Spring框架(最全)
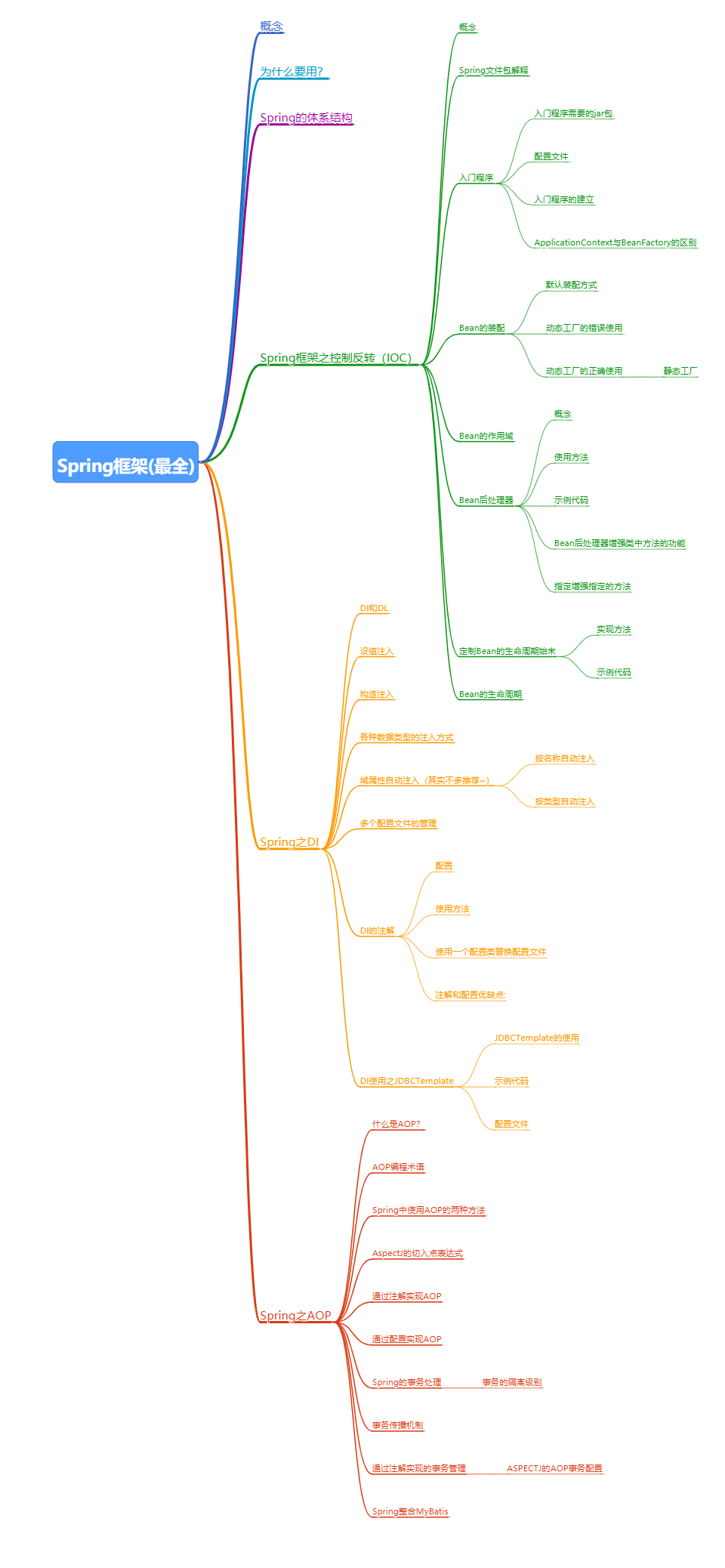
概念
S pring是一个开放源代码的设计层面框架,它解决的是业务逻辑层和其他各层的松耦合问题,因此它将面向接口的编程思想贯穿整个系统应用。Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson创建。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EE full-stack(一栈式) 轻量级开源框架。Spring的核心是控制反转(IOC)和面向切面(AOP)。
为什么要用?
