实验四
#include <stdio.h> #define N 4 void test1() { int a[N] = {1, 9, 8, 4}; int i; // 输出数组a占用的内存字节数 printf("sizeof(a) = %d\n", sizeof(a)); // 输出int类型数组a中每个元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) printf("%p: %d\n", &a[i], a[i]); // 输出数组名a对应的值 printf("a = %p\n", a); } void test2() { char b[N] = {'1', '9', '8', '4'}; int i; // 输出数组b占用的内存字节数 printf("sizeof(b) = %d\n", sizeof(b)); // 输出char类型数组b中每个元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) printf("%p: %c\n", &b[i], b[i]); // 输出数组名b对应的值 printf("b = %p\n", b); } int main() { printf("测试1: int类型一维数组\n"); test1(); printf("\n测试2: char类型一维数组\n"); test2(); return 0; }
实验4.1数据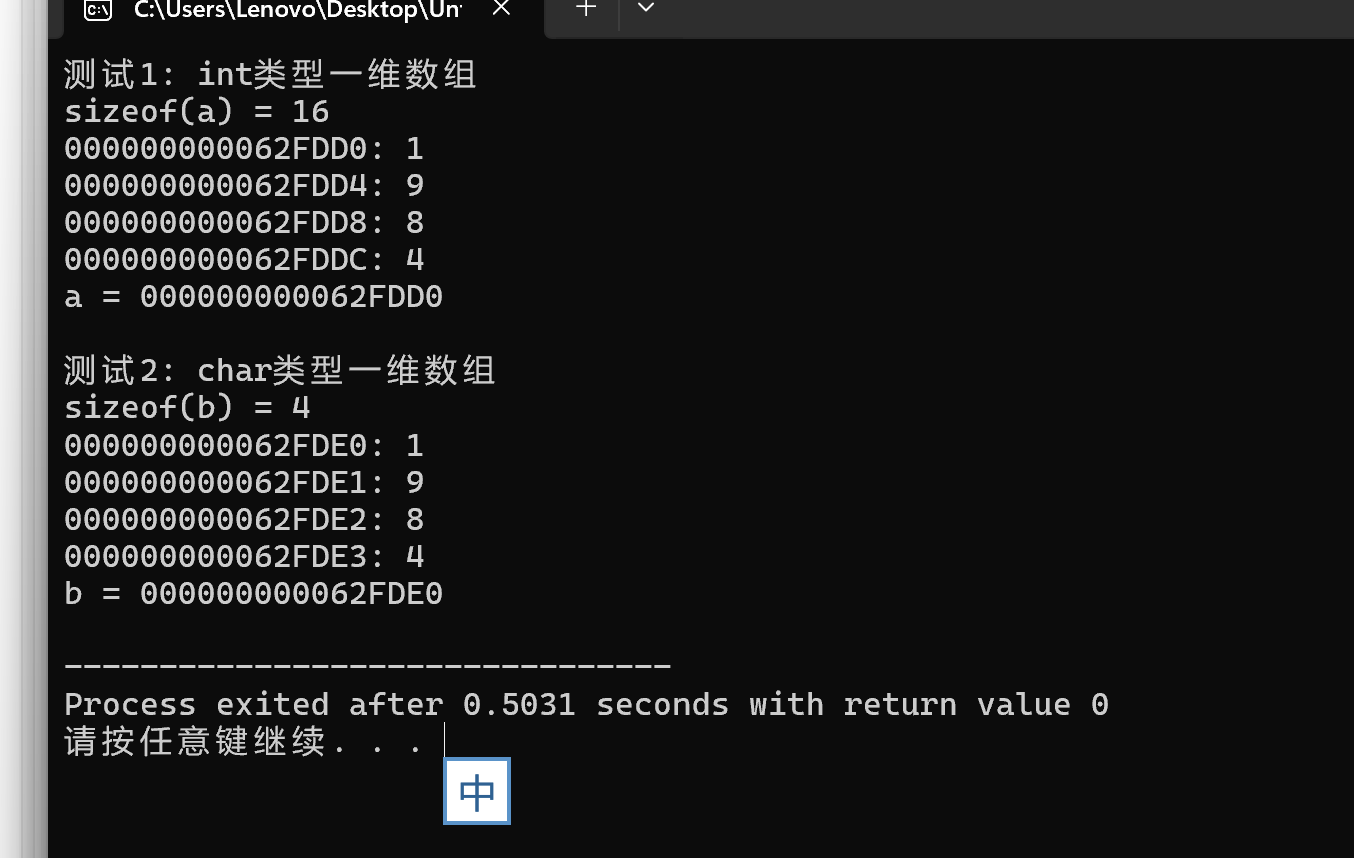
问题1:int型数组是连续存放的,每个元素占用4个内存字节单元,数组名a对应的值和&a[0]是一样的
问题2:char类型数组是连续存在的,每个元素占用4个内存字节单元,数组名b对应的值和&b[0]是一样的
#include <stdio.h> #define N 2 #define M 4 void test1() { int a[N][M] = {{1, 9, 8, 4}, {2, 0, 4, 9}}; int i, j; // 输出int类型二维数组a占用的内存字节数 printf("sizeof(a) = %d\n", sizeof(a)); // 输出int类型二维数组a中每个元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) for (j = 0; j < M; ++j) printf("%p: %d\n", &a[i][j], a[i][j]); printf("\n"); // 