Java学习笔记-基础语法Ⅸ-文件
File
File是文件和路径名的抽象表示,File封装的并不是一个真正存在的文件,是一个路径名,可以存在也可以不存在
常用方法:
- 创建文件:createNewFile()
- 创建目录:mkdir()
- 创建多级目录:mkdirs()
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 最好不要这样写,如果创建文件,最好指明文件类型
// File f1 = new File("D:\\javaee.txt");
File f1 = new File("D:\\javaee.txt");
System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
File f2 = new File("D:\\javaee");
System.out.println(f2.mkdir());
File f3 = new File("D:\\JavaSe\\java");
System.out.println(f3.mkdir());
File f4 = new File("D:\\JavaSe\\java");
System.out.println(f4.mkdirs());
}
}
File类别判断和获取功能:
- isDirectory:测试此抽象路径名表示的File是否为目录
- isFile:是否为文件
- exists:是否存在
- getAbsolutePath:绝对路径名字符串
- getPath:路径名字符串
- getName:文件或目录的名称
- list:目录中的文件和目录的名称字符串数组
- listFiles:目录中的文件和目录的File对象数组
import java.io.File;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("C:\\Users\\yourname\\Desktop\\code\\java_project");
boolean exists = f.exists();
System.out.println(exists);
System.out.println(f.isFile());
System.out.println(f.isDirectory());
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(f.getPath());
System.out.println(f.getName());
System.out.println(f.list());
System.out.println(f.listFiles());
String[] file_list = f.list();
for(String s:file_list){
System.out.println(s);
}
File[] listFiles = f.listFiles();
for(File x:listFiles){
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
File有了list方法,但是还是有listFiles方法,这时因为list生成的就是String,而listFiles生成的File对象,这样还可以继续使用File中的方法
删除目录时注意事项:如果一个目录中有内容(目录,文件),不能直接删除,而应该先删除目录中的内容
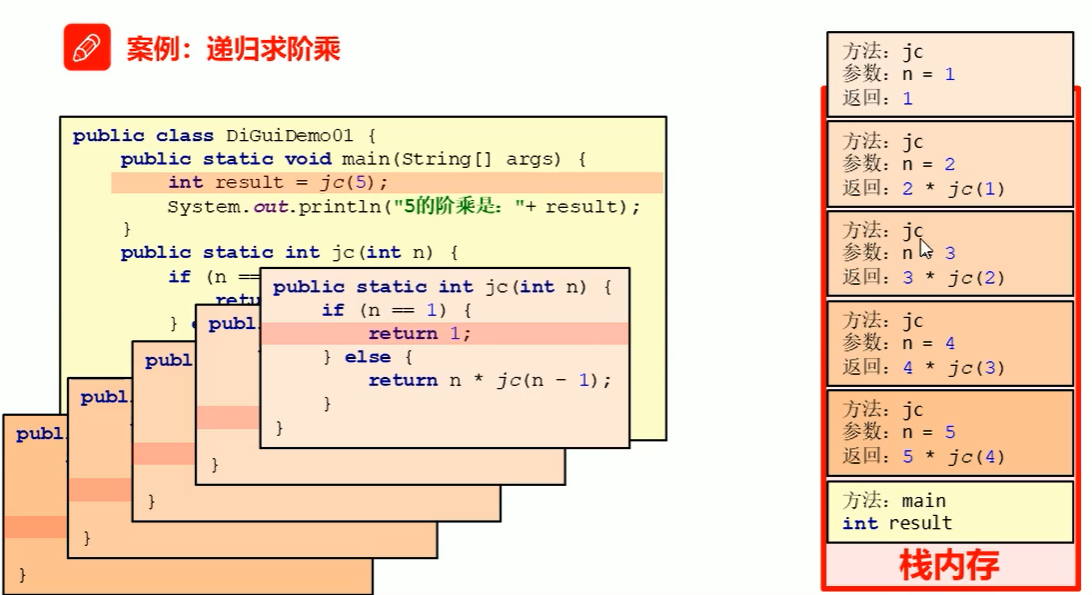
递归
递归指的是方法定义中调用方法本身的现象
递归需要有递归出口和递归规则
递归求5的阶乘的过程:
题目:

import java.io.File;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\yourname\\Desktop\\code\\java_project");
fileOutPut(file);
}
public static void fileOutPut(File f){
if(f.isFile()){
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}else{
File[] files = f.listFiles();
for(File file:files){
fileOutPut(file);
}
}
}
}
IO流
流是一种抽象的概念,是对数据传输的总成,也就是说数据在设备间的传输成为流,流的本质是数据传输
IO流就是用来处理设备间数据传输问题的,如文件复制、文件上传、文件下载
分类:
- 数据流向:输入流和输出流
- 数据类型:字节流和字符流
可以读懂的就用字符流,读不懂的用字节流,不知道用什么就用字节流
字节流抽象基类:
- InputStream:这个抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类
- OutputStream:这个抽象类是表示字节输出流的所有类的超类
