synchronized 解决方案
4.2 synchronized 解决方案
为了避免临界区的竞态条件发生,有多种手段可以达到目的。
- 阻塞式的解决方案:synchronized,Lock
- 非阻塞式的解决方案:原子变量
本次课使用阻塞式的解决方案:synchronized,来解决上述问题,即俗称的【对象锁】,它采用互斥的方式让同一时刻至多只有一个线程能持有【对象锁】,其它线程再想获取这个【对象锁】时就会阻塞住。这样就能保证拥有锁的线程可以安全的执行临界区内的代码,不用担心线程上下文切换。
注意
虽然 java 中互斥和同步都可以采用 synchronized 关键字来完成,但它们还是有区别的:
- 互斥是保证临界区的竞态条件发生,同一时刻只能有一个线程执行临界区代码
- 同步是由于线程执行的先后、顺序不同、需要一个线程等待其他线程运行到某个点
synchronized
语法
synchronized(对象) // 线程1, 线程2(blocked)
{
临界区
}
解决
package com.mock.thread;
/**
* @Author zhangch
* @Date 2022/11/2 9:23
*/
public class ThreadSynchronized {
private static int counter = 0;
private static final Object room = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
synchronized (room) {
counter++;
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
synchronized (room) {
counter--;
}
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(counter);
}
}
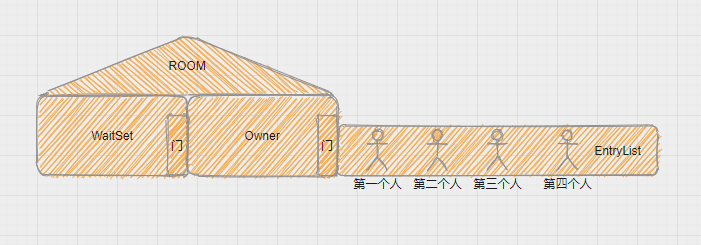
你可以做这样的类比:
synchronized(对象)中的对象,可以想象为一个房间(room),有唯一入口(门)房间只能一次进入一人进行计算,线程 t1,t2 想象成两个人- 当线程 t1 执行到
synchronized(room)时就好比 t1 进入了这个房间,并锁住了门拿走了钥匙,在门内执行count++代码 - 这时候如果 t2 也运行到了
synchronized(room)时,它发现门被锁住了,只能在门外等待,发生了上下文切换,阻塞住了 - 这中间即使 t1 的 cpu 时间片不幸用完,被踢出了门外(不要错误理解为锁住了对象就能一直执行下去哦),这时门还是锁住的,t1 仍拿着钥匙,t2 线程还在阻塞状态进不来,只有下次轮到 t1 自己再次获得时间片时才能开门进入
- 当 t1 执行完
synchronized{}块内的代码,这时候才会从 obj 房间出来并解开门上的锁,唤醒 t2 线程把钥匙给他。t2 线程这时才可以进入 obj 房间,锁住了门拿上钥匙,执行它的count--代码.
用图表示
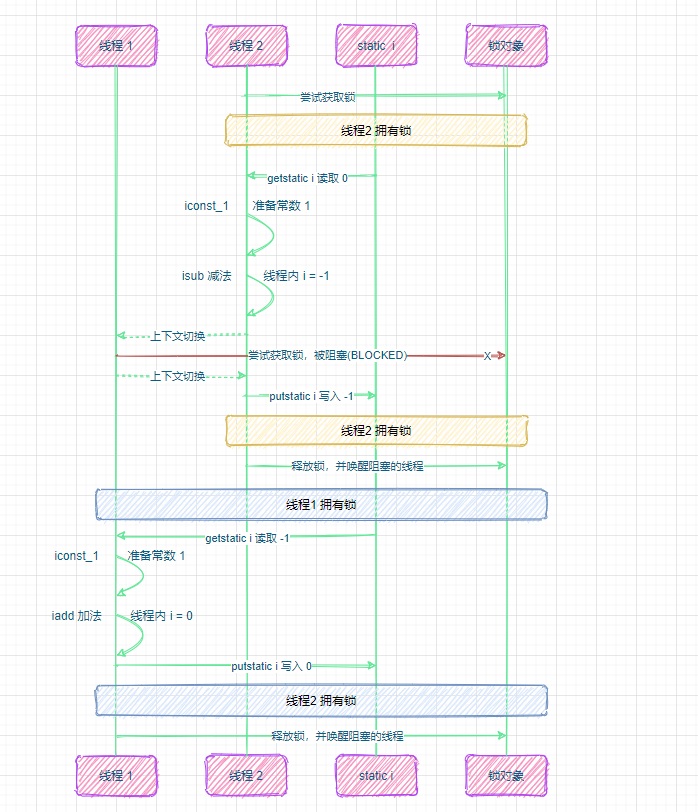
思考
synchronized 实际是用对象锁保证了临界区内代码的原子性,临界区内的代码对外是不可分割的,不会被线程切换所打断。
为了加深理解,请思考下面的问题
- 如果把
synchronized(obj)放在 for 循环的外面,如何理解?-- 原子性 - 如果 t1
synchronized(obj1)而 t2synchronized(obj2)会怎样运作?-- 锁对象 - 如果 t1
synchronized(obj)而 t2 没有加会怎么样?如何理解?-- 锁对象
面向对象改进
把需要保护的共享变量放入一个类
package com.mock.thread;
/**
* @Author zhangch
* @Date 2022/11/2 9:56
*/
public class ThreadSynchronized2 {
static class Room {
int value = 0;
public void increment() {
synchronized (this) {
value++;
}
}
public void decrement() {
synchronized (this) {
value--;
}
}
public int get() {
synchronized (this) {
return value;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadSynchronized2.Room room = new ThreadSynchronized2.Room();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 5000; j++) {
room.increment();
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
room.decrement();
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(room.get());
}
}
作者:天下没有收费的bug
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须在文章页面给出原文链接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号