输出int类型二维数组名a, 以及,a[0], a[1]的值 printf("a = %p\n", a); printf("a[0] = %p\n", a[0]); printf("a[1] = %p\n", a[1]); printf("\n"); } void test2() { char b[N][M] = {{'1', '9', '8', '4'}, {'2', '0', '4', '9'}}; int i, j; // 输出char类型二维数组b占用的内存字节数 printf("sizeof(b) = %d\n", sizeof(b)); // 输出char类型二维数组b中每个元素的地址、值 for (i = 0; i < N; ++i) for (j = 0; j < M; ++j) printf("%p: %c\n", &b[i][j], b[i][j]); printf("\n"); // 输出char类型二维数组名b, 以及,b[0], b[1]的值 printf("b = %p\n", b); printf("b[0] = %p\n", b[0]); printf("b[1] = %p\n", b[1]); } int main() { printf("测试1: int型两维数组"); test1(); printf("\n测试2: char型两维"); test2(); return 0; }
实验数据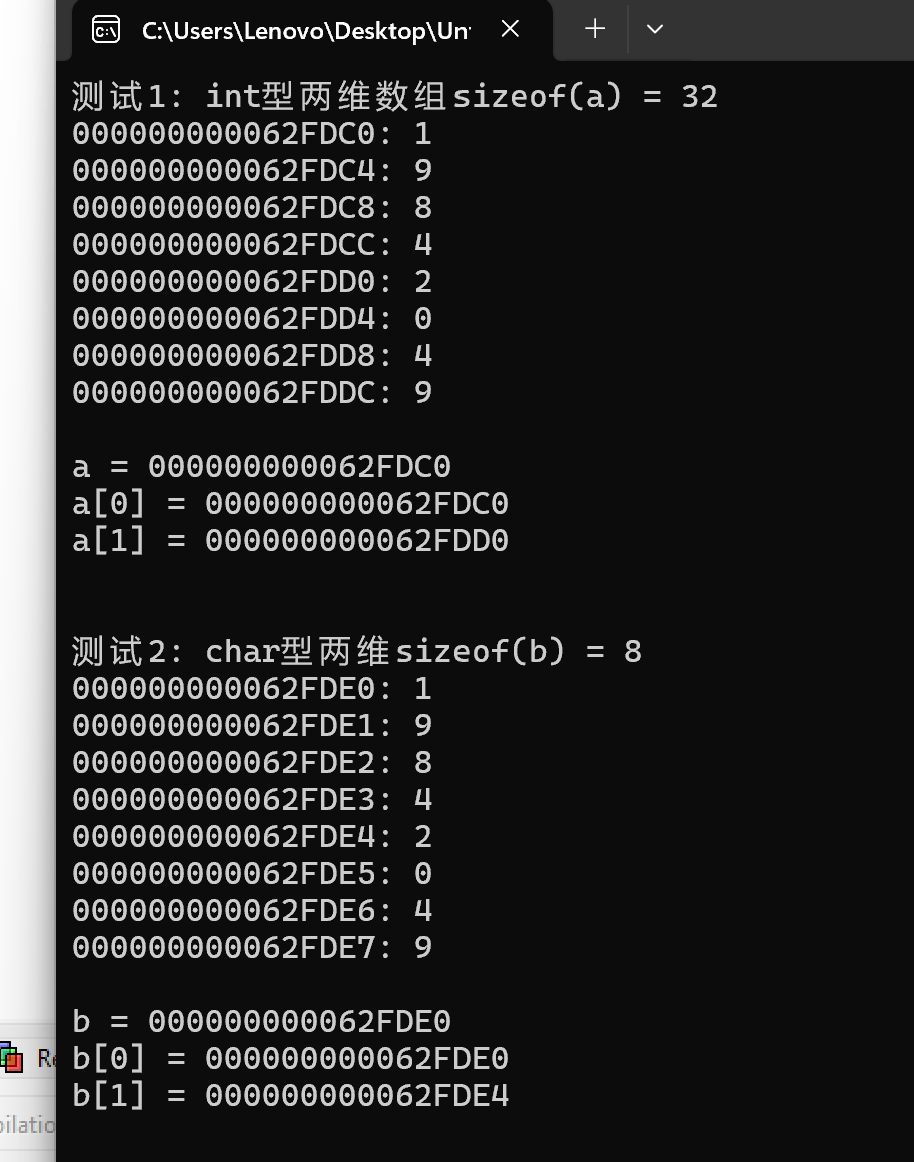
问题1:int型二维数组a在内存中是“按行连续存放”的,每个元素占用4个内存字节单元,数组名a的值、a[0]的值、&a[0][0]的值在数字字面值上是一样的
问题2:char型二维数组b在内存中是“按行连续存放”的,每个元素占用4个内存字节单元,数组名b的值、b[0]的值、&b[0][0]的值在数字字面值上是一样的
问题3:a[0]和a[1]的值相差16,b[0]和b[1]的值相差4
规律:相邻的两行元素的地址相差的值为一行元素占用的内存字节单元
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define N 80 void swap_str(char s1[], char s2[]); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { printf("测试1: 用两个一维char数组,实现两个字符串交换\n"); test1(); printf("\n测试2: 用二维char数组,实现两个字符串交换\n"); test2(); return 