题目集1~3总结
一.前言
Java编程语言是当今最流行的编程语言之一,由于其跨平台性、面向对象性和安全性等特点,受到广泛的应用。
作为一名计算机专业的学生,在学习Java编程语言时,我们需要完成多个作业来巩固所学知识。
在前三次Java作业中,我们已经学习了Java的基础知识和常用技术,通过完成这些作业,我们更深入地了解了Java编程语言的特点和使用方法。
下面对这三次作业做一个简单的总结:
1.知识点:
重点掌握JAVA语言的输入输出,类的使用,if,for,switch,while等基本语句的使用。
2.题量与难度:
题量适中,菜单系列题目相对来说较为困难。
3.题目:
实验一:身体质量指数(BMI)测算 长度质量计量单位换算 奇数求和 房产税费计算2022 游戏角色选择 学号识别 判断三角形类型 巴比伦法求平方根近似值 二进制数值提取
实验二:菜单计价程序-1、2 jmu-java-日期类的基本使用 小明走格子
实验三:菜单计价程序-3 有重复的数据 去掉重复的数据 单词统计与排序 面向对象编程(封装性) GPS测绘中度分秒转换 判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数
二.设计与分析
1.实验一
7-1 身体质量指数(BMI)测算

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
double weight = in.nextDouble();
double height = in.nextDouble();
if (weight <= 727 && weight >= 0 && height >= 0 && height <= 2.72 )
{
double BIM = weight /( height * height);
if (BIM < 18.5)
{
System.out.println("thin");
}
else if (BIM >= 18.5 && BIM < 24)
{
System.out.println("fit");
}
else if (BIM >= 24 && BIM < 28)
{
System.out.println("overweight");
}
else if(BIM >= 28)
{
System.out.println("fat");
}
}
else
System.out.println("input out of range");
}
}
本题输入身高体重,计算出身体的BMI值,并运用 if 判断语句对不同范围的BMI值进行区分,分为thin,fit,overweight,fat四个状态,对于超出范围的数值输出input out of range。
7-2 长度质量计量单位换算

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main (String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
double weight = in.nextDouble();
double size = in.nextDouble();
double bang = weight /0.45359237;
double yingcun = size/ 0.0254;
System.out.print((float) bang +" " +(float) yingcun);
}
}
本题是对于质量和长度的单位换算,将千克换算为磅,米换算为英寸。
7-3 奇数求和

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int j=0,sum=0;
for( j =0;j<10;j++)
{
int i= in.nextInt();
if (i%2 != 0)
{
sum = sum +i;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
本题运用了for循环语句与if判断语句,依次输入10个整数,对每个整数做是否为奇数的判断,i除以2的余数不为0时i为奇数,将i与sum相加求和。
7-4 房产税费计算2022

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = in.nextInt();
int money = in.nextInt();
int price = in.nextInt();
double area = in.nextDouble();
double qishui = 0;
if (number ==1)
{
if (area <= 90 )
{
qishui = price * 10000*0.01;
}
else if (area > 90 && area <= 144)
{
qishui = price *10000* 0.015;
}
else if ( area > 144)
{
