第3章:Vue-cli3 开发单文件组件
1、快速原型开发
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h3>{{msg}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "vue-cli3开发单文件组件"
};
},
created () {
;
},
methods: {
name() {
}
},
computed: {
name() {
return this.data
}
},
components: {
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
h3{
color: red;
}
</style>
执行结果为:
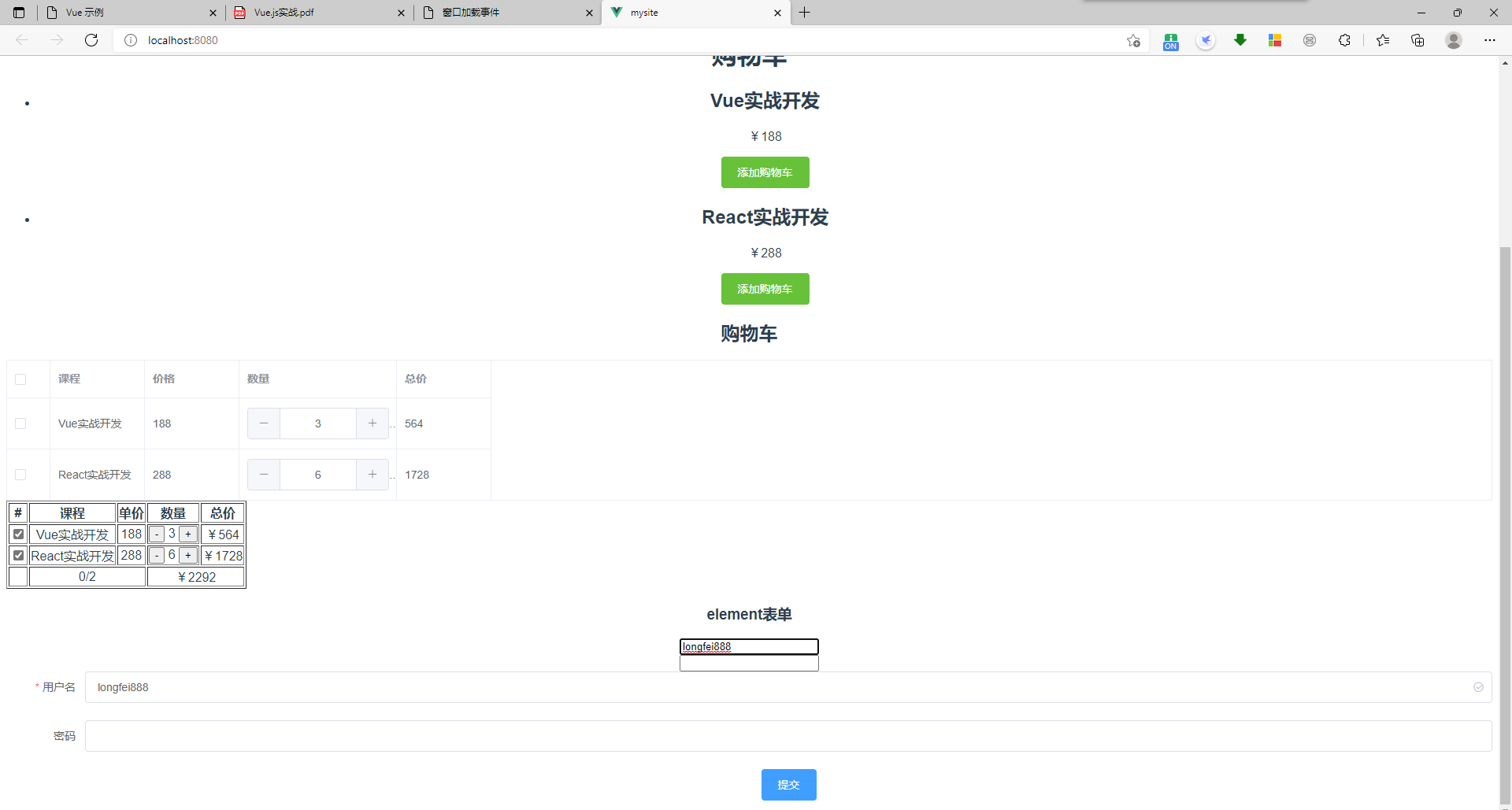
2、购物车项目搭建
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in carList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :cart='carList' :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
export default {
name: 'app',
data(){
return{
carList:[
{id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
{id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
],
title:"购物车"
};
},
components:{
MyCart
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
// Cart.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{title}}</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>总价</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="c in cart" :key="c.id">
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="c.active"> <!-- //active的作用默认都是选中 -->
</td>
<td>{{c.title}}</td>
<td>{{c.price}}</td>
<td>
<button>-</button>
{{c.count}}
<button>+</button>
</td>
<td>¥{{c.price*c.count}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'cart',
props:['title','cart']//父组件通过props向子组件传递数据
} //在创建JavaScript模块时,export 语句用于从模块中导出实时绑定的函数、对象或原始值,以便其他程序可以通过 import 语句使用它们。
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
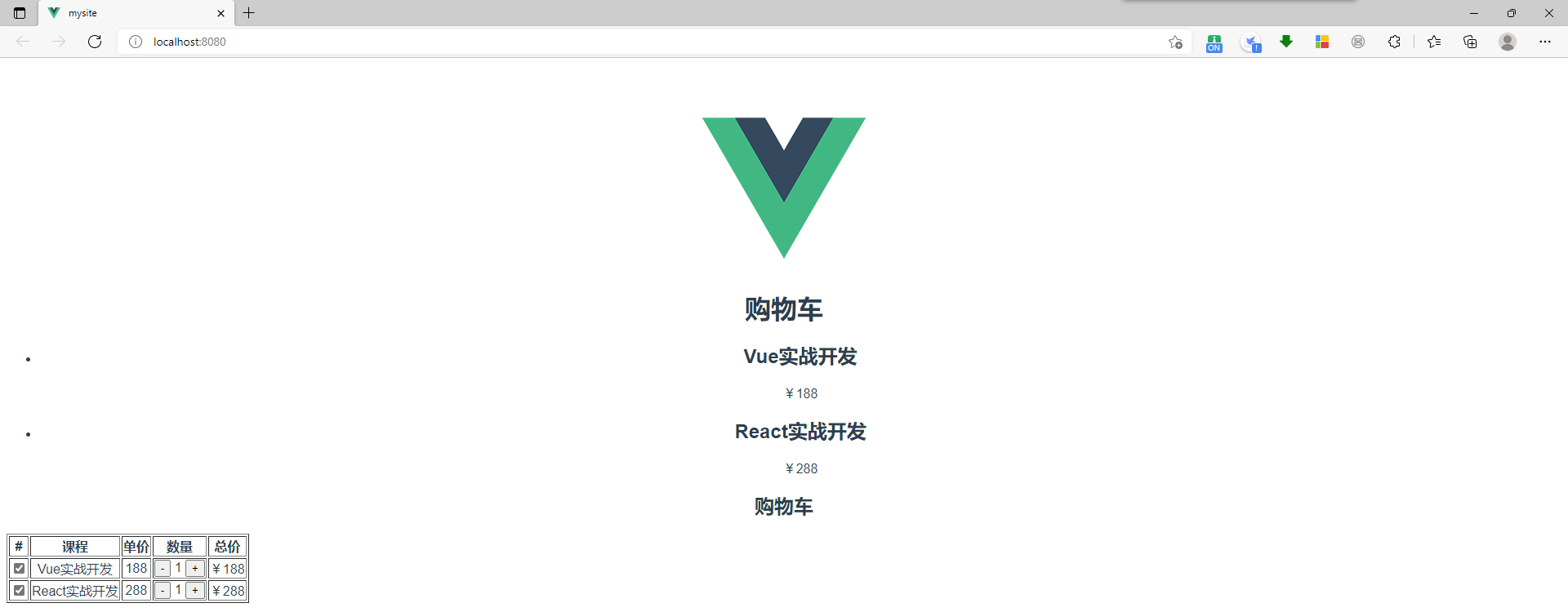
运行结果:
3、购物车项目操作
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in carList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :cart='carList' :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
export default {
name: 'app',
data(){
return{
carList:[
{id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
{id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
],
title:"购物车"
};
},
components:{
MyCart
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
// Cart.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{title}}</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>总价</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(c,index) in cart" :key="c.id"> <!-- //index是当前的索引 -->
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="c.active"> <!-- //active的作用默认都是选中 -->
</td>
<td>{{c.title}}</td>
<td>{{c.price}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="substract(index)">-</button> <!-- //substract是减去的意思 -->
{{c.count}}
<button @click="add(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>¥{{c.price*c.count}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td colspan="2">{{activeCount}}/{{count}}</td> <!-- //colspan意思是横向合并两格 -->
<td colspan="2">¥{{total}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'cart',
props:['title','cart'], //父组件通过props向子组件传递数据
methods:{
remove(i){
if(window.confirm('确定是否要删除?')){ //弹窗让用户确认是否真的要删除数据。
this.cart.splice(i,1); //从这条数据开始,删除一条数据。
}
},
substract(i){
let count = this.cart[i].count;
count > 1 ? (this.cart[i].count -= 1) : this.remove(i);
},
add(i){
this.cart[i].count++;
}
},
computed: { //computed是计算属性。
count() {
return this.cart.length;
},
activeCount(){
return this.cart.filter(v=>v.active).length; //filter是过滤的意思,过滤出来每个对象
},
total(){
// let sum = 0;
// this.cart.forEach(c => { //forEach遍历的意思
// if(c.active){
// sum += c.price*c.count;
// }
// });
// return sum;
return this.cart.reduce((sum,c)=>{ //reduce是一个回调函数,有两个参数,第一个参数是回调函数,第二个是起始值。
if (c.active){
sum += c.price * c.count;
}
return sum;
},0);
}
},
} //在创建JavaScript模块时,export 语句用于从模块中导出实时绑定的函数、对象或原始值,以便其他程序可以通过 import 语句使用它们。
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
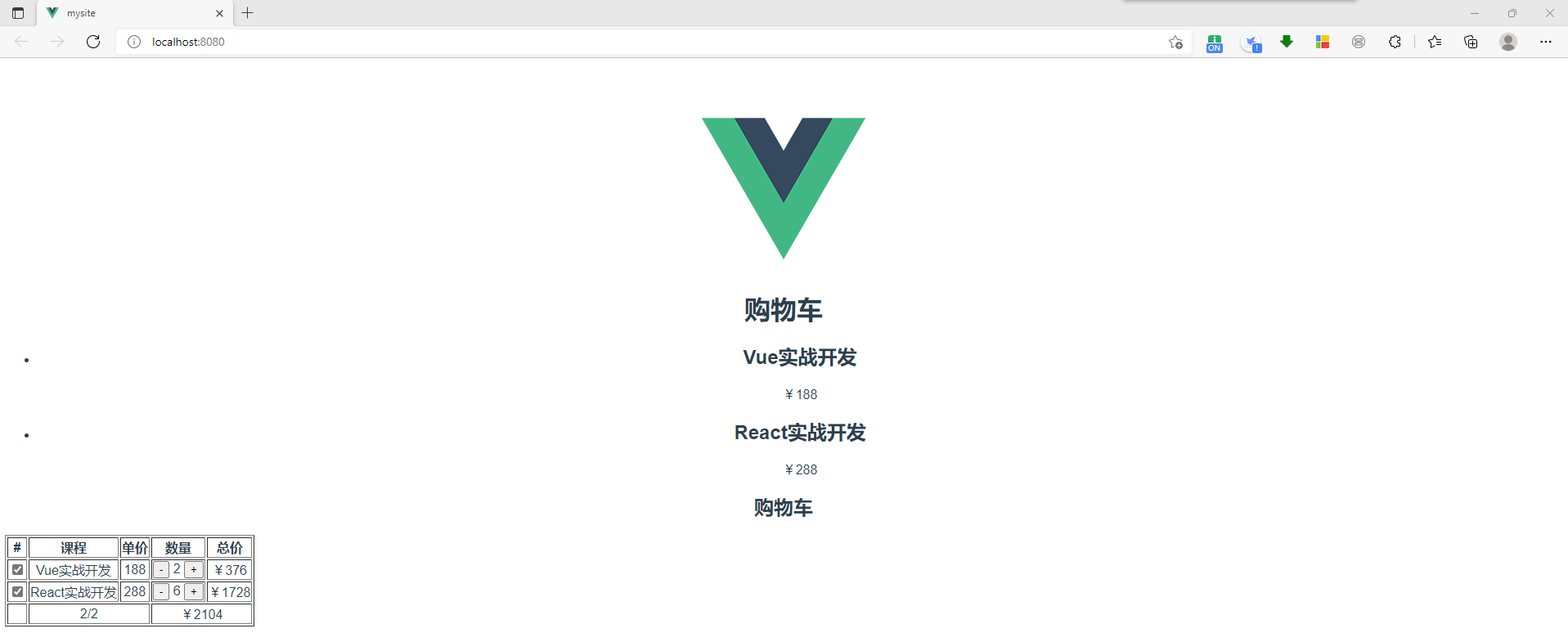
结果:
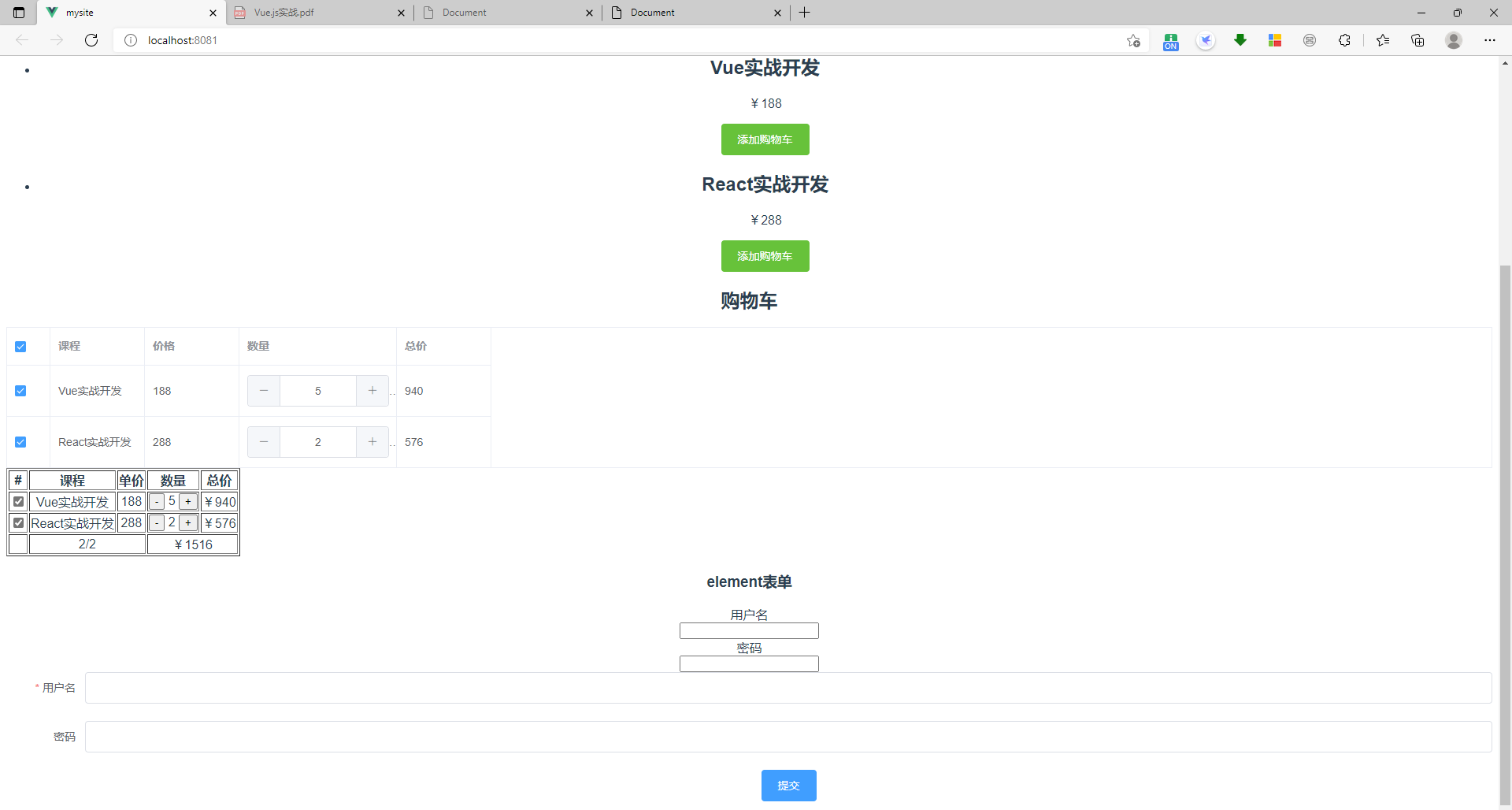
4、Mock模拟数据 模拟后端数据
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in cartList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :cart='cartList' :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
export default {
name: 'app',
data(){
return{
cartList:[],
// carList:[
// {id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
// {id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
// ],
title:"购物车"
};
},
async created (){
// this.$http.get('/api/cartList')
// .then(res=>{
// this.cartList = res.data.result;
// }).catch(err=>{
// console.log(err);
// })
try {
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/cartList')
this.cartList = res.data.result;
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
components:{
MyCart
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
// Cart.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{title}}</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>总价</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(c,index) in cart" :key="c.id"> <!-- //index是当前的索引 -->
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="c.active"> <!-- //active的作用默认都是选中 -->
</td>
<td>{{c.title}}</td>
<td>{{c.price}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="substract(index)">-</button> <!-- //substract是减去的意思 -->
{{c.count}}
<button @click="add(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>¥{{c.price*c.count}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td colspan="2">{{activeCount}}/{{count}}</td> <!-- //colspan意思是横向合并两格 -->
