
}
}
return ret_str;
}
};
然而,看看大佬写的 c++ 代码,我有些弱爆了。。。
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
string ret = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ) {
int l = i - 1, r = i + 1;
while (l >= 0 && r < s.size() && s[l] == s[r]) {
l --, r ++;
}
if (r - l - 1 > ret.size()) { //(r - 1) - (l = 1) + 1
ret = s.substr(l + 1, r - l - 1);
}
l = i, r = i + 1;
while (l >= 0 && r < s.size() && s[l] == s[r]) {
l --, r ++;
}
if (r - l - 1 > ret.size()) { //(r - 1) - (l = 1) + 1
ret = s.substr(l + 1, r - l - 1);
}
}
return ret;
}
};
对应的 Python 代码
class Solution:
def longestPalindrome(self, s: str) -> str:
n = len(s)
max_len = 1
if n == 0:
return ""
real_left, real_right = 0, 0
for i in range(n):
# odd
l, r = i - 1, i + 1
while l >= 0 and r < n and s[l] == s[r]:
l -= 1
r += 1
if r - l - 1 > real_right - real_left + 1:
real_left, real_right = l + 1, r - 1
l, r = i, i + 1
while l >= 0 and r < n and s[l] == s[r]:
l -= 1
r += 1
if r - l - 1 > real_right - real_left + 1:
real_left, real_right = l + 1, r - 1
return s[real_left:real_right + 1]
Hash 字符串 + 二分
暴力做法的思路就是我们枚举回文的中心点,然后不断的向外扩散,不断枚举,查看以某字符为中心点的最大回文半径。分析暴力所存在的问题,不难发现,他枚举寻找最大回文半径这个地方过于耗时。每次寻找 ** 最大,我们都应该想想是否可以使用二分呢?比较字符串的相等,当然是没有办法使用二分的;但是我们将字符串进行 Hash 之后就可以了!
所以说 字符串 Hash + 二分的做法,其实是对暴力算法的改进!
同时,为了避免像是暴力做法中的就讨论,我们这里对字符串插入了 特殊字符'#' (只需要不在原字符串中出现即可)。
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int N = 2010, BASE = 259;
ULL hl[N], hr[N], p[N];
char str[N];
int n;
class Solution {
public:
ULL get_left(int i, int j) {
return hl[j] - hl[i - 1] * p[j - i + 1];
}
ULL get_right(int i, int j) {
return hr[i] - hr[j + 1] * p[j - i + 1];
}
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
// 处理字符串
n = s.size();
s = ' ' + s;
for (int i = n * 2; i > 0; i -= 2) {
str[i] = s[i / 2];
str[i - 1] = '#';
}
n = n * 2 + 1;
str[n] = '#';
str[n + 1] = '\0';
// 字符串 Hash
p[0] = 1, hl[0] = 0, hr[n + 1] = 0;
for (int i = 1, j = n; i <= n; i ++, j -- ) {
p[i] = p[i - 1] * BASE;
hl[i] = hl[i - 1] * BASE + str[i];
hr[j] = hr[j + 1] * BASE + str[j];
}
// 二分查找回文半径
int l, r, mid;
int real_left = 0, real_right = 0;
int cur_len = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
l = 0, r = min(i - 1, n - i);
while (l < r) {
mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if (get_left(i - mid, i) == get_right(i, i + mid)) {
l = mid;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
if (cur_len < l) {
cur_len = l;
real_left = i - l;
real_right = i + l;
}
}
string ret = "";
for (int i = real_left; i <= real_right; i ++ ) {
if (str[i] != '#') {
ret = ret + str[i];
}
}
return ret;
}
};
对应的 Python 代码
马拉车算法
不会 Manacher的可以去百度,Bilibili上也有很多的讲解视频。
首先,我想先给出一个平常的Manacher算法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2000010;
int p[N];
char s[N], str[N];
int len1, len2;
void Init() {
len1 = strlen(s);
str[0] = '@';
str[1] = '#';
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i ++ ) {
str[i * 2 + 2] = s[i];
str[i * 2 + 3] = '#';
}
len2 = len1 * 2 + 1;
str[len2 + 1] = '$'; // 因为我们并未对他的边界进行特判,所以说这里的东西,纯纯就是哨兵
}
void Manacher() {
// id 指的是中心点,mx指的是中心点尚未到达的点
int id = 0, mx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len2; i ++ ) {
if (mx > i) p[i] = min(p[2 * id - i], mx - i);
else p[i] = 1;
while (str[i + p[i]] == str[i - p[i]]) {
p[i] ++;
}
if (i + p[i] > mx) {
mx = i + p[i];