qishui = price *10000* 0.03;
}
}
else if(number !=1)
{
qishui = price *10000* 0.03;
}
double yinhua = 0;
yinhua = money *10000*0.0005;
double jiaoyi = 0;
jiaoyi = 3*area;
double cehui = 0;
cehui = 1.36*area;
System.out.print((float)qishui+" "+(float)yinhua+" "+(float)jiaoyi+" "+(float)cehui);
}
}
本题运用if判断语句对是否为首次购房和是否超过144平方米进行判断计算出不同情况对应的契税和其他税款。
7-5 游戏角色选择

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int zz = in.nextInt();
int js = in.nextInt();
if(zz>0&&zz<5&&js>0&&js<5)
{
switch (zz)
{
case 1:System.out.print("人类 ");break;
case 2:System.out.print("精灵 ");break;
case 3:System.out.print("兽人 ");break;
case 4:System.out.print("暗精灵 ");break;
}
switch (js)
{
case 1:System.out.print("战士");break;
case 2 :System.out.print("法师");break;
case 3:System.out.print("射手");break;
}
}
else
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
}
本题运用if判断语句对输入数值是否在选项范围内进行判断,若不在范围内输出“Wrong Format”,再运用switch语句对不同的输入情况有不同的输出结果。
7-6 学号识别

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.next();
String year = s.substring (0,2);
String college = s.substring (2,4);
String classes = s.substring (4,6);
String number = s.substring (6);
if (s.length() != 8)
{
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
return;
}
if(college.equals("01"))
{
college = "材料学院";
}
else if(college.equals("02"))
{
college = "机械学院";
}
else if(college.equals("03"))
{
college = "外语学院";
}
else if(college.equals("20"))
{
college = "软件学院";
}
else
{
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
return;
}
System.out.print("入学年份:20"+year+"年\n"+ "学院:"+college+"\n"+ "班级:"+classes+"\n"+ "学号:"+number);
}
}
本题运用了if的判断语句,通过输入的学号来判断入学年份,学院,班级及学号。
新知识点:length(),substring(),equals()的运用。
(1)length属于String类,length()用于求String字符串对象的长度,而length用于求String字符串数组长度。数组名.Length: 数组属性,字符串名.length(): 字符串的求长度的方法。
(2)通过subString()方法来进行字符串截取
1、只传一个参数:subString(int beginIndex)
将字符串从索引号为beginIndex开始截取,一直到字符串末尾。(注意索引值从0开始);
2、传入两个参数:substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
从索引号beginIndex开始到索引号endIndex结束(返回结果包含索引为beginIndex的字符不包含索引我endIndex的字符)
(3)1.是一个方法,而非运算符
2.只能适用于引用数据类型
3.Object类中equls()的定义:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
Object类定义的equals()和==的作用是相同的,比较俩地址值是否相同。
