4. 链表
1. 哈希表

2. 有序表

代码示例
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Test {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
value = val;
}
}
public static class NodeComparator implements Comparator<Node> {
@Override
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
return o1.value - o2.value;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node nodeA = null;
Node nodeB = null;
Node nodeC = null;
// hashSet1的key是基础类型 -> int类型
HashSet<Integer> hashSet1 = new HashSet<>();
hashSet1.add(3);
System.out.println(hashSet1.contains(3));
hashSet1.remove(3);
System.out.println(hashSet1.contains(3));
System.out.println("========1=========");
// hashSet2的key是非基础类型 -> Node类型
nodeA = new Node(1);
nodeB = new Node(1);
HashSet<Node> hashSet2 = new HashSet<>();
hashSet2.add(nodeA);
System.out.println(hashSet2.contains(nodeA));
System.out.println(hashSet2.contains(nodeB));
hashSet2.remove(nodeA);
System.out.println(hashSet2.contains(nodeA));
System.out.println("========2=========");
// hashMap1的key是基础类型 -> String类型
HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap1 = new HashMap<>();
String str1 = "key";
String str2 = "key";
hashMap1.put(str1, 1);
System.out.println(hashMap1.containsKey(str1));
System.out.println(hashMap1.containsKey(str2));
System.out.println(hashMap1.get(str1));
System.out.println(hashMap1.get(str2));
hashMap1.put(str2, 2);
System.out.println(hashMap1.containsKey(str1));
System.out.println(hashMap1.containsKey(str2));
System.out.println(hashMap1.get(str1));
System.out.println(hashMap1.get(str2));
hashMap1.remove(str1);
System.out.println(hashMap1.containsKey(str1));
System.out.println(hashMap1.containsKey(str2));
System.out.println("========3=========");
// hashMap2的key是非基础类型 -> Node类型
nodeA = new Node(1);
nodeB = new Node(1);
HashMap<Node, String> hashMap2 = new HashMap<>();
hashMap2.put(nodeA, "A节点");
System.out.println(hashMap2.containsKey(nodeA));
System.out.println(hashMap2.containsKey(nodeB));
System.out.println(hashMap2.get(nodeA));
System.out.println(hashMap2.get(nodeB));
hashMap2.put(nodeB, "B节点");
System.out.println(hashMap2.containsKey(nodeA));
System.out.println(hashMap2.containsKey(nodeB));
System.out.println(hashMap2.get(nodeA));
System.out.println(hashMap2.get(nodeB));
System.out.println("========4=========");
// treeSet的key是非基础类型 -> Node类型
