泛型类
JDK1.5开始的泛型
在定义集合的时候同时定义集合中对象的类型
可以在定义Collection时指定
也可以循环时用Iteratorr指定
好处:
增强程序的可读性和稳定性。


下面为泛型类改进
package com.liushuaishuai;
public class Generic<T> {
private T t;
public Generic() {
}
public Generic(T t) {
this.t = t;
}
public T getT() {
return t;
}
public void setT(T t) {
this.t = t;
}
}
泛型类 测试类:
package com.liushuaishuai;
public class GenericDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Generic<String> g1 = new Generic<String>();
g1.setT("林青霞");
Generic<Integer> g2 = new Generic<Integer>();
g2.setT(30);
System.out.println(g1.getT()+","+g2.getT());
}
}
下面为泛型方法改进
泛型方法格式:

package com.liushuaishuai;
/*
public class Generic<T> {
private T t;
public Generic() {
}
public Generic(T t) {
this.t = t;
}
public T getT() {
return t;
}
public void setT(T t) {
this.t = t;
}
}
*/
//泛型类改进
/*
public class Generic<T> {
public void show(T t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
}
*/
//泛型方法改进
public class Generic {
public<T> void show(T t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
}
泛型方法测试:
package com.liushuaishuai;
public class GenericDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Generic<String> g1 = new Generic<String>();
g1.setT("林青霞");
Generic<Integer> g2 = new Generic<Integer>();
g2.setT(30);
System.out.println(g1.getT()+","+g2.getT());
*/
Generic g3 = new Generic();
g3.show("林青霞");
g3.show(30);
g3.show(true);
}
}

接口类
package com.Test01;
public interface Generic<T> {
public <T> void show(T t);
}
接口的实现类
package com.Test01;
public class GenericImpl<T> implements Generic<T> {
@Override
public <T> void show(T t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
}
测试类
package com.Test01;
public class GenericDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Generic g1 = new GenericImpl();
g1.show("hello");
g1.show(30);
g1.show(true);
g1.show(12.34);
}
}
结果
:hello
30
true
12.34

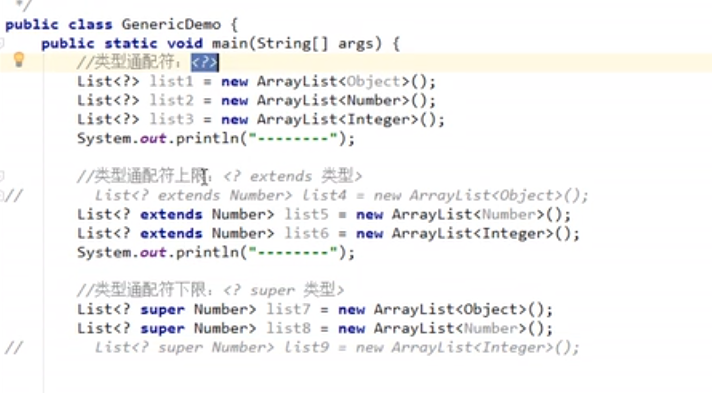


package com.Test01;
public class GenericDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Generic g1 = new GenericImpl();
g1.show("hello");
g1.show(30);
g1.show(true);
g1.show(12.34);
*/
System.out.println(sum(12,15,13,14));
}
public static int sum(int...a) {
int sum =0;
for(int i = 0;i<a.length;i++) {
sum += a[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
可变参数的使用

package com.liushuaishuai;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
/*
1,Arrays工具中有一个静态方法:
public static <T> list<T> asList(T....a):返回指定数组支持的固定大小
2,List接口中有一个静态方法:
public static <E> list<E> of (E...elements);返回包含任意数量元素的不可变列表
3,Set接口中有一个静态方法:
public static <E> Set<E> of (E...elements):返回一个包含任意数量元素的不可变集合
*/
public class ArgsDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello", "world", "java");
// list.add("javaee");//UnsupportedOperationException
//list.remove("world");//UnsupportedOperationException: remove
// public static <T> list<T> asList(T....a):返回指定数组支持的固定大小
list.set(1,"666");
System.out.println(list);//[hello, 666, java]
System.out.println("-------------------------");
// public static <E> list<E> of (E...elements);返回包含任意数量元素的不可变列表
List<String> list1 = List.of("hello", "world", "javase", "javaee");
//list1.add("GG");//UnsupportedOperationException
//list1.remove("world");//UnsupportedOperationException
//list1.set(1,"666"); //UnsupportedOperationException
System.out.println(list1);
System.out.println("---------------------");
// public static <E> Set<E> of (E...elements):返回一个包含任意数量元素的不可变集合
// Set<String> set = Set.of("hello", "world", "java", "55","55");//IllegalArgumentException
Set<String> set = Set.of("hello", "world", "java", "55");
//set.add("ll");//UnsupportedOperationException
// set.remove("hello");//UnsupportedOperationException
// set.
System.out.println(set);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号