难点及踩坑点:
(1)public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
该方法用于截取字符串中,从beginIndex到索引的endIndex-1之间的的字符串,即截取的字符串不包括endIndex这个索引对应的字符,所以endIndex的最大值为整个字符串的长度,所以使用这个方法的时候需要特别注意容易发生字符串截取越界的问题。
(2)1.equals是object类中的方法,只能用于判断引用类型。
2.equals方法默认判断的是地址是否相等,子类中往往重写该方法,用于判断内容是否相等。比如String和Integer类中的equals源代码。
7-7 判断三角形类型

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
double a=in.nextDouble();
double b=in.nextDouble();
double c=in.nextDouble();
if(a>=1&&a<=200&&b>=1&&b<=200&&c>=1&&c<=200)
{
if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&b+c>a)
{
if(a==b&&b==c)
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle");
else
{
if((a==b)||(b==c)|(a==c))
{
if((a*a+b*b-c*c<0.1)||(a*a+c*c-b*b<0.1)||(b*b+c*c-a*a<0.1))//不要用a*a+b*b==c*c
System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
else
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");
}
else
{
if((a*a+b*b-c*c<0.1)||(a*a+c*c-b*b<0.1)||(b*b+c*c-a*a<0.1))
System.out.println("Right-angled triangle");
else
System.out.println("General triangle");
}
}
}
else
System.out.println("Not a triangle");
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
本题运用if判断语句,输入三条边的数值判断这三条边是否能构成一个三角形,若能构成再对三角形的类型进行判断,分为一般三角形,等腰三角形,等边三角形,直角三角形,等腰直角三角形。
7-8 巴比伦法求平方根近似值

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
float n=in.nextFloat();
float LastGuess=in.nextFloat();
float NextGuess=0;
if(n>0&&LastGuess>0)
{
NextGuess=(LastGuess+n/LastGuess)/2;
while(Math.abs(NextGuess-LastGuess)>=0.00001)
{
LastGuess=NextGuess;
NextGuess = (LastGuess+n/LastGuess)/2;
}
System.out.print(LastGuess);
}
else{
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
本题运用了if判断语句与while循环语句利用巴比伦法求平方根近似值,熟悉的掌握浮点数float的运用。
7-9 二进制数值提取

代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in);
String a = in.nextLine();
String b = "";
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++) {
if(a.charAt(i)=='0'||a.charAt(i)=='1') {
b += a.charAt(i);
}else if(a.charAt(i)=='-') {
if(a.charAt(i+1)=='1') {
System.out.print(b);
return;
}
}
}
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
}
本题运用了if判断语句与for循环语句来完成该题代码的实现。
新知识点:charAt()的运用。
1.Java 中String 类的 charAt() 方法返回给定索引号处的 char 值。 索引号从 0 开始到 n-1,其中 n 是字符串的长度。