nodeA = new Node(5);
nodeB = new Node(3);
nodeC = new Node(7);
TreeSet<Node> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
// 以下的代码会报错,因为没有提供Node类型的比较器
try {
treeSet.add(nodeA);
treeSet.add(nodeB);
treeSet.add(nodeC);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("错误信息:" + e.getMessage());
}
treeSet = new TreeSet<>(new NodeComparator());
// 以下的代码没问题,因为提供了Node类型的比较器
try {
treeSet.add(nodeA);
treeSet.add(nodeB);
treeSet.add(nodeC);
System.out.println("这次节点都加入了");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("========5=========");
// 展示有序表常用操作
TreeMap<Integer, String> treeMap1 = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap1.put(7, "我是7");
treeMap1.put(5, "我是5");
treeMap1.put(4, "我是4");
treeMap1.put(3, "我是3");
treeMap1.put(9, "我是9");
treeMap1.put(2, "我是2");
System.out.println(treeMap1.containsKey(5));
System.out.println(treeMap1.get(5));
System.out.println(treeMap1.firstKey() + ", 我最小");
System.out.println(treeMap1.lastKey() + ", 我最大");
System.out.println(treeMap1.floorKey(8) + ", 在表中所有<=8的数中,我离8最近");
System.out.println(treeMap1.ceilingKey(8) + ", 在表中所有>=8的数中,我离8最近");
System.out.println(treeMap1.floorKey(7) + ", 在表中所有<=7的数中,我离7最近");
System.out.println(treeMap1.ceilingKey(7) + ", 在表中所有>=7的数中,我离7最近");
treeMap1.remove(5);
System.out.println(treeMap1.get(5) + ", 删了就没有了哦");
System.out.println("========6=========");
}
}

3. 链表


代码示例
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test{
// 单向链表
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
// 构造函数
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
// 双向链表
public static class DoubleNode{
public int value;
public DoubleNode last;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
// 反转单链表
public static Node reverseList(Node head){
Node pre = null;
Node nex = null;
while(head != null){
nex = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = nex;
}
return pre;
}
// 反转双链表
// 函数重载
public static DoubleNode reverseList(DoubleNode head){
DoubleNode pre = null;
DoubleNode nex = null;
while(head != null){
nex = head.next;
head.next = pre;
head.last = nex;
pre = head;
head = nex;
}
return pre;
}
// 输出单链表
public static void printLinkedList(Node head){
System.out.print("单链表的输出结果是:");
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 输出双链表
public static void printDoubleLinkedList(DoubleNode head){
