Spark streaming tutorial
本篇我们介绍一些spark流式计算的基础概念,并实现一个例子加以说明。
spark streaming
spark streaming 是以spark为核心的流式处理框架,内部通过批处理的方式对数据加以加工。输出结果是周期内的统计数据而并非实时数据。
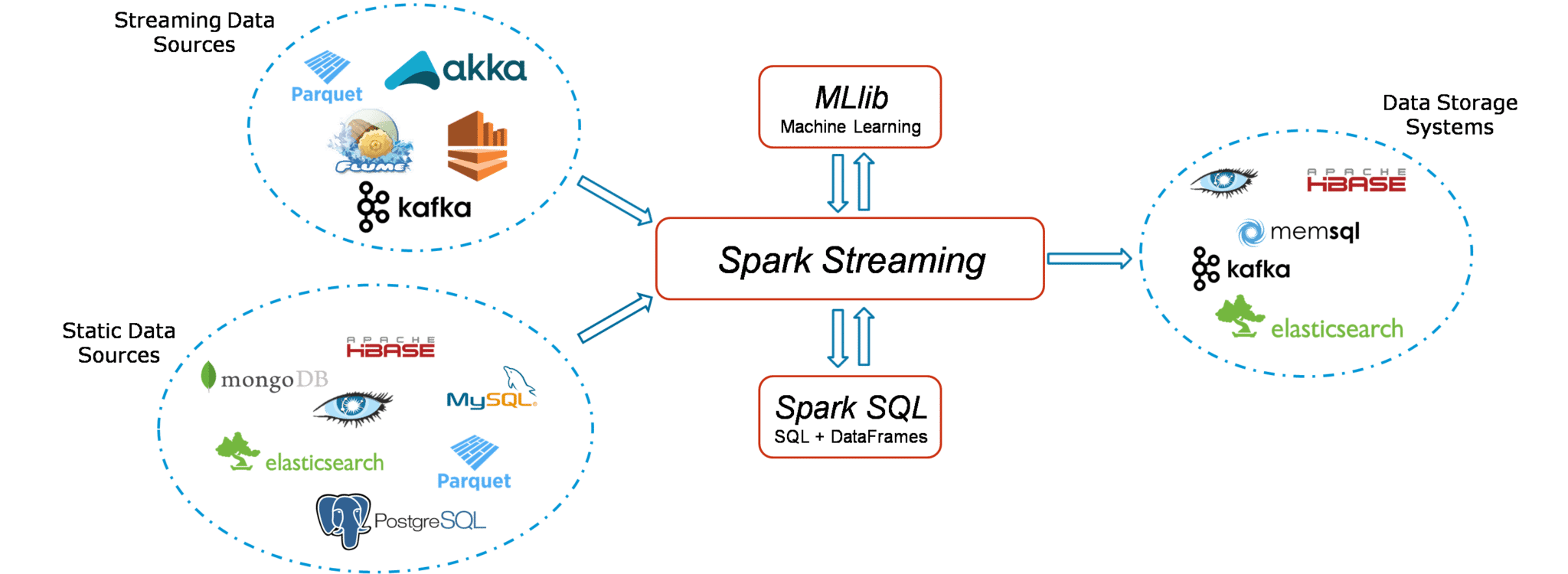
工作方式:


生态:
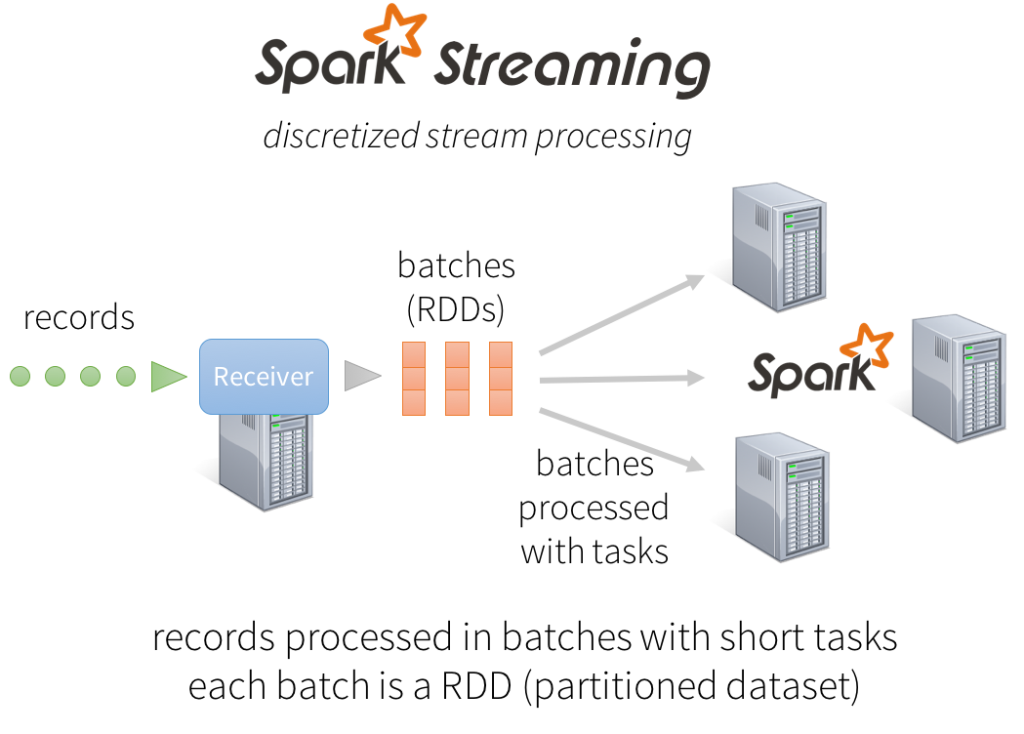
Dstream:a DStream is represented as a sequence of RDDs.
