前三次作业总结
前三次PTA作业总结
前言:
知识点:
(1)第一次题目集:java.util.Scanner方法的运用,if else条件语句、System.out.println分类输出,且和或条件语句,除法和求余运算,一维数组,排序;
(2)第二次题目集:类的创建,日期类的使用,类的封装,多个类的设计;
(3)第三次题目集:多各类的设计,时间类的使用。
体量与难度:
前三次作业难度也不是很大,只有个别题目难以实现,前两次作业对于面向对象考察的不是特别深,多数时候都是考察对数据类型的使用是否准确以及程序的鲁棒性,大部分都是格式上的要求。
到了第三次作业,考察了对类的使用,以及字符串的一些方法和面向对象的特型。
这三次作业也确实让我学到了东西,初学java学起来还是有点吃力,对于类的概念还是不是特别深,多做做题目也好,巩固巩固所学的知识。
设计与分析
第一次作业:
7-6 NCHU_学号识别:
判断学号再输出信息
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int number = sc.nextInt(); int count = 1; int yuan1 = number / 10 / 10 / 10 / 10 % 100; //System.out.print(yuan1); int year = number / 10 / 10 / 10 / 10 / 10 / 10; //System.out.println(year); int classnum = number / 10 / 10 % 100; //System.out.println(classnum); int num = number % 100; String fillString = fillString(num, 2); //System.out.println(fillString); while (number / 10 != 0) { number = number / 10; count++; } if (count != 8 || (yuan1 != 1 && yuan1 != 2 && yuan1 != 3 && yuan1 != 20)) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { System.out.println("入学年份:20" + year + "年"); if (yuan1 == 1) { System.out.println("学院:材料学院"); } else if (yuan1 == 2) { System.out.println("学院:机械学院"); } else if (yuan1 == 3) { System.out.println("学院:外语学院"); } else if (yuan1 == 20) { System.out.println("学院:软件学院"); } System.out.println("班级:" + classnum); System.out.println("学号:" + fillString); } } public static String fillString(int num, int digit) { return String.format("%0" + digit + "d", num); } }
这里我用取余的方式将入学年份,学院号,班级号,班级内部学号从学号中分别取出,再加以判断,最后输出想要的结果,应该是还有更简便的方法,学艺不精,希望能够加以改进。
7-7 判断三角形类型:
输入三角形三条边,判断该三角形为什么类型的三角形
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); float a = sc.nextFloat(); float b = sc.nextFloat(); float c = sc.nextFloat(); if (a < 1 || a > 200 || b < 1 || b > 200 || c < 1 || c > 200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { if (a + b <= c || a + c <= b || b + c <= a) { System.out.println("Not a triangle"); } else if (a == b && a == c && b == c) { System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); } else if ((a == b || a == c || b == c) && (Math.abs(a * a + b * b - c * c) < 0.000001 || Math.abs(a * a + c * c - b * b) < 0.000001 || Math.abs(c * c + b * b - a * a) < 0.000001)) { System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); } else if (a == b || a == c || b == c) { System.out.println("Isosceles triangle"); } else if (Math.abs(a * a + b * b - c * c) < 0.000001 || Math.abs(a * a + c * c - b * b) < 0.000001 || Math.abs(c * c + b * b - a * a) < 0.000001) { System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); } else { System.out.println("General triangle"); } } } }
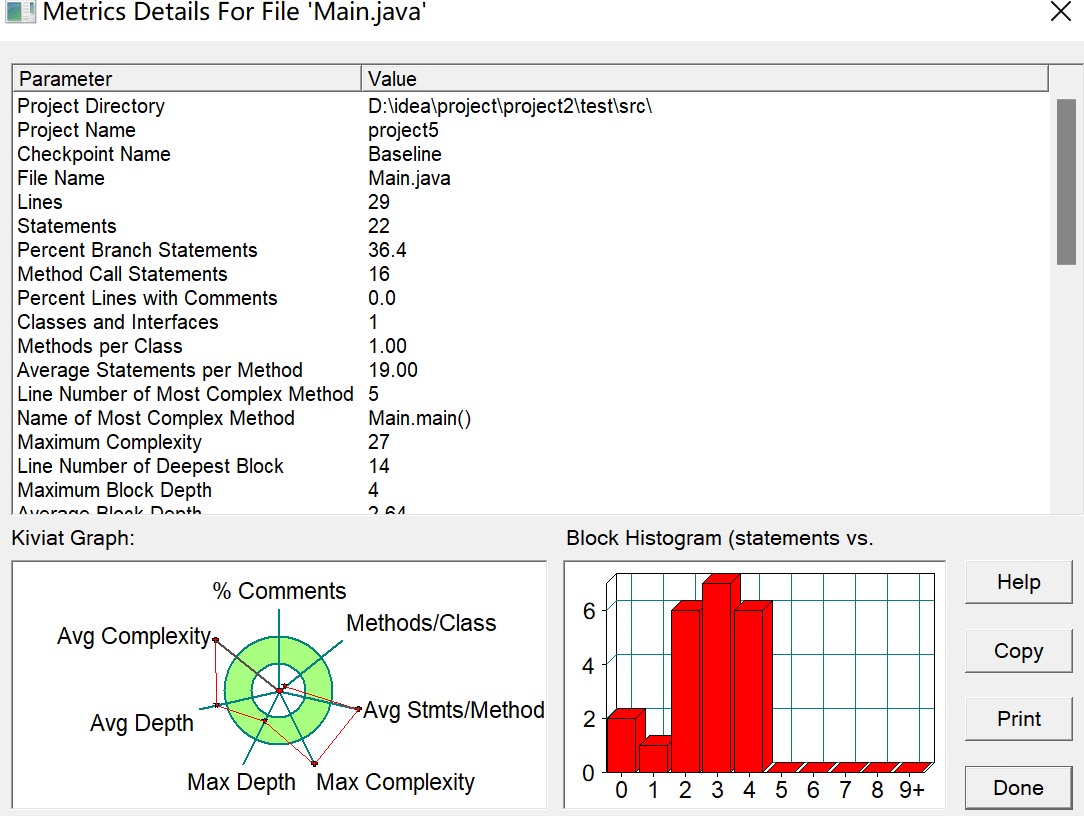