System.out.print("双链表的输出结果是:");
DoubleNode end = null;
while (head != null){
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
end = head;
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("双链表的输出结果是:");
while (end != null){
System.out.print(end.value + " ");
end = end.last;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 插入链表数据
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
printLinkedList(head1);
head1 = reverseList(head1);
printLinkedList(head1);
System.out.println();
DoubleNode head2 = new DoubleNode(2);
head2.next = new DoubleNode(3);
head2.next.last = head2;
head2.next.next = new DoubleNode(4);
head2.next.next.last = head2.next;
head2.next.next.next = new DoubleNode(5);
head2.next.next.next.last = head2.next.next;
printDoubleLinkedList(head2);
printDoubleLinkedList(reverseList(head2));
}
}

代码示例
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test{
// 单向链表
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
// 构造函数
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void samePart(Node node1, Node node2)
{
System.out.print("两个单链表相同的值为:");
while (node1 != null && node2 != null){
if(node1.value < node2.value) node1 = node1.next;
else if(node1.value > node2.value) node2 = node2.next;
else {
System.out.print(node1.value + " ");
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next;
}
}
}
public static void printLinkedList(Node head){
System.out.print("单链表输出的结果是:");
while (head != null){
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 插入链表数据
Node node1 = new Node(2);
node1.next = new Node(3);
node1.next.next = new Node(5);
node1.next.next.next = new Node(6);
Node node2 = new Node(1);
node2.next = new Node(2);
node2.next.next = new Node(5);
node2.next.next.next = new Node(7);
node2.next.next.next.next = new Node(8);
printLinkedList(node1);
printLinkedList(node2);
// 打印公共部分
samePart(node1, node2);
}
}


O(1)空间复杂度的实现方法图解如图所示:

代码示例
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test{
// 单向链表
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
// 构造函数
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
// o(N)的空间复杂度函数
public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
// 使用临时变量
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
while (head != null){
if(head.value != stack.pop().value) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