<td colspan="2">¥{{total}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'cart',
props:['title','cart'], //父组件通过props向子组件传递数据
methods:{
remove(i){
if(window.confirm('确定是否要删除?')){ //弹窗让用户确认是否真的要删除数据。
this.cart.splice(i,1); //从这条数据开始,删除一条数据。
}
},
substract(i){
let count = this.cart[i].count;
count > 1 ? (this.cart[i].count -= 1) : this.remove(i);
},
add(i){
this.cart[i].count++;
}
},
computed: { //computed是计算属性。
count() {
return this.cart.length;
},
activeCount(){
return this.cart.filter(v=>v.active).length; //filter是过滤的意思,过滤出来每个对象
},
total(){
// let sum = 0;
// this.cart.forEach(c => { //forEach遍历的意思
// if(c.active){
// sum += c.price*c.count;
// }
// });
// return sum;
return this.cart.reduce((sum,c)=>{ //reduce是一个回调函数,有两个参数,第一个参数是回调函数,第二个是起始值。
if (c.active){
sum += c.price * c.count;
}
return sum;
},0);
}
},
} //在创建JavaScript模块时,export 语句用于从模块中导出实时绑定的函数、对象或原始值,以便其他程序可以通过 import 语句使用它们。
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
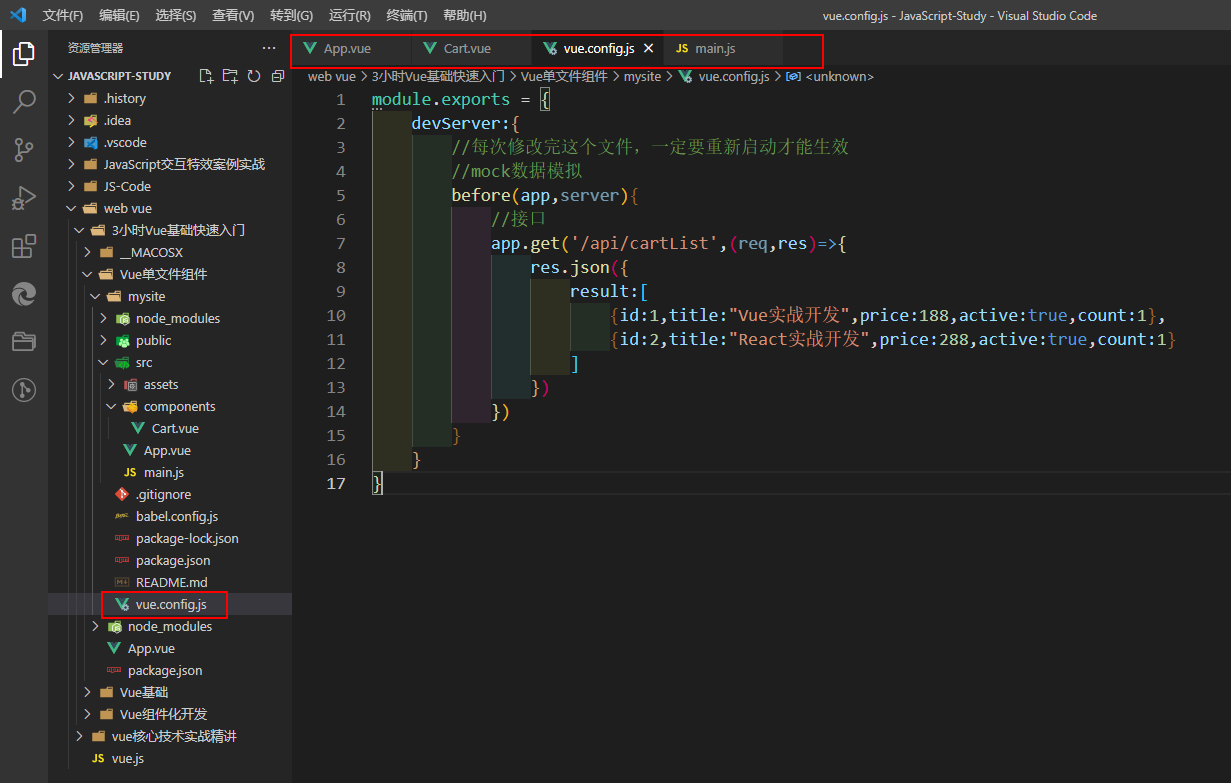
//vue.config.js里面的内容
module.exports = {
devServer:{
//每次修改完这个文件,一定要重新启动才能生效
//mock数据模拟
before(app,server){
//接口
app.get('/api/cartList',(req,res)=>{
res.json({
result:[
{id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1},
{id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
]
})
})
}
}
}
// main.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import axios from 'axios'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.prototype.$http = axios;
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
结果:
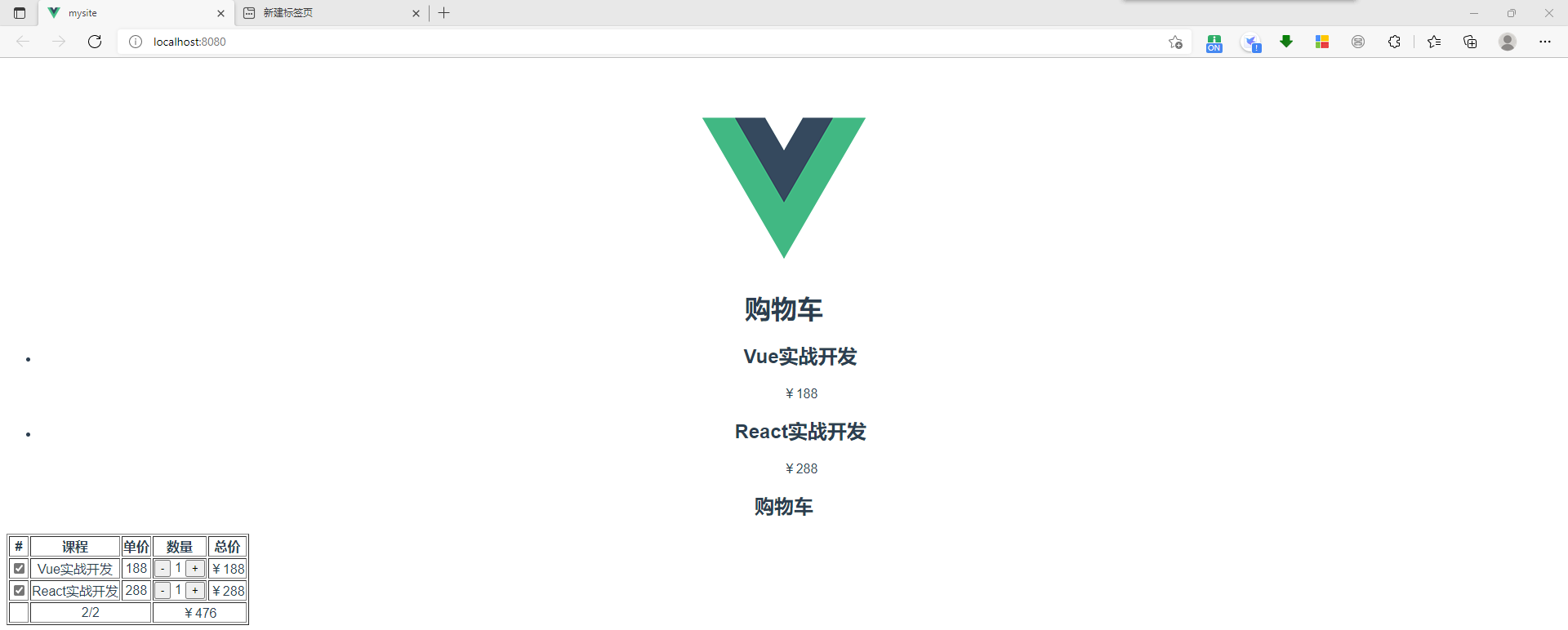
5、如何做数据持久化 刷新网页,购物车里面的数据还在
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<!-- //展示购物车的列表 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in cartList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
<button @click="addCart(index)">添加购物车</button>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
export default {
name: 'app',
methods:{
addCart(i){
const good = this.cartList[i];
this.$bus.$emit('addCart',good); //分发事件
}
},
data(){ //这里的data存储着本地数据
return{
cartList:[],
// carList:[
// {id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
// {id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
// ],
title:"购物车"
};
},
async created (){
// this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //这里是请求数据
// .then(res=>{
// this.cartList = res.data.result;
// }).catch(err=>{
// console.log(err);
// })
try { //try是用来处理接口错误的,成功的时候走try里面的内容,失败的时候走error。
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //await等待结果
this.cartList = res.data.result; //这里接收到的数据传递到my-cart这个文件中。
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
components:{
MyCart
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
// Cart.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{title}}</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>总价</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(c,index) in cart" :key="c.id"> <!-- //index是当前的索引 -->
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="c.active">
<!-- //active的作用默认都是选中。vue使用v-model实现这些标签数据的双向绑定,它会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素。-->
</td>
<td>{{c.title}}</td>
<td>{{c.price}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="substract(index)">-</button> <!-- //substract是减去的意思 -->
{{c.count}}
<button @click="add(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>¥{{c.price*c.count}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td colspan="2">{{activeCount}}/{{count}}</td> <!-- //colspan意思是横向合并,值是合并的格数,这里为两格 -->
<td colspan="2">¥{{total}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'cart',
props:['title'], //父组件通过props向子组件传递数据
data() {
return {
cart: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('cart')) || []
};
},
watch:{ //监听数组cart
cart:{
handler(n){ //handler(n,o) n=new o=old 意思是新值和旧值
this.setLocalData(n);
},
deep:true //值true,是深度监听
}
},
created () {
this.$bus.$on('addCart',good=>{ //接收事件,传递的数据good
const ret = this.cart.find(v=>v.id===good.id);
if(!ret){ //这里是如果没有数据!ret是没有数据的意思
//购物车没有数据
this.cart.push(good); //给购物车添加数据
} else{
ret.count += 1; //购物车里有数据,直接数量加1
}
});
},
methods:{
setLocalData(n){
//计算总课数
localStorage.setItem('cart',JSON.stringify(n)); // 传进来的数组转换成字符串存储起来
},
remove(i){
if(window.confirm('确定是否要删除?')){ //弹窗让用户确认是否真的要删除数据。
this.cart.splice(i,1); //从这条数据开始,删除一条数据。
}
},
substract(i){
let count = this.cart[i].count;
count > 1 ? (this.cart[i].count -= 1) : this.remove(i);
},
add(i){
this.cart[i].count++;
}
},
computed: { //computed是计算属性。
count() {
return this.cart.length;
},
activeCount(){
return this.cart.filter(v=>v.active).length; //filter是过滤的意思,过滤出来每个对象
},
total(){
// let sum = 0;
// this.cart.forEach(c => { //forEach遍历的意思
// if(c.active){
// sum += c.price*c.count;
// }
// });
// return sum;
return this.cart.reduce((sum,c)=>{ //reduce是一个回调函数,有两个参数,第一个参数是回调函数,第二个是起始值。
if (c.active){
sum += c.price * c.count;
}
return sum;
},0);
}
},
} //在创建JavaScript模块时,export 语句用于从模块中导出实时绑定的函数、对象或原始值,以便其他程序可以通过 import 语句使用它们。
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
// main.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import axios from 'axios' //axios是网上下载下来的
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止启动生产消息,Vue有两个模式,生产模式和开发模式。
//开发模式:npm run dev是前端自己开发用的 ,生产模式:npm run build 打包之后给后端放在服务端上用的
Vue.prototype.$http = axios; //挂载axios。
