一、实验目的:
1. 掌握类的设计、定义、实现和测试
2. 理解和掌握const引用、const修饰形参、const成员函数
3. 理解和掌握友元函数
4. 理解和掌握static成员
5. 掌握以多文件结构组织源码文件的方法
6. 了解C++标准库和现代C++编程
7. 体会和理解面向对象编程与结构化编程在编程解决实际问题时思维方式的不同
二、实验内容
实验任务三:
不使用C++标准库,自行设计并实现一个复数类Complex,使其满足如下要求:
数据成员
用来表示复数的实部real和虚部imag,实部、虚部,均为小数形式。
函数成员
构造函数
支持以下方式定义复数对象:
成员函数
get_real() 返回复数实部
get_imag() 返回复数虚部
show() 用于输出复数。要求以 3 + 4i , 3 - 4i 这样的形式输出
add() 用于把一个复数加到自身,比如 c1.add(c2) ,相当于 c1 += c2
友元函数
add() 用于实现两个复数相加,返回复数。比如 c3 = add(c1, c2);
is_equal() 用于判断两个复数是否相等,返回true/false。比如 is_equal(c1, c2)
abs() 用于对复数进行取模运算
分析后的Complex.hpp如下:
#ifndef COMPLEX_HPP
#define COMPLEX_HPP
#include
#include
//complex类的定义
class Complex {
private:
double sb, xb;//实部和虚部
public:
Complex() :sb(0), xb(0) {}//不带参数的构造函数 实部虚部都为0
Complex(double s) {//带一个参数的构造函数
sb = s;
xb = 0;
}
Complex(double s, double x) {//带两个参数的构造函数
sb = s;
xb = x;
}
Complex(const Complex& p) { //复制构造函数
sb = p.sb;
xb = p.xb;
}
//类内函数定义
double getSb() const;
double getXb() const;
void show() const;//c2为const
void add(const Complex& p);//相加
//友元
friend bool ifequal(const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2);
friend Complex add(const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2);
friend double abs(Complex& p);
~Complex() {}
};
double Complex::getSb() const {
return sb;
}
double Complex::getXb() const {
return xb;
}
void Complex::show() const {
using namespace std;
if (xb > 0)
cout << sb << " + " << xb << "i";
else if (xb < 0)
cout << sb << " - " << -xb << "i";
else
cout << sb;
}
void Complex::add(const Complex& p) {
sb = sb + p.getSb();
xb = xb + p.getXb();
}
Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) {
Complex c(c1.sb + c2.sb, c1.xb + c2.xb);
return c;
}
bool ifequal(const Complex& p1, const Complex& p2) {
if (p1.sb == p2.sb && p1.xb == p2.xb) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
double abs(Complex& p) {
return sqrt(p.sb * p.sb + p.xb * p.xb);
}
#endif
#pragma once
由于先写的Complex类,其中有部分函数成员名称与PDF有较小出入,因此task3部分函数成员名也做了相应更改,task3如下:
#include "Complex.h"
#include
int main()
{
using namespace std;
Complex c1(3, -4);
const Complex c2(4.5);
Complex c3(c1);
cout << "c1 = ";
c1.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "c2 = ";
c2.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "c2.xb = " << c2.getXb() << endl;
cout << "c3 = ";
c3.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "abs(c1) = ";
cout << abs(c1) << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c3 : " << ifequal(c1, c3) << endl;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << ifequal(c1, c2) << endl;
Complex c4;
c4 = add(c1, c2);
cout << "c4 = c1 + c2 = ";
c4.show();
cout << endl;
