实验五 多态
任务1
1.实验代码

#pragma once #include <string> // 发行/出版物类:Publisher (抽象类) class Publisher { public: Publisher(const std::string &name_ = ""); // 构造函数 virtual ~Publisher() = default; public: virtual void publish() const = 0; // 纯虚函数,作为接口继承 virtual void use() const = 0; // 纯虚函数,作为接口继承 protected: std::string name; // 发行/出版物名称 }; // 图书类: Book class Book: public Publisher { public: Book(const std::string &name_ = "", const std::string &author_ = ""); // 构造函数 public: void publish() const override; // 接口 void use() const override; // 接口 private: std::string author; // 作者 }; // 电影类: Film class Film: public Publisher { public: Film(const std::string &name_ = "", const std::string &director_ = ""); // 构造函数 public: void publish() const override; // 接口 void use() const override; // 接口 private: std::string director; // 导演 }; // 音乐类:Music class Music: public Publisher { public: Music(const std::string &name_ = "", const std::string &artist_ = ""); public: void publish() const override; // 接口 void use() const override; // 接口 private: std::string artist; // 音乐艺术家名称 };

#include <iostream> #include <string> #include "publisher.hpp" // Publisher类:实现 Publisher::Publisher(const std::string &name_): name {name_} { } // Book类: 实现 Book::Book(const std::string &name_ , const std::string &author_ ): Publisher{name_}, author{author_} { } void Book::publish() const { std::cout << "Publishing book《" << name << "》 by " << author << '\n'; } void Book::use() const { std::cout << "Reading book 《" << name << "》 by " << author << '\n'; } // Film类:实现 Film::Film(const std::string &name_, const std::string &director_):Publisher{name_},director{director_} { } void Film::publish() const { std::cout << "Publishing film <" << name << "> directed by " << director << '\n'; } void Film::use() const { std::cout << "Watching film <" << name << "> directed by " << director << '\n'; } // Music类:实现 Music::Music(const std::string &name_, const std::string &artist_): Publisher{name_}, artist{artist_} { } void Music::publish() const { std::cout << "Publishing music <" << name << "> by " << artist << '\n'; } void Music::use() const { std::cout << "Listening to music <" << name << "> by " << artist << '\n'; }