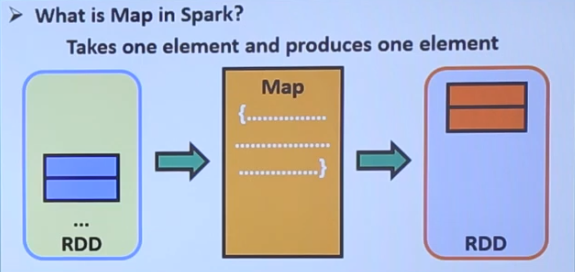
map和flatmap
任何数据在spark中都表示为RDD。map和flatmap是RDD提供的两个函数。map可以添加自己的映射逻辑将数据进行转变,flatmap和map的区别就是它的输出可能不止一个RDD。
map()
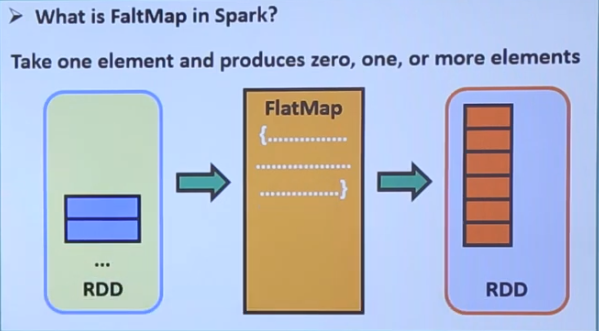
flatmap()
Simple example would be applying a flatMap to Strings and using split function to return words to new RDD.
Welcome to TutorialKart Learn Apache Spark Learn to work with RDD
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
public class RDDflatMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// configure spark
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Read Text to RDD")
.setMaster("local[2]").set("spark.executor.memory","2g");
// start a spark context
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(sparkConf);
// provide path to input text file
String path = "data/rdd/input/sample.txt";
// read text file to RDD
JavaRDD<String> lines = sc.textFile(path);
// flatMap each line to words in the line
JavaRDD<String> words = lines.flatMap(s -> Arrays.asList(s.split(" ")).iterator());
// collect RDD for printing
for(String word:words.collect()){
System.out.println(word);
}
}
}
17/11/29 12:33:59 INFO DAGScheduler: ResultStage 0 (collect at RDDflatMapExample.java:26) finished in 0.513 s 17/11/29 12:33:59 INFO DAGScheduler: Job 0 finished: collect at RDDflatMapExample.java:26, took 0.793858 s Welcome to TutorialKart Learn Apache Spark Learn to work with RDD 17/11/29 12:33:59 INFO SparkContext: Invoking stop() from shutdown hook
最后可以使用 ~$ spark-submit 将jar包提交查看效果
Spark streaming Example
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.spark.examples.streaming;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import scala.Tuple2;
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.StorageLevels;
import org.apache.spark.streaming.Durations;
import org.apache.spark.streaming.api.java.JavaDStream;
import org.apache.spark.streaming.api.java.JavaPairDStream;
import org.apache.spark.streaming.api.java.JavaReceiverInputDStream;
import org.apache.spark.streaming.api.java.JavaStreamingContext;
/**
* Counts words in UTF8 encoded, '\n' delimited text received from the network every second.
*
* Usage: JavaNetworkWordCount <hostname> <port>
* <hostname> and <port> describe the TCP server that Spark Streaming would connect to receive data.
*
* To run this on your local machine, you need to first run a Netcat server
* `$ nc -lk 9999`
* and then run the example
* `$ bin/run-example org.apache.spark.examples.streaming.JavaNetworkWordCount localhost 9999`
*/
public final class JavaNetworkWordCount {
private static final Pattern SPACE = Pattern.compile(" ");
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: JavaNetworkWordCount <hostname> <port>");
System.exit(1);
}
StreamingExamples.setStreamingLogLevels();
// Create the context with a 1 second batch size
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("JavaNetworkWordCount");
JavaStreamingContext ssc = new JavaStreamingContext(sparkConf, Durations.seconds(1));
// Create a JavaReceiverInputDStream on target ip:port and count the
// words in input stream of \n delimited text (eg. generated by 'nc')
// Note that no duplication in storage level only for running locally.
// Replication necessary in distributed scenario for fault tolerance.
JavaReceiverInputDStream<String> lines = ssc.socketTextStream(
args[0], Integer.parseInt(args[1]), StorageLevels.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER);
JavaDStream<String> words = lines.flatMap(x -> Arrays.asList(SPACE.split(x)).iterator());
JavaPairDStream<String, Integer> wordCounts = words.mapToPair(s -> new Tuple2<>(s, 1))
.reduceByKey((i1, i2) -> i1 + i2);
wordCounts.print();
ssc.start();
ssc.awaitTermination();
}
}
reference:
https://www.tutorialkart.com/apache-spark/spark-rdd-flatmap/
https://spark.apache.org/docs/2.2.0/streaming-programming-guide.html#discretized-streams-dstreams


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号