- 解耦,简化开发(高内聚低耦合)
Spring可以看作一个大工厂,统一管理和维护所有对象,属性,关系等。Spring的Bean由工厂生成。 - 事务处理的支持
通过简单的配置就能实现事务管理,无需手动配置,方便程序扩展 - 方便测试
Spring对Junit4的支持可以通过注解更方便的进行测试 - 可以集成其他优秀框架
可以单用Spring进行开发,同时Spring也支持使用各种优秀框架。(Mybatis,Hibernate等) - AOP编程
Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能
Spring的体系结构

Spring框架之控制反转(IOC)
概念
Spring中IOC可以解决主业务耦合的问题,程序中使用的核心对象,不需要像以前那样NEW(),Spring的容器给我们创建。
Spring文件包解释




入门程序
入门程序需要的jar包
- 四个核心包
- beans.jar
- core.jar
- context.jar
- springexpression .jar
- 3个依赖包
- logging.jar
- log4j.jar(不显示日志信息可以不加)
- junit.jar
![入门程序jar包 入门程序jar包]()
配置文件
- 位置:任意,一般存放在src
- 名称:任意,一般使用applicationContext.xml
- 配置文件的约束头
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
<bean> 配置需要创建的对象
id :用于之后从spring容器获得实例时使用的
class :需要创建实例的全限定类名
-->
<bean id="..." class="..." />
</beans>入门程序的建立
注意:为了方便截取代码,我的每个packge都放了一个对应的配置文件,所以在测试代码中,path路径为packge里的路径。如果放在src中,就不用写包的路径了。
SomeService.java:
public interface SomeService {
void doSome();
}SomeServiceImpl.java:
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSome() {
System.out.println("gogogogogogogogo");
}
}applicationContext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 默认方法 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.woniuxy.spring01.SomeServiceImpl"/>
</beans>SpringText.java:创建Bean默认方式
public void test01() {
//底层使用的技术,dom4j解析XML,反射,工厂模式
//对象的创建交给Spring容器,不需要new
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
SomeService someService=(SomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
someService.doSome();
}SpringText.java:使用IO创建
public void test02() {
//注意这里是文件系统IO的路径规范
String path="D:\\cdoe\\SpringText\\src\\com\\woniuxy\\spring01\\applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext fc=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(path);
SomeService someService = (SomeService) fc.getBean("someService");
someService.doSome();
}SpringText.java:使用已经废弃的Beanfactory创建Bean
public void test03() {
//使用Beanfactory
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
XmlBeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource(path));
SomeService someService=(SomeService) bf.getBean("someService");
someService.doSome();
}ApplicationContext与BeanFactory的区别
- ApplicationContext在容器初始化的时候,会将所有的bean对象创建。优点是::第一次请求响应速度块。缺点是:过多的销毁和占用系统资源
- BeanFactory在调用getBean()方法,获取对象时才会创建,缺点是第一次会惩罚。
Bean的装配
默认装配方式
public void test01() {
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
SomeService someService=(SomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
someService.doSome();
}动态工厂的错误使用
创建工厂类:SomeServiceFactory.java
public class SomeServiceFactory {
public SomeService getSomeService() {
return new SomeServiceImpl();
}
}applicationContext.xml:
<bean id="someService" class="com.woniuxy.spring01.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="factory" class="com.woniuxy.spring01.SomeServiceFactory"/>SpringText.java:
public void test04() {
//动态工厂错误使用
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
//获取容器
ApplicationContext fc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
//从容器中获得对象
SomeServiceFactory someServiceFactory=(SomeServiceFactory) fc.getBean("factory");
//调用方法
someServiceFactory.getSomeService().doSome();
//注意:这是一个错误用法,将工厂当成了一个普通Bean来使用,不但没有解耦,反而使结构更复杂
}动态工厂的正确使用
创建工厂类:SomeServiceFactory.java
public class SomeServiceFactory {
public SomeService getSomeService() {
return new SomeServiceImpl();
}
}