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue(); //添加事件总线,将
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
结果:刷新网页后,购物车里面的数据还在。
6、Vue中使用第三方组件(element-ui)
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<!-- //展示购物车的列表 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in cartList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
<el-button @click="addCart(index)" type='success'>添加购物车</el-button>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
export default {
name: 'app',
methods:{
addCart(i){
const good = this.cartList[i];
this.$bus.$emit('addCart',good); //分发事件
}
},
data(){ //这里的data存储着本地数据
return{
cartList:[],
// carList:[
// {id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
// {id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
// ],
title:"购物车"
};
},
async created (){
// this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //这里是请求数据
// .then(res=>{
// this.cartList = res.data.result;
// }).catch(err=>{
// console.log(err);
// })
try { //try是用来处理接口错误的,成功的时候走try里面的内容,失败的时候走error。
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //await等待结果
this.cartList = res.data.result; //这里接收到的数据传递到my-cart这个文件中。
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
components:{
MyCart
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
// Cart.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{title}}</h2>
<el-table
ref="multipleTable"
:data="cart"
border
tooltip-effect="dark"
style="width: 100%"
@selection-change="handleSelectionChange">
<el-table-column type="selection" width="55"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="title" label="课程" width="120"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="price" label="价格" width="120"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="数量" width="200">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<el-input-number v-model="scope.row.count" :min="1" :max="100" label="描述文字"></el-input-number>
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="总价" width="120">
<template slot-scope="scope">
{{scope.row.count * scope.row.price}}
</template>
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>总价</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(c,index) in cart" :key="c.id"> <!-- //index是当前的索引 -->
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="c.active">
<!-- //active的作用默认都是选中。vue使用v-model实现这些标签数据的双向绑定,它会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素。-->
</td>
<td>{{c.title}}</td>
<td>{{c.price}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="substract(index)">-</button> <!-- //substract是减去的意思 -->
{{c.count}}
<button @click="add(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>¥{{c.price*c.count}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td colspan="2">{{activeCount}}/{{count}}</td> <!-- //colspan意思是横向合并,值是合并的格数,这里为两格 -->
<td colspan="2">¥{{total}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'cart',
props:['title'], //父组件通过props向子组件传递数据
data() {
return {
cart: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('cart')) || [], //刷新网页的时候,获取对应的数据,格式化一下,如果没有值,返回空值
multipleSelection:[]
};
},
watch:{ //监听数组cart,cart是数组,需要深度监听
cart:{
handler(n){ //handler(n,o) n=new o=old 意思是新值和旧值
this.setLocalData(n);
},
deep:true //值true,是深度监听
}
},
created () {
this.$bus.$on('addCart',good=>{ //接收事件,传递的数据good
const ret = this.cart.find(v=>v.id===good.id);
if(!ret){ //这里是如果没有数据!ret是没有数据的意思
//购物车没有数据
this.cart.push(good); //给购物车添加数据
} else{
ret.count += 1; //购物车里有数据,直接数量加1
}
});
},
methods:{
toggleSelection(rows) {
if (rows) {
rows.forEach(row => {
this.$refs.multipleTable.toggleRowSelection(row);
});
} else {
this.$refs.multipleTable.clearSelection();
}
},
handleSelectionChange(val) {
this.multipleSelection = val;
console.log(this.multipleSelection);
},
setLocalData(n){
//计算总课数
localStorage.setItem('cart',JSON.stringify(n)); // 传进来的数组转换成字符串存储起来
},
remove(i){
if(window.confirm('确定是否要删除?')){ //弹窗让用户确认是否真的要删除数据。
this.cart.splice(i,1); //从这条数据开始,删除一条数据。
}
},
substract(i){
let count = this.cart[i].count;
count > 1 ? (this.cart[i].count -= 1) : this.remove(i);
},
add(i){
this.cart[i].count++;
}
},
computed: { //computed是计算属性。
count() {
return this.cart.length;
},
activeCount(){
return this.multipleSelection.filter(v=>v.active).length; //filter是过滤的意思,过滤出来每个对象
},
total(){
// let sum = 0;
// this.cart.forEach(c => { //forEach遍历的意思
// if(c.active){
// sum += c.price*c.count;
// }
// });
// return sum;
return this.cart.reduce((sum,c)=>{ //reduce是一个回调函数,有两个参数,第一个参数是回调函数,第二个是起始值。
if (c.active){
sum += c.price * c.count;
}
return sum;
},0);
}
},
} //在创建JavaScript模块时,export 语句用于从模块中导出实时绑定的函数、对象或原始值,以便其他程序可以通过 import 语句使用它们。
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
// main.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import axios from 'axios' //axios是网上下载下来的
import './plugins/element.js'
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止启动生产消息,Vue有两个模式,生产模式和开发模式。
//开发模式:npm run dev是前端自己开发用的 ,生产模式:npm run build 打包之后给后端放在服务端上用的
Vue.prototype.$http = axios; //挂载axios。
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue(); //添加事件总线,将
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
// element.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import { Button,Table,TableColumn,InputNumber} from 'element-ui'
Vue.use(Button)
Vue.use(Table)
Vue.use(TableColumn)