此题需要注意的一点就是直角三角形的判定,因为计算机无法输入完全精确的数字,永远都是接近,所以在一些长度大小带根号的边的三角形中通过计算机的计算会存在一些误差,因此直角三角形的判断语句应该是两直角边平方之和与第三边平方的差小于某一很小的数,这样才能较为精确地判断直角
第二次作业:
7-1 成绩计算-1-类、数组的基本运用:
创建学生类,包含
属性:学号(String)、姓名(String)、语文成绩(int)、数学成绩(int)、物理成绩(int)
方法:计算总分、计算平均分
输入5个学生的信息,将每个学生的信息封装在一个学生对象中。
import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Scanner; class student { String id; String name; int chinese; int math; int phy; } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); student[] stus = new student[5]; DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.00"); int[] sum = new int[5]; double[] average = new double[5]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { student stu1 = new student(); stu1.id = sc.next(); stu1.name = sc.next(); stu1.chinese = sc.nextInt(); stu1.math = sc.nextInt(); stu1.phy = sc.nextInt(); stus[i] = stu1; sum[i] = stus[i].chinese + stus[i].math + stus[i].phy; average[i]=(double)sum[i]/3; } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println(stus[i].id+" "+stus[i].name+" " +sum[i]+" "+df.format(average[i])); } } }
这道题创建学生类对象,实现对学生成绩的计算,这道题的主要难点就是最后的平均值取两位小数的方法,主要输出的格式。
7-2 成绩计算-2-关联类:
创建成绩类,包含:
属性:平时成绩(int)、期末成绩(int)
方法:计算总成绩(计算规则:平时成绩*0.4+期末成绩*0.6,保留整数部分,小数部分直接丢弃)
创建学生类,包含:
属性:学号(String)、姓名(String)、语文成绩(成绩类)、数学成绩(成绩类)、物理成绩(成绩类)
方法:计算总分、计算平均分
输入3个学生的信息,将每个学生的信息封装在一个学生对象中。
import java.util.Scanner; import java.text.DecimalFormat; class score { int startscore; int endscore; public score() { } public score(int startscore, int endscore) { this.startscore = startscore; this.endscore = endscore; } /** * 获取 * * @return startscore */ public int getStartscore() { return startscore; } /** * 设置 * * @param startscore */ public void setStartscore(int startscore) { this.startscore = startscore; } /** * 获取 * * @return endscore */ public int getEndscore() { return endscore; } /** * 设置 * * @param endscore */ public void setEndscore(int endscore) { this.endscore = endscore; } public int scoresum(int startscore, int endscore) { int scoresum = (int) (startscore * 0.4 + endscore * 0.6); return scoresum; } } class student { String id; String name; //String subject; score chinese; score math; score phy; public student() { } public student(String id, String name, score chinese, score math, score phy) { this.id = id; this.name = name; //this.subject = subject; this.chinese = chinese; this.math = math; this.phy = phy; } /** * 获取 * * @return id */ public String getId() { return id; } /** * 设置 * * @param id */ public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } /** * 获取 * * @return name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * 设置 * * @param name */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * 获取 * * @return