applicationContext.xml:
``` xml
SpringText.java:
public void test05() {
//动态工厂正确使用
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext fc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
SomeService service = (SomeService) fc.getBean("someService");
service.doSome();
}静态工厂
创建工厂类:SomeServiceFactory.java
public class SomeServiceFactory {
public staic SomeService getSomeService() {
return new SomeServiceImpl();
}
}
applicationContext.xml:
``` xml
<!-- 静态工厂 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.woniuxy.spring01.SomeServiceFactory" factory-method="getSomeService"/>SpringText.java:
public void test06() {
//静态工厂
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext fc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
SomeService service = (SomeService) fc.getBean("someService");
service.doSome();
}Bean的作用域
applicationContext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- scope="singleton":单例设计模式 -->
<!-- scope="prototype":原型设计模式 -->
<bean id="someService" class="com.woniuxy.spring01.SomeServiceImpl" scope="prototype"/>
</beans>SpringText.java:
public void test01() {
//测试原型模式下输出ture or false
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
SomeService someService1=(SomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
SomeService someService2=(SomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
System.out.println(someService1==someService2);
}Bean后处理器
概念
- AOP的底层实现和他有关
- AOP就是增强:底层使用动态代理或者cglib
- Bean后处理器是一个特殊的bean。
使用方法
自定义一个类,实现bean后处理器的接口--BeanPostProcessor,容器中配一个该类的一个bean,这个bean不需要id,容器中的bean对象在创建时都会自动执行bean后处理器中的两个方法。
示例代码
MyBeanPostProcessor.java类:
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
//bean:当前容器初始化的bean对象
//beanname:当前bean对象的name
//增强当前对象,返回值就是当前对象增强之后的对象
//如果只是做日志记录操作,不增强该对象的功能,不能返回NULL,直接返回原来的bean
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象初始化之前执行");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象初始化完毕执行");
return bean;
}
}applicationContext.xml:
<bean id="someService" class="com.woniuxy.spring01.SomeServiceImpl" scope="singleton"/>
<bean class="com.woniuxy.spring01.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>SpringText.java:
public void test01() {
String path="com/woniuxy/spring01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
SomeService someService=(SomeService) ac.getBean("someService");
someService.doSome();
}测试结果:

Bean后处理器增强类中方法的功能
只需要对MyBeanPostProcessor.java类进行修改即可
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象初始化之前执行");
Object stongBean = Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//相当于交叉业务--切面
System.out.println("前置增强");
Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args);
System.out.println("后置增强");
return obj;
}
});
return stongBean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象初始化完毕执行");
return bean;
}
}测试结果:

指定增强指定的方法
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{
//bean:当前容器初始化的bean对象
//beanname:当前bean对象的name
//增强当前对象,返回值就是当前对象增强之后的对象
//如果只是做日志记录操作,不增强该对象的功能,不能返回NULL,直接返回原来的bean
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象初始化之前执行");
Object stongBean = Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//判断增强的方法
if(method.getName().equals("doSome")) {
System.out.println("前置增强");
Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args);
System.out.println("后置增强");
return obj;
}else {
Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args);
return obj;