0; } void test1() { char views1[N] = "hey, C, I hate u."; char views2[N] = "hey, C, I love u."; printf("交换前: \n"); puts(views1); puts(views2); swap_str(views1, views2); printf("交换后: \n"); puts(views1); puts(views2); } void test2() { char views[2][N] = {"hey, C, I hate u.", "hey, C, I love u."}; printf("交换前: \n"); puts(views[0]); puts(views[1]); swap_str(views[0], views[1]); printf("交换后: \n"); puts(views[0]); puts(views[1]); } void swap_str(char s1[N], char s2[N]) { char tmp[N]; strcpy(tmp, s1); strcpy(s1, s2); strcpy(s2, tmp); }
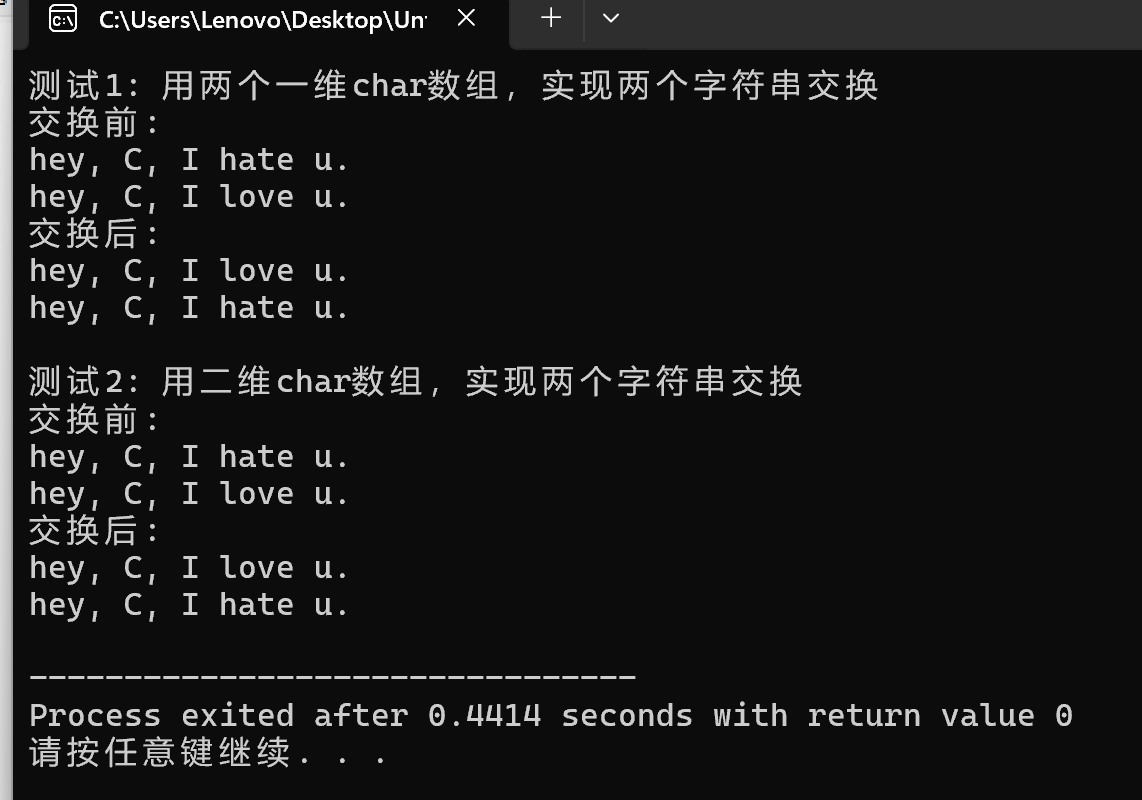
问题:当数组作为函数参数时,实际上传递的是数组首元素的地址(即指针),而不是整个数组。二维字符数组,其本身可以表示指向第一个元素的指针,但无法表示指向第二个元素的指针,所以要加[]即:一维字符数组,可以直接使用数组名访问;二维字符数组,需使用数组#include <stdio.h>
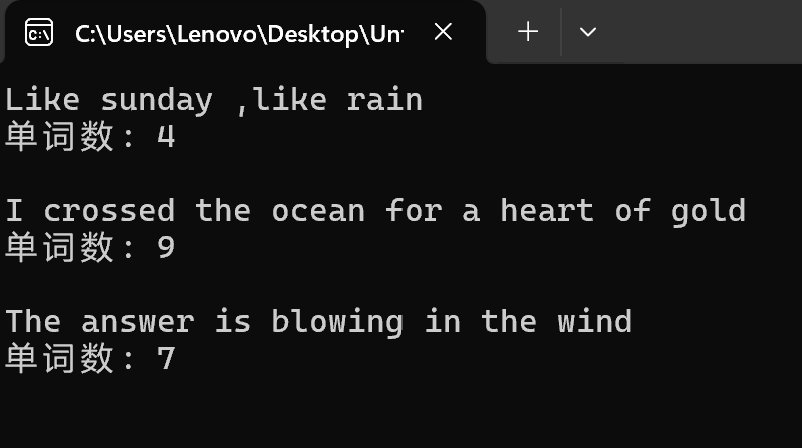
#define N 80 int count(char x[]); int main() { char words[N+1]; int n; while(gets(words) != NULL) { n = count(words); printf("单词数: %d\n\n", n); } return 0; } int count(char x[]) { int i; int word_flag = 0; // 用作单词标志,一个新单词开始,值为1;单词结束,值为0 int cnt = 0; // 统计单词个数 for(i = 0; x[i] != '\0'; i++) { if(x[i] == ' ') word_flag = 0; else if(word_flag == 0) { word_flag = 1; cnt++; } } return cnt; #incl#define N 1000