id = i;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int cur_cnt = 0;
while (scanf("%s", s), strcmp(s, "END")) {
Init();
Manacher();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len2; i ++ ) {
ans = max(p[i] - 1, ans);
}
printf("Case %d: %d\n", ++ cur_cnt, ans);
}
return 0;
}
将该算法应用到我们的题目上(是说话,马拉车算法挺好写的):
const int N = 2010;
char str[N];
int len1, len2;
int p[N];
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
// initial
len1 = s.size();
str[0] = '@';
str[1] = '#';
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i ++ ) {
str[i * 2 + 2] = s[i];
str[i * 2 + 3] = '#';
}
len2 = len1 * 2 + 1;
str[len2 + 1] = '$'; // @ 和 $ 这两个符号就是起到了收尾烧饼的作用,因为我们并不会判断马拉车过程中是否会越界
// Manacher
int mx = 0, id = 0;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len2; i ++ ) {
if (i < mx) p[i] = min(p[2 * id - i], mx - i);
else p[i] = 1;
while (str[i + p[i]] == str[i - p[i]]) { // 需要哨兵看管
p[i] ++;
}
if (mx < i + p[i]) {
mx = i + p[i];
id = i;
}
if (p[i] - 1 > ans) {
ans = p[i] - 1;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= len2; i ++ ) {
if (p[i] - 1 == ans) {
string ret = "";
for (int j = i - p[i] + 1; j <= i + p[i] - 1; j ++ ) {
if (str[j] != '#') {
ret += str[j];
}
}
return ret;
}
}
return "";
}
};
找的大佬的 python Manacher 算法,并按照自己的习惯进行了注释和修改
N = 2000010
info = [0 for i in range(N)] # 就是我们的回文半径 P
s = input()
cur_cnt = 1
while s != 'END':
# 下一步是初始化,对源字符串进行处理,抛去奇偶性
s = '@#' + '#'.join([s[i] for i in range(len(s))]) + '#$'
# 进行 Manacher 算法
id, mx = 0, 0
ans = 0
# print(s)
for i in range(1, len(s) - 1):
# 下面这个 if else 的使用很有意思,因为我很少这样用。。。
info[i] = min(info[2 * id - i], mx - i) if mx > i else 1
while s[i + info[i]] == s[i - info[i]]:
info[i] += 1
if mx < i + info[i]:
mx = i + info[i]
id = i
ans = max(ans, info[i] - 1)
print('Case ' + str(cur_cnt) + ': ' + str(ans))
cur_cnt += 1
s = input()
对应的 Python 代码
N = 2010
info = [0 for i in range(N)]
class Solution:
def longestPalindrome(self, s: str) -> str:
# initial the string
s = '@#' + '#'.join([ch for ch in s]) + '#$'
# Manacher
mx, id = 0, 0
max_left, max_right = 0, 0
for i in range(1, len(s) - 1):
info[i] = min(info[id * 2 - i], mx - i) if mx > i else 1
while s[i + info[i]] == s[i - info[i]]:
info[i] += 1
if i + info[i] > mx:
mx = i + info[i]
id = i
if max_right - max_left < 2 * info[i] - 1:
max_left, max_right = i - info[i] + 1, i + info[i] - 1
return s[max_left + 1:max_right:2]
6. ZigZag Conversion
使用指针指向当前的层数
就是假如说 numRows = 5, 当前层数应该是 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1,不断这样指向当前的层数,存入到我们的 string 字符串中即可
对应的 C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
string convert(string s, int numRows) {
if (numRows == 1) {
return s;
}
vector<string> vs(numRows + 1);
int cur_ptr = 1;
bool down = true;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ) {
vs[cur_ptr] += s[i];
if (down) {
if (cur_ptr != numRows)
cur_ptr += 1;
else
cur_ptr -= 1, down = false;
} else {
if (cur_ptr != 1)
cur_ptr -= 1;
else
cur_ptr += 1, down = true;
}
}
string ret = "";
for (int i = 1; i < vs.size(); i ++ ) {
ret += vs[i];
}
return ret;
}
};
对应的 Python 代码
class Solution:
def convert(self, s: str, numRows: int) -> str:
if numRows == 1:
return s
cur_level, down = 1, True
str_list = ["" for i in range(numRows + 1)]
for ch in s:
str_list[cur_level] += ch
if down:
if cur_level == numRows:
cur_level -= 1
down = False
else:
cur_level += 1
else:
if cur_level == 1:
cur_level += 1
down = True
else:
cur_level -= 1
ret = ""
for i in range(1, numRows + 1):
ret += str_list[i]
return ret
风格不同的python代码
首先是,一个思路和我一模一样的代码,但是精简程度,把我看哭了
class Solution:
def convert(self, s: str, numRows: int) -> str:
# 两种不需要处理的特判
if numRows == 1 or len(s) <= numRows:
return s
res = [""] * numRows # 等价于 res = ["" for i in range(numRows)]
cur_row, step = 0, 1
for ch in s:
res[cur_row] += ch
if cur_row == 0:
step = 1
elif cur_row == numRows - 1:
step = -1
cur_row += step
return "".join(res)
这里重网上找了一个差不多思路,但是代码风格有些不同的python代码,主要是用了
res = [[] for i in range(numRows)]
ret += ''.join(res[i])
我觉着比较有趣
class Solution:
def convert(self, s: str, numRows: int) -> str:
# 两种不需要处理的特判
if numRows == 1 or len(s) <= numRows:
return s
# 比较有趣的生成数组的方法
res = [[] for i in range(numRows)] # res 是一个列表的列表,用来记录每一行的字符串
cur_idx, n = 0, len(s)
while cur_idx < n:
for i in range(0, numRows):
if cur_idx < n:
res[i].append(s[cur_idx])
cur_idx += 1
else:
break
for i in range(numRows - 2, 0, -1):
if cur_idx < n:
res[i].append(s[cur_idx])
cur_idx += 1
else:
break
ret = ""
for i in range(len(res)):
ret += ''.join(res[i])
return ret
7. Reverse Integer
使用 long long 进行模拟
c++ 代码
typedef long long LL;
class Solution {
public:
int reverse(LL x) {
bool is_positive = true;
if (x >= 0) {
is_positive = true;
} else {
is_positive = false;
x = -x;
}
LL down_x = -(1LL << 31), up_x = (1LL << 31) - 1;
cout << up_x << endl << down_x << endl;
LL ret = 0LL;
while (x) {
ret = ret * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
if (is_positive == false) {
ret = -ret;
}
if (ret <= up_x && ret >= down_x) {
return ret;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
};
python 代码可以直接使用有趣的字符串翻转
class Solution:
def reverse(self, x: int) -> int:
y = abs(x)
str_x = str(y)
# 字符串翻转的方法
# print(''.join(reversed(str_x)))
str_x = str_x[::-1]
str_x.lstrip('0')
if x < 0:
str_x = '-' + str_x
str_x = int(str_x)
# print(str_x)
if -2 ** 31 <= str_x <= 2 ** 31 - 1: # 注意这个表达式,看起来很是舒服
return str_x
else:
return 0
更为精简一些
主要是使用了切片
class Solution:
def reverse(self, x: int) -> int:
str_res = str(x)[::-1] if x >= 0 else '-' + str(x)[1:][::-1]
res = int(str_res)
if -2 ** 31 <= res <= 2 ** 31 - 1:
return res
else:
return 0
8. String to Integer (atoi)
C++暴力模拟
比较坑的是,需要去除首部 0
typedef long long LL;
class Solution {
public:
int myAtoi(string s) {
// 首先去除行前的空格
int st = 0;
while (s[st] == ' ') st ++;
// 然后查看 +-号
bool is_positive = true;
if (s[st] == '+') {
is_positive = true;
st += 1;
} else if (s[st] == '-') {
is_positive = false;
st += 1;
} else {
is_positive = true;
}
// 这里需要去除几个零。。。。。绝绝子
while (s[st] == '0') st ++;
// 查看小数的部分
int ed = st;
while (ed < s.size() && s[ed] >= '0' && s[ed] <= '9')
ed ++;
// 特判是否超出范围
LL upper_boundary = (1LL << 31) - 1, lower_boundary = -(1LL << 31);
if (ed - st >= 11) {
if (is_positive) {
return upper_boundary;
} else {
return lower_boundary;
}
}
// 进行数字转换
LL num = 0;
for (int i = st; i < ed; i ++ ) {
num = num * 10 + s[i] - '0';
}
if (is_positive == false) {
num = -num;
}
// 返回结果
if (num >= upper_boundary) {
return upper_boundary;
} else if (num <= lower_boundary) {
return lower_boundary;
} else {
return num;
}
}
};
Python使用自身特性
lstrip
int 强制类型转化 str
不过这些特判比较麻烦,全是 '+'或者'-',这是空字符串,或者是全是字母
class Solution:
def myAtoi(self, s: str) -> int:
s = s.lstrip(' ')
if s == '':
return 0
st, ed = 0, 0
