2021年1月31日 Map双列集合
Map的定义要点:
-
每个元素都是键值对存在
- 建不可以重复
- <K,V> 中键和值可以是任意类型
Map常用方法:
- 测试一下put方法的用法
HashMap<Integer,String> hm = new HashMap<>(); hm.put(1,"Tom"); System.out.println(hm.put(2,"Alice"));//null System.out.println(hm);//{1=Tom, 2=Alice} hm.put(1,"Bruce"); System.out.println(hm);//{1=Bruce, 2=Alice} System.out.println(hm.remove(2));//Alice System.out.println(hm);//{1=Bruce}
- get方法如果获取不到就要会返回null
HashMap<Integer,String> hm = new HashMap<>(); hm.put(1,"Tom"); System.out.println(hm.get(2));//null hm.remove(1); System.out.println(hm.size());//0
Map怎么遍历?
方式一:通过键找值
步骤:先获取所有键组成的集合(是个Set),然后遍历这个集合里所有的建,再通过建找值
代码示例如下:
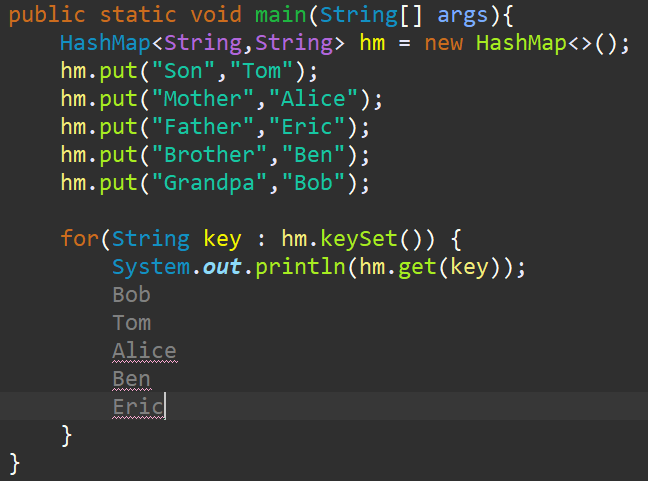
方式二:通过 Entry键值对对象
Map.Entry<K,V>是个接口,通过多态形式引用匿名实现类。
Map子类对象的entrySet()方法可以返回一个Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>的集合
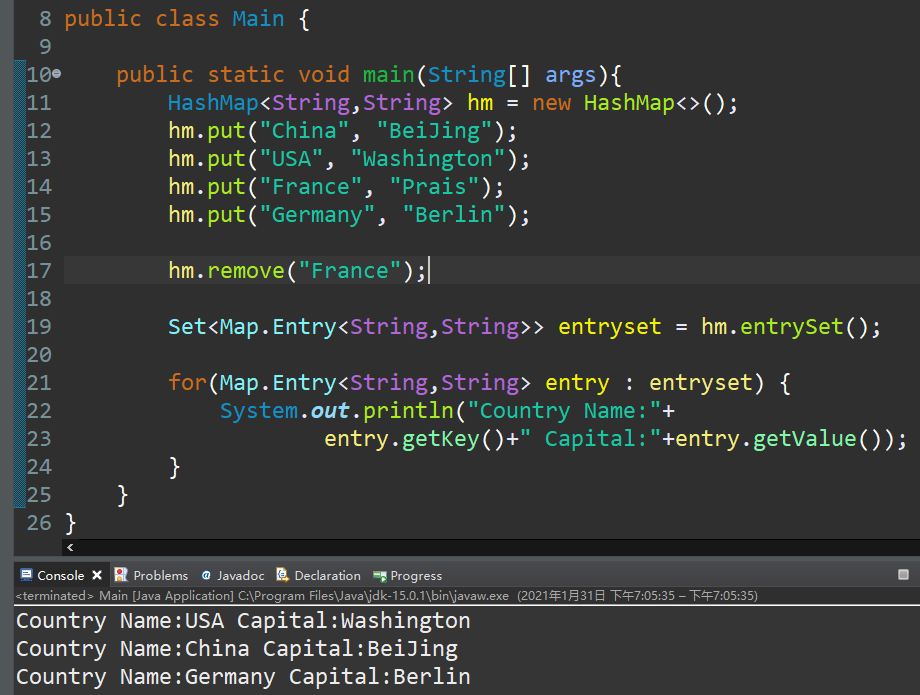
如果该HashMap中,键为自定义类型,为了保证键不重复,需要重写hashCode和equals方法:
现在需求是建立一个HashMap,能存长方形(长、宽)和它的面积:
首先定义长方形类,定义长宽属性并定义全参构造方法和toString、hashcode、equals方法
class Rect{ private int Width; private int Height; public int getWidth() { return Width; } public void setWidth(int width) { Width = width; } public int getHeight() { return Height; } public void setHeight(int height) { Height = height; } public Rect(int width, int height) { super(); Width = width; Height = height; } @Override public String toString() { return "Rect [Width=" + Width + ", Height=" + Height + "]"; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Width+Height;//这里这样写是为了让旋转九十度相同的正方形hashcode是相等的 } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Rect other = (Rect) obj; if (Height == other.Height&&Width==other.Width) return true; if (Height == other.Width&&Height==other.Width) return true;//长宽对应宽长相同的也叫同一个长方形 return false; } }
由此可见equals和hashcode的重写需要根据实际情况决定
接下来使用两种方法遍历
HashMap<Rect,Integer> rects = new HashMap<>(); rects.put(new Rect(3,4), 12); rects.put(new Rect(4,3), 12); rects.put(new Rect(3,3), 9); rects.put(new Rect(3,5), 15); rects.put(new Rect(5,3), 15); //使用keySet遍历: for(Rect r:rects.keySet()) { System.out.println(r+" size:"+rects.get(r)); } //使用entrySet遍历: Set<Map.Entry<Rect, Integer>> entrySet = rects.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry<Rect, Integer> entrys : entrySet) { System.out.println(entrys.getKey()+" size:"+entrys.getValue()); }
集合嵌套:
ArrayList套ArrayList,类似于二维数组:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建矩阵 ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> matrix = new ArrayList<>(); //创建第一行并添加数据 ArrayList<Integer> row1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Collections.addAll(row1, 1,2,3); //创建第二行并添加数据 ArrayList<Integer> row2 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Collections.addAll(row2, 4,5,6); //创建第三行并添加数据 ArrayList<Integer> row3 