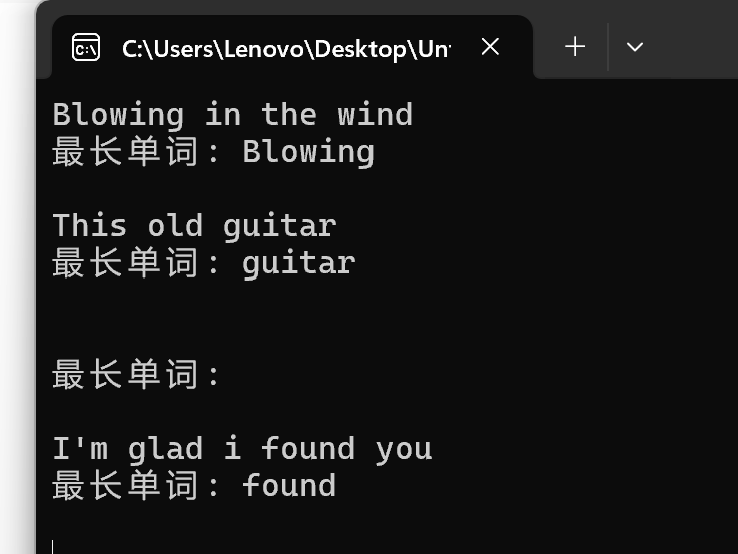
int main() { char line[N]; int word_len; // 记录当前单词长度 int max_len; // 记录最长单词长度 int end; // 记录最长单词结束位置 int i; while(gets(line) != NULL) { word_len = 0; max_len = 0; end = 0; i = 0; while(1) { // 跳过连续空格 while(line[i] == ' ') { word_len = 0; // 单词长度置0,为新单词统计做准备 i++; } // 在一个单词中,统计当前单词长度 while(line[i] != '\0' && line[i] != ' ') { word_len++; i++; } // 更新更长单词长度,并,记录最长单词结束位置 if(max_len < word_len) { max_len = word_len; end = i; // end保存的是单词结束的下一个坐标位置 } // 遍历到文本结束时,终止循环 if(line[i] == '\0') break; } // 输出最长单词 printf("最长单词: "); for(i = end - max_len; i < end; ++i) printf("%c", line[i]); printf("\n\n"); } return 0;
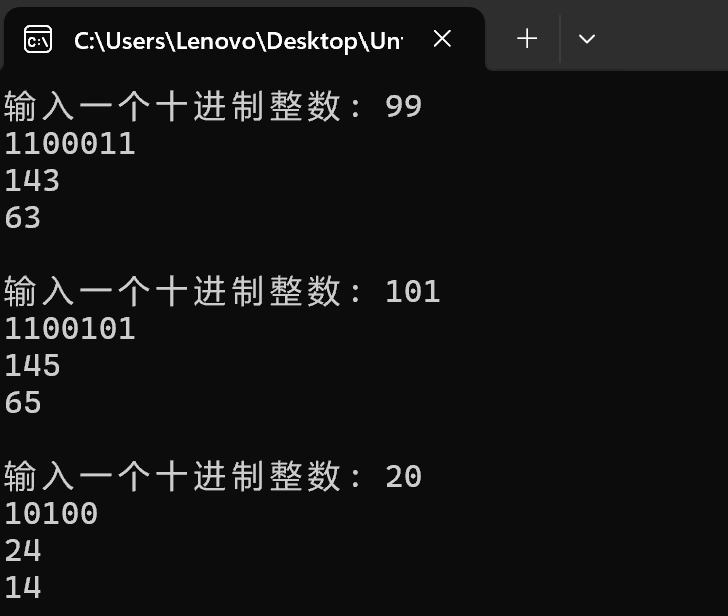
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 100 void dec_to_n(int x, int n); // 函数声明 int main() { int x; printf("输入一个十进制整数: "); while(scanf("%d", &x) != EOF) { dec_to_n(x, 2); // 函数调用: 把x转换成二进制输出 dec_to_n(x, 8); // 函数调用: 把x转换成八进制输出 dec_to_n(x, 16); // 函数调用: 把x转换成十六进制输出 printf("\n输入一个十进制整数: "); } system("pause"); return 0; } // 函数定义 // 功能: 把十进制数x转换成n进制,打印输出 // 