SpringBean的工作原理
在 Spring 中,那些组成应用程序的主体及由 Spring IOC 容器所管理的对象,被称之为 bean。简单地讲,bean 就是由 IOC 容器初始化、装配及管理的对象,除此之外,bean 就与应用程序中的其他对象没有什么区别了。而 bean 的定义以及 bean 相互间的依赖关系将通过配置元数据来描述。
Spring中的bean默认都是单例的,这些单例Bean在多线程程序下如何保证线程安全呢? 例如对于Web应用来说,Web容器对于每个用户请求都创建一个单独的Sevlet线程来处理请求,引入Spring框架之后,每个Action都是单例的,那么对于Spring托管的单例Service Bean,如何保证其安全呢? Spring的单例是基于BeanFactory也就是Spring容器的,单例Bean在此容器内只有一个,Java的单例是基于 JVM,每个 JVM 内只有一个实例。
2|0bean的作用域
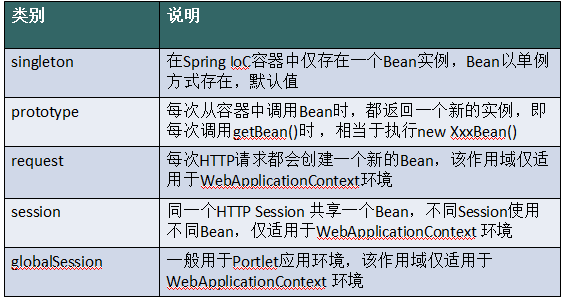
创建一个bean定义,其实质是用该bean定义对应的类来创建真正实例的“配方”。把bean定义看成一个配方很有意义,它与class很类似,只根据一张“处方”就可以创建多个实例。不仅可以控制注入到对象中的各种依赖和配置值,还可以控制该对象的作用域。这样可以灵活选择所建对象的作用域,而不必在Java Class级定义作用域。Spring Framework支持五种作用域,分别阐述如下表。
五种作用域中,request、session 和 global session 三种作用域仅在基于web的应用中使用(不必关心你所采用的是什么web应用框架),只能用在基于 web 的 Spring ApplicationContext 环境。
1. singleton——唯一 bean 实例
当一个 bean 的作用域为 singleton,那么Spring IoC容器中只会存在一个共享的 bean 实例,并且所有对 bean 的请求,只要 id 与该 bean 定义相匹配,则只会返回bean的同一实例。 singleton 是单例类型(对应于单例模式),就是在创建起容器时就同时自动创建了一个bean的对象,不管你是否使用,但我们可以指定Bean节点的 lazy-init=”true” 来延迟初始化bean,这时候,只有在第一次获取bean时才会初始化bean,即第一次请求该bean时才初始化。 每次获取到的对象都是同一个对象。注意,singleton 作用域是Spring中的缺省作用域。要在XML中将 bean 定义成 singleton ,可以这样配置:
也可以通过 @Scope 注解(它可以显示指定bean的作用范围。)的方式
2. prototype——每次请求都会创建一个新的 bean 实例
当一个bean的作用域为 prototype,表示一个 bean 定义对应多个对象实例。 prototype 作用域的 bean 会导致在每次对该 bean 请求(将其注入到另一个 bean 中,或者以程序的方式调用容器的 getBean() 方法)时都会创建一个新的 bean 实例。prototype 是原型类型,它在我们创建容器的时候并没有实例化,而是当我们获取bean的时候才会去创建一个对象,而且我们每次获取到的对象都不是同一个对象。根据经验,对有状态的 bean 应该使用 prototype 作用域,而对无状态的 bean 则应该使用 singleton 作用域。 在 XML 中将 bean 定义成 prototype ,可以这样配置:
通过 @Scope 注解的方式实现就不做演示了。
3. request——每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的bean,该bean仅在当前HTTP request内有效
request只适用于Web程序,每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的bean,同时该bean仅在当前HTTP request内有效,当请求结束后,该对象的生命周期即告结束。 在 XML 中将 bean 定义成 request ,可以这样配置:
4. session——每一次HTTP请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该bean仅在当前 HTTP session 内有效
session只适用于Web程序,session 作用域表示该针对每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的 bean,同时该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP session 内有效.与request作用域一样,可以根据需要放心的更改所创建实例的内部状态,而别的 HTTP session 中根据 userPreferences 创建的实例,将不会看到这些特定于某个 HTTP session 的状态变化。当HTTP session最终被废弃的时候,在该HTTP session作用域内的bean也会被废弃掉。
5. globalSession
global session 作用域类似于标准的 HTTP session 作用域,不过仅仅在基于 portlet 的 web 应用中才有意义。Portlet 规范定义了全局 Session 的概念,它被所有构成某个 portlet web 应用的各种不同的 portle t所共享。在global session 作用域中定义的 bean 被限定于全局portlet Session的生命周期范围内。
3|0bean的生命周期
Spring Bean是Spring应用中最最重要的部分了。所以来看看Spring容器在初始化一个bean的时候会做那些事情,顺序是怎样的,在容器关闭的时候,又会做哪些事情。
spring版本:4.2.3.RELEASE
鉴于Spring源码是用gradle构建的,我也决定舍弃我大maven,尝试下洪菊推荐过的gradle。运行beanLifeCycle模块下的junit test即可在控制台看到如下输出,可以清楚了解Spring容器在创建,初始化和销毁Bean的时候依次做了那些事情。
先来看看,Spring在Bean从创建到销毁的生命周期中可能做得事情。
initialization 和 destroy
有时我们需要在Bean属性值set好之后和Bean销毁之前做一些事情,比如检查Bean中某个属性是否被正常的设置好值了。Spring框架提供了多种方法让我们可以在Spring Bean的生命周期中执行initialization和pre-destroy方法。
1.实现InitializingBean和DisposableBean接口
这两个接口都只包含一个方法。通过实现InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法可以在Bean属性值设置好之后做一些操作,实现DisposableBean接口的destroy()方法可以在销毁Bean之前做一些操作。
例子如下:
这种方法比较简单,但是不建议使用。因为这样会将Bean的实现和Spring框架耦合在一起。
2.在bean的配置文件中指定init-method和destroy-method方法
Spring允许我们创建自己的 init 方法和 destroy 方法,只要在 Bean 的配置文件中指定 init-method 和 destroy-method 的值就可以在 Bean 初始化时和销毁之前执行一些操作。
例子如下:
配置文件中的配置:
需要注意的是自定义的init-method和post-method方法可以抛异常但是不能有参数。
这种方式比较推荐,因为可以自己创建方法,无需将Bean的实现直接依赖于spring的框架。
3.使用@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解
除了xml配置的方式,Spring 也支持用 @PostConstruct和 @PreDestroy注解来指定 init 和 destroy 方法。这两个注解均在javax.annotation 包中。为了注解可以生效,需要在配置文件中定义org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor或context:annotation-config
例子如下:
配置文件:
实现*Aware接口 在Bean中使用Spring框架的一些对象