2.如果给定的索引号大于或等于此字符串长度或负数,则返回 StringIndexOutOfBoundsException。
3.定义:public char charAt(int index)
难点及踩坑点:
1.index是一个int类型的参数。
2.参数是一个char值。
3.返回该字符串的索引值。
4.索引号从 0 开始到 n-1。
2.实验二
7-1 菜单计价程序-1

题目分析:在程序实现过程中,我们需要设计菜品类、菜谱类、点菜记录类和订单类。菜品类表示一个菜品的信息,包括菜名和单价,可以根据份额计算出当前的价格。菜谱类表示一个菜谱,包含了所有菜品的信息,可以根据菜名查找到对应的菜品。点菜记录类表示一条点菜记录,包含了点的菜品、份额和计算价格的方法。订单类表示一个订单,包含了多条点菜记录,可以计算出订单的总价。
代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
class Dish {
String name;
int price;
public Dish(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public int getPrice(int portion) {
if (portion == 1) {
return Math.round(price);
} else if (portion == 2) {
return Math.round(price * 1.5f);
} else if (portion == 3) {
return Math.round(price * 2f);
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
class Menu {
Dish[] dishes;
public Menu(Dish[] dishes) {
this.dishes = dishes;
}
public Dish searchDish(String dishName) {
for (Dish dish : dishes) {
if (dish.name.equals(dishName)) {
return dish;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dish[] dishes = {
new Dish("西红柿炒蛋", 15),
new Dish("清炒土豆丝", 12),
new Dish("麻婆豆腐", 12),
new Dish("油淋生菜", 9)
};
Menu menu = new Menu(dishes);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int totalprice = 0;
while (true) {
String input = scanner.nextLine();
if (input.equals("end")) {
break;
}
String[] tokens = input.split(" ");
String dishName = tokens[0];
int portion = Integer.parseInt(tokens[1]);
Dish dish = menu.searchDish(dishName);
if (dish == null) {
System.out.println(dishName+" does not exist");
continue;
}
int price = dish.getPrice(portion);
totalprice += price;
}
System.out.println(totalprice);
}
}
类图如下
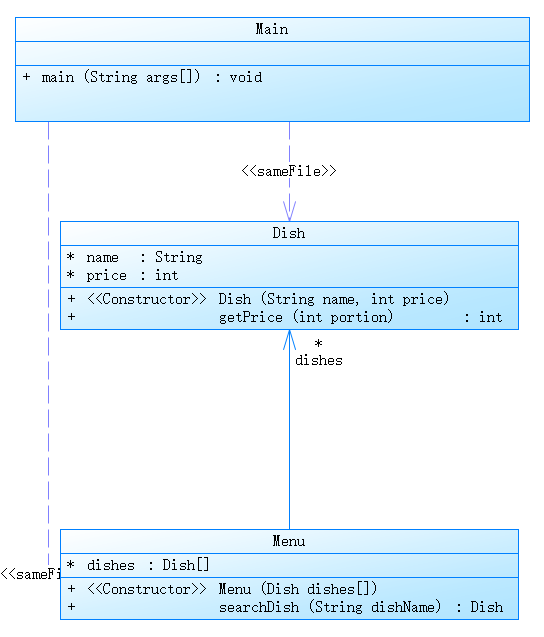
新知识点:Math.round(),split(),
1.Math.round()可以简单的理解为四舍五入函数,在负数的情况下0.5不进位。
2. split 函数是用于按指定字符(串)或正则去分割某个字符串,结果以字符串数组形式返回;
3.Integer.parseInt(String)就是将String字符类型数据转换为Integer整型数据,如果遇到不能转换的字符则会抛出异常!简而言之,这个代码就是用来把任何进制的数据转化成10进制的数据。
(1)parseInt(String s)
将字符串s转换为十进制的数字,默认为十进制
(2)parseInt(String s,int radix)
radix代表转换的进制,不写默认为十进制
7-2 菜单计价程序-2

题目分析 :该题目是7-1的迭代,相比于7-1多了删除功能。我创造了boolean delARecordByOrderNum的方法来删除订单数量,并判断是否删除成功。在代码实现过程中,需要注意输入格式,例如菜单和订单的记录格式不同。