补足函数实现 // ××× void dec_to_n(int x, int n){ char ans[N];//保存结果 char map[17]="0123456789ABCDEF"; int d,r;//d商,r余数 int cnt,i; cnt=0; while(1) { d=x/n; r=x%n; ans[cnt++]=map[r]; if(d==0) break; x=d; } for(i=cnt-1;i>=0;--i) printf("%c",ans[i]); printf("\n"); }
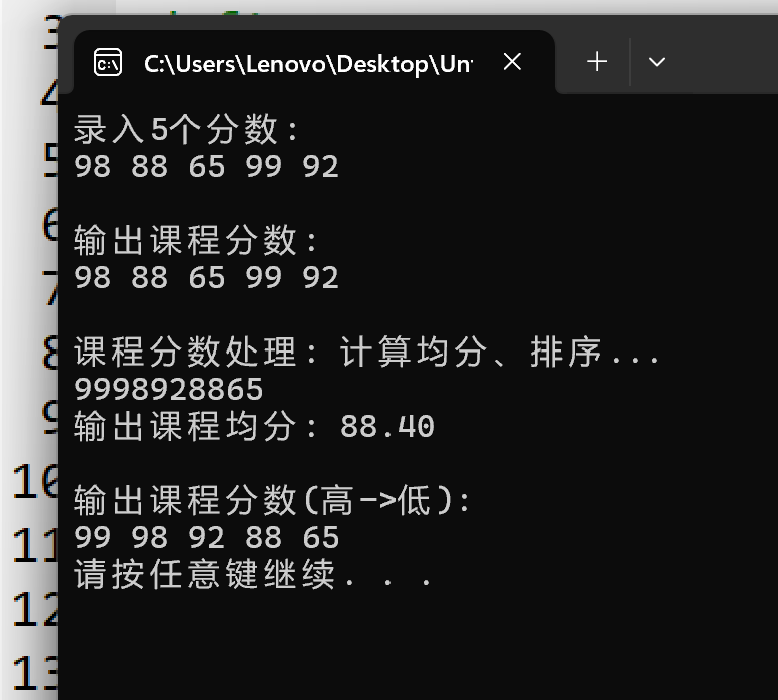
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 5 // 函数声明 void input(int x[], int n); void output(int x[], int n); double average(int x[], int n); void bubble_sort(int x[], int n); int main() { int scores[N]; double ave; printf("录入%d个分数:\n", N); input(scores, N); printf("\n输出课程分数: \n"); output(scores, N); printf("\n课程分数处理: 计算均分、排序...\n"); ave = average(scores, N); bubble_sort(scores, N); printf("\n输出课程均分: %.2f\n", ave); printf("\n输出课程分数(高->低):\n"); output(scores, N); system("pause"); return 0; } // 函数定义 // 输入n个整数保存到整型数组x中 void input(int x[], int n) { int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%d", &x[i]); } // 输出整型数组x中n个元素 void output(int x[], int n) { int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%d ", x[i]); printf("\n"); } double average(int x[], int n){ int i; int sum=0; double