有些时候我们需要在 Bean 的初始化中使用 Spring 框架自身的一些对象来执行一些操作,比如获取 ServletContext 的一些参数,获取 ApplicaitionContext 中的 BeanDefinition 的名字,获取 Bean 在容器中的名字等等。为了让 Bean 可以获取到框架自身的一些对象,Spring 提供了一组名为*Aware的接口。
这些接口均继承于org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware标记接口,并提供一个将由 Bean 实现的set*方法,Spring通过基于setter的依赖注入方式使相应的对象可以被Bean使用。
网上说,这些接口是利用观察者模式实现的,类似于servlet listeners,目前还不明白,不过这也不在本文的讨论范围内。
介绍一些重要的Aware接口:
- ApplicationContextAware: 获得ApplicationContext对象,可以用来获取所有Bean definition的名字。
- BeanFactoryAware:获得BeanFactory对象,可以用来检测Bean的作用域。
- BeanNameAware:获得Bean在配置文件中定义的名字。
- ResourceLoaderAware:获得ResourceLoader对象,可以获得classpath中某个文件。
- ServletContextAware:在一个MVC应用中可以获取ServletContext对象,可以读取context中的参数。
- ServletConfigAware: 在一个MVC应用中可以获取ServletConfig对象,可以读取config中的参数。
BeanPostProcessor
上面的*Aware接口是针对某个实现这些接口的Bean定制初始化的过程,
Spring同样可以针对容器中的所有Bean,或者某些Bean定制初始化过程,只需提供一个实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类即可。 该接口中包含两个方法,postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization。 postProcessBeforeInitialization方法会在容器中的Bean初始化之前执行, postProcessAfterInitialization方法在容器中的Bean初始化之后执行。
例子如下:
要将BeanPostProcessor的Bean像其他Bean一样定义在配置文件中
总结
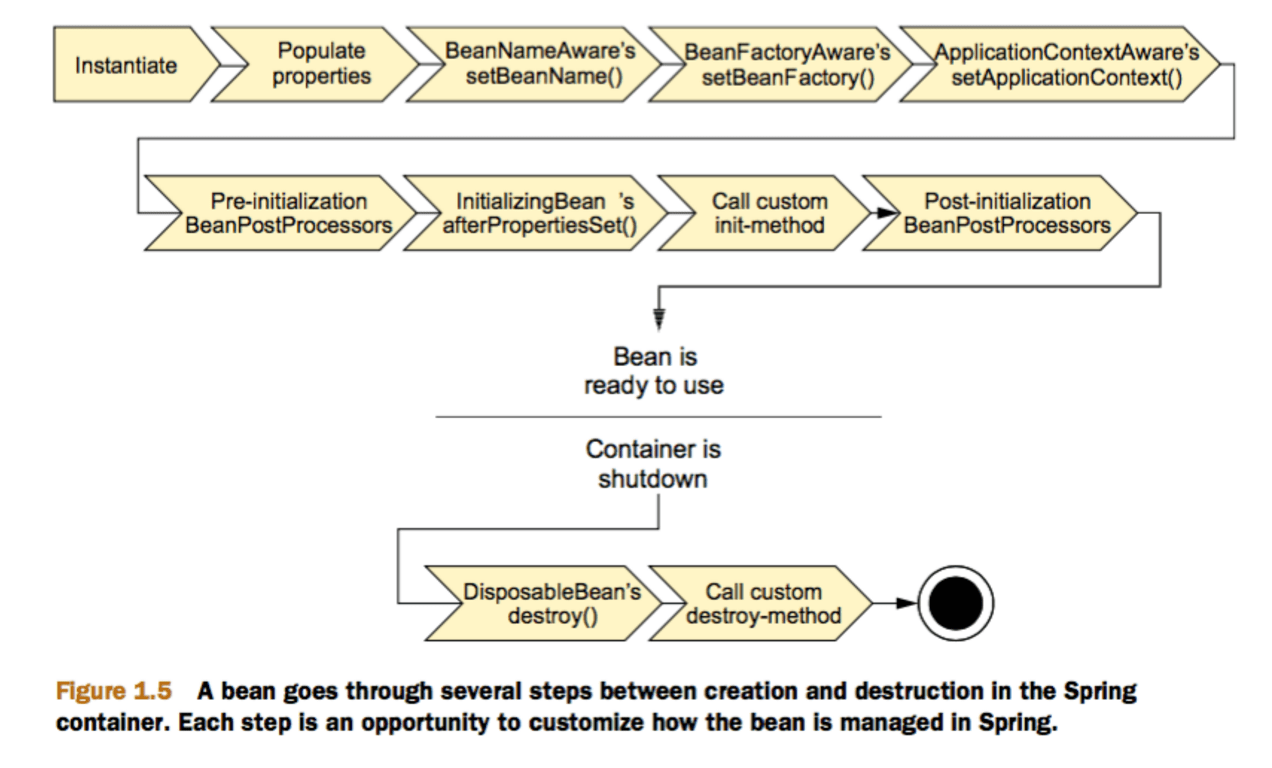
所以。。。结合第一节控制台输出的内容,Spring Bean的生命周期是这样纸的:
- Bean容器找到配置文件中 Spring Bean 的定义。
- Bean容器利用Java Reflection API创建一个Bean的实例。
- 如果涉及到一些属性值 利用set方法设置一些属性值。
- 如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,调用setBeanName()方法,传入Bean的名字。
- 如果Bean实现了BeanClassLoaderAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象的实例。
- 如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象的实例。
- 与上面的类似,如果实现了其他*Aware接口,就调用相应的方法。
- 如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法
- 如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,执行afterPropertiesSet()方法。
- 如果Bean在配置文件中的定义包含init-method属性,执行指定的方法。
- 如果有和加载这个Bean的Spring容器相关的BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