#include <memory> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "publisher.hpp" void test1() { std::vector<Publisher *> v; v.push_back(new Book("Harry Potter", "J.K. Rowling")); v.push_back(new Film("The Godfather", "Francis Ford Coppola")); v.push_back(new Music("Blowing in the wind", "Bob Dylan")); for(Publisher *ptr: v) { ptr->publish(); ptr->use(); std::cout << '\n'; delete ptr; } } void test2() { std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Publisher>> v; v.push_back(std::make_unique<Book>("Harry Potter", "J.K. Rowling")); v.push_back(std::make_unique<Film>("The Godfather", "Francis Ford Coppola")); v.push_back(std::make_unique<Music>("Blowing in the wind", "Bob Dylan")); for(const auto &ptr: v) { ptr->publish(); ptr->use(); std::cout << '\n'; } } void test3() { Book book("A Philosophy of Software Design", "John Ousterhout"); book.publish(); book.use(); } int main() { std::cout << "运行时多态:纯虚函数、抽象类\n"; std::cout << "\n测试1: 使用原始指针\n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: 使用智能指针\n"; test2(); std::cout << "\n测试3: 直接使用类\n"; test3(); }
2.实验截图
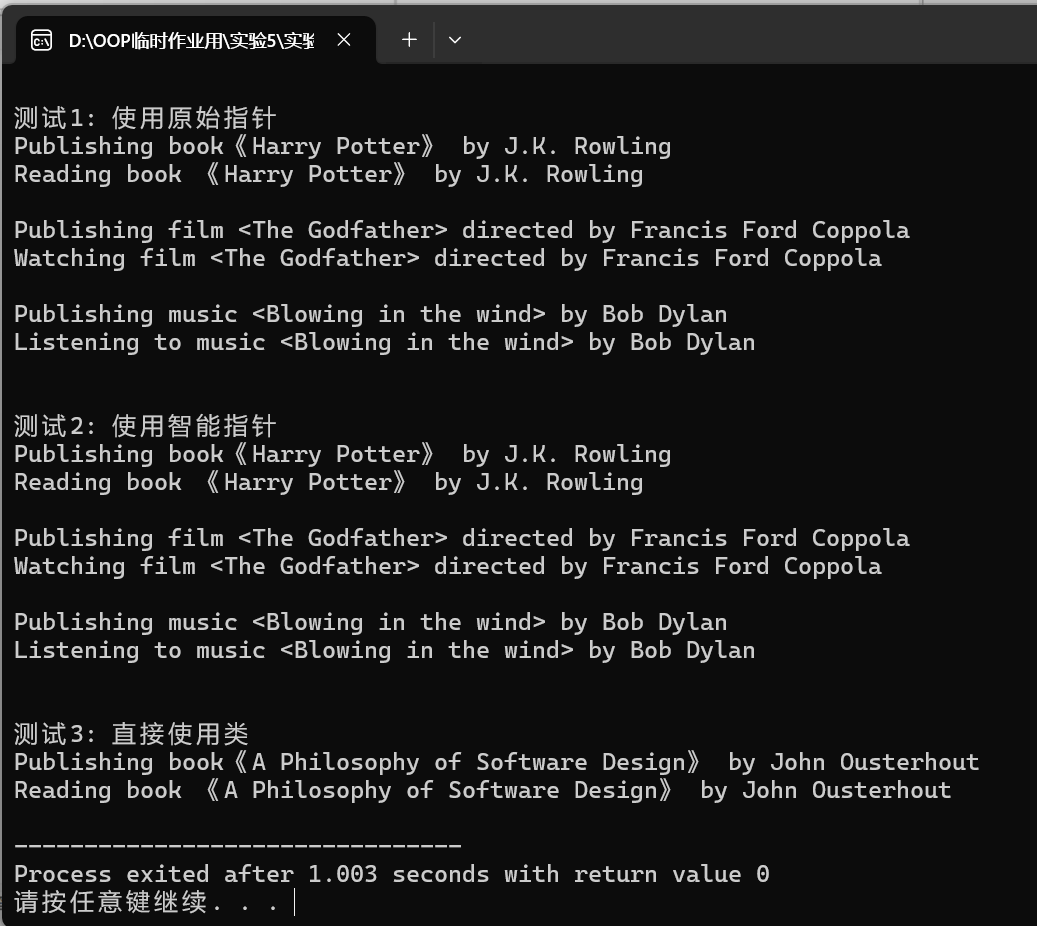
3.问题回答
1.(1)纯虚函数导致publisher是一个抽象类,virtual void publish() const = 0和virtual void use() const = 0他们俩都是纯虚函数
(2)不可以编译,因为抽象没有实体,会报错
2.(1)必须实现上面提到的两个纯虚函数,
//...
void publish() const override;
void use() const override;
三者完整的声明一样,只是所属类不同
(2)
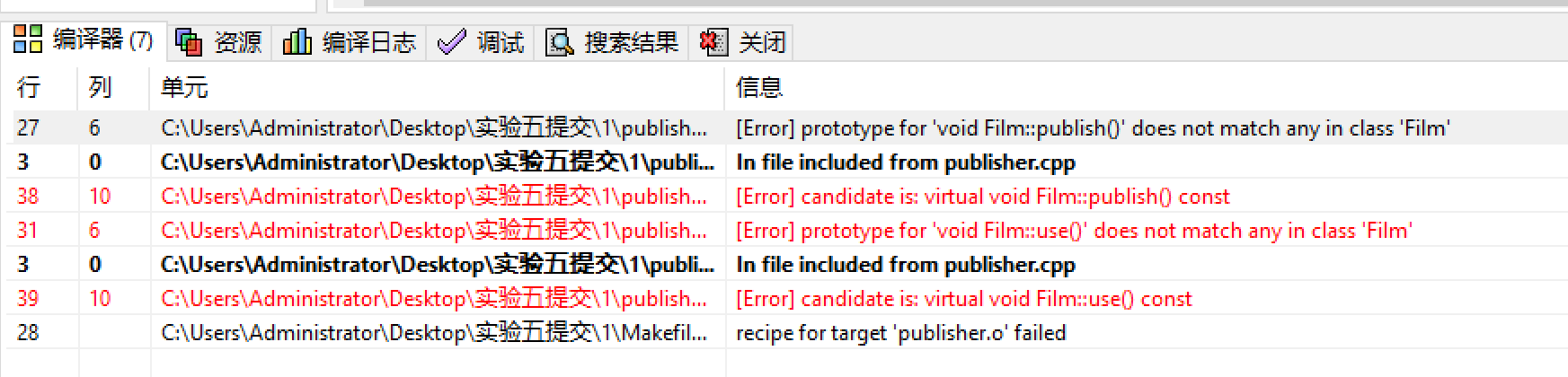
3.(1)Publisher*
(2)book,film,music这三者类的对象
(3)加上以后会在删除内存时删除派生类对象,不加virtual就会只删除基类所占的内存
任务2
1.实验代码