- 子类名特点:子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名的后缀
// FileOutputStream的write的三种写
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("./My_File/demo.txt",true);
fos.write(98);
byte[] bys = "abcde".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
fos.write(bys);
fos.write(bys,1,3);
fos.close();
}
}
如果想换行,则需要输入
文件名.write("\n".getBytes())
在ASCII码中,换行符为10
finally
在异常处理时提供finally块来执行所有清除操作,比如IO流中的释放资源
字节流读数据
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./My_File/demo.txt");
int by;
while((by=fis.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)by);
}
}
}
字节流复制文件
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("My_File/demo.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("My_File/src/demo6/demo.txt");
int by;
while((by=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(by);
}
}
}
字节数组读数据
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("My_File/src/demo7/hello.txt");
byte [] bys = new byte[5];
// byte [] bys = new byte[20];
int len = fis.read(bys);
System.out.println("第一次读取情况:");
System.out.println(len);
// System.out.println(new String(bys));
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,len));
len = fis.read(bys);
System.out.println("第二次读取情况:");
System.out.println(len);
// System.out.println(new String(bys));
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,len));
len = fis.read(bys);
System.out.println("第三次读取情况:");
System.out.println(len);
// System.out.println(new String(bys));
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,len));
}
}
实际上用字节数组读数据为改进的代码:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("My_File/demo.txt");
byte [] bys = new byte[1024];
int read;
while((read=fis.read(bys))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,read));
}
}
}
注意,如果是直接读,返回的是读出的值,int类型
如果是读字节,那么把读出的数据存储到byte中,返回的是读出的长度,int类型
复制图片:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("My_File/src/demo9/mn.jpg");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("mn.jpg");
byte [] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fis.read(bys))!=-1){
fos.write(bys);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
字节缓冲流:
字节缓冲输出流可以向底层输出流写入字节,而不必为写入的每个字节导致系统底层的调用