Vue.use(InputNumber)
//vue.config.js里面的内容
module.exports = {
devServer:{
//每次修改完这个文件,一定要重新启动才能生效
//mock数据模拟 模拟后端数据
before(app){
//接口
app.get('/api/cartList',(req,res)=>{ //req是请求,res是响应
res.json({
result:[
{id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1},
{id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
]
})
})
}
}
}
结果:
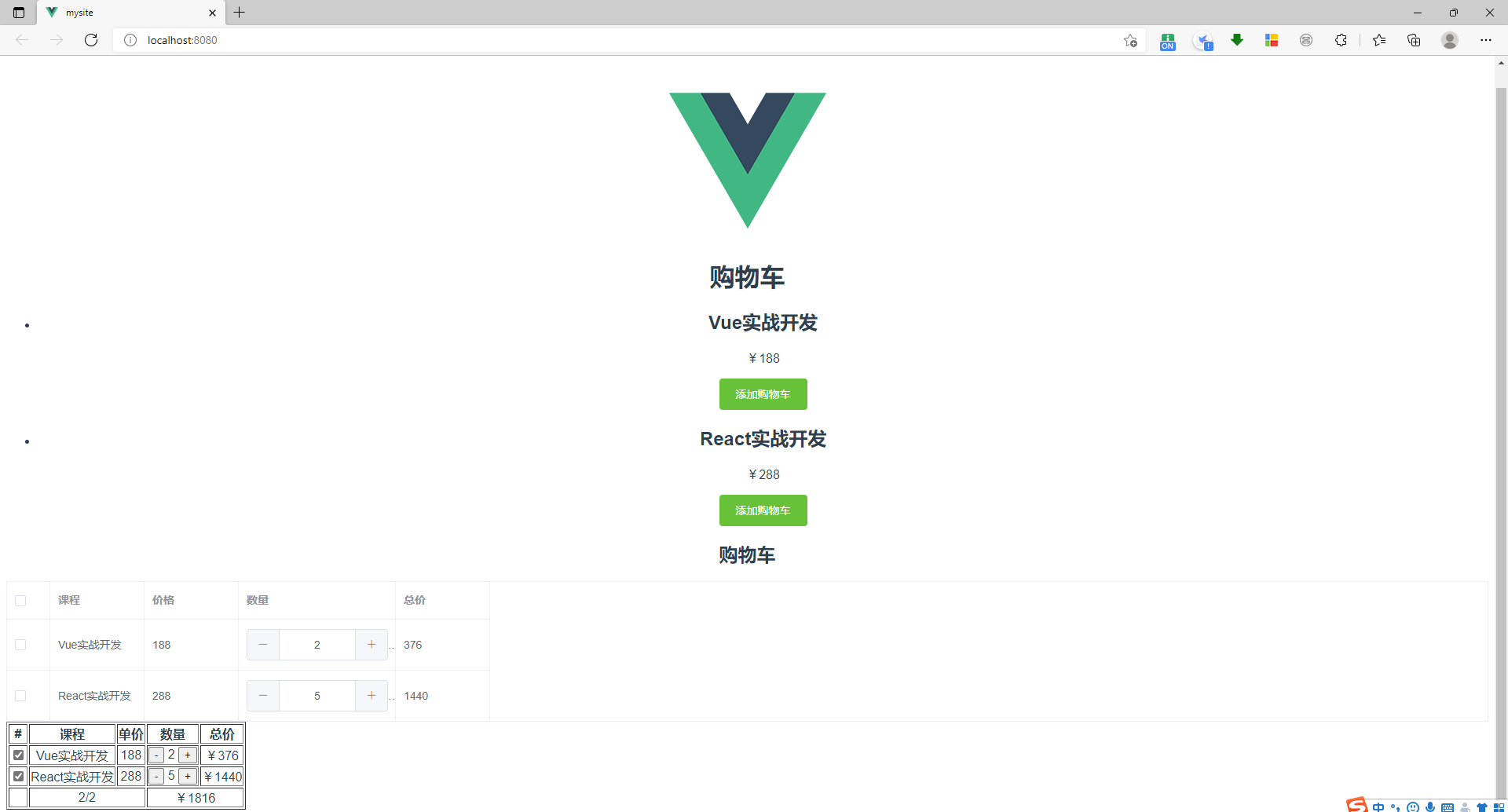
7、Element 表单组件分析
// FormItem.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h3>element表单</h3>
<el-form
:model="ruleForm"
status-icon
:rules="rules"
ref="ruleForm"
label-width="100px"
class="demo-ruleForm"
>
<el-form-item label="用户名" prop="name">
<el-input type="text" v-model="ruleForm.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="pwd">
<el-input type="password" v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('ruleForm')">提交</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//Form 定义数据模型 负责定义校验规则
//FormItem 绑定label prop校验和显示错误信息
//Input 负责双向数据绑定 通知FormItem做检验
//provide inject 内部共享数据
export default{
name:'FormElement',
data(){
return{
ruleForm:{
name:'',
pwd:''
},
rules:{
name:[
{required:true,message:'请输入名称'},
{min:6,max:10,message:'请输入6~10位用户名'}
],
pwd:[{require:true,message:'请输入密码'}],
}
}
},
methods:{
submitForm(name){
this.$refs[name].validate(valid=>{
console.log(valid);
if(valid){
alert('验证成功,可以提交')
}else{
alert('error 提交');
return false;
}
});
}
}
}
</script>
// Cart.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{title}}</h2>
<el-table
ref="multipleTable"
:data="cart"
border
tooltip-effect="dark"
style="width: 100%"
@selection-change="handleSelectionChange">
<el-table-column type="selection" width="55" prop='active'></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="title" label="课程" width="120"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="price" label="价格" width="120"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="数量" width="200">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<el-input-number v-model="scope.row.count" :min="1" :max="100" label="描述文字"></el-input-number>
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="总价" width="120">
<template slot-scope="scope">{{scope.row.count * scope.row.price}}</template>
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>总价</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(c,index) in cart" :key="c.id"> <!-- //index是当前的索引 -->
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="c.active">
<!-- //active的作用默认都是选中。vue使用v-model实现这些标签数据的双向绑定,它会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素。-->
</td>
<td>{{c.title}}</td>
<td>{{c.price}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="substract(index)">-</button> <!-- //substract是减去的意思 -->
{{c.count}}
<button @click="add(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>¥{{c.price*c.count}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td colspan="2">{{activeCount}}/{{count}}</td> <!-- //colspan意思是横向合并,值是合并的格数,这里为两格 -->
<td colspan="2">¥{{total}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'cart',
props:['title'], //父组件通过props向子组件传递数据
data() {
return {
cart: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('cart')) || [], //刷新网页的时候,获取对应的数据,格式化一下,如果没有值,返回空值
multipleSelection:[]
};
},
watch:{ //监听数组cart,cart是数组,需要深度监听
cart:{
handler(n){ //handler(n,o) n=new o=old 意思是新值和旧值
this.setLocalData(n);
},
deep:true //值true,是深度监听
}
},
created () {
this.$bus.$on('addCart',good=>{ //接收事件,传递的数据good
const ret = this.cart.find(v=>v.id===good.id);
if(!ret){ //这里是如果没有数据!ret是没有数据的意思
//购物车没有数据
this.cart.push(good); //给购物车添加数据
} else{
ret.count += 1; //购物车里有数据,直接数量加1
}
});
},
methods:{
toggleSelection(rows) {
if (rows) {
rows.forEach(row => {
this.$refs.multipleTable.toggleRowSelection(row);
});
} else {
this.$refs.multipleTable.clearSelection();
}
},
handleSelectionChange(val) {
this.multipleSelection = val;
console.log(this.multipleSelection);
},
setLocalData(n){
//计算总课数
localStorage.setItem('cart',JSON.stringify(n)); // 传进来的数组转换成字符串存储起来
},
remove(i){
if(window.confirm('确定是否要删除?')){ //弹窗让用户确认是否真的要删除数据。
this.cart.splice(i,1); //从这条数据开始,删除一条数据。
}
},
substract(i){
let count = this.cart[i].count;
count > 1 ? (this.cart[i].count -= 1) : this.remove(i);
},
add(i){
this.cart[i].count++;
}
},
computed: { //computed是计算属性。
count() {
return this.cart.length;
},
activeCount(){
return this.multipleSelection.filter(v=>v.active).length; //filter是过滤的意思,过滤出来每个对象
},
total(){
// let sum = 0;
// this.cart.forEach(c => { //forEach遍历的意思
// if(c.active){
// sum += c.price*c.count;
// }
// });
// return sum;
return this.cart.reduce((sum,c)=>{ //reduce是一个回调函数,有两个参数,第一个参数是回调函数,第二个是起始值。
if (c.active){
sum += c.price * c.count;
}
return sum;
},0);
}
},
} //在创建JavaScript模块时,export 语句用于从模块中导出实时绑定的函数、对象或原始值,以便其他程序可以通过 import 语句使用它们。
</script>
<style scoped> /*//在vue组件中,在style标签上添加scoped属性,以表示它的样式作用于当下的模块,很好的实现了样式私有化的目的*/
</style>
// element.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import { Button,Table,TableColumn,InputNumber,Form,FormItem,Input} from 'element-ui' //分批安装element插件。
Vue.use(Button)
Vue.use(Table)
Vue.use(TableColumn)
Vue.use(InputNumber)
Vue.use(Form)
Vue.use(FormItem)
Vue.use(Input)
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<!-- //展示购物车的列表 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in cartList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