代码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
class Dish {
String name;
int price;
int num;
int getPrice(int portion) {
int qu = 0;
if (portion == 1) {
qu = price * num;
} else if (portion == 2) {
qu = Math.round((float) (price * 1.5)) * num;
} else if (portion == 3) {
qu = price * 2 * num;
}
return qu;
}
}
class Menu {
Dish[] dishs = new Dish[1000];
int cnt = 0;
Dish searthDish(String dishName){
Dish temd = null;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
if(dishName.equals(dishs[i].name)){
temd = dishs[i];
}
}
return temd;
}
Dish addDish(String dishName,int price){
Dish dish = new Dish();
dish.name = dishName;
dish.price = price;
cnt++;
return dish;
}
}
class Record {
int orderNum;
Dish di = new Dish();
int portion;
int exist = 1;
int getPrice(){
return di.getPrice(portion);
}
}
class Order {
Record[] records = new Record[1000];
int cnt = 0;
int getTotalPrice(){
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
if(records[i].exist==0)
continue;
sum=sum+records[i].getPrice();
}
return sum;
}
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){
Record record1 = new Record();
record1.di.name = dishName;
record1.orderNum = orderNum;
record1.portion = portion;
record1.di.num = num;
cnt++;
return record1;
}
boolean delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum){
if(orderNum>cnt||orderNum<=0){
return false;
}else
records[orderNum-1].exist=0;
return true;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Menu menu = new Menu();
Order order = new Order();
int j,l;
j=l=0;
Dish tt;
while(true){
int cnt = 0;
String st = sc.nextLine();
for(int i=0;i<st.length();i++){
String te = st.substring(i,i+1);
if(te.equals(" ")){
cnt++;
}
}
if(st.equals("end"))
break;
if(cnt==1){
String[] temp = st.split(" ");
if(temp[1].equals("delete")){
if(!order.delARecordByOrderNum(Integer.parseInt(temp[0]))){
System.out.println("delete error;");
}
}else{
menu.dishs[l] = menu.addDish(temp[0],Integer.parseInt(temp[1]));
l++;
}
}
if(cnt==3){
String[] temp1 = st.split(" ");
order.records[j]=order.addARecord(Integer.parseInt(temp1[0]),temp1[1],Integer.parseInt(temp1[2]),Integer.parseInt(temp1[3]));