c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 += c2, " << "c1 = ";
c1.show();
cout << endl;
}
其运行结果如下:
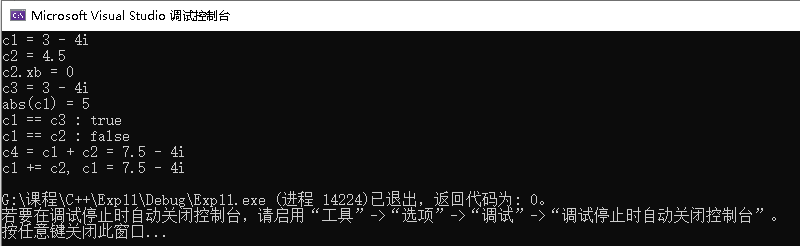
实验任务四:
设计并实现一个用户类User,并在主函数中使用和测试这个类。具体要求如下:
数据成员
每个用户有用户名(name)、密码(passwd)、联系邮箱(email)三个属性。
还有一个类属性,用于记录用户总数n。
函数成员
构造函数
如果定义用户对象时未设置密码和邮箱,密码默认为6个1,联系邮箱默认为空串。
成员函数
set_email()
设置邮箱。提示用户从键盘输入邮箱。
change_passwd()
修改密码。修改密码前,要求先输入旧的密码,验证无误后,才允许修改;如果输入旧
密码时,连续三次输入错误,则提示用户稍后再试,暂时退出修改密码程序。
print_info()
打印用户名、密码、联系邮箱。其中,密码以6个*方式显示。
任务4中要求编写user类,其数据成员有三个,分别是姓名,密码和邮箱,同时还要统计一共能够出现过的用户数量,其函数成员有修改密码,打印信息和设置邮箱,分析过后的user类如下:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class User{
private:
string name;
string passwd;
string email;
static int n;
public:
User(string a):name(a),passwd("111111"),email(""){}//一个参数的构造函数
User(string a, string p , string e ) : name(a), passwd(p), email(e) { n++; }//三个参数的构造函数
User(User &u) : name(u.name), passwd(u.passwd), email(u.email) { n++; }//复制构造函数
void set_email(){//设置邮箱
cout << "Enter email address:";
cin >> email;
while (email.find('@') == -1){
cout << "The @ should be included. Please input again:";
cin >> email;
}
cout << "email is set successfully..." << endl;
}
void change_passwd() {//修改密码
int i = 0;
string now;
while (i != 3)
{
if (i == 0)
cout << "Enter old password:";
else
cout << "Please re_enter again:";
cin >> now;
if (now == passwd)
{
cout << "Enter new password:";
cin >> passwd;
while (passwd.length() < 6)
{
cout << "The length of the password should more than six.";
cout << "Please input again:";
cin >> passwd;
}
cout << "new password is set sucessfully..." << endl;
return;
}
else
{
cout << "password input error.";
i++;
}
}
if (i == 3)
cout << "Please try after a while." << endl;
}
void print_info(){//展示信息
cout << "name: " << name << endl;
cout << "password:******" << endl;
cout << "email :" << email << endl;
}
static void print_n()
{
cout << "there are " << n << " users." << endl;
}
~User() { n--; }//析构函数
};
int User::n = 1;
task4如下:
#include "User.h"
#include
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "testing 1......" << endl;
User user1("Jonny", "92197", "xyz@hotmail.com");
user1.print_info();
cout << endl
<< "testing 2......" << endl
<< endl;
User user2("Leonard");
user2.change_passwd();
user2.set_email();
user2.print_info();
User::print_n();
}
运行结果如图:
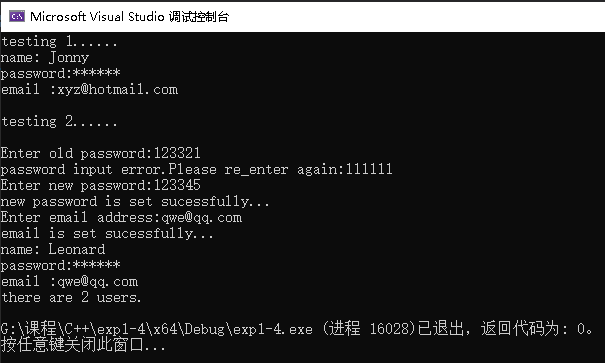
三、实验结论
本次实验主要在理解和掌握const引用、const修饰形参、const成员函数以及 理解和掌握友元函数和static成员。
①const修饰的对象(常引用)只能读不能更新数据(复制构造函数)
②通过const对象只能调用其const函数,不可以调用非const函数成员
③像记录该类有多少个对象这种类属性成员必须用static关键词修饰
④友元是单向的,也不具有传递性
⑤虽然友元函数声明在类内部,但它是普通函数,不是类内函数。类内成员函数可以直接访问类的私有数据,不必再用到友元这个工具。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号