subject */ /* public String getSubject() { return subject; } */ /** * 设置 * * @param subject */ /*public void setSubject(String subject) { this.subject = subject; }*/ /** * 获取 * * @return chinese */ public score getChinese() { return chinese; } /** * 设置 * * @param chinese */ public void setChinese(score chinese) { this.chinese = chinese; } /** * 获取 * * @return math */ public score getMath() { return math; } /** * 设置 * * @param math */ public void setMath(score math) { this.math = math; } /** * 获取 * * @return phy */ public score getPhy() { return phy; } /** * 设置 * * @param phy */ public void setPhy(score phy) { this.phy = phy; } public double startaverage(score chinesescore, score mathscore, score physcore) { double startaverage =(chinesescore.startscore+mathscore.startscore+physcore.startscore)*1.00/3; return startaverage; } public double endaverage(score chinesescore, score mathscore, score physcore) { double endaverage =(chinesescore.endscore+mathscore.endscore+physcore.endscore)*1.00/3; return endaverage; } public int all(score chinesescore, score mathscore, score physcore){ return (chinesescore.scoresum(chinesescore.getStartscore(),chinesescore.getEndscore())+ mathscore.scoresum(mathscore.getStartscore(),mathscore.getEndscore()) +physcore.scoresum(physcore.getStartscore(),physcore.getEndscore())); } public double allaverage(score chinesescore, score mathscore, score physcore){ double average=(chinesescore.scoresum(chinesescore.getStartscore(),chinesescore.getEndscore())+ mathscore.scoresum(mathscore.getStartscore(),mathscore.getEndscore()) +physcore.scoresum(physcore.getStartscore(),physcore.getEndscore()))*1.00/3; return average; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); student[] stus = new student[3]; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { String ID = in.next(); String name = in.next(); String subject = in.next(); score mathscore = new score(in.nextInt(),in.nextInt()); String ID1 = in.next(); String name1 = in.next(); String subject1 = in.next(); score chinesescore = new score(in.nextInt(),in.nextInt()); String ID2 = in.next(); String name2 = in.next(); String subject2 = in.next(); score physcore = new score(in.nextInt(),in.nextInt()); stus[i] = new student(ID,name,mathscore,chinesescore,physcore); } for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { int all = stus[j].all(stus[j].getChinese(),stus[j].getMath(),stus[j].getPhy()); double averageall = stus[j].allaverage(stus[j].getChinese(),stus[j].getMath(),stus[j].getPhy()); double averagestart = stus[j].startaverage(stus[j].getChinese(),stus[j].getMath(),stus[j].getPhy()); double averageend = stus[j].endaverage(stus[j].getChinese(),stus[j].getMath(),stus[j].getPhy()); System.out.println(stus[j].getId() + " "+stus[j].getName() + " " + all + " "+ String.format("%.2f",averagestart ) + " " +String.format("%.2f",averageend ) + " " +String.format("%.2f",averageall )); } } }