tt = menu.searthDish(order.records[j].di.name);
if(tt==null){
System.out.println(order.records[j].di.name+" does not exist");
}else{
order.records[j].di.price = tt.price;
System.out.println(order.records[j].orderNum+" "+order.records[j].di.name+" "+order.records[j].di.getPrice(order.records[j].portion));
}
j++;
}
}
System.out.print(order.getTotalPrice());
}
}
类图如下
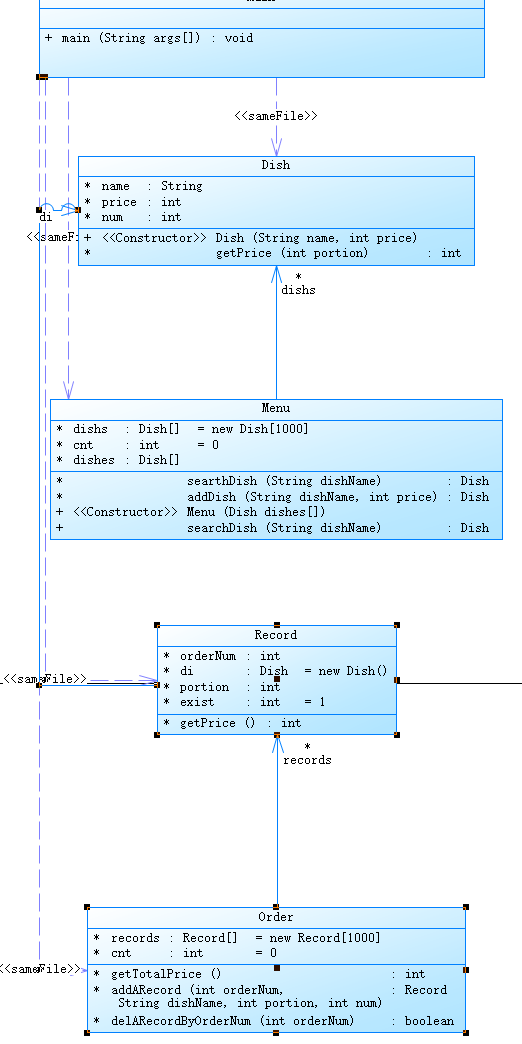
当用户输入 "序号 delete" 格式的信息时,需要找到对应序号的订单信息并进行删除。这就需要在order类里创建delARecordByOrderNum方法去删除。同时存储数据需要设计适当的数据结构来存储菜单和订单的信息,并能够方便地进行操作和计算。例如,可以使用数组或列表来存储菜单和订单信息。
3.实验三
7-1 菜单计价程序-3

题目分析:该题目继续迭代前面的两个题目,多了桌号以及时间相关的内容。在程序设计中,需要合理地组织各个类和方法,实现代码的复用和扩展。需要注意输入信息的格式和解析方法,以及时间的比较和折扣的计算方法。需要特别注意的是,我都第一个代码并没有取得满分,而是有一个测试点一直没有过去。后来在作业结束后,我又花费了一些时间去完善代码,并通过了之前的测试点。
代码如下
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Menu mu = new Menu();
Table[] tablemes = new Table[10];
int j = 0;
int l = 0;
int k = 0;
Dish tt;
int cntTable = 0;
int count;
String[] temp;
int a1,a2,a3,a4,a5;
while (true) {
String st = sc.nextLine();
temp = st.split(" ");
if(st.equals("end"))
break;
count = temp.length;
if (count == 2) {
if (temp[1].equals("delete")) {
a1 = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
int c = tablemes[cntTable].odt.delARecordByOrderNum(a1);
tablemes[cntTable].sum-=c;
} else {
a2 = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
mu.dishs[j] = mu.addDish(temp[0], a2);
j++;
}
}
else if (count == 4) {
if (temp[0].equals("table")) {
cntTable++;
l = 0;
tablemes[cntTable] = new Table();
tablemes[cntTable].AheadProcess(st);
System.out.println("table " + cntTable + ": ");
} else {
a3 =Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
a4 = Integer.parseInt(temp[2]);
a5=Integer.parseInt(temp[3]);
tablemes[cntTable].odt.addARecord(a3, temp[1],a4 , a5);
tt = mu.searthDish(temp[1]);
if (tt != null) {
tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].d = tt;
int a = tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].getPrice();
System.out.println(tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].orderNum + " " + tt.name + " " +a );
tablemes[cntTable].sum +=a;
}
l++;
}
}
else if (count == 5) {
a1 = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