<el-button @click="addCart(index)" type='success'>添加购物车</el-button>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
<FormItem></FormItem>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
//@相当于src目录
import FormItem from '@/components/FormItem.vue';
import Formltem from './components/Formltem.vue';
export default {
name: 'app',
methods:{
addCart(i){
const good = this.cartList[i];
this.$bus.$emit('addCart',good); //分发事件
}
},
data(){ //这里的data存储着本地数据
return{
cartList:[],
// carList:[
// {id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
// {id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
// ],
title:"购物车"
};
},
async created (){
// this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //这里是请求数据
// .then(res=>{
// this.cartList = res.data.result;
// }).catch(err=>{
// console.log(err);
// })
try { //try是用来处理接口错误的,成功的时候走try里面的内容,失败的时候走error。
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //await等待结果
this.cartList = res.data.result; //这里接收到的数据传递到my-cart这个文件中。
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
components:{
MyCart, //MyCart是一个局部模板,因为在<div id:'app'></div>下面挂载着,只能在这下面使用。
FormItem
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
//vue.config.js里面的内容
module.exports = {
devServer:{
//每次修改完这个文件,一定要重新启动才能生效
//mock数据模拟 模拟后端数据
before(app){
//接口
app.get('/api/cartList',(req,res)=>{ //req是请求,res是响应
res.json({
result:[
{id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1},
{id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
]
})
})
}
}
}
// main.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import axios from 'axios' //axios是网上下载下来的
import './plugins/element.js' //安装的插件element
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止启动生产消息,Vue有两个模式,生产模式和开发模式。
//开发模式:npm run dev是前端自己开发用的 ,生产模式:npm run build 打包之后给后端放在服务端上用的
Vue.prototype.$http = axios; //挂载axios。
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue(); //添加事件总线
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
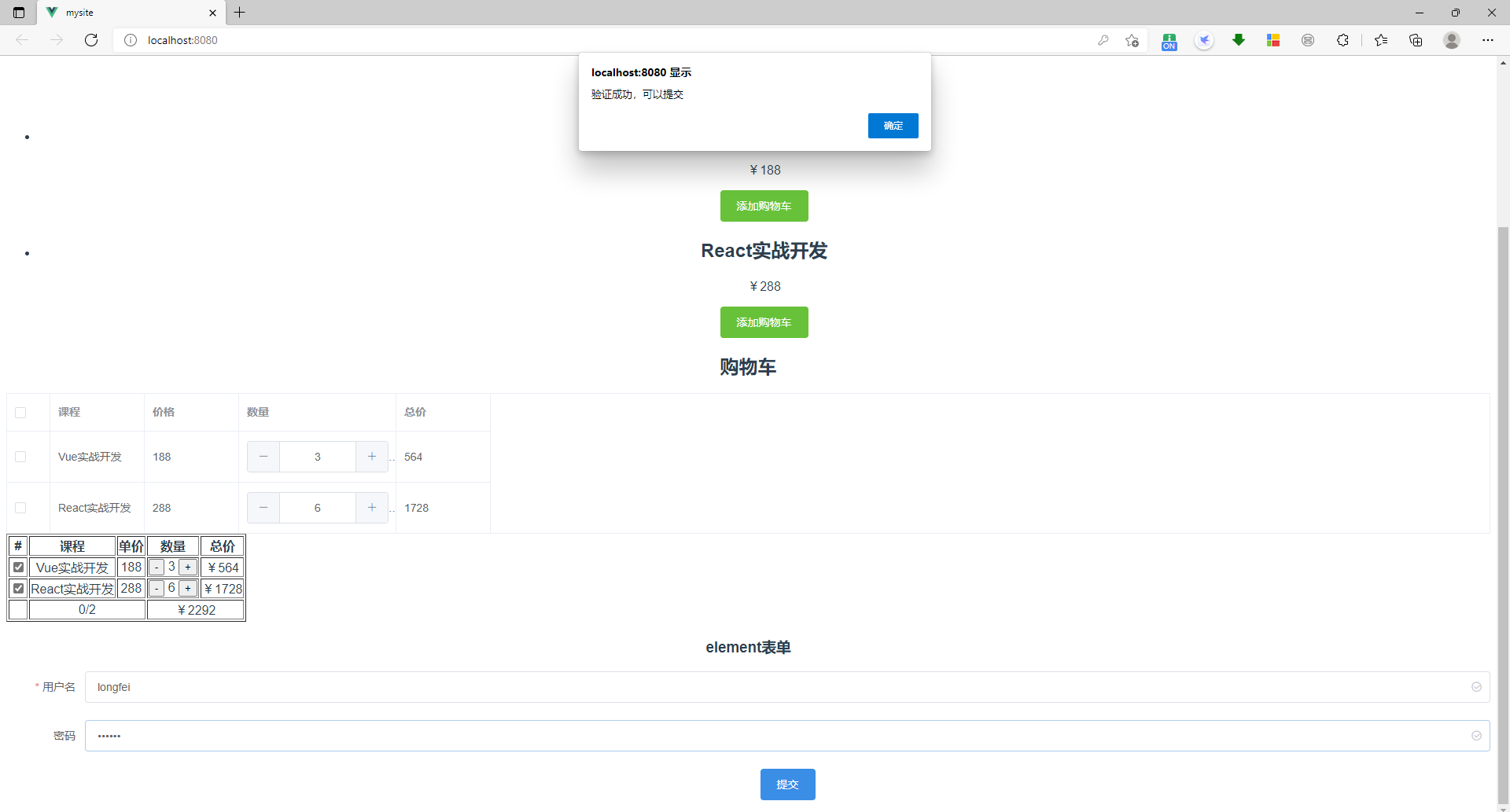
分析问题:

8、表单组件设计-Input实现双向数据绑定
// Input.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<!-- v-model是 v-bind:value v-on:input 的合并 -->
<input type="type" :value="inputVal" @input="handleInput">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
type: {
type: String,
default: 'text'
},
value:{
type:String,
default:''
}
},
data() {
return {
inputVal: this.value
}
},
methods: {
handleInput(e) {
// 赋值
// 实现双向数据绑定
this.inputVal = e.target.value
this.$emit('input', this.inputVal);
// 通知父组件值的更新
this.$parent.$emit('validate',this.inputVal)
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
// FormElement.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h3>element表单</h3>
<!-- 自己的组件 -->
<m-input v-model="ruleForm.name"></m-input>
<m-input type='password' v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></m-input>
<!-- <MInput v-model="ruleForm.name"></MInput> -->
<!-- <MInput type='password' v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></MInput> -->
<el-form
:model="ruleForm"
status-icon
:rules="rules"
ref="ruleForm"
label-width="100px"
class="demo-ruleForm"
>
<el-form-item label="用户名" prop="name">
<el-input type="text" v-model="ruleForm.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="pwd">
<el-input type="password" v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('ruleForm')">提交</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//Form 定义数据模型 负责定义校验规则
//FormItem 绑定label prop校验和显示错误信息
//Input 负责双向数据绑定 通知FormItem做检验
//provide inject 内部共享数据
import MInput from './Input';
export default{
name:'FormElement',
components: {
MInput,
},
data(){
return{
ruleForm:{ //ref:'ruleForm'绑定了用户名和密码。绑定from组件,获取组件对象。
name:'',
pwd:''
},
rules:{ //绑定了规则
name:[
{required:true,message:'请输入名称'}, //必须的,值为true。
{min:6,max:10,message:'请输入6~10位用户名'}
],
pwd:[{require:true,message:'请输入密码'}],
}
}
},
methods:{
submitForm(name){
this.$refs[name].validate(valid=>{
console.log(valid);
if(valid){
alert('验证成功,可以提交')
}else{
alert('error 提交');
return false;
}
});
}
}
}
</script>
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<!-- //展示购物车的列表 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in cartList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
<el-button @click="addCart(index)" type='success'>添加购物车</el-button>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
<FormElement></FormElement>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
//@相当于src目录
import FormElement from '@/components/FormElement.vue';
export default {
name: 'app',
methods:{
addCart(i){
const good = this.cartList[i];
this.$bus.$emit('addCart',good); //分发事件
}
},
data(){ //这里的data存储着本地数据
return{
cartList:[],
// carList:[
// {id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
// {id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
// ],
title:"购物车"
};
},
async created (){
// this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //这里是请求数据
// .then(res=>{
// this.cartList = res.data.result;
// }).catch(err=>{
// console.log(err);
// })
try { //try是用来处理接口错误的,成功的时候走try里面的内容,失败的时候走error。
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //await等待结果
this.cartList = res.data.result; //这里接收到的数据传递到my-cart这个文件中。
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
components:{
MyCart, //MyCart是一个局部模板,因为在<div id:'app'></div>下面挂载着,只能在这下面使用。
FormElement