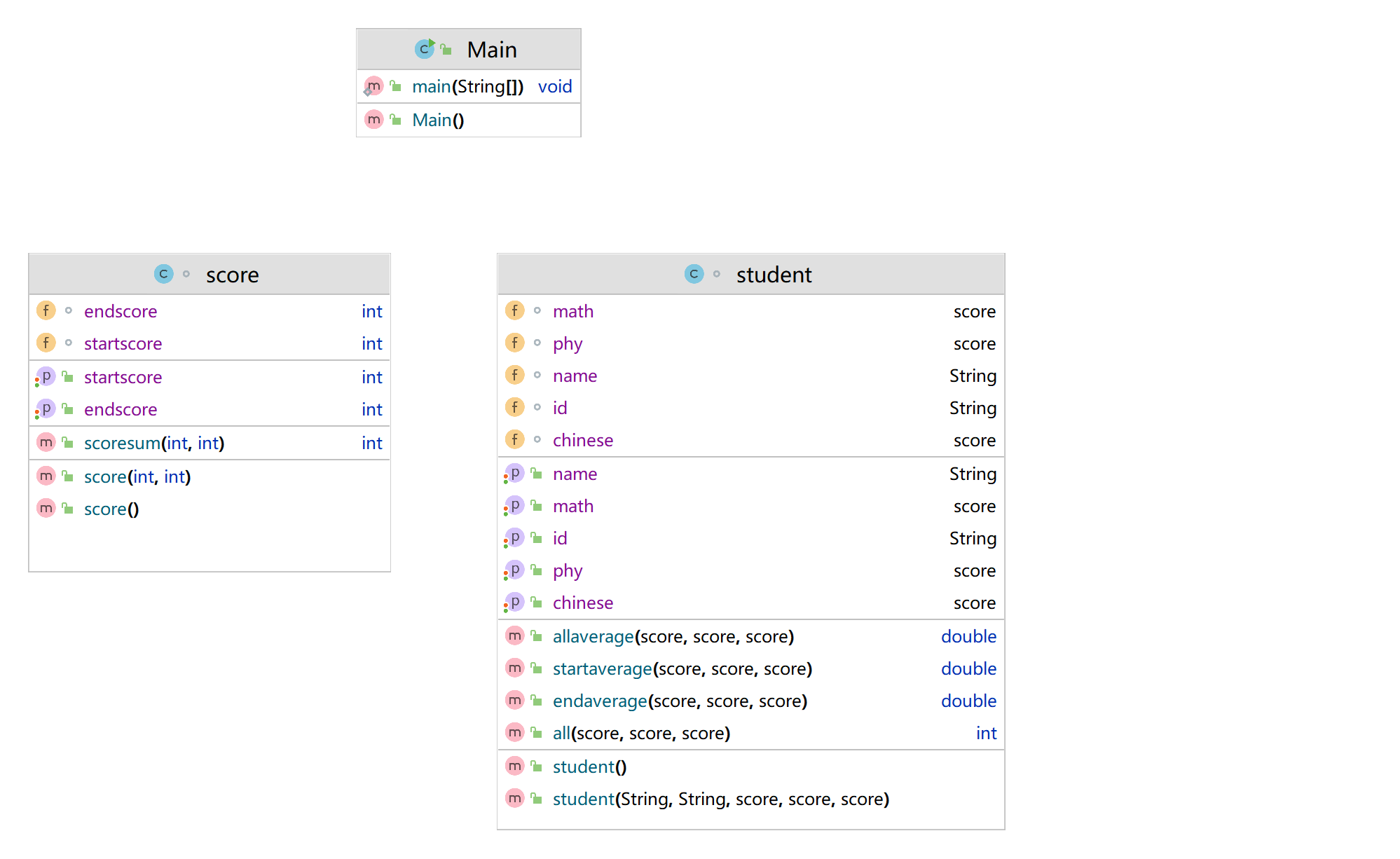
这道题算是上一道题的加强,创建一个成绩类和一个学生类,在学生类中实现一系列求值得操作,一开始那个课程顺序不一致的测试点一直过不去,用的是让输入得课程字符串去匹配数学语文物理,后来不知道是哪里的问题过不了,索性不匹配直接让值随便取,就不需要考虑科目不成绩不对得问题(求值也不管是哪门成绩),刚开始得方法应该也是可以写,不过那里有点瑕疵;
7-7 菜单计价程序-1:
份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份)不同份额菜价的计算方法:
小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。
中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。
小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。
如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Menu menus = new Menu(); Dish dish = new Dish("西红柿炒蛋", 15); menus.add(dish); dish = new Dish("清炒土豆丝", 12); menus.add(dish); dish = new Dish("麻婆豆腐", 12); menus.add(dish); dish = new Dish("油淋生菜", 9); menus.add(dish); String s = sc.next(); Order orders = new Order(menus); while (s.equals("end") == false) { int portion = sc.nextInt(); if (orders.addARecord(s, portion) == null) { System.out.println(s + " does not exist"); } s = sc.next(); } System.out.println(orders.getTotalPrice()); } } class Dish { String dishname; int unit_price; Dish(String dishname, int unit_price) { this.dishname = dishname; this.unit_price = unit_price; } int getPrice(int portion) { //计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3, int price = 0; if (portion == 1) price = unit_price; if (portion == 2) price = (int)(unit_price*1.5); if (portion == 3) price = unit_price * 2; return price; } } class Menu { ArrayList<Dish> menus = new ArrayList<>(); void add(Dish dish) { menus.add(dish); } Dish searthDish(String dishName) { for (int i = 0; i < menus.size(); i++) { if (menus.get(i).dishname.equals(dishName)) return menus.get(i); } return null; } } class Record { Dish dish; int portion; Record(Dish dish, int portion) { this.dish = dish; this.portion = portion; } int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格 { int price = dish.getPrice(portion); return price; } } class Order { ArrayList<Record> records = new ArrayList<>(); Menu menus; Order(Menu menus) { this.menus = menus; } Record addARecord(String dishName, int portion)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。 { Dish dish = menus.searthDish(dishName); Record record = null; if (dish != null) { record = new Record(dish, portion); records.add(record); } return record; } int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价 { int allprice = 0; for (int i = 0; i < records.size(); i++) { allprice += records.get(i).getPrice(); } return allprice; } }