a2 = Integer.parseInt(temp[3]);
a3 = Integer.parseInt(temp[4]);
tablemes[cntTable].odt.addARecord( a1, temp[2], a2, a3);
tt = mu.searthDish(temp[2]);
if (tt != null) {
tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].d.unit_price = tt.unit_price;
int b = tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].getPrice();
System.out.println(temp[1] + " table " + tablemes[cntTable].tableNum + " pay for table " + temp[0] + " " + b);
tablemes[cntTable].sum += b;
}
l++;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < cntTable + 1; i++) {
tablemes[i].Gettottalprice();
}
}
}
class Dish {
String name;
int unit_price;
int getPrice(int portion) {
int peic = 0;
if (portion == 1) {
peic = unit_price ;
} else if (portion == 2) {
peic = Math.round((float) (unit_price * 1.5)) ;
} else if (portion == 3) {
peic = (unit_price * 2) ;
}
return peic;
}
}
class Menu {
Dish[] dishs = new Dish[10];
int count = 0;
Dish searthDish(String dishName){
Dish temd = null;
for(int i=count-1;i>=0;i--){
if(dishName.equals(dishs[i].name)){
temd = dishs[i];
break;
}
}
if(temd==null){
System.out.println(dishName+" does not exist");
}
return temd;
}
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price){
Dish dh = new Dish();
dh.name = dishName;
dh.unit_price = unit_price;
count++;
return dh;
}
}
class Record {
int orderNum;
Dish d = new Dish();
int num = 0;
int portion;
int getPrice(){
return d.getPrice(portion)*num;
}
}
class Order {
Record[] records = new Record[10];
int count = 0;
void addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){
records[count] = new Record();
records[count].d.name = dishName;
records[count].orderNum = orderNum;
records[count].portion = portion;
records[count].num = num;
count++;
}
int delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum){
if(orderNum>count||orderNum<=0){
System.out.println("delete error;");
return 0;
}else {
return records[orderNum - 1].getPrice();
}
}
}
class Table {
int tableNum;
String tableDtime;
int year,month,day,week,hh,mm,ss;
int sum = 0;
Order odt = new Order();
float discnt = -1;
void Gettottalprice(){
if(discnt>0){
sum = Math.round(sum*discnt);
System.out.println("table " + tableNum + ": " + sum);