}
}
});
return stongBean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象初始化完毕执行");
return bean;
}
}定制Bean的生命周期始末
实现方法
在实现类中定义初始化执行的方法,销毁执行的方法,绑定到配置文件中即可。
示例代码
Bean的生命周期
Spring框架中Bean的生命周期比较复杂,一共有11个阶段。
- 构造器
- 属性赋值(set)
- 实现BeanNameAware,知道配置文件中,ID值。
- 实现BeanFactoryAware,找到Bean的创建工厂
- Bean后处理器中Bean初始化执行之前方法---创建类,实现BeanPostProcessor接口。
- 实现InitializingBean,正在初始化Bean。
- Setup---初始化完毕
- Bean后处理器中Bean初始化完成之后方法---创建类,实现BeanPostProcessor接口。
- 执行主业务方法。
- 实现disposableBean接口,Bean销毁之前
- teardown---对象销毁之后
![enter description here enter description here]()
Spring之DI
Spring实现IOC的核心机制是DI(依赖注入)。通俗来说就是ServiceImpl类中,有Dao 对象,那就是ServiceImpl依赖了Dao。
DI和DL
实现IOC的技术手段:DI(依赖注入)和 DL(依赖查找),Spring中的核心机制就是DI(依赖注入)。
- DI:Depedency Injection,依赖注入。依赖注入就是将服务注入到使用它的地方。对象只提供普通的方法让容器去决定依赖关系,容器全权负责组件的装配,它会把符合依赖关系的对DI(依赖注入)。通俗来说就是ServiceImpl类中,有Dao 对象,那就是ServiceImpl依赖了Dao。象通过属性(JavaBean中的setter)或者是构造子传递给需要的对象。
- DL:Dependency Lookup,依赖查找。容器中的受控对象通过容器的API来查找自己所依赖的资源和协作对象。这种方式虽然降低了对象间的依赖,但是同时也使用到了容器的API,造成了我们无法在容器外使用和测试对象。 依赖查找是一种更加传统的IoC实现方式。
设值注入
DI设置注入的底层使用无参构造+setxxx(),所以在类中必须要有SET和无参构造方法。
Student.java:
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private School school;
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Student(int id, String name, School school) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.school = school;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", school=" + school + "]";
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public School getSchool() {
return school;
}
public void setSchool(School school) {
this.school = school;
}
}School.java:
public class School {
private String name;
public School() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public School(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "School [name=" + name + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 当类中存在对象时 -->
<!-- property属性 name属性名 value 属性值-->
<bean id="student" class="com.woniuxy.spring02.Student">
<property name="id" value="1" />
<property name="name" value="ltp"/>
<!-- 给属性对象赋值需要用ref -->
<property name="school" ref="school"/>
</bean>
<bean id="school" class="com.woniuxy.spring02.School">
<property name="name" value="Chengdu Neusoft University"></property>
</bean>
</beans> 构造注入
底层使用的带参构造器(可以不写无参构造和setxxx()),但是实际开发中一般都不使用这种。
只需要改一下配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 其中index是指定第几个属性,如果和属性中参数顺序一致,可以省略 -->
<bean id="school" class="com.woniuxy.spring02.School">
<property name="name" value="Chengdu Neusoft University"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.woniuxy.spring02.Student">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="1"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="ltp"/>
<constructor-arg index="2" ref="school"/>
</bean>
</beans> 各种数据类型的注入方式
定义一个类,并存入各种数据类型。
Some.java:(注意至少需要添加set,无惨构造,为了方便查看,我粘贴的代码没有添加)
public class Some {
String[] strs;
School[] schools;
List<String> listStrs;
List<School> listSchools;
Set<String> sets;
Map<String, String> mapStrs;
Map<String, School> maoSchools;
Properties props;
}配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- -->
<bean id="school01" class="com.woniuxy.spring03.School">
<property name="name">
<value>oldsoft</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="school02" class="com.woniuxy.spring03.School">
<property name="name">
<value>newsoft</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- -->