这题复杂的即使理清各个类得逻辑关系,通过各个类实现对订单总价得计算;将点菜记录类和菜谱类设计为数组集合类型,更方便对里面的数据进行处理;开始写时候差点将份额和单词搞混,要仔细检查。这道题主要是对各个类的设计,虽然多了几个,但好在都不太复杂。耐下心写应该是没有问题;
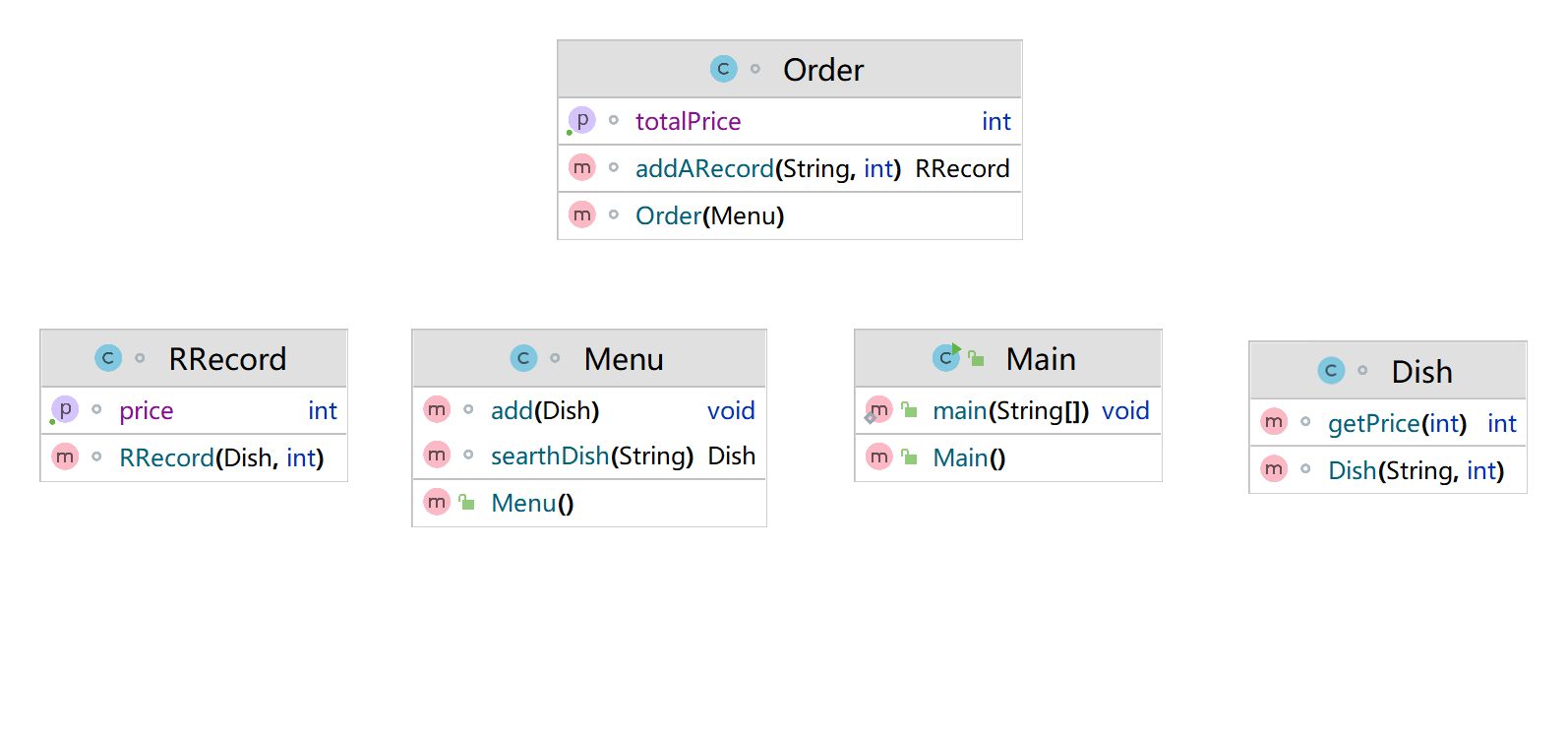
7-8 jmu-java-日期类的基本使用:
- 给定一个日期,判定是否为合法日期。如果合法,判断该年是否闰年,该日期是当年第几天、当月第几天、当周第几天、。
- 给定起始日期与结束日期,判定日期是否合法且结束日期是否早于起始日期。如果均合法,输出结束日期与起始日期之间的相差的天数、月数、念书。
import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.ParsePosition; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.time.Year; import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String stime = sc.nextLine(); String[] list = stime.split("-"); int year = Integer.parseInt(list[0]); int mouth = Integer.parseInt(list[1]); int day = Integer.parseInt(list[2]); String qujian_time = sc.nextLine(); boolean flag = istime(stime, "yyyy-MM-dd"); if (judgement(year, mouth, day) == true && flag == true) { Calendar cend = Calendar.getInstance(); cend.set(year, mouth - 1, day); int Weekday = cend.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); int Mounthday = cend.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH); int Yeardya = cend.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR); if (Weekday == 1) { Weekday = 7; } else { Weekday = Weekday - 1; } Year firstYear = Year.of(year); if (firstYear.isLeap()) { System.out.println(stime + "是闰年."); } System.out.println(stime + "是当年第" + Yeardya + "天" + ",当月第" + Mounthday + "天,当周第" + Weekday + "天."); } else { System.out.println(stime + "无效!"); } String[] list1 = qujian_time.split(" "); boolean stime1 = istime(list1[0], "yyyy-MM-dd"); boolean stime2 = istime(list1[1], "yyyy-MM-dd"); if (stime1 == false || stime2 == false) { System.out.println(list1[0] + "或" + list1[1] + "中有不合法的日期."); System.exit(0); } DateFormat dateformat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); try { Date startime = dateformat.parse(list1[0]);//开始时间 String[] s1 = list1[0].split("-"); int stime1t1 = Integer.parseInt(s1[1]); int stime1t2 = Integer.parseInt(s1[0]); String[] s2 = list1[1].split("-"); int stime2t1 = Integer.parseInt(s2[1]); int stime2t2 = Integer.parseInt(s2[0]); Date endtime = dateformat.parse(list1[1]); int temp1 = 0, temp2 = 0, temp3 = 0; if (startime.before(endtime)) { Year yearflag = Year.of(stime1t2); temp3 = stime2t2 - stime1t2; Calendar cend1 = Calendar.getInstance(); //这里有bug必须减1 cend1.set(stime1t2, stime1t1 - 1, Integer.parseInt(s1[2])); // 设置年月日,时分秒将默认采用当前值 int yearDay = cend1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR); Calendar cend2 = Calendar.getInstance(); //这里有bug必须减1 cend2.set(stime2t2, stime2t1 - 1, Integer.parseInt(s2[2])); // 设置年月日,时分秒将默认采用当前值 int yearDa2y = cend2.