ave; for(i=0;i<n;++i){ sum=sum+x[i]; } ave = (double)1.0*sum/n; return ave; } void bubble_sort(int x[], int n){ int i,j,t; for(j=0;j<N-1;j++) for(i=0;i<N-j-1;i++) if(x[i]<x[i+1]) { t=x[i]; x[i]=x[i+1]; x[i+1]=t; } for(i=0;i<N;i++) printf("%d",x[i]); }
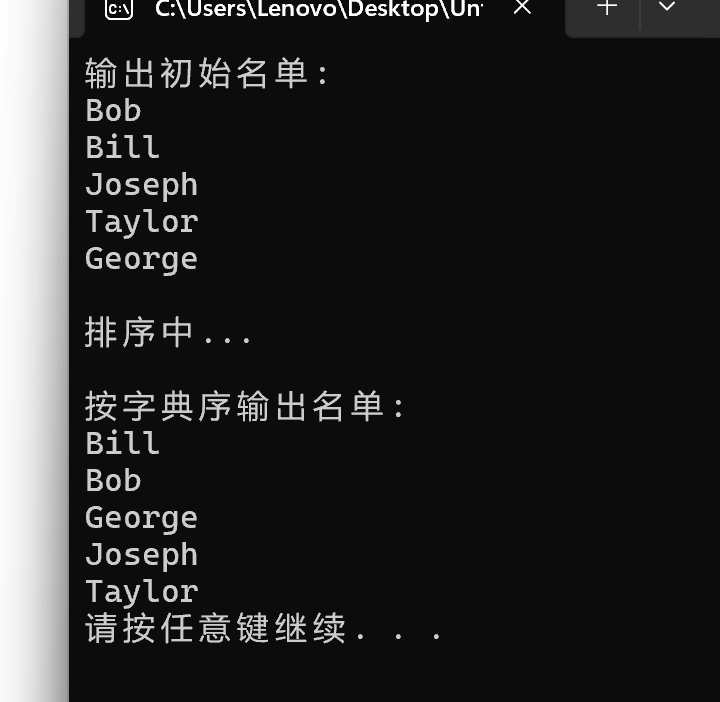
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 5 #define M 20 // 函数声明 void output(char str[][M], int n); void bubble_sort(char str[][M], int n); int main() { char name[][M] = {"Bob", "Bill", "Joseph", "Taylor", "George"}; int i; printf("输出初始名单:\n"); output(name, N); printf("\n排序中...\n"); bubble_sort(name, N); // 函数调用 printf("\n按字典序输出名单:\n"); output(name, N); system("pause"); return 0; } // 函数定义 // 功能:按行输出二维数组中的字符串 void output(char str[][M], int n) { int i; for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%s\n", str[i]); } // 函数定义 // 功能:使用冒泡排序算法对二维数组str中的n个字符串按字典序排序 // 补足函数bubble_sort()实现 // ××× void bubble_sort(char str[][M], int n){ int i,j; char t[M]; for(j=0;j<n-1;j++){ for(i=0;i<n-j-1;i++){ if(strcmp(str[i],str[i+1])>0){ strcpy(t,str[i]); strcpy(str[i],str[i+1]); strcpy(str[i+1],t); }}} }