if s[0] == '+' or s[0] == '-':
ed = 1 # 这个 ed = 1,保证了 + - 号不被判断,但是又被 st 包含其中,可以被转换
while ed < len(s) and '0' <= s[ed] <= '9':
ed += 1
s = s[st:ed]
x = int(s) if s != '' and s != '+' and s != '-' else 0
if x > 2 ** 31 - 1:
return 2 **31 - 1
elif x < -2 ** 31:
return -2 ** 31
else:
return x
9. Palindrome Number
使用数字
c++代码
typedef long long LL;
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
// 特判负数
if (x < 0) {
return false;
}
// 颠倒过来的数字
LL y = 0, z = x;
while (z) {
y = y * 10 + z % 10;
z /= 10;
}
// 判断是否相等
return x == y;
}
};
python代码:
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, x: int) -> bool:
if x < 0:
return False
y, z = 0, x
while z != 0:
y = y * 10 + z % 10
z //= 10
return x == y
使用字符串
c++代码
typedef long long LL;
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
// 特判负数
if (x < 0) {
return false;
}
// 颠倒过来的数字
string s = "";
while (x) {
s += '0' + x %10;
x /= 10;
}
// 判断是否相等
for (int i = 0; i < s.size() / 2; i ++ ) {
if (s[i] != s[s.size() - i - 1]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
甚至还可以:
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
string y = to_string(x);
return y == string(y.rbegin(), y.rend());
}
};
python代码:
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, x: int) -> bool:
x = str(x)
return x == x[::-1]
10. Regular Expression Matching
进行暴力DFS
c++代码
class Solution {
public:
string s, p;
int n, m;
bool isMatch(string s1, string p1) {
s = s1, p = p1;
n = s.size(), m = p.size();
return dfs(0, 0);
}
bool dfs(int i, int j) {
if (i == n && j == m) { // match
return true;
} else if (j == m) { // && i != n
return false;
}
// 判断 * 的问题
int cur_ed = -1;
if (j + 1 < m && p[j + 1] == '*') {
cur_ed = j + 2;
while (cur_ed < m && p[cur_ed] == '*')
cur_ed ++;
}
if (cur_ed == -1) { // 没有 *
if (p[j] == '.') {
return dfs(i + 1, j + 1);
} else {
return s[i] == p[j] && dfs(i + 1, j + 1);
}
} else { // 至少后面存在一个 *
if (p[j] == '.') {
for (int k = i; k <= n; k ++ ) { // 一个不匹配到全部匹配
if (dfs(k, cur_ed)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} else {
if (dfs(i, cur_ed)) { // 一个都不匹配
return true;
}
for (int k = i; k < n; k ++ ) { // 判断是否可以字母对应上
if (s[k] == p[j]) {
if (dfs(k + 1, cur_ed)) {
return true;
}
} else {
return false; // 中间存在不匹配的现象了
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
};
使用 动态规划 DP

c++代码
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int n = s.size(), m = p.size();
s = ' ' + s;
p = ' ' + p;
vector<vector<bool> > f(n + 1, vector<bool>(m + 1));
// memset(f, false, sizeof f);
f[0][0] = true;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) {
if (p[j] != '*') {
if (i == 0) {
continue;
} else {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] && (s[i] == p[j] || p[j] == '.');
}
} else {
f[i][j] = f[i][j - 2];
if (i > 0 && (s[i] == p[j-1] || p[j-1] == '.')) {
f[i][j] = f[i][j] || f[i-1][j];
}
}
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
};
python代码
class Solution:
def isMatch(self, s: str, p: str) -> bool:
s, p = ' ' + s, ' ' + p
n, m = len(s), len(p)
f = [[False] * m for i in range(n)]
f[0][0] = True
for i in range(n):
for j in range(1, m):
if p[j] != '*':
f[i][j] = i > 0 and f[i-1][j-1] and (s[i] == p[j] or p[j] == '.')
else:
f[i][j] = f[i][j-2] or i > 0 and f[i-1][j] and (s[i] == p[j-1] or p[j-1] == '.')
return f[n-1][m-1]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号