// o(N/2)的空间复杂度函数
public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return true;
// 快慢指针找到中点位置
Node right = head.next; // 用来记录中点位置
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
right = right.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (right != null){
stack.push(right);
right = right.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
if(head.value != stack.pop().value)
return false;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
// O(1)的空间复杂度函数
public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return true;
Node n1 = head;
Node n2 = head;
while(n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null){
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next.next;
}
n2 = n1.next;
n1.next = null;
Node n3 = null;
// 列表的倒序
while (n2 != null) {
n3 = n2.next; // 记录下一个节点的位置
n2.next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
}
n3 = n1; // last node
n2 = head; // first node
boolean res = true;
while (n1 != null && n2 != null){
if(n1.value != n2.value){
res = false;
break;
}
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
// 还原链表
n1 = n3.next;
n3.next = null;
while (n1 != null){
n2 = n1.next;
n1.next = n3;
n3 = n1;
n1 = n2;
}
return res;
}
// 输出链表
public static void printLinkedList(Node head){
System.out.print("单链表输出的结果是:");
while (head != null){
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 插入链表数据
Node head = null;
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | ");
System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | ");
System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | ");
printLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
}
}

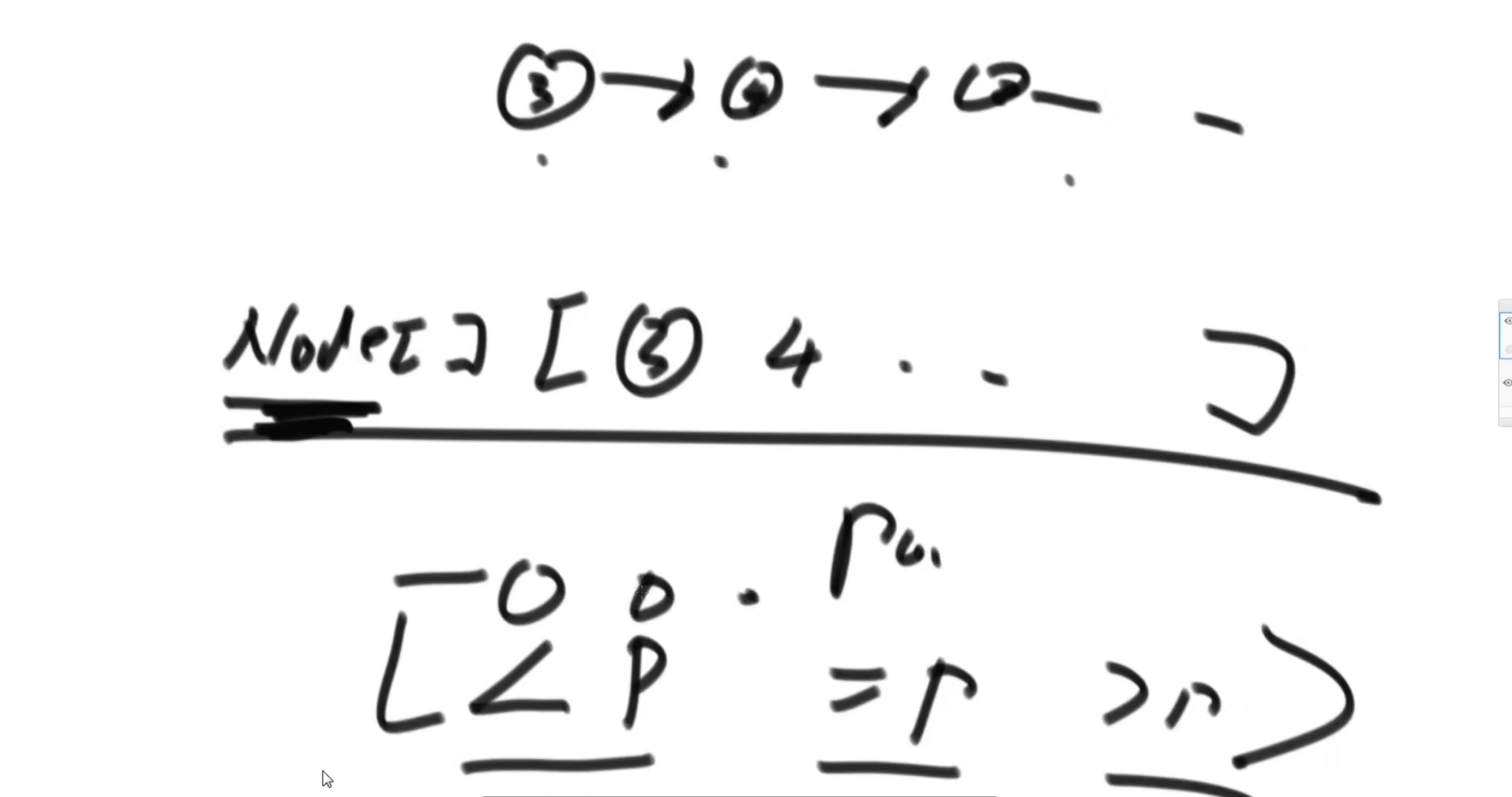
代码示例
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test{
// 单向链表
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
// 构造函数
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
/**
* 1. 数组中排序,排序后连接成链表
*/
public static Node listPartition1(Node head, int pivot){
// 处理边界情况
if(head == null) return head;
// 计算数组大小
Node cur = head;
int i = 0;
while (cur != null){
i++;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 创建并存储数组
Node[] nodeArr = new Node[i];
i = 0;
cur = head;
for (i = 0; i < nodeArr.length; i++) {
nodeArr[i] = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 数组partition
arrPartition(nodeArr, pivot);