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
// Cart.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{title}}</h2>
<el-table
ref="multipleTable"
:data="cart"
border
tooltip-effect="dark"
style="width: 100%"
@selection-change="handleSelectionChange">
<el-table-column type="selection" width="55" prop='active'></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="title" label="课程" width="120"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="price" label="价格" width="120"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="数量" width="200">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<el-input-number v-model="scope.row.count" :min="1" :max="100" label="描述文字"></el-input-number>
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="总价" width="120">
<template slot-scope="scope">{{scope.row.count * scope.row.price}}</template>
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>课程</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>总价</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(c,index) in cart" :key="c.id"> <!-- //index是当前的索引 -->
<td>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="c.active">
<!-- //active的作用默认都是选中。vue使用v-model实现这些标签数据的双向绑定,它会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素。-->
</td>
<td>{{c.title}}</td>
<td>{{c.price}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="substract(index)">-</button> <!-- //substract是减去的意思 -->
{{c.count}}
<button @click="add(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>¥{{c.price*c.count}}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td colspan="2">{{activeCount}}/{{count}}</td> <!-- //colspan意思是横向合并,值是合并的格数,这里为两格 -->
<td colspan="2">¥{{total}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'cart',
props:['title'], //父组件通过props向子组件传递数据
data() {
return {
cart: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('cart')) || [], //刷新网页的时候,获取对应的数据,格式化一下,如果没有值,返回空值
multipleSelection:[]
};
},
watch:{ //监听数组cart,cart是数组,需要深度监听
cart:{
handler(n){ //handler(n,o) n=new o=old 意思是新值和旧值
this.setLocalData(n);
},
deep:true //值true,是深度监听
}
},
created () {
this.$bus.$on('addCart',good=>{ //接收事件,传递的数据good
const ret = this.cart.find(v=>v.id===good.id);
if(!ret){ //这里是如果没有数据!ret是没有数据的意思
//购物车没有数据
this.cart.push(good); //给购物车添加数据
} else{
ret.count += 1; //购物车里有数据,直接数量加1
}
});
},
methods:{
toggleSelection(rows) {
if (rows) {
rows.forEach(row => {
this.$refs.multipleTable.toggleRowSelection(row);
});
} else {
this.$refs.multipleTable.clearSelection();
}
},
handleSelectionChange(val) {
this.multipleSelection = val;
console.log(this.multipleSelection);
},
setLocalData(n){
//计算总课数
localStorage.setItem('cart',JSON.stringify(n)); // 传进来的数组转换成字符串存储起来
},
remove(i){
if(window.confirm('确定是否要删除?')){ //弹窗让用户确认是否真的要删除数据。
this.cart.splice(i,1); //从这条数据开始,删除一条数据。
}
},
substract(i){
let count = this.cart[i].count;
count > 1 ? (this.cart[i].count -= 1) : this.remove(i);
},
add(i){
this.cart[i].count++;
}
},
computed: { //computed是计算属性。
count() {
return this.cart.length;
},
activeCount(){
return this.multipleSelection.filter(v=>v.active).length; //filter是过滤的意思,过滤出来每个对象
},
total(){
// let sum = 0;
// this.cart.forEach(c => { //forEach遍历的意思
// if(c.active){
// sum += c.price*c.count;
// }
// });
// return sum;
return this.cart.reduce((sum,c)=>{ //reduce是一个回调函数,有两个参数,第一个参数是回调函数,第二个是起始值。
if (c.active){
sum += c.price * c.count;
}
return sum;
},0);
}
},
} //在创建JavaScript模块时,export 语句用于从模块中导出实时绑定的函数、对象或原始值,以便其他程序可以通过 import 语句使用它们。
</script>
<style scoped> /*//在vue组件中,在style标签上添加scoped属性,以表示它的样式作用于当下的模块,很好的实现了样式私有化的目的*/
</style>
//vue.config.js里面的内容
module.exports = {
devServer:{
//每次修改完这个文件,一定要重新启动才能生效
//mock数据模拟 模拟后端数据
before(app){
//接口
app.get('/api/cartList',(req,res)=>{ //req是请求,res是响应
res.json({
result:[
{id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1},
{id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
]
})
})
}
}
}
// main.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import axios from 'axios' //axios是网上下载下来的
import './plugins/element.js' //安装的插件element
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止启动生产消息,Vue有两个模式,生产模式和开发模式。
//开发模式:npm run dev是前端自己开发用的 ,生产模式:npm run build 打包之后给后端放在服务端上用的
Vue.prototype.$http = axios; //挂载axios。
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue(); //添加事件总线
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
// element.js里面的内容
import Vue from 'vue'
import { Button,Table,TableColumn,InputNumber,Form,FormItem,Input} from 'element-ui' //分批安装element插件。
Vue.use(Button)
Vue.use(Table)
Vue.use(TableColumn)
Vue.use(InputNumber)
Vue.use(Form)
Vue.use(FormItem)
Vue.use(Input)
结果:
9、表单组件-设计FormItem组件
此节添加了FormItem.vue组件,更改了FormElement.vue组件,其它的都没有更改。
// FormItem.vue里面的内容 <template> <div> <label v-if='label'>{{label}}</label> <!-- //判断,v-if。如果有label显示label。 --> <!-- 槽的作用 --> <slot></slot> <!-- 显示检验的错误信息 --> <p v-if="validateStatus==='error'" class="error">{{errorMessage}}</p> </div> </template> <script> //0.label 和 prop实行 //1.获取当前输入框的规则 //2.如果输入框和rule不匹配,显示错误信息 //3.Input组件中涌入输入内容时,通知FormItem做校验(校验的方法) //4.使用async-validator做检验 export default { data() { return { validateStatus: '', //检验的状态值 errorMessage:'' //显示的错误信息 }; }, props:{ label:{ type:String, default:'' }, prop:{ type:String, default:'' } } } </script> <style scoped> .error{ color: red; } </style>