<bean id="some" class="com.woniuxy.spring03.Some">
<!-- 普通数组的注入 -->
<property name="strs">
<array>
<value>abc</value>
<value>def</value>
</array>
</property>
<!-- 对象数组的注入 -->
<property name="schools">
<array>
<ref bean="school01"/>
<ref bean="school02"/>
</array>
</property>
<!-- list集合的注入 -->
<property name="listStrs">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- list对象集合的注入 -->
<property name="listSchools">
<list>
<ref bean="school02"/>
<ref bean="school01"/>
</list>
</property>
<!-- set集合的注入 -->
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- map集合的注入 -->
<property name="mapStrs">
<map>
<entry key="1" value="LTP"></entry>
<entry key="1" value="LTPPP"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!-- map对象集合的注入 -->
<property name="maoSchools">
<map>
<entry key="1" value-ref="school01"></entry>
<entry key="2" value-ref="school02"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!-- property的注入 -->
<property name="props">
<props>
<prop key="aa">aaa</prop>
<prop key="bb">bbb</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans> 域属性自动注入(其实不多推荐~)
为什么要用自动注入,因为在bean很多或者自定义的类很多的情况下,就要在xml文件里一直写bean并且还要将每个属性以set(构造方法)入参的方式引入bean里,这样耦合性也会变高,也比较麻烦。所以我们需要使用Spring的自动注入,可以在XML文件中实现,也可以使用注解(注解的方式后面讲注解的地方统一再说)实现。
按名称自动注入
还是一个学生类,一个学校类,学生类有一个属性是学校。在XML文件中,使用按名称自动注入的方式来实现。
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 按名称自动注入的方式,会自动查找配置文件与学生类的School属性名相同的bean -->
<bean id="student" class="com.woniuxy.spring04.Student" autowire="byName">
<property name="id" value="1" />
<property name="name" value="ltp"/>
</bean>
<bean id="school" class="com.woniuxy.spring04.School">
<property name="name" value="Chengdu Neusoft University"></property>
</bean>
</beans> 按类型自动注入
使用按类型自动注入,只需要将autowire的值变为byType即可。但是要注意,当文件中有两个该注入类型时候,会出错,当当前类和子类对象都在配置文件中注册,会出错。
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 按类型自动注入的方式,会自动查找配置文件与学生类的School属性名相同的bean -->
<bean id="student" class="com.woniuxy.spring04.Student" autowire="byType">
<property name="id" value="1" />
<property name="name" value="ltp"/>
</bean>
<bean id="school" class="com.woniuxy.spring04.School">
<property name="name" value="Chengdu Neusoft University"></property>
</bean>
</beans> 多个配置文件的管理
例如项目结构如下:

需要同时使用spring-student和spring-school这两个配置文件。在测试类中引用方式如下:
方式一:
public class Spring02Test {
@Test
public void test01() {
String path1="com/woniuxy/spring05/string-student.xml";
String path2="com/woniuxy/spring05/string-school.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path1,path2);
Student student= (Student) ac.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student);
}
}方式二:
public class Spring02Test {
@Test
public void test01() {
//使用通配符
String path="com/woniuxy/spring05/string-*.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
Student student= (Student) ac.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student);
}
}方式三:
创建total.xml,导入类路径中的配置文件统一管理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 在配置文件中配置配置类路径 ,添加classpath-->
<import resource="Classpath:com/woniuxy/spring05/string-*.xml"/>
</beans> 测试文件引用这个total即可。
DI的注解
IOC的DI注解,底层使用了AOP,要添加AOP的jar包并添加context约束。
配置
- 添加AOP的jar包
![enter description here enter description here]()
- 添加约束头
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
</beans>
使用方法
1.在配置文件中配置组件扫描器
2.使用注解命令~
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!-- 配置组件扫描器,告诉框架去指定的包下去查找注解 -->