#pragma once #include <string> // 图书描述信息类Book: 声明 class Book { public: Book(const std::string &name_, const std::string &author_, const std::string &translator_, const std::string &isbn_, double price_); friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out, const Book &book); private: std::string name; // 书名 std::string author; // 作者 std::string translator; // 译者 std::string isbn; // isbn号 double price; // 定价 };

#include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include "book.hpp" // 图书描述信息类Book: 实现 Book::Book(const std::string &name_, const std::string &author_, const std::string &translator_, const std::string &isbn_, double price_):name{name_}, author{author_}, translator{translator_}, isbn{isbn_}, price{price_} { } // 运算符<<重载实现 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out, const Book &book) { using std::left; using std::setw; out << left; out << setw(15) << "书名:" << book.name << '\n' << setw(15) << "作者:" << book.author << '\n' << setw(15) << "译者:" << book.translator << '\n' << setw(15) << "ISBN:" << book.isbn << '\n' << setw(15) << "定价:" << book.price; return out; }

#pragma once #include <string> #include "book.hpp" // 图书销售记录类BookSales:声明 class BookSale { public: BookSale(const Book &rb_, double sales_price_, int sales_amount_); int get_amount() const; // 返回销售数量 double get_revenue() const; // 返回营收 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out, const BookSale &item); private: Book rb; double sales_price; // 售价 int sales_amount; // 销售数量 };

#include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include "booksale.hpp" // 图书销售记录类BookSales:实现 BookSale::BookSale(const Book &rb_, double sales_price_, int sales_amount_): rb{rb_}, sales_price{sales_price_}, sales_amount{sales_amount_} { } int BookSale::get_amount() const { return sales_amount; } double BookSale::get_revenue() const { return sales_amount * sales_price; } // 运算符<<重载实现 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out, const BookSale &item) { using std::left; using std::setw; out << left; out << item.rb << '\n' << setw(15) << "售价:" << item.sales_price << '\n' << setw(15) << "销售数量:" << item.sales_amount << '\n' << setw(15) << "营收:" << item.get_revenue(); return out; }

#include <algorithm> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "booksale.hpp" // 按图书销售数量比较 bool compare_by_amount(const BookSale &x1, const BookSale &x2) { return x1.get_amount() > x2.get_amount(); } void test() { using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::getline; using std::sort; using std::string; using std::vector; using std::ws; vector<BookSale> sales_records; // 图书销售记录表 int books_number; cout << "录入图书数量: "; cin >> books_number; cout << "录入图书销售记录\n"; for(int i = 0; i < books_number; ++i) { string name, author, translator, isbn; double price; cout << string(20, '-') << "第" << i+1 << "本图书信息录入" << string(20, '-') << '\n'; cout << "录入书名: "; getline(cin>>ws, name); cout << "录入作者: "; getline(cin>>ws, author); cout << "录入译者: "; getline(cin>>ws, translator); cout << "录入isbn: "; getline(cin>>ws, isbn); cout << "录入定价: "; cin >> price; Book book(name, author, translator, isbn, price); double sales_price; int sales_amount; cout << "录入售价: "; cin >> sales_price; cout << "录入销售数量: "; cin >> sales_amount; BookSale record(book, sales_price, sales_amount); sales_records.push_back(record); } // 按销售册数排序 sort(sales_records.begin(), sales_records.end(), compare_by_amount); // 按销售册数降序输出图书销售信息 cout << string(20, '=') << "图书销售统计" << string(20, '=') << '\n'; for(auto &record: sales_records) { cout << record << '\n'; cout << string(40, '-') << '\n'; } } int main() { test(); }
2.实验截图
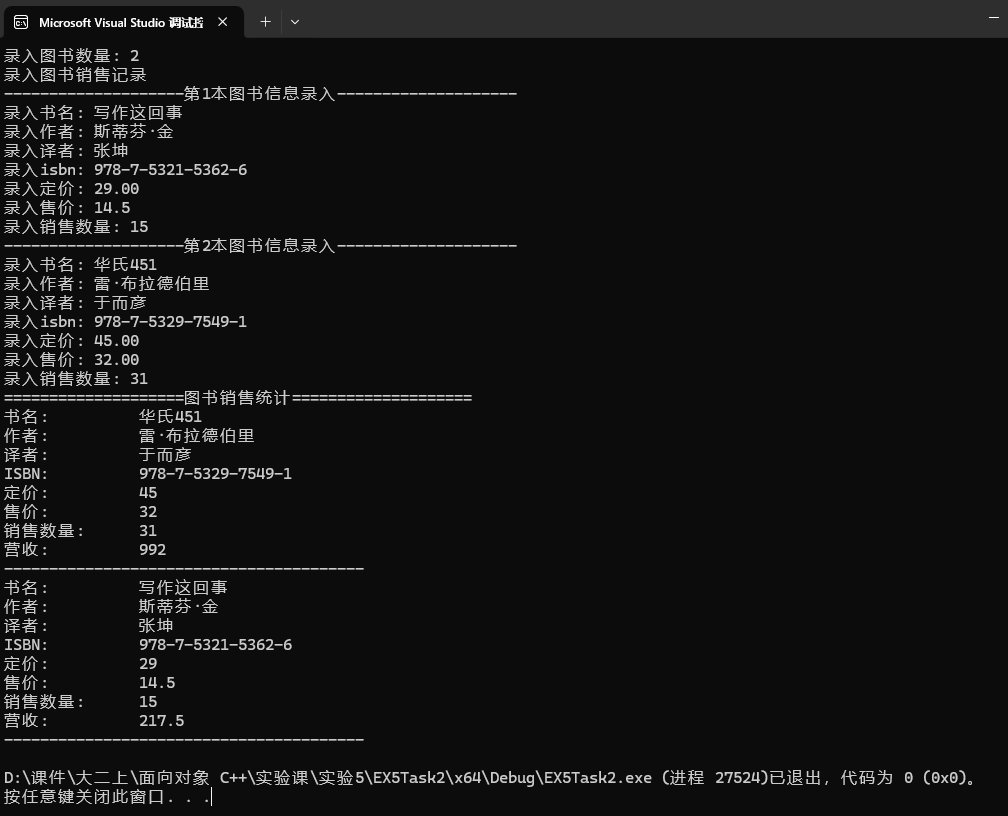
3.问题回答
1.(1)两处,一个是book类,一个是booksale类
(2)第一处:
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out, const BookSale &item) {
using std::left;
using std::setw;
out << left;
out << item.rb << '\n'
<< setw(15) << "售价:" << item.sales_price << '\n'
<< setw(15) << "销售数量:" << item.sales_amount << '\n'
<< setw(15) << "营收:" << item.get_revenue();
return out;
}
第二处:
for(auto &record: sales_records) {
cout << record << '\n';
cout << string(40, '-') << '\n';
}
2.(1)使用sort函数以及定义函数,将销量大的排在前面,后面新加的进行比较,再次排列
任务4
1.实验代码