// FormElement.vue里面的内容 <template> <div> <h3>element表单</h3> <!-- 自己的组件 --> <m-form-item label="用户名" prop="name"> <m-input v-model="ruleForm.name"></m-input> </m-form-item> <m-form-item label='密码' prop='pwd'> <m-input type='password' v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></m-input> </m-form-item> <el-form :model="ruleForm" status-icon :rules="rules" ref="ruleForm" label-width="100px" class="demo-ruleForm" > <el-form-item label="用户名" prop="name"> <el-input type="text" v-model="ruleForm.name"></el-input> </el-form-item> <el-form-item label="密码" prop="pwd"> <el-input type="password" v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></el-input> </el-form-item> <el-form-item> <el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('ruleForm')">提交</el-button> </el-form-item> </el-form> </div> </template> <script> //Form 定义数据模型 负责定义校验规则 //FormItem 绑定label prop校验和显示错误信息 //Input 负责双向数据绑定 通知FormItem做检验 //provide inject 内部共享数据 import MInput from './Input'; import MFormItem from './FormItem.vue' export default{ name:'FormElement', components: { MInput, MFormItem }, data(){ return{ ruleForm:{ //ref:'ruleForm'绑定了用户名和密码。绑定from组件,获取组件对象。 name:'', pwd:'' }, rules:{ //绑定了规则 name:[ {required:true,message:'请输入名称'}, //必须的,值为true。 {min:6,max:10,message:'请输入6~10位用户名'} ], pwd:[{require:true,message:'请输入密码'}], } } }, methods:{ submitForm(name){ this.$refs[name].validate(valid=>{ console.log(valid); if(valid){ alert('验证成功,可以提交') }else{ alert('error 提交'); return false; } }); } } } </script>
10、表单组件设计-如何正确设计表单校验规则
// FormItem.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<label v-if='label'>{{label}}</label> <!-- //判断,v-if。如果有label显示label,如果没有,不显示。 -->
<!-- 槽的作用 Input输入框插入进来,即FormItem的子组件插入进来-->
<slot></slot>
<!-- 显示检验的错误信息 判断错误状态,如果相等,显示错误信息-->
<p v-if='validateStatus==="error"' class="error">{{errorMessage}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import schema from 'async-validator'
//0.label 和 prop实行
//1.获取当前输入框的规则
//2.如果输入框和rule不匹配,显示错误信息
//3.Input组件中涌入输入内容时,通知FormItem做校验(校验的方法)
//4.使用async-validator做检验
// npm i async-validator -S
export default {
name:'FormItem',
data() {
return {
validateStatus: '', //检验的状态值
errorMessage:'' //显示的错误信息
};
},
inject:['form'],
methods: {
validate(value) {
console.log(value); //输入框的值
// let descriptor = {}; //此对象要存储校验规则
//获取校验对象 =>Form组件对象 =>rules[this.prop]
// descriptor[this.prop] = this.form.rules[this.prop];
const descriptor = { //上面的两行代码等价于这一句话。
[this.prop]: this.form.rules[this.prop]
}
const validator = new schema(descriptor)
// let obj = {};
// obj[this.prop] = value;
validator.validate({[this.prop]:value},error=>{
if(error){
//显示错误
this.validateStatus = 'error';
this.errorMessage = error[0].message;
}else{
//错误置空
this.validateStatus = '';
this.errorMessage = '';
}
})
}
},
created () {
this.$on('validate',this.validate);
},
props:{
label:{
type:String,
default:''
},
prop:{ //name或者是pwd
type:String,
default:''
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.error{
color: red;
}
</style>
// FormElement.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h3>element表单</h3>
<!-- //自己的组件 -->
<m-form :model="ruleForm" :rules="rules">
<m-form-item label="用户名" prop="name"> <!-- //绑定label用户名 -->
<m-input v-model="ruleForm.name"></m-input>
</m-form-item>
<m-form-item label='密码' prop='pwd'>
<m-input type='password' v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></m-input>
</m-form-item>
</m-form>
<el-form
:model="ruleForm"
status-icon
:rules="rules"
ref="ruleForm"
label-width="100px"
class="demo-ruleForm"
>
<el-form-item label="用户名" prop="name">
<el-input type="text" v-model="ruleForm.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="pwd">
<el-input type="password" v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('ruleForm')">提交</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//Form 定义数据模型 负责定义校验规则
//FormItem 绑定label prop校验和显示错误信息
//Input 负责双向数据绑定 通知FormItem做检验
//provide inject 内部共享数据
import MInput from './Input';
import MFormItem from './FormItem.vue';
import MForm from './Form.vue';
export default{
name:'FormElement',
components: {
MInput,
MFormItem,
MForm
},
data(){
return{
ruleForm:{ //ref:'ruleForm'绑定了用户名和密码。绑定from组件,获取组件对象。
name:'',
pwd:''
},
rules:{ //绑定了规则
name:[
{required:true,message:'请输入名称'}, //必须的,值为true。
{min:6,max:10,message:'请输入6~10位用户名'}
],
pwd:[{require:true,message:'请输入密码'}],
}
}
},
methods:{
submitForm(name){
this.$refs[name].validate(valid=>{
console.log(valid);
if(valid){
alert('验证成功,可以提交')
}else{
alert('error 提交');
return false;
}
});
}
}
}
</script>
// Form.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
provide(){
return{
form:this
}
},
props: {
model: {
type: Object,
required:true
},
rules:{
type:Object
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
</style>
// App.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<!-- //展示购物车的列表 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in cartList" :key="item.index"> <!--//v-for循环遍历对象数组 -->
<h2>{{item.title}}</h2>
<p>¥{{item.price}}</p>
<el-button @click="addCart(index)" type='success'>添加购物车</el-button>
</li>
</ul>
<my-cart :title="title"></my-cart> <!--//这里的my-cart标签,同等于MyCart标签 -->
<FormElement></FormElement>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyCart from './components/Cart'; //MyCart自定义的称名,也可以起其它名称
//@相当于src目录
import FormElement from '@/components/FormElement.vue';