<!-- com.woniuxy.spring06:扫描当前包及其子包
com.woniuxy.spring06.*:扫描当前包的子包
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.woniuxy.spring06"></context:component-scan>
</beans> 注解常用命令:

Spring提供了各层的对应注解,
@Repository :给DAO层使用
@Service :给Service使用
@Controller :给MVC的控制器使用
其它注解命令
| 命令 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| @Scope("prototype") | 将默认的单例设计模式改变为原型设计模式 |
| @PostConstruct | 放到类中的方法上,类初始化成功将会执行 |
| @PreDestroy | 放到类中的方法上,类销毁将会执行 |
| @compont | 声明这是一个类,相当于配置中的<> |
使用一个配置类替换配置文件
在Springboot中推荐使用这种方式。
创建配置类:
//告诉框架,当前这个类是一个充当配置文件的类
@Configuration
public class Myconfig {
@Bean(name="student",autowire=Autowire.BY_TYPE)
public Student getStudent() {
return new Student(1,"ltp");
}
@Bean(name="School")
public School getSchool() {
return new School("softunverserty");
}
}注解和配置优缺点:
- 注解:简单,写在源代码中,修改了注解的属性,代码必须重写编译
- 配置文件:修改配置文件,重启服务器,配置生效。优先级高于注解
DI使用之JDBCTemplate
包含了JDBC操作的模板方法, 简化开发。
JDBCTemplate的使用
1.在实现类继承JdbcDaoSupport。
2.使用this.getJdbcTemplate()方法
注意:DAO的bean元素,要配置上datasource属性。
示例代码

配置文件
- 创建数据源连接的Properties文件。
- 配置文件中指定Properties文件的路径。
- DAO的bean元素,配置上datasource属性。
- 配置数据源,使用内置连接池 或者 c3p0等连接池。

配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!-- 指定数据库配置文件的路径 ,不需要ID值 -->
<!-- 方法一 -->
<!-- <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"></property>
</bean> -->
<!-- 指定数据库配置文件的路径:方法二,使用context约束 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="acountDao" class="com.Spring.Dao.impl.AcountDaoImpl">
<!-- Dao需要连接数据库的数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源,使用内置连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>Spring之AOP
什么是AOP?
AOP是面向切面编程。它是一种编程思想,主要实现的目的是针对业务处理过程中的切面进行提取,它所面对的是处理过程中的某个步骤或阶段,以获得逻辑过程中各部分之间低耦合性的隔离效果。Spring框架实现了这种思想,Spring实现的不太好,AspectJ实现的更好。Spring也引入了AspectJ。
AOP编程术语
- 切面(Aspect)
切面泛指交叉业务逻辑。上例中的事务处理、日志处理就可以理解为切面。常用的切面有通知与顾问。实际就是对主业务逻辑的一种增强。 - 织入(Weaving)
织入是指将切面代码插入到目标对象的过程。 - 连接点(JoinPoint)
连接点指可以被切面织入的方法。通常业务接口中的方法均为连接点。 - 切入点(Pointcut)
切入点指切面具体织入的方法。在 StudentServiceImpl 类中,若 doSome()将被增强,而doOther()不被增强,则 doSome()为切入点,而 doOther()仅为连接点。 - 目标对象(Target)
目标对象指将要被增强的对象。即包含主业务逻辑的类的对象。 - 通知(Advice)
通知是切面的一种实现,可以完成简单织入功能(织入功能就是在这里完成的)。通知定义了增强代码切入到目标代码的时间点,是目标方法执行之前执行,还是之后执行等。通知类型不同,切入时间不同。切入点定义切入的位置,通知定义切入的时间。
Spring中使用AOP的两种方法
- Spring自带的AOP实现。需要导入aop联盟包,spring-aop包。
![enter description here enter description here]()
![enter description here enter description here]()
- Spring引入AspectJ实现。导入aop联盟包,spring-aop包,AspectJ核心jar包,spring-aspect整合包。
![enter description here enter description here]()
![enter description here enter description here]()
![enter description here enter description here]()
AspectJ的切入点表达式

通过以上来理解一下下面几个例子:

通过注解实现AOP
- 相关类设计
public interface SomeService {
void doSome();
String doOther();
void testService();
}
//实现接口
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
@Override
public void doSome() {
System.out.println("doSome");
}
@Override
public String doOther() {
System.out.println("doother");
return "abc";
}
@Override
public void testService() {
System.out.println("testservice");
}
}
//创建AOP的类,
//该注解告诉系统,当前类是切面类的方法,就是被织入的交叉业务
@Aspect
public class Myaspect {
//此处写AOP代码
}
}
- 配置文件
![enter description here enter description here]()
- 五种AOP通知的配置举例
- 前置通知,指定方法执行之前执行。
- 后置通知,指定方法执行之后执行。
- 环绕通知,指定方法执行前后执行。
- 异常通知,指定方法发生异常时执行
- 最后通知,无论方法是否发生异常,都要执行。
代码如下:
//before指定该方法是前置通知,之内写入目标方法,通过切入点表达式指定。
@Before("execution(* *..SomeService.do*(..))")