字节缓冲输入流和字节缓冲输出流差不多,都是为了提高效率的
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("My_File/src/demo10/demo.txt"));
bos.write("Hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
bos.write(97);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("My_File/src/demo10/demo.txt"));
byte [] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,len));
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
如果像我这样写,是不会有输出的,因为先写,并且都还没关闭文件,也就是还没结束写的过程就去读,是不会有结果的,可以把bos.close()放到bis开始前
为什么有字符流,因为例如汉字之类的可能直接输出会出现乱码
// My_File/demo.txt文件中有汉字
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("My_File/demo.txt");
// 读方法一
/*
int read;
while((read = fis.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)read);
}
*/
// 读方法二
byte [] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fis.read(bys))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,len));
}
fis.close();
}
}
用方法一即一个字节一个字节读取会出现乱码,而用字节数组则不会有这样的问题
字符流=字节流+编码表
上述过程包含了解码问题,new String的时候按照默认的UTF-8进行了解码
对上述代码换成字符流进行读取
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class DemoModify {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("My_File/demo.txt"));
int ch;
while((ch=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
}
}
同样是读read(),但是前面的字节流会乱码,而字符流不会
这时因为字符流中的read一次读一个字符,而默认的UTF-8是一个字符对应3个字节(汉字),然后解码出来就是正常的汉字
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("test.txt"));
osw.write(97);
// 如果使用了close,那么不需要使用flush
osw.flush();
osw.close();
}
}
字符流复制文件
import java.io.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("My_File/src/demo12/Test.java"));
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("My_File/src/demo13/Test.java"));
// 一次读一个字符
/*
int len;
while((len=isr.read())!=-1){
osw.write(len);
}
*/
// 一次读一个字符数组
char [] ch = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len=isr.read(ch))!=-1){
osw.write(ch,0,len);
}
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
}
在上面介绍的字符流中,InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter有编码解码功能,其子类FileReader和FileWriter没有这两个功能,但是简洁很多,而且构造方法中,不用传入InputStream和OutputStream,可以直接传入字符串或者文件
字符缓冲流
- BufferedWriter(writer out)
- BufferedReader(Reader in)
字符缓冲流特有功能
- void newLine():写一行行分隔符,行分隔符字符串由系统属性定义
- public String readLine():读一行文字,结果包含行的内容的字符串,不包括任何终止字符,如果到达结尾,则为null
