线程中断
一、使用interrupt()中断线程
当一个线程运行时,另一个线程可以调用对应的Thread对象的interrupt()方法来中断它,该方法只是在目标线程中设置一个标志,表示它已经被中断,并立即返回。这里需要注意的是,如果只是单纯的调用interrupt()方法,线程并没有实际被中断,会继续往下执行。
下面一段代码演示了休眠线程的中断:
1 public class SleepInterrupt extends Object implements Runnable{ 2 public void run(){ 3 try{ 4 System.out.println("in run() - about to sleep for 20 seconds"); 5 Thread.sleep(20000); 6 System.out.println("in run() - woke up"); 7 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 8 System.out.println("in run() - interrupted while sleeping"); 9 //处理完中断异常后,返回到run()方法人口, 10 //如果没有return,线程不会实际被中断,它会继续打印下面的信息 11 return; 12 } 13 System.out.println("in run() - leaving normally"); 14 } 15 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 SleepInterrupt si = new SleepInterrupt(); 19 Thread t = new Thread(si); 20 t.start(); 21 //主线程休眠2秒,从而确保刚才启动的线程有机会执行一段时间 22 try { 23 Thread.sleep(2000); 24 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 System.out.println("in main() - interrupting other thread"); 28 //中断线程t 29 t.interrupt(); 30 System.out.println("in main() - leaving"); 31 } 32 }
运行结果如下:

二、待决中断
在上面的例子中,sleep()方法的实现检查到休眠线程被中断,它会相当友好地终止线程,并抛出InterruptedException异常。另外一种情况,如果线程在调用sleep()方法前被中断,那么该中断称为待决中断,它会在刚调用sleep()方法时,立即抛出InterruptedException异常。
下面的代码演示了待决中断:
1 public class PendingInterrupt extends Object { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 //如果输入了参数,则在mian线程中中断当前线程(亦即main线程) 4 if( args.length > 0 ){ 5 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); 6 } 7 //获取当前时间 8 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 9 try{ 10 Thread.sleep(2000); 11 System.out.println("was NOT interrupted"); 12 }catch(InterruptedException x){ 13 System.out.println("was interrupted"); 14 } 15 //计算中间代码执行的时间 16 System.out.println("elapsedTime=" + ( System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime)); 17 } 18 }
如果PendingInterrupt不带任何命令行参数,那么线程不会被中断,最终输出的时间差距应该在2000附近(具体时间由系统决定,不精确),如果PendingInterrupt带有命令行参数,则调用中断当前线程的代码,但main线程仍然运行,最终输出的时间差距应该远小于2000,因为线程尚未休眠,便被中断,因此,一旦调用sleep()方法,会立即打印出catch块中的信息。执行结果如下:

这种模式下,main线程中断它自身。除了将中断标志(它是Thread的内部标志)设置为true外,没有其他任何影响。线程被中断了,但main线程仍然运行,main线程继续监视实时时钟,并进入try块,一旦调用sleep()方法,它就会注意到待决中断的存在,并抛出InterruptException。于是执行跳转到catch块,并打印出线程被中断的信息。最后,计算并打印出时间差。
三、使用isInterrupted()方法判断中断状态
可以在Thread对象上调用isInterrupted()方法来检查任何线程的中断状态。这里需要注意:线程一旦被中断,isInterrupted()方法便会返回true,而一旦sleep()方法抛出异常,它将清空中断标志,此时isInterrupted()方法将返回false。
下面的代码演示了isInterrupted()方法的使用:
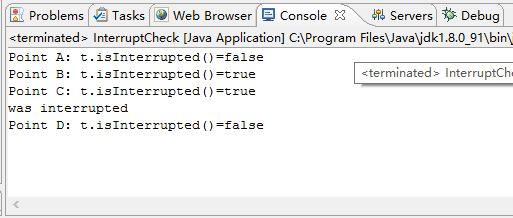
1 public class InterruptCheck extends Object{ 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); 4 System.out.println("Point A: t.isInterrupted()=" + t.isInterrupted()); 5 //待决中断,中断自身 6 t.interrupt(); 7 System.out.println("Point B: t.isInterrupted()=" + t.isInterrupted()); 8 System.out.println("Point C: t.isInterrupted()=" + t.isInterrupted()); 9 10 try{ 11 Thread.sleep(2000); 12 System.out.println("was NOT interrupted"); 13 }catch( InterruptedException x){ 14 System.out.println("was interrupted"); 15 } 16 //抛出异常后,会清除中断标志,这里会返回false 17 System.out.println("Point D: t.isInterrupted()=" + t.isInterrupted()); 18 } 19 }
运行结果如下:
四、使用Thread.interrupted()方法判断中断状态
可以使用Thread.interrupted()方法来检查当前线程的中断状态(并隐式重置为false)。又由于它是静态方法,因此不能在特定的线程上使用,而只能报告调用它的线程的中断状态,如果线程被中断,而且中断状态尚不清楚,那么,这个方法返回true。与isInterrupted()不同,它将自动重置中断状态为false,第二次调用Thread.interrupted()方法,总是返回false,除非中断了线程。
如下代码演示了Thread.interrupted()方法的使用:
1 public class InterruptReset extends Object { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println( 4 "Point X: Thread.interrupted()=" + Thread.interrupted()); 5 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); 6 System.out.println( 7 "Point Y: Thread.interrupted()=" + Thread.interrupted()); 8 System.out.println( 9 "Point Z: Thread.interrupted()=" + Thread.interrupted()); 10 } 11 }
运行结果如下:

从结果中可以看出,当前线程中断自身后,在Y点,中断状态为true,并由Thread.interrupted()自动重置为false,那么下次调用该方法得到的结果便是false
补充




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号