public void betfore() {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
//所有的通知方法都可以使用JoinPoint:代表当前的切入点
@Before("execution(* *..SomeService.do*(..))")
public void betfore(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println("前置通知"+jp);
}
//后置通知的注解
@AfterReturning("execution(* *..SomeService.do*(..))")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("后置通知");
}
//returning可以获取目标方法的返回值,但是不能修改目标方法的返回值。
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* *..SomeService.do*(..))",returning="result")
public void afterReturning(Object result) {
System.out.println("后置通知"+result);
}
//环绕通知,目标方法执行之前之后都会执行~可以真正修改目标方法的返回值
@Around("execution(* *..SomeService.doOther(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//通过proceedingJoinPoint来调用目标方法
System.out.println("环绕前增强");
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();//调用目标方法,并取得返回值
System.out.println("环绕后增强");
return proceed.toString().toUpperCase();
}
//异常通知,发生异常时,织入的方法
@AfterThrowing("execution(* *..SomeService.testService(..))")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("发生异常");
}
//最终通知,无论有没有异常都要执行,类似于异常处理的finally
@After("execution(* *..SomeService.testService(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("最终通知");
} 通过配置实现AOP
- 注册事务管理器。
- 注册事务代理类。
- 在代理类指定事务管理器
- 在代理类指定目标对象并指定哪些方法使用事务。
配置文件:
<!-- 注册事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 注册事务代理类 -->
<bean id="ServiceProxy" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 指定事务管理器 -->
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
<!-- 目标对象 -->
<property name="target" ref="stockService"/>
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props>
<!-- 指定哪些方法要添加事务,给目标类中指定的方法配置事务属性
隔离方法和传播机制
-->
<prop key="open*">ISOLATION_DEFAULT,PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
<prop key="buyStock">ISOLATION_DEFAULT,PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>Spring的事务处理
事务的隔离级别
- 读未提交:脏读
- 读已提交:SQL Server,Oracle的默认隔离级别,不可重复度
- 可重复读:MySQL的默认隔离级别,幻读
- 串行化:整张表上加上锁,效率低
事务传播机制
doSome()调用doOther()方法,直接的事务处理方式
默认市容required,doSome方法有事务处理,doOther也有事务处理,将doOther中的事务,加入到doSome方法的事务中,作为一个事务执行。
doSome方法没有事务,doOther方法有事务,doSome开启事务,加入到doOther中,作为一个统一事务执行。
通过注解实现的事务管理
- 配置约束头,添加
- 注册事务管理器
- 配置注解驱动
- 在Service方法添加注解
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!-- 指定数据库配置文件的路径 ,不需要ID值 -->
<!-- 方法一 -->
<!-- <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"></property>
</bean> -->
<!-- 指定数据库配置文件的路径:方法二,使用context约束 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 注入Service -->
<bean id="stockService" class="com.Spring.service.impl.StockServiceImpl">
<property name="acountDao" ref="acountDao" />
<property name="stockDao" ref="stockDao" />
</bean>
<!-- 注入acountDao -->
<bean id="acountDao" class="com.Spring.Dao.impl.AcountDaoImpl">
<!-- Dao需要连接数据库的数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 注入stockDao -->
<bean id="stockDao" class="com.Spring.Dao.impl.StockDaoImpl">
<!-- Dao需要连接数据库的数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源,使用内置连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!-- 注册事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置注解驱动 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>在service中在需要添加事务的地方添加注解:
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void openStock(String sname, int smoney) {
stockDao.insertStock(sname, smoney);
}解决受查exception不回滚的问题:rollbackFor=Exception.class。
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,rollbackFor=Exception.class)
public void buyStock(String aname, int money, String sname, int smoney) throws Exception {
acountDao.updateAcount(aname, money);
if(true) {
throw new Exception();
}
stockDao.updateStock(sname, smoney);
}ASPECTJ的AOP事务配置
- 配置约束头
- 注册事务管理器
- 注册事务通知