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR); if (yearflag.isLeap(stime1t2)) { int temp = yearDa2y + (366 - yearDay); for (int i = stime1t2 + 1; i < stime2t2; i++) { if (yearflag.isLeap(i)) { temp1 += 366; } else { temp1 += 365; } } temp1 += temp; } else { int temp = yearDa2y + (365 - yearDay); for (int i = stime1t2 + 1; i < stime2t2; i++) { if (yearflag.isLeap(i)) { temp1 += 366; } else { temp1 += 365; } } temp1 += temp; } temp2 = Integer.parseInt(s2[1]) - Integer.parseInt(s1[1]); } if (endtime.before(startime)) { System.out.println(list1[1] + "早于" + list1[0] + ",不合法!"); System.exit(0); } if ((judgement(stime1t2, stime1t1, Integer.parseInt(s1[2])) == true) && judgement(stime2t2, stime2t1, Integer.parseInt(s2[2])) == true) { System.out.println(list1[1] + "与" + list1[0] + "之间相差" + temp1 + "天," + "所在月份相差" + temp2 + ",所在年份相差" + temp3 + "."); } else { System.out.println(list1[0] + "或" + list1[1] + "中有不合法的日期."); } } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static boolean istime(String date, String format) { if (date == null || date.isEmpty() || format == null || format.isEmpty()) { return false; } if (format.replaceAll("'.+?'", "").indexOf("y") < 0) { format += "/yyyy"; DateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("/yyyy"); date += formatter.format(new Date()); } String regex = "^\\d{4}\\-(0[1-9]|1[012])\\-(0[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01])$"; if (!date.matches(regex)) { return false; } DateFormat formates = new SimpleDateFormat(format); formates.setLenient(false); ParsePosition pp = new ParsePosition(0); Date dates = formates.parse(date, pp); if (date == null || pp.getErrorIndex() > 0) { return false; } if (pp.getIndex() != date.length()) { return false; } if (formates.getCalendar().get(Calendar.YEAR) > 9999) { return false; } return true; } public static boolean judgement(int year, int mounth, int day) { boolean flag = false; if (mounth == 1 || mounth == 3 || mounth == 5 || mounth == 7 || mounth == 8 || mounth == 10 || mounth == 12) { if (day <= 31) { flag = true; } else { flag = false; } } else if (mounth < 1 || mounth > 12) { flag = false; } else if (mounth == 2) { if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)) { if (day > 29) { flag = false; } else { flag = true; } } else { if (day > 28) { flag = false; } else { flag = true; } } } else { if (day > 30) { flag = false; } else { flag = true; } } return flag; } }
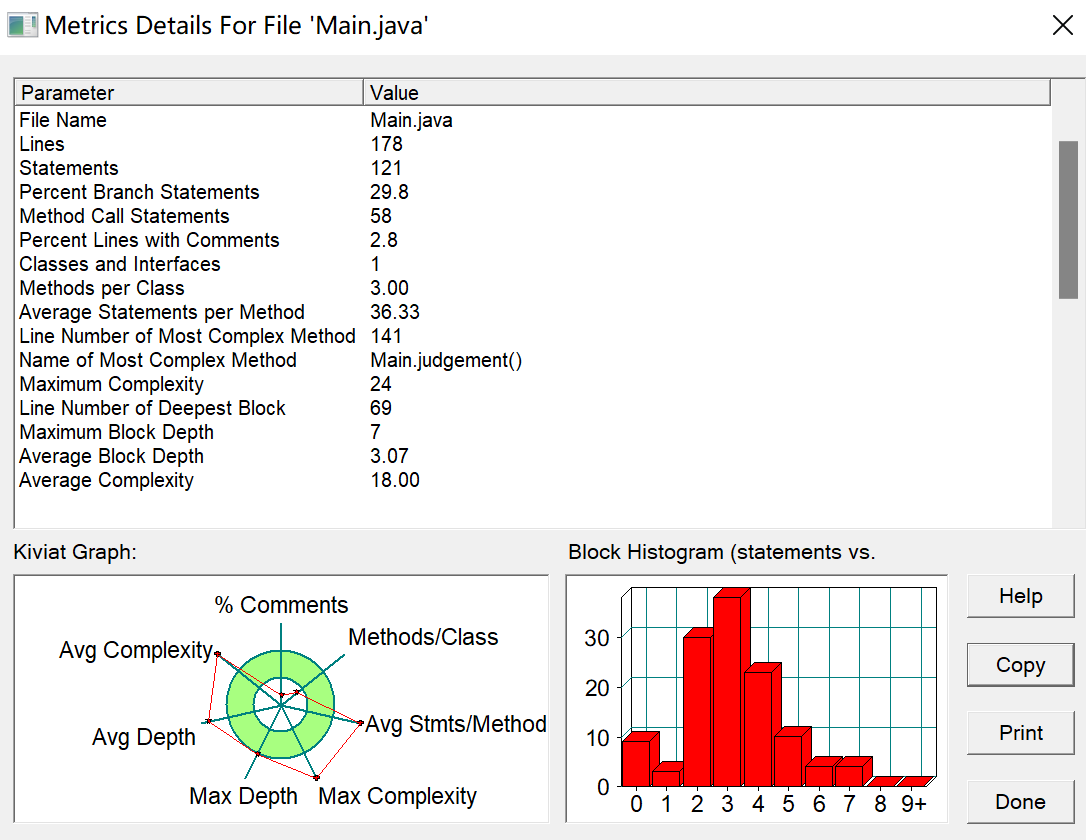
这题难就难在对时间类的使用上,如何判断输入的时间格式对或不对,怎么将输入的时间格式改成自己想要的时间格式,怎样使用自己想要的时间数据,怎样判断输入的时间是否是闰年,以及是闰年该怎样处理;通过对输入的字符串时间处理得到输入事件的年月日,再通过函数isTime判断时间的输入格式对不对,通过对时间类的使用将得到的年月日装换成我们想要的年月日格式,再通过judgement函数判断是否是闰年,最后在进行一系列判断,最后输出结果。我觉得这道题的核心在于各种情况的条件判断,各种特殊情况的考虑。
第三次作业