export default {
name: 'app',
methods:{
addCart(i){
const good = this.cartList[i];
this.$bus.$emit('addCart',good); //分发事件
}
},
data(){ //这里的data存储着本地数据
return{
cartList:[],
// carList:[
// {id:1,title:"Vue实战开发",price:188,active:true,count:1}, //active的值为true,默认选中,为false,默认不选中
// {id:2,title:"React实战开发",price:288,active:true,count:1}
// ],
title:"购物车"
};
},
async created (){
// this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //这里是请求数据
// .then(res=>{
// this.cartList = res.data.result;
// }).catch(err=>{
// console.log(err);
// })
try { //try是用来处理接口错误的,成功的时候走try里面的内容,失败的时候走error。
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/cartList') //await等待结果
this.cartList = res.data.result; //这里接收到的数据传递到my-cart这个文件中。
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
},
components:{
MyCart, //MyCart是一个局部模板,因为在<div id:'app'></div>下面挂载着,只能在这下面使用。
FormElement
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; /*/font-family为段落设置字体*/
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; /*/字体抗锯齿渲染*/
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
警告:
11、Form组件检验方法完结
只记录更改的内容:
// Form.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
provide(){
return{
form:this
}
},
props: {
model: {
type: Object,
required:true
},
rules:{
type:Object
}
},
created () {
//缓存需要校验的表单项
this.fileds = [];
this.$on('formItemAdd',item=>{
this.fileds.push(item);
});
},
methods: {
validate(callback) {
//获取所有的验证结果统一处理,只要有一个失败就失败
//tasks保存着验证之后的多个promise对象
const tasks = this.fileds.map(item=>tiem.validate());
let ret = true;
Promise.all(tasks).then(results=>{
results.forEach(valid=>{
if(!valid){
ret = false
}
})
callback(ret)
})
}
},
}
//1.声明props 获取数据模型(model)和校验规则对象
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
</style>
// FormItem.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<label v-if='label'>{{label}}</label> <!-- //判断,v-if。如果有label显示label,如果没有,不显示。 -->
<!-- 槽的作用 Input输入框插入进来,即FormItem的子组件插入进来-->
<slot></slot>
<!-- 显示检验的错误信息 判断错误状态,如果相等,显示错误信息-->
<p v-if='validateStatus==="error"' class="error">{{errorMessage}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import schema from 'async-validator'
//0.label 和 prop实行
//1.获取当前输入框的规则
//2.如果输入框和rule不匹配,显示错误信息
//3.Input组件中涌入输入内容时,通知FormItem做校验(校验的方法)
//4.使用async-validator做检验
// npm i async-validator -S
export default {
name:'FormItem',
data() {
return {
validateStatus: '', //检验的状态值
errorMessage:'' //显示的错误信息
};
},
inject:['form'],
mounted () {
if(this.prop){ //必须判断,因为Form组件的子组件可能不是FormItem
this.$paren.$emit('formItemAdd', this);
};
},
methods: {
validate(value) {
return new Promise(resolve=>{
// let descriptor = {}; //此对象要存储校验规则
//获取校验对象 =>Form组件对象 =>rules[this.prop]
// descriptor[this.prop] = this.form.rules[this.prop];
const descriptor = { //上面的两行代码等价于这一句话。
[this.prop]: this.form.rules[this.prop]
}
const validator = new schema(descriptor)
// let obj = {};
// obj[this.prop] = value;
validator.validate({[this.prop]:value},error=>{
if(error){
//显示错误
this.validateStatus = 'error';
this.errorMessage = error[0].message;
resolve(false);
}else{
//错误置空
this.validateStatus = '';
this.errorMessage = '';
resolve(true);
}
})
})
}
},
created () {
this.$on('validate',this.validate);
},
props:{
label:{
type:String,
default:''
},
prop:{ //name或者是pwd
type:String,
default:''
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.error{
color: red;
}
</style>
// FormElement.vue里面的内容
<template>
<div>
<h3>element表单</h3>
<!-- //自己的组件 -->
<m-form :model="ruleForm" :rules="rules">
<m-form-item label="用户名" prop="name"> <!-- //绑定label用户名 -->
<m-input v-model="ruleForm.name"></m-input>
</m-form-item>
<m-form-item label='密码' prop='pwd'>
<m-input type='password' v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></m-input>
</m-form-item>
<m-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm2('ruleForm')">提交</el-button>
</m-form-item>
</m-form>
<el-form
:model="ruleForm"
status-icon
:rules="rules"
ref="ruleForm"
label-width="100px"
class="demo-ruleForm"
>
<el-form-item label="用户名" prop="name">
<el-input type="text" v-model="ruleForm.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="pwd">
<el-input type="password" v-model="ruleForm.pwd"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('ruleForm')">提交</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//Form 定义数据模型 负责定义校验规则//
//FormItem 绑定label prop校验和显示错误信息//
//Input 负责双向数据绑定 通知FormItem做检验//
//provide inject 内部共享数据
import MInput from './Input';
import MFormItem from './FormItem.vue';
import MForm from './Form.vue';
export default{
name:'FormElement',
components: {
MInput,
MFormItem,
MForm
},
data(){
return{
ruleForm:{ //ref:'ruleForm'绑定了用户名和密码。绑定from组件,获取组件对象。
name:'',
pwd:''
},
rules:{ //绑定了规则
name:[
{required:true,message:'请输入名称'}, //必须的,值为true。
{min:6,max:10,message:'请输入6~10位用户名'}
],
pwd:[{require:true,message:'请输入密码'}],
}
}
},
methods:{
submitForm(name){
console.log(naem); //ruleForm
this.$refs[name].validate(valid=>{
console.log(valid);
if(valid){
alert('验证成功,可以提交')
}else{
alert('error 提交');
return false;
}
});
},
//自己写的校验事件
submitForm2(name){
this.$refs[name].validate(valid=>{
console.log(valid);
if(valid){
alert('验证成功,可以提交')
}else{
alert('error 提交');
return false;
}
});
}
}
}
</script>
作者:龙飞
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:独学而无友,则孤陋而寡闻。做一个灵魂有趣的人!
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号