#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <string> class MachinePet { protected: std::string nickname; public: MachinePet(const std::string &name) : nickname(name) {} virtual ~MachinePet() = default; std::string get_nickname() const { return nickname; } virtual std::string talk() const = 0; }; class PetCat : public MachinePet { public: using MachinePet::MachinePet; std::string talk() const override { return "Neko miao"; } }; class PetDog : public MachinePet { public: using MachinePet::MachinePet; std::string talk() const override { return "Yinu woof"; } };

#include <iostream> #include <memory> #include <vector> #include "pet.hpp" void test1() { std::vector<MachinePet *> pets; pets.push_back(new PetCat("miku")); pets.push_back(new PetDog("da huang")); for(MachinePet *ptr: pets) { std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << '\n'; delete ptr; // 须手动释放资源 } } void test2() { std::vector<std::unique_ptr<MachinePet>> pets; pets.push_back(std::make_unique<PetCat>("miku")); pets.push_back(std::make_unique<PetDog>("da huang")); for(auto const &ptr: pets) std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << '\n'; } void test3() { // MachinePet pet("little cutie"); // 编译报错:无法定义抽象类对象 const PetCat cat("miku"); std::cout << cat.get_nickname() << " says " << cat.talk() << '\n'; const PetDog dog("da huang"); std::cout << dog.get_nickname() << " says " << dog.talk() << '\n'; } int main() { std::cout << "测试1: 使用原始指针\n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: 使用智能指针\n"; test2(); std::cout << "\n测试3: 直接使用类\n"; test3(); }
2.实验截图
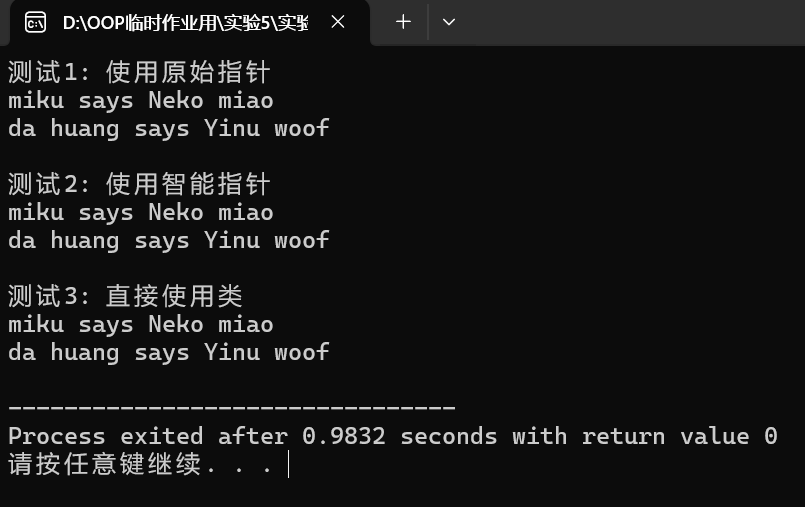
任务
1.实验代码