- 当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,执行destroy()方法。
- 当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean在配置文件中的定义包含destroy-method属性,执行指定的方法。
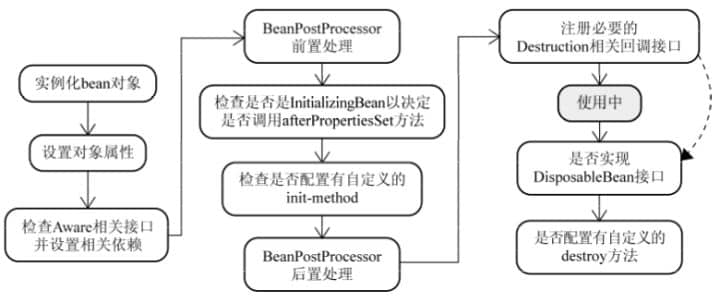
用图表示一下(图来源:http://www.jianshu.com/p/d00539babca5):
与之比较类似的中文版本:
其实很多时候我们并不会真的去实现上面说描述的那些接口,那么下面我们就除去那些接口,针对bean的单例和非单例来描述下bean的生命周期:
单例管理的对象
当scope=”singleton”,即默认情况下,会在启动容器时(即实例化容器时)时实例化。但我们可以指定Bean节点的lazy-init=”true”来延迟初始化bean,这时候,只有在第一次获取bean时才会初始化bean,即第一次请求该bean时才初始化。如下配置:
如果想对所有的默认单例bean都应用延迟初始化,可以在根节点beans设置default-lazy-init属性为true,如下所示:
默认情况下,Spring 在读取 xml 文件的时候,就会创建对象。在创建对象的时候先调用构造器,然后调用 init-method 属性值中所指定的方法。对象在被销毁的时候,会调用 destroy-method 属性值中所指定的方法(例如调用Container.destroy()方法的时候)。写一个测试类,代码如下:
life.xml配置如下:
测试代码:
运行结果:
非单例管理的对象
当scope=”prototype”时,容器也会延迟初始化 bean,Spring 读取xml 文件的时候,并不会立刻创建对象,而是在第一次请求该 bean 时才初始化(如调用getBean方法时)。在第一次请求每一个 prototype 的bean 时,Spring容器都会调用其构造器创建这个对象,然后调用init-method属性值中所指定的方法。对象销毁的时候,Spring 容器不会帮我们调用任何方法,因为是非单例,这个类型的对象有很多个,Spring容器一旦把这个对象交给你之后,就不再管理这个对象了。
为了测试prototype bean的生命周期life.xml配置如下:
测试程序:
运行结果:
可以发现,对于作用域为 prototype 的 bean ,其destroy方法并没有被调用。如果 bean 的 scope 设为prototype时,当容器关闭时,destroy 方法不会被调用。对于 prototype 作用域的 bean,有一点非常重要,那就是 Spring不能对一个 prototype bean 的整个生命周期负责:容器在初始化、配置、装饰或者是装配完一个prototype实例后,将它交给客户端,随后就对该prototype实例不闻不问了。 不管何种作用域,容器都会调用所有对象的初始化生命周期回调方法。但对prototype而言,任何配置好的析构生命周期回调方法都将不会被调用。清除prototype作用域的对象并释放任何prototype bean所持有的昂贵资源,都是客户端代码的职责(让Spring容器释放被prototype作用域bean占用资源的一种可行方式是,通过使用bean的后置处理器,该处理器持有要被清除的bean的引用)。谈及prototype作用域的bean时,在某些方面你可以将Spring容器的角色看作是Java new操作的替代者,任何迟于该时间点的生命周期事宜都得交由客户端来处理。
Spring 容器可以管理 singleton 作用域下 bean 的生命周期,在此作用域下,Spring 能够精确地知道bean何时被创建,何时初始化完成,以及何时被销毁。而对于 prototype 作用域的bean,Spring只负责创建,当容器创建了 bean 的实例后,bean 的实例就交给了客户端的代码管理,Spring容器将不再跟踪其生命周期,并且不会管理那些被配置成prototype作用域的bean的生命周期




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号