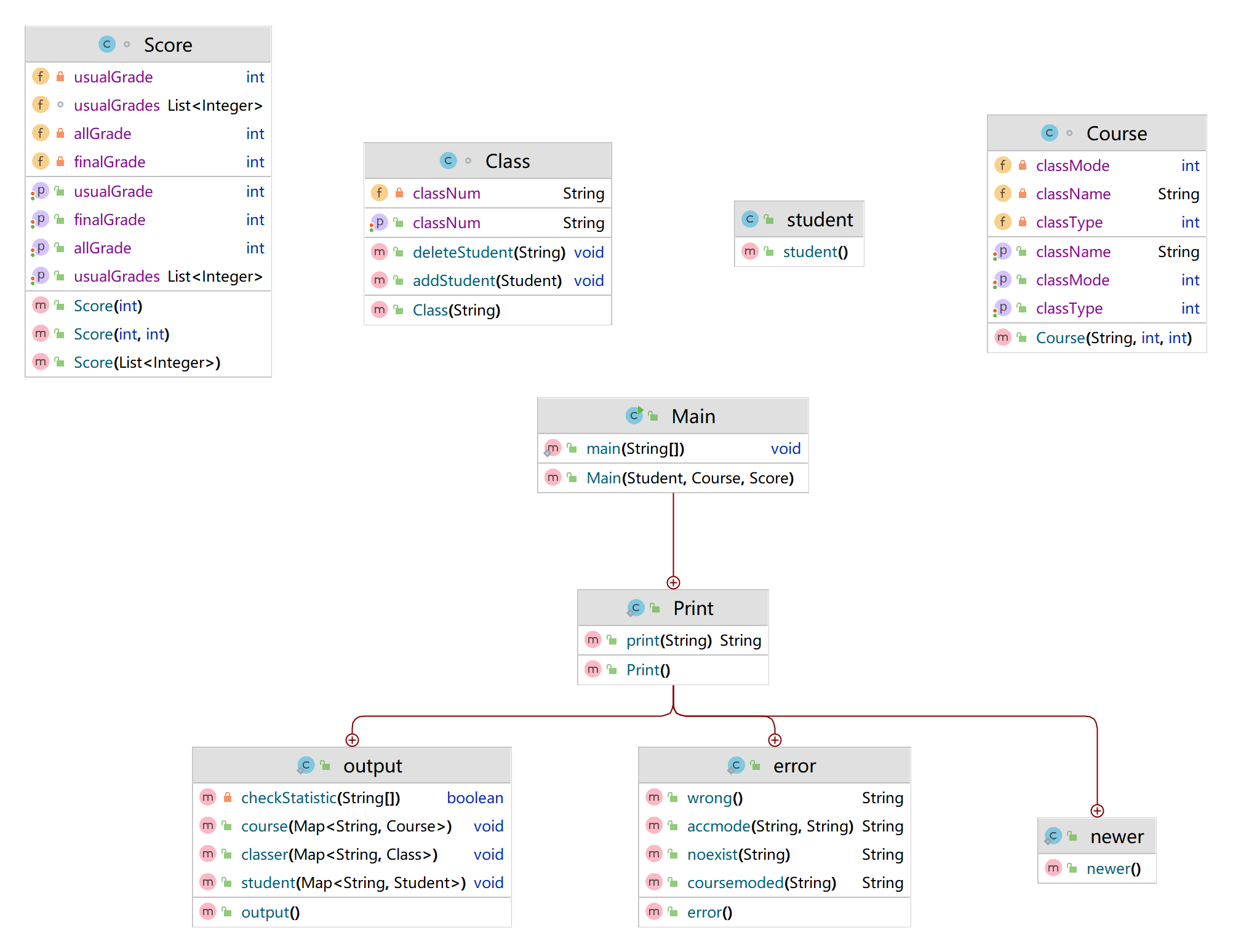
7-2 课程成绩统计程序-1:
某高校课程从性质上分为:必修课、选修课,从考核方式上分为:考试、考察。
考试的总成绩由平时成绩、期末成绩分别乘以权重值得出,比如平时成绩权重0.3,期末成绩权重0.7,总成绩=平时成绩*0.3+期末成绩*0.7。
考察的总成绩直接等于期末成绩
必修课的考核方式必须为考试,选修课可以选择考试、考察任一考核方式。
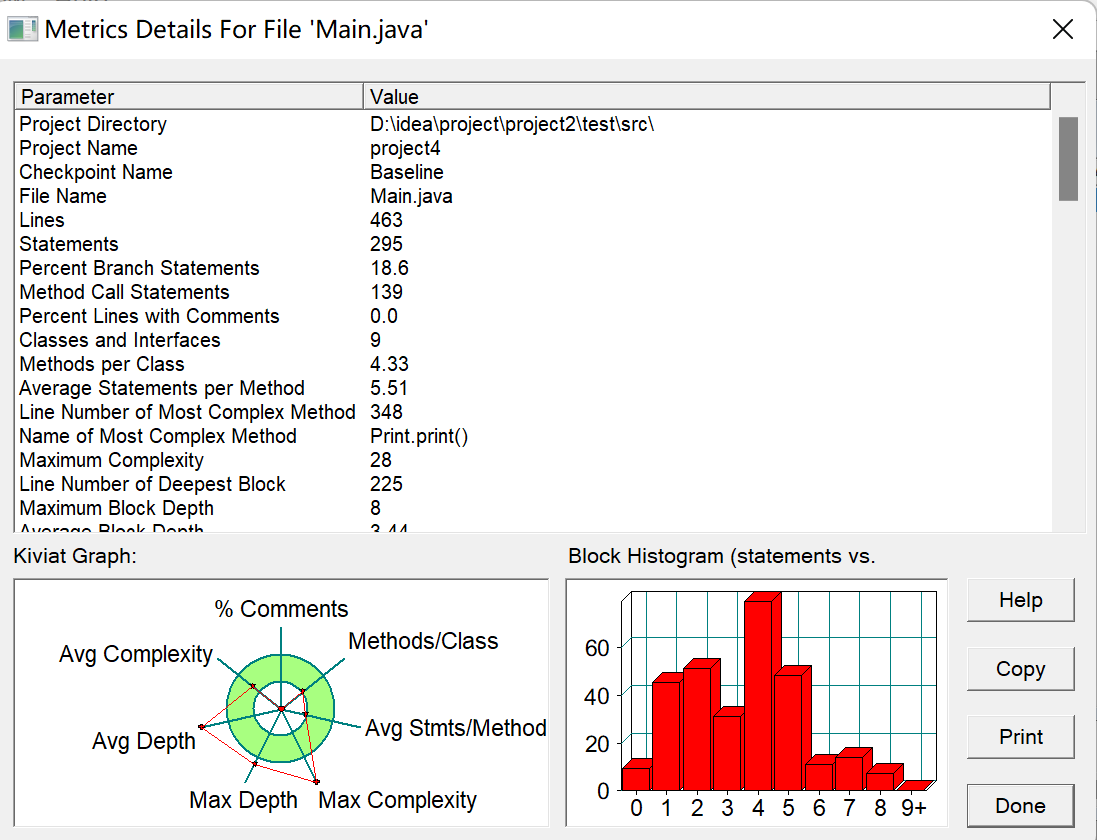
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.*; class Student { private String name; private String studentNum; Student(String name, String studentNum) { setName(name); setStudentNum(studentNum); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getStudentNum() { return studentNum; } public void setStudentNum(String studentNum) { this.studentNum = studentNum; } } class Course { private String className; private int classType; private int classMode; public Course(String className, int classType, int classMode) { this.className = className; this.classType = classType; this.classMode = classMode; } public String getClassName() { return className; } public void setClassName(String className) { this.className = className; } public int getClassType() { return classType; } public void setClassType(int classType) { this.classType = classType; } public int getClassMode() { return classMode; } public void setClassMode(int classMode) { this.classMode = classMode; } } class Score { List<Integer> usualGrades; private int allGrade = 0; private int finalGrade = 0; private int usualGrade = 0; public Score(int finalGrade) { this.finalGrade = finalGrade; this.allGrade = finalGrade; } public Score(int finalGrade, int usualGrade) { this.finalGrade = finalGrade; this.usualGrade = usualGrade; this.allGrade = (int) (finalGrade * 0.7 + usualGrade * 0.3); } public List<Integer> getUsualGrades() { return usualGrades; } public void setUsualGrades(List<Integer> usualGrades) { this.usualGrades = usualGrades; } public void setAllGrade(int allGrade) { this.allGrade = allGrade; } public int getFinalGrade() { return finalGrade; } public void setFinalGrade(int finalGrade) { this.finalGrade = finalGrade; } public int getUsualGrade() { return usualGrade; } public void setUsualGrade(int usualGrade) { this.usualGrade = usualGrade; } public Score(List<Integer> usualGrades) { this.usualGrades = usualGrades; for (int x : usualGrades) { this.allGrade += x; } this.allGrade = this.allGrade / usualGrades.size(); } public int getAllGrade() { return this.allGrade; } } class Class { private String classNum; HashMap<String, Student> students; public Class(String classNum) { this.classNum = classNum; } public void setClassNum(String classNum) { this.classNum = classNum; } public String getClassNum() { return classNum; } public void addStudent(Student student) { students.put(student.getStudentNum(), student); } public void deleteStudent(String