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 105 int is_repeated(char x[]); int main(){ char num[N]; while(scanf("%s",num)!=EOF){ if(is_repeated(num)) printf("YES\n"); else printf("NO\n"); } system("pause"); return 0; } int is_repeated(char x[]){ int cnt[10]={0}; int i,j; for(i=0;x[i]!='\0';++i){ j=x[i]-'0'; cnt[j]++; if(cnt[j]>1) return 1; } return 0; }
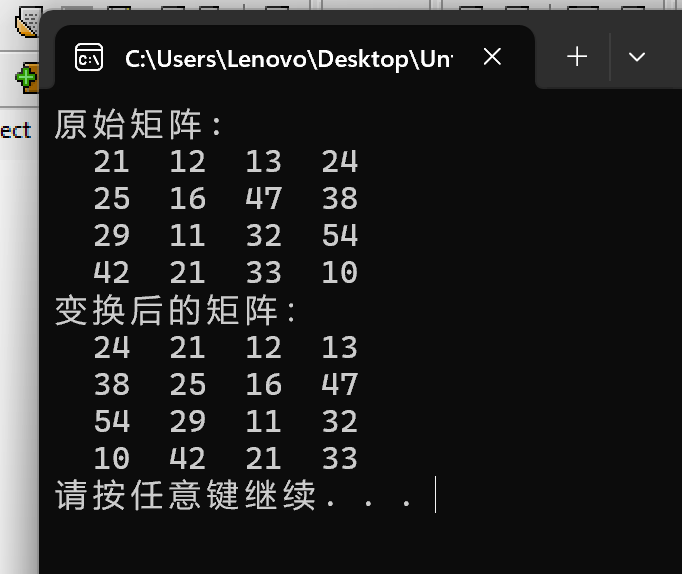
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 100 #define M 4 void output(int x[][N], int n); void rotate_to_right(int x[][N], int n); int main() { int t[][N] = {{21, 12, 13, 24}, {25, 16, 47, 38}, {29, 11, 32, 54}, {42, 21, 33, 10}}; printf("原始矩阵:\n"); output(t, M); rotate_to_right(t, M); printf("变换后的矩阵:\n"); output(t, M); system("pause"); return 0; } void output(int x[][N], int n) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) printf("%4d", x[i][j]); printf("\n"); } } void rotate_to_right(int x[][N], int n){ int i,j; int a[M][N]; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ a[i][n-1]=x[i][n-1]; for(j=0;j<n;j++){ x[i][n-1-j]=x[i][n-j-2]; } x[i][0]=a[i][n-1];} }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号