// 数组链接
for (i = 1; i < nodeArr.length; i++) {
nodeArr[i-1].next = nodeArr[i];
}
nodeArr[i-1].next = null;
return nodeArr[0];
}
public static void arrPartition(Node[] nodeArr, int pivot){
int small = -1;
int big = nodeArr.length;
int index = 0;
while (index != big){
if(nodeArr[index].value < pivot){
swap(nodeArr, ++small, index++);
}else if(nodeArr[index].value > pivot){
swap(nodeArr, index, --big);
}else
index++;
}
}
public static void swap(Node[] nodeArr, int i, int j){
Node node = nodeArr[i];
nodeArr[i] = nodeArr[j];
nodeArr[j] = node;
}
/**
* 2. 六个变量
*/
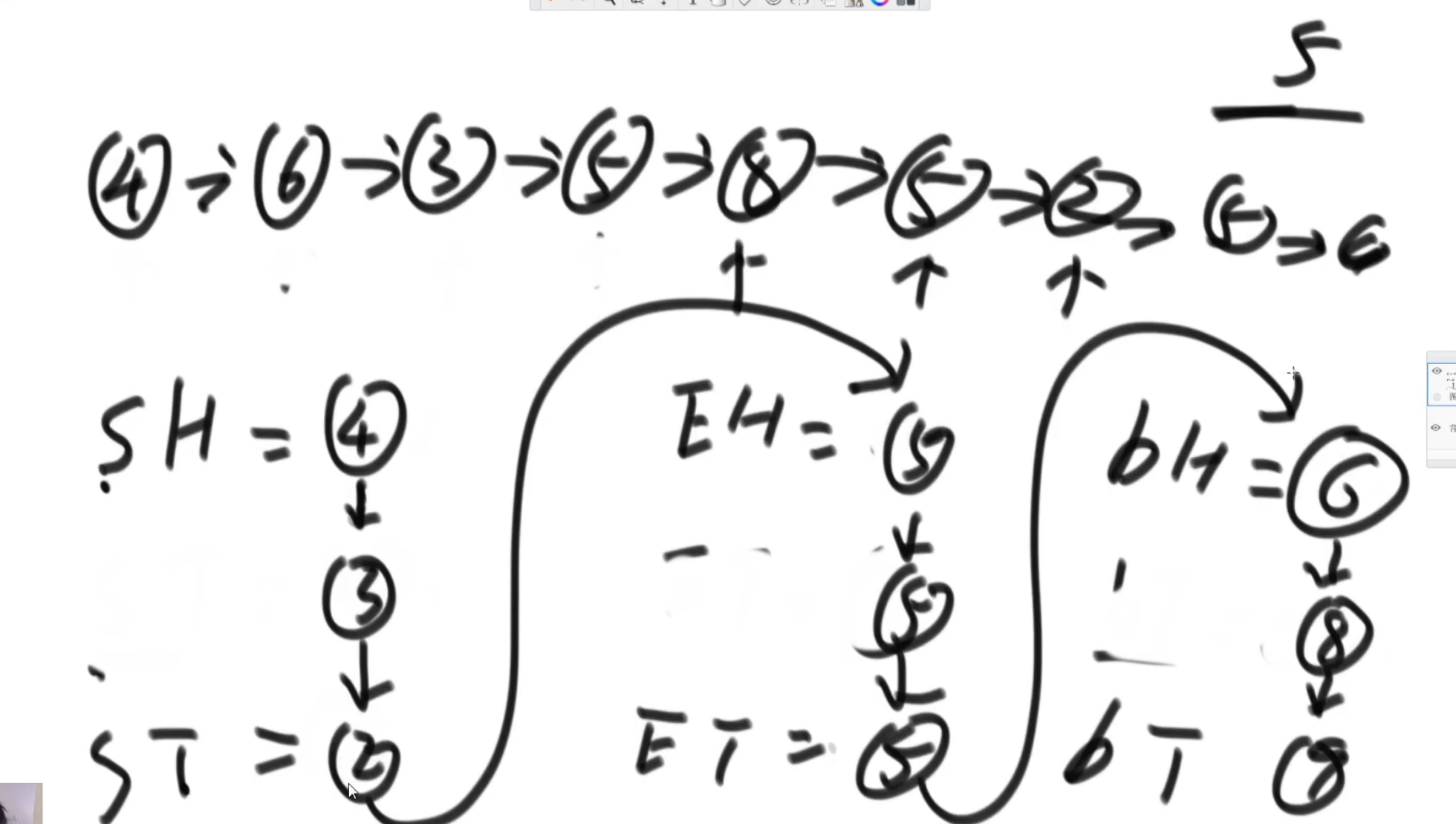
public static Node listPartition2(Node head, int pivot){
Node sH = null;
Node sT = null;
Node eH = null;
Node eT = null;
Node bH = null;
Node bT = null;
Node next = null;
while (head != null){
next = head.next;
head.next = null;
if(head.value < pivot){
if(sH == null){
sH = head;
sT = head;
}else{
sT.next = head;
sT = head;
}
}
else if(head.value > pivot){
if(bH == null){
bH = head;
bT = head;
}else{
bT.next = head;
bT = head;
}
}
else{
if(eH == null){
eH = head;
eT = head;
}else{
eT.next = head;
eT = head;
}
}
head = next;
}
// 链接几个区域
// 小于和等于区域
if(sT != null){
sT.next = eH;
eT = eT == null ? sT : eT;
}
if(eT != null){
eT.next = bH;
}
return sH != null ? sH : eH != null ? eH : bH;
}
// 输出链表
public static void printLinkedList(Node head){
System.out.print("单链表输出的结果是:");
while (head != null){
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head1 = new Node(7);
head1.next = new Node(9);
head1.next.next = new Node(1);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(8);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
printLinkedList(head1);
head1 = listPartition1(head1, 5);
// head1 = listPartition2(head1, 5);
printLinkedList(head1);
}
}

代码示例
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test{
// 单向链表
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node rand;
// 构造函数
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
// 复制链表方式1 —— 哈希表
public static Node copyListWithRand1(Node head){
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null){
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
// 复制链表方式2 —— 复制链表
public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head){
if(head == null) return head;
Node cur = head;
Node next = null;
// 复制链表