}else {
System.out.println("table " + tableNum + " out of opening hours");
}
}
void AheadProcess(String tableDtime){
this.tableDtime = tableDtime;
processTime();
discount();
}
void processTime(){
String[] temp = tableDtime.split(" ");
tableNum = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
String[] temp1 = temp[2].split("/");
String[] temp2 = temp[3].split("/");
year = Integer.parseInt(temp1[0]);
month = Integer.parseInt(temp1[1]);
day = Integer.parseInt(temp1[2]);
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(year, (month-1), day);
week = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
if(week==1)
week = 7;
else
week--;
hh = Integer.parseInt(temp2[0]);
mm = Integer.parseInt(temp2[1]);
ss = Integer.parseInt(temp2[2]);
}
void discount(){
if(week>=1&&week<=5)
{
if(hh>=17&&hh<20)
discnt=0.8F;
else if(hh==20&&mm<30)
discnt=0.8F;
else if(hh==20&&mm==30&&ss==0)
discnt=0.8F;
else if(hh>=11&&hh<=13||hh==10&&mm>=30)
discnt=0.6F;
else if(hh==14&&mm<30)
discnt=0.6F;
else if(hh==14&&mm==30&&ss==0)
discnt=0.6F;
}
else
{
if(hh>=10&&hh<=20)
discnt= 1.0F;
else if(hh==9&&mm>=30)
discnt= 1.0F;
else if(hh==21&&mm<30||hh==21&&mm==30&&ss==0)
discnt= 1.0F;
}
}
}
类图如下
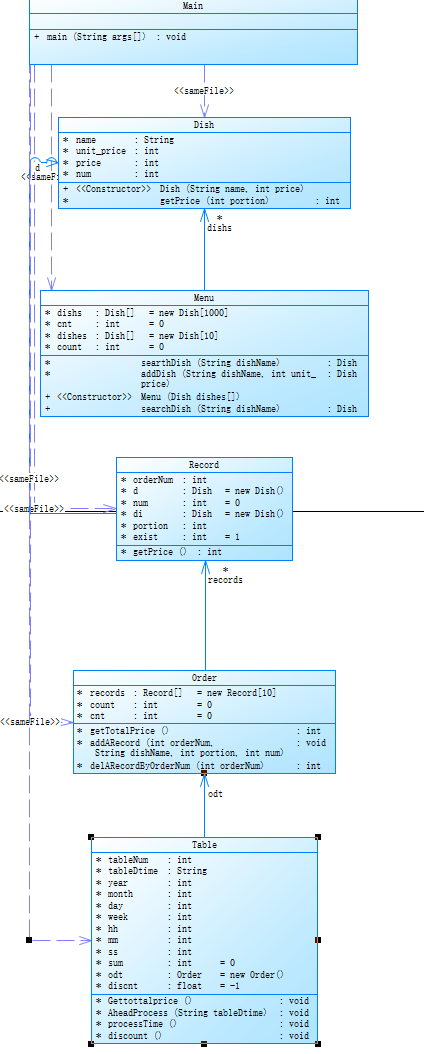
本题不仅要处理时间,也要处理桌号,很麻烦,存储数据的时候很容易出现纰漏。根据迭代前几次的经验,我在代码中定义了几个类,分别是:Dish(菜品),Menu(菜单),Record(订单记录),Order(订单),Table(餐桌)。在Main类中。循环中读取输入,根据输入的不同格式进行不同的操作,例如添加菜品到菜单,为指定餐桌添加订单,删除订单记录,代点菜等。最后,在循环结束后计算每个餐桌的总价。
三.错误分析
7-2 有重复的数据
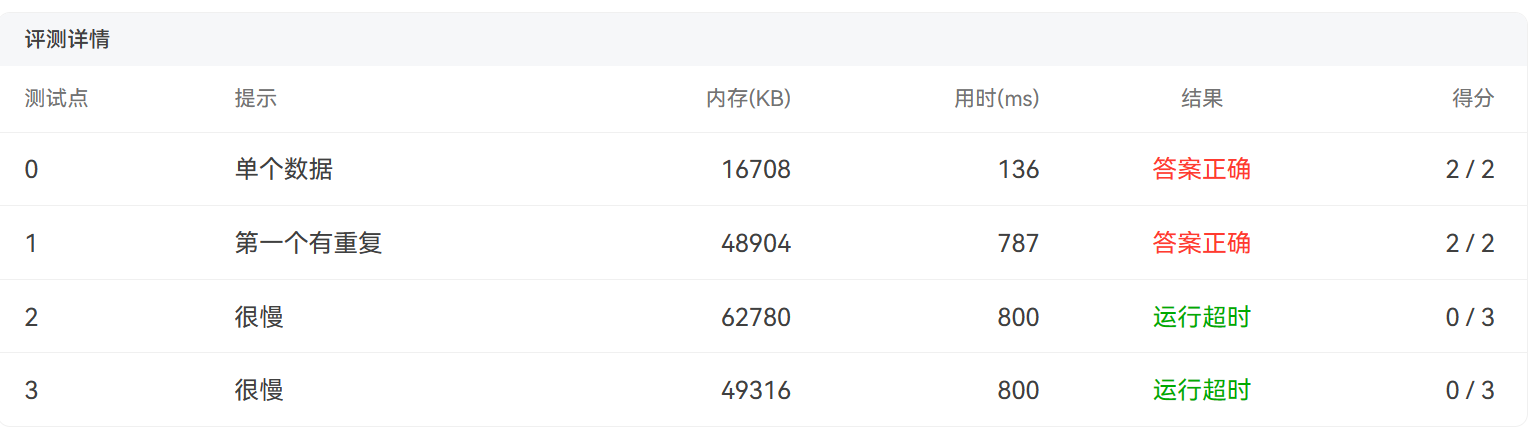
对于很慢很慢这两个测试点真的不知道错在了哪里!
7-3 去掉重复的数据
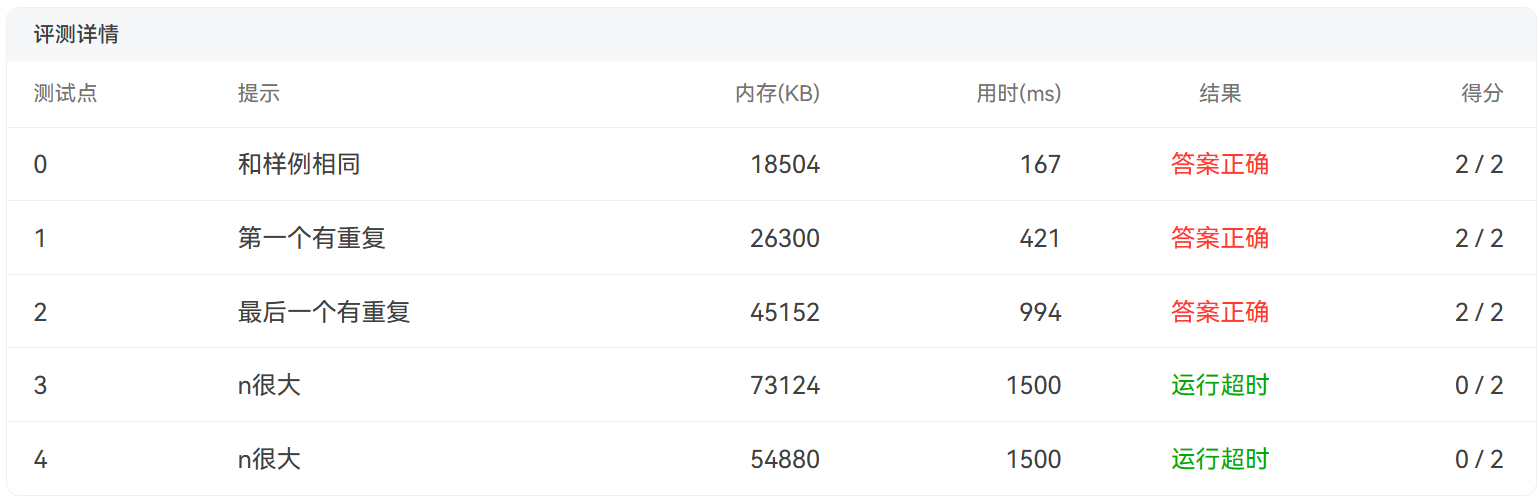
n的范围太大导致运行速度较慢运行超时,但也没找到改进的方法。
7-3 jmu-java-日期类的基本使用
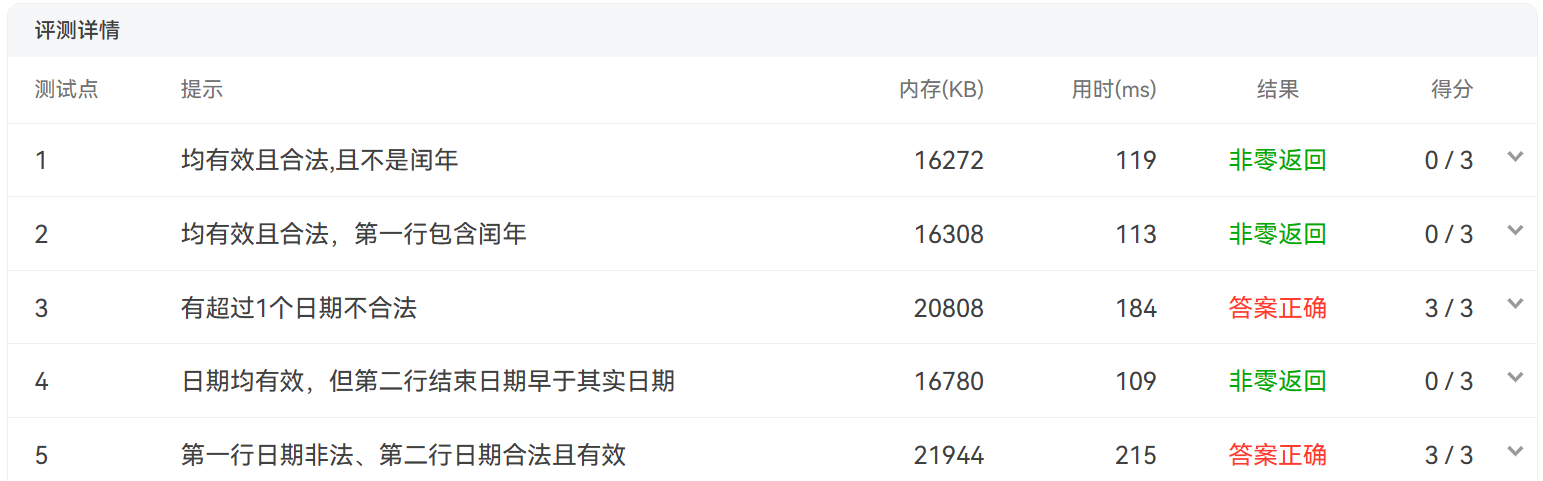
测试点1,2,4没有没有通过,后来选择LocalDate来表示相关的时间。并且是在计算月份差和年份差的时候,可能会出现一些特殊情况,比如跨年、跨月等情况。
四.总结
1.实验一难度较低,主要是一些基础语法的练习,熟悉Java编程语言的基本语法和规则,以及Java编译器的使用方法。
2.实验二开始加入了菜单系列题目,菜单一还能写的出来,从菜单二开始难度较高,需要熟练的掌握Java中类的使用及Object和String类中一些方法的使用。其中,最主要的是对类的使用,如类的继承、封装和多态性等。更加深入地理解面向对象的编程思想,熟悉Java编程语言的类和对象的使用方法。
3.实验三题量较大,重点是对Javabean的基本使用,类的广泛应用。通过这些练习,我们可以更深入地掌握Java编程语言的常用技术,如数据结构、输入输出、异常处理等。
五.改进建议
逻辑有些混乱,不能理清思路导致不能流畅地写出代码,并且使用的算法较为复杂,有些题目是可以用到更简单的方法,有许多简单易懂的算法和思路。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号