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Collections.addAll(row3, 7,8,9); //将三行添加至矩阵 Collections.addAll(matrix, row1,row2,row3); //遍历矩阵 //方式1:增强for循环 for(ArrayList<Integer> row : matrix) { for(Integer col:row) { System.out.print(col+" "); } System.out.println(); } //方式2:迭代器 Iterator<ArrayList<Integer>> AL_iter = matrix.iterator(); while(AL_iter.hasNext()) { ArrayList<Integer> row = AL_iter.next(); Iterator<Integer> INT_iter = row.iterator(); while(INT_iter.hasNext()) { Integer _int = INT_iter.next(); System.out.print(_int+" "); } System.out.println(); } } }
HashMap套HashMap(复杂):
原理:一个子HashMap作为父HashMap的键类型
HashMap<Integer,HashMap<String,Double>> Scores = new HashMap<>(); //创建1班 HashMap<String,Double> class1 = new HashMap<>(); class1.put("张三", 65.7); class1.put("李四", 87.9); class1.put("张三", 95.3); //创建2班 HashMap<String,Double> class2 = new HashMap<>(); class2.put("王五", 83.5); class2.put("赵六", 98.3); class2.put("田七", 66.7); //将子HashMap存入父HashMap中 Scores.put(1, class1); Scores.put(2, class2);
共有4种遍历方式:
1、增强for遍历keySet
for(Integer classnum:Scores.keySet()) { HashMap<String,Double> eachclass = Scores.get(classnum); for(String studentName:eachclass.keySet()) { System.out.println(classnum+"班,姓名:"+studentName+" 成绩:"+eachclass.get(studentName)); } }
2、增强for遍历entrySet
for(Map.Entry<Integer, HashMap<String,Double>> classNumAndClass:Scores.entrySet()) { Integer classNum = classNumAndClass.getKey(); for(Map.Entry<String, Double> nameAndScore:classNumAndClass.getValue().entrySet()) { System.out.println(classNum+"班,姓名:"+nameAndScore.getKey()+" 成绩:"+nameAndScore.getValue()); } }
3、迭代器遍历keySet
Iterator<Integer> OuterIt = Scores.keySet().iterator(); while(OuterIt.hasNext()) { Integer OuterKey = OuterIt.next(); HashMap<String,Double> InnerHashMap = Scores.get(OuterKey); Iterator<String> InnerIt = InnerHashMap.keySet().iterator(); while(InnerIt.hasNext()) { String InnerKey = InnerIt.next(); System.out.println(OuterKey+"班,姓名:"+InnerKey+" 成绩:"+InnerHashMap.get(InnerKey)); } }
4、迭代器遍历entrySet
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, HashMap<String,Double>>> OuterIt= Scores.entrySet().iterator(); while(OuterIt.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<Integer, HashMap<String,Double>> OuterEntry = OuterIt.next(); Integer OuterKey = OuterEntry.getKey(); HashMap<String,Double> OuterValue = OuterEntry.getValue(); Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Double>> InnerIt = OuterValue.entrySet().iterator(); while(InnerIt.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<String,Double> InnerEntry = InnerIt.next(); System.out.println(OuterKey+"班,姓名:"+InnerEntry.getKey()+" 成绩:"+InnerEntry.getValue()); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号