studentNum) { students.remove(studentNum); } } public class Main { Student student; Course course; Score score; public Main(Student student, Course course, Score score) { this.student = student; this.course = course; this.score = score; } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader sc = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); Print print = new Print(); StringBuilder f1 = new StringBuilder(); boolean flag = false; while (true) { String f0 = sc.readLine(); if (f0 != null && "end".equals(f0.trim())) { if (f1.length() > 0) { System.out.println(f1); } print.output.student(print.newer.students); print.output.course(print.newer.courses); print.output.classer(print.newer.classes); break; } String pprint = print.print(f0); if (pprint != null && pprint.trim().length() > 0) { if (!flag) { f1.append(pprint); flag = true; } else { f1.append("\n").append(pprint); } } } } public static class Print { public static class output { private boolean checkStatistic(String[] s) { if (Print.newer.list != null && !Print.newer.list.isEmpty()) { for (Main statistic : Print.newer.list) { if (statistic.student.getStudentNum().equals(s[0]) && statistic.student.getName().equals(s[1]) && statistic.course.getClassName().equals(s[2])) { return true; } } } return false; } public void student(Map<String, Student> students) { Set<String> set = students.keySet(); String[] arr = set.toArray(new String[0]); Arrays.sort(arr); for (String key : arr) { int temp1 = 0, temp2 = -1; for (Main statistic : Print.newer.list) { if (students.get(key).getStudentNum().equals(statistic.student.getStudentNum())) { if (temp2 == -1) { temp2 = 0; } temp1 += statistic.score.getAllGrade(); temp2++; } } if (temp2 == -1) { System.out.println(students.get(key).getStudentNum() + " " + students.get(key).getName() + " did not take any exams"); continue; } temp1 = temp1 / temp2; System.out.println(students.get(key).getStudentNum() + " " + students.get(key).getName() + " " + temp1); } } public void course(Map<String, Course> courses) { Set<String> set = courses.keySet(); String[] arr = set.toArray(new String[0]); Arrays.sort(arr); for (String key : arr) { int x = 0, y = -1, f = 0, u = 0, uy = -1, s = -1; for (Main statistic : Print.newer.list) { if (courses.get(key).getClassName().equals(statistic.course.getClassName())) { if (y == -1) { y = 0; } if (courses.get(key).getClassMode() == 1 && uy == -1) { uy = 0; } if (courses.get(key).getClassMode() == 3 && s == -1) { s = 0; } x += statistic.score.getAllGrade(); f += (statistic.score).getFinalGrade(); if (statistic.score.getUsualGrade() != 0) { u += (statistic.score).getUsualGrade(); uy++; } y++; } } if (y == -