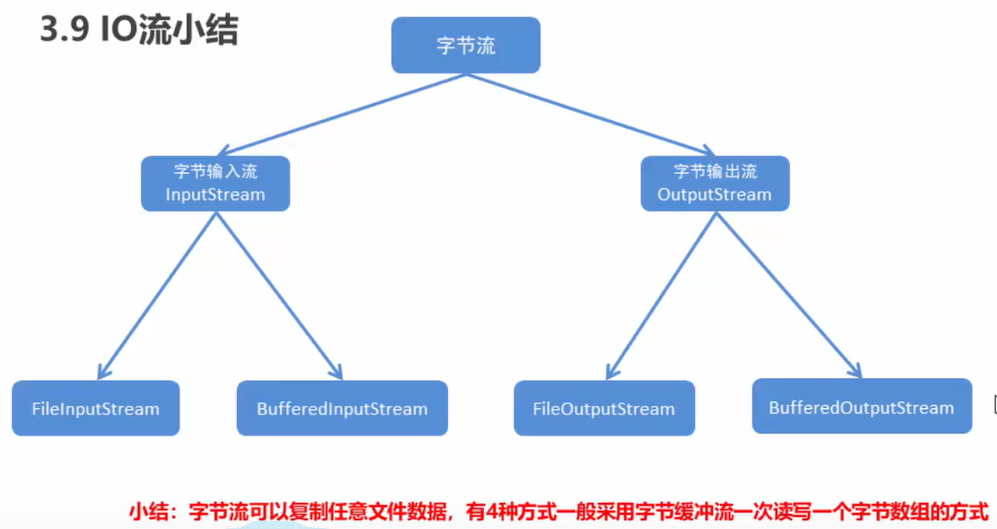
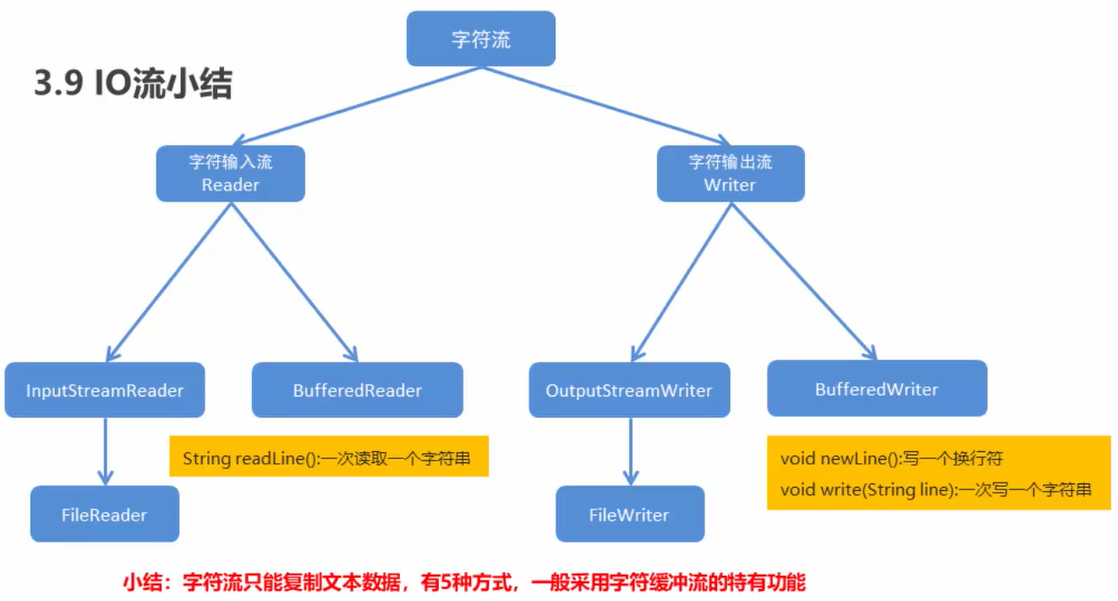
用自己的话对文件内容小结:
- 首先是File类,File类创建的是一个文件对象,可以进行
createNewFile、mkdir、mkdirs,并且还有list、listFiles、isDirectory、getName等函数 - 然后是字节流,字节流中,可以直接传入文件名的字符串,这样
write时会自动创建文件 - 字节流中,可以一次读一个字节,或者一次读一个字节数组,读字节数组时,建议输出时加上
0,len这样的内容,不然会出现空值 - 字节流每次调用都会使用系统底层的东西,建议使用缓冲字节流,缓冲字节流创建时是stream类型的,要注意下
- 接着是字符流,字符流是字节流+编码方式,当然也可以继续用字节流中的字节数组读取,这样会有解码,也可以使用字符流,但是注意构造方法传入的参数,
FileReader和FileWriter都可以直接传入字符串
复制单级文件夹
import java.io.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 将My_File/src/demo7文件复制到D:Java_Content中,如果不存在文件夹则创建
File src_file = new File("My_File/src/demo7");
String src_fileName = src_file.getName();
File dest_File = new File("D:/Java_Content",src_fileName);
dest_File.mkdirs();
File[] src_files = src_file.listFiles();
for(File file:src_files){
String fileName = file.getName();
File dest_file = new File(dest_File,fileName);
copyFile(file,dest_file);
}
}
private static void copyFile(File file, File dest_file) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest_file));
byte [] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1){
bos.write(bys,0,len);
}
}
}
复制多级文件
import java.io.*;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 将My_Set文件夹复制到D盘
File src_folder = new File("My_Set");
File dest_folder = new File("d:");
copyFolder(src_folder,dest_folder);
}
private static void copyFolder(File src_folder, File dest_folder) throws IOException {
if(src_folder.isDirectory()){
String src_folderName = src_folder.getName();
File new_folder = new File(dest_folder,src_folderName);
if(!new_folder.exists()){
new_folder.mkdirs();
}
File[] listFiles = src_folder.listFiles();
for(File file:listFiles){
copyFolder(file,new_folder);
}
}else{
File dest_file = new File(dest_folder,src_folder.getName());
copyContent(src_folder,dest_file);
}
}
private static void copyContent(File src_folder, File dest_file) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src_folder));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest_file));
byte [] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1){
bos.write(bys,0,len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号