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!-- 指定数据库配置文件的路径 ,不需要ID值 -->
<!-- 方法一 -->
<!-- <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"></property>
</bean> -->
<!-- 方法二,使用context约束 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 注入Service -->
<bean id="stockService" class="com.Spring.service.impl.StockServiceImpl">
<property name="acountDao" ref="acountDao" />
<property name="stockDao" ref="stockDao" />
</bean>
<!-- 注入acountDao -->
<bean id="acountDao" class="com.Spring.Dao.impl.AcountDaoImpl">
<!-- Dao需要连接数据库的数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 注入stockDao -->
<bean id="stockDao" class="com.Spring.Dao.impl.StockDaoImpl">
<!-- Dao需要连接数据库的数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源,使用内置连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!-- 注册事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 注册事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txadvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 配置事务方法 -->
<tx:method name="open*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!-- rollback-for="Exception":解决受查异常不回滚问题 -->
<tx:method name="buyStock" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED"
rollback-for="Exception"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))" id="pointcut"/>
<!-- 顾问,就是对通知的封装 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans> Spring整合MyBatis
第三方框架的核心类的对象,由Spring框架容器来管理。所以我们在添加jar包的时候需要添加spring的整合包。
- 添加jar包
![enter description here enter description here]()
- 建立项目结构
![enter description here enter description here]()
- 修改配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!-- 使用context约束,获取jdbc的properties -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:mysqljdbc.properies"/>
<!-- 注册SelSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatisconfig.xml" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 指定包动态扫描 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.woniuxy.dao"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.woniuxy.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl">
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源,使用内置连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!-- 注册事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 注册事务代理类 -->
<bean id="ServiceProxy" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean">
<!-- 指定事务管理器 -->
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
<!-- 目标对象 -->
<property name="target" ref="studentService"/>
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props>
<!-- 指定哪些方法要添加事务,给目标类中指定的方法配置事务属性
隔离方法和传播机制 -->
<prop key="addStudent">ISOLATION_DEFAULT,PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
<!-- <prop key="buyStock">ISOLATION_DEFAULT,PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> -->
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans> - 修改Mybatis配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 别名配置 -->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.woniuxy.entity"/>
</typeAliases>
<mappers>
<package name="com.woniuxy.dao"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>5.修改web.xml文件,添加监听器(在seclet中创建唯一的工厂)
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>6.selvlet
public class StudentServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ApplicationContext ac=(ApplicationContext) this.getServletContext().
getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
Student student=new Student(1,"ltpfsdfa",50,20);
studentService.addStudent(student);
}
}注意:
- 该项目中修改了连接池为c3p0,所以配置文件中的datasource相应需要修改为对应的属性。
- 该配置中,增加了spring的事务处理。如果单纯为整合Mybatis可不写。
- 命名一定要用规范的驼峰命名法,不然程序底层获取不到属性。
- sqlSessionFactoryBeanName的值为一个String而不是对象,不要用ref获取,会出错。
- 在servlet中获取为了防止多个工厂建立,损耗内存,使用listener监听器,来建立唯一的工厂。









 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号