#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<string> template<typename T> class Complex { private: T real, imag; public: Complex(T r = 0, T i = 0) : real(r), imag(i) {} Complex(const Complex<T>& other) : real(other.real), imag(other.imag) {} T get_real() const { return real; } T get_imag() const { return imag; } Complex<T>& operator+=(const Complex<T>& rhs) { real += rhs.real; imag += rhs.imag; return *this; } friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Complex<T>& c) { os << c.real << (c.imag >= 0 ? "+" : "") << c.imag << "i"; return os; } friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Complex<T>& c) { char sign, i_char; is >> c.real >> sign >> c.imag >> i_char; if (sign == '-') c.imag = -c.imag; return is; } friend Complex<T> operator+(const Complex<T>& a, const Complex<T>& b) { return Complex<T>(a.real + b.real, a.imag + b.imag); } friend bool operator==(const Complex<T>& lhs, const Complex<T>& rhs) { return lhs.real == rhs.real && lhs.imag == rhs.imag; } };

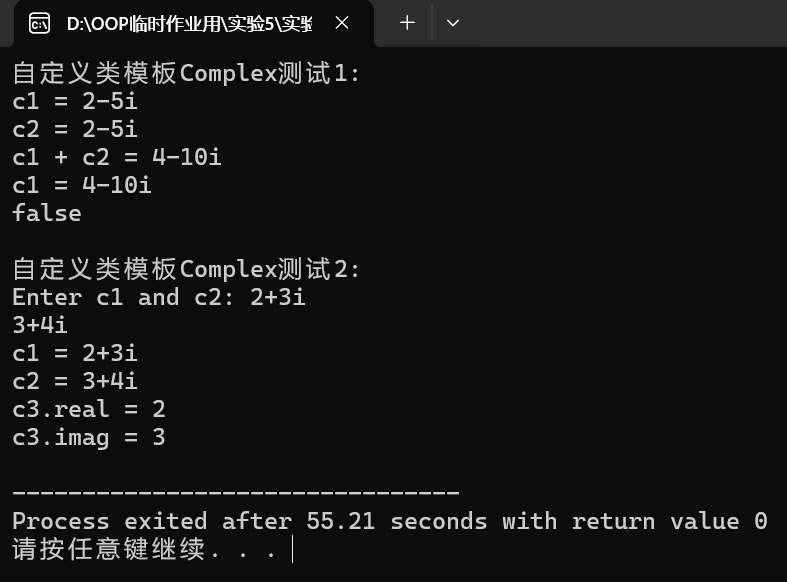
#include <iostream> #include "Complex.hpp" void test1() { using std::cout; using std::boolalpha; Complex<int> c1(2, -5), c2(c1); cout << "c1 = " << c1 << '\n'; cout << "c2 = " << c2 << '\n'; cout << "c1 + c2 = " << c1 + c2 << '\n'; c1 += c2; cout << "c1 = " << c1 << '\n'; cout << boolalpha << (c1 == c2) << '\n'; } void test2() { using std::cin; using std::cout; Complex<double> c1, c2; cout << "Enter c1 and c2: "; cin >> c1 >> c2; cout << "c1 = " << c1 << '\n'; cout << "c2 = " << c2 << '\n'; const Complex<double> c3(c1); cout << "c3.real = " << c3.get_real() << '\n'; cout << "c3.imag = " << c3.get_imag() << '\n'; } int main() { std::cout << "自定义类模板Complex测试1: \n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n自定义类模板Complex测试2: \n"; test2(); }
2.实验截图
实验总结
通过这次实验,我对抽象类与纯虚函数更加熟练,了解了抽象类至少包含一个纯虚函数(= 0),了解了虚析构函数确保派生类对象被正确销毁,防止内存泄漏的重要作用;
对模板类,友元函数与运算符重载有了更深的认识。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号