while(cur != null){
next = cur.next;
cur.next = new Node(cur.value);
cur.next.next = next;
cur = next;
}
// 寻找 random 节点
cur = head;
Node curCopy = null;
while (cur != null){
next = cur.next.next;
curCopy = cur.next;
curCopy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null;
cur = next;
}
Node res = head.next; // 链表的头结点
cur = head;
while (cur != null){
next = cur.next.next;
curCopy = cur.next;
cur.next = next;
curCopy.next = next != null ? next.next : null;
cur = next;
}
return res;
}
// 输出链表
public static void printRandLinkedList(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
System.out.println("order:");
while (cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
cur = head;
System.out.println("rand:");
while (cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.rand == null ? "- " : cur.rand.value + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
Node res1 = null;
Node res2 = null;
printRandLinkedList(head);
res1 = copyListWithRand1(head);
printRandLinkedList(res1);
res2 = copyListWithRand2(head);
printRandLinkedList(res2);
printRandLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=================================");
head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 1 -> 6
head.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 2 -> 6
head.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next; // 3 -> 5
head.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next; // 4 -> 3
head.next.next.next.next.rand = null; // 5 -> null
head.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next; // 6 -> 4
printRandLinkedList(head);
res1 = copyListWithRand1(head);
printRandLinkedList(res1);
res2 = copyListWithRand2(head);
printRandLinkedList(res2);
printRandLinkedList(head);
System.out.println("=========================");
}
}

(0)问题解析

(1)无环链表相交问题
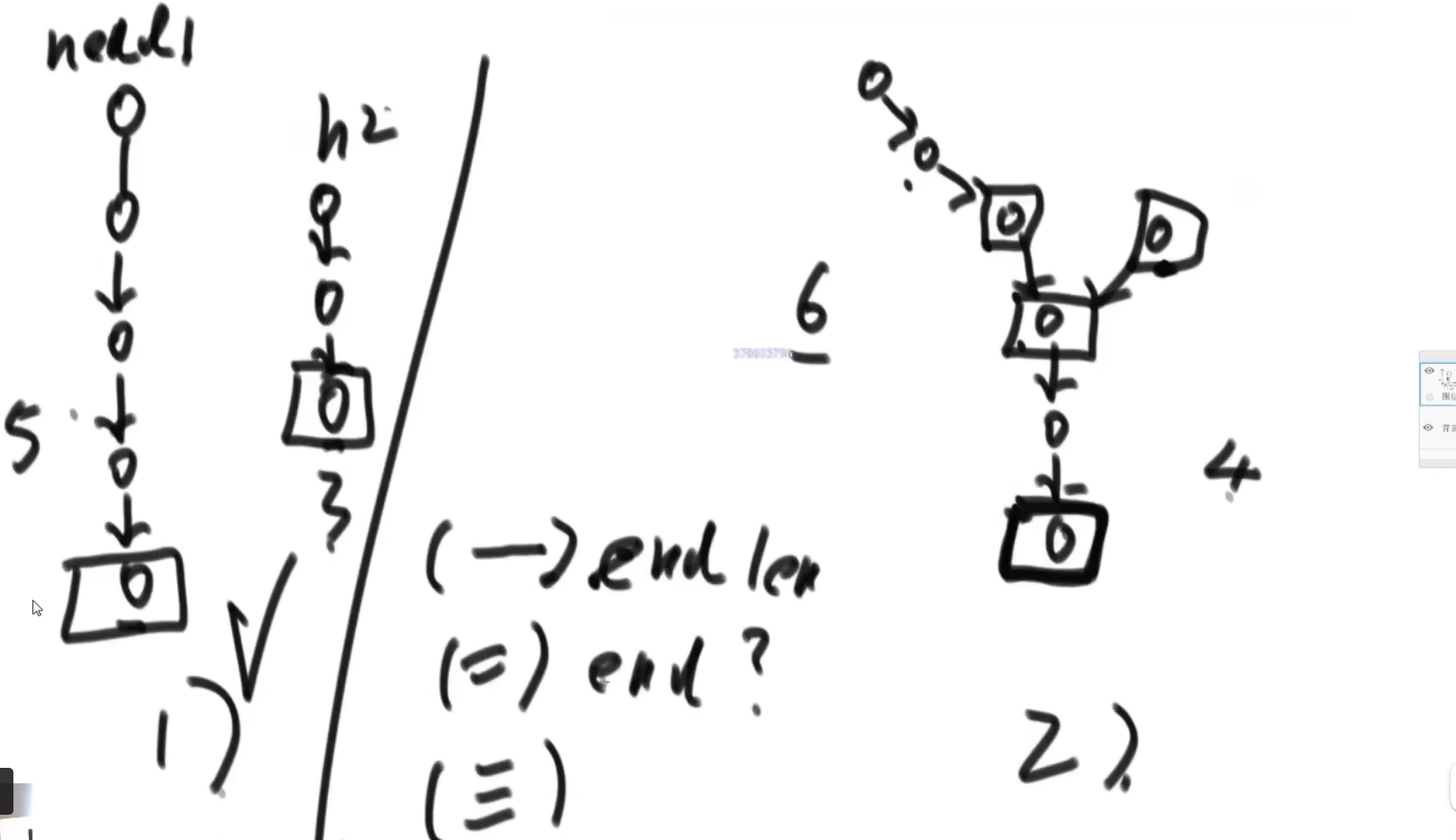
(2)有环链表相交问题
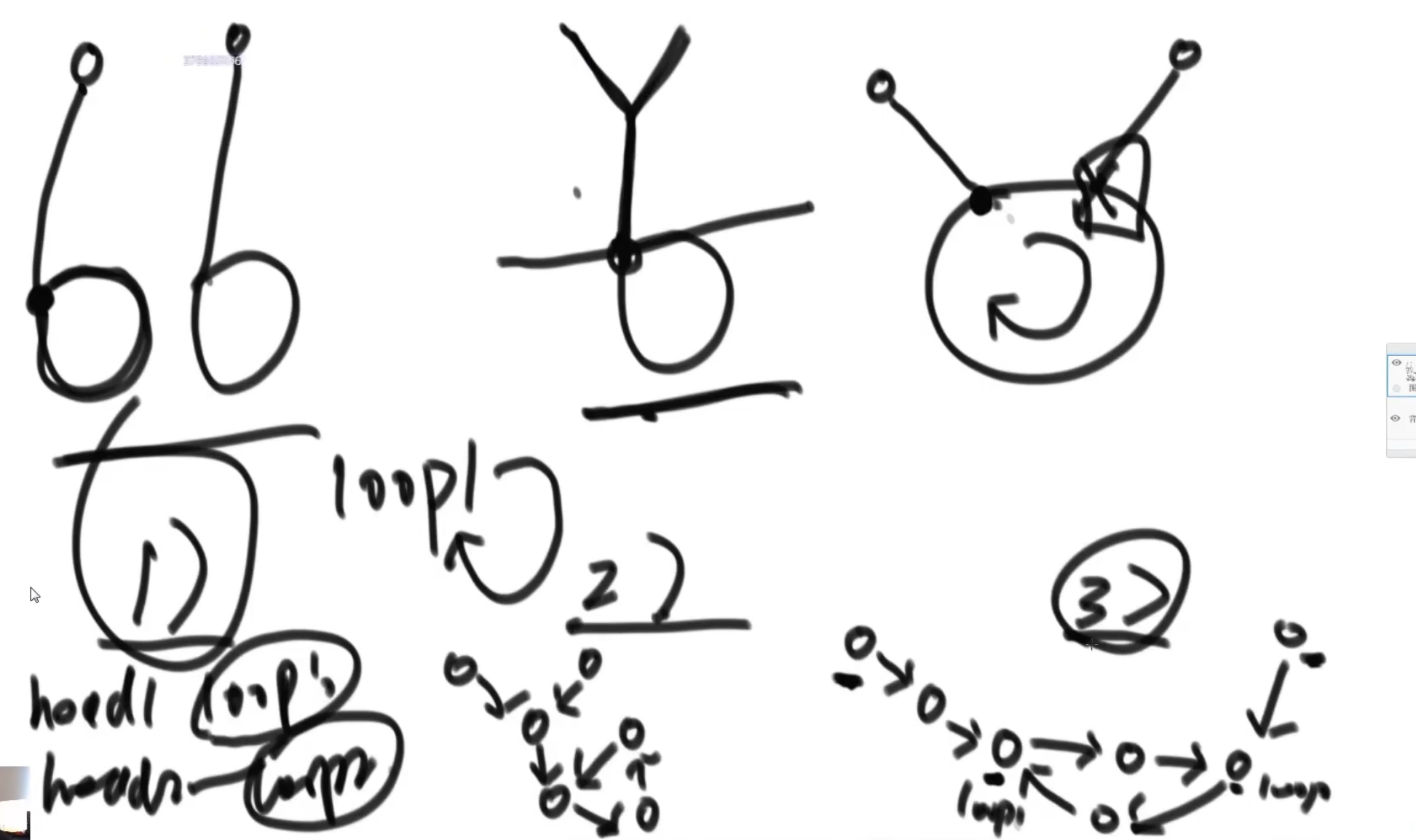
代码示例
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test{
// 单向链表
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
// 构造函数
public Node(int data){
this.value = data;
}
}
// 判断是否有入环节点
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head){
if(head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) // 不构成环
return null;
Node n1 = head.next;
Node n2 = head.next.next;
while (n1 != n2){
if(n2.next == null || n2.next.next == null) // 走到末尾
return null;
n2 = n2.next.next;
n1 = n1.next;
} // 找到相同位置
n2 = head; // 将快指针恢复到原点位置
while (n1 != n2){
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
return n1;
}
// 无环链表的相交节点
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2){
if(head1 == null || head2 == null)
return null;
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1.next != null){
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2.next != null){
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if(cur1 != cur2){ // 如果末尾节点不相同,则直接判定无相同节点
return null;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; // 判断谁是长链表
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0){
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur1 != cur2){ // 寻找长链表
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
// 有环列表的相交节点
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2){
Node cur1 = null;
Node cur2 = null;
if(loop1 == loop2){ // 这种情况和无环链表相交相同,代码类似
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while (cur1 != loop1){
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != loop2){
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0){
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next; // 长链表走相同步
}
while (cur1 != cur2){ // 找到相交节点
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
else{
// 不相交,或者相交节点不在相同的入环节点
cur1 = loop1.next;
while (cur1 != loop1){
if(cur1 == loop2)
return loop1;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return null;
}
}
// 有环链表主函数调用
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2){
if(head1 == null || head2 == null)
return null;
Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1); // 判断是否有环
Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2); // 判断是否有环
if(loop1 == null && loop2 == null) // 如果均无环,则调用无环链表的相同节点函数
return noLoop(head1, head2);
if(loop1 != null && loop2 != null) // 如果均有环,则调用有环链表的相同节点函数
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);
return null; // 不存在
}
// 主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
// 0->9->8->6->7->null
Node head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4...
head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4
// 0->9->8->2...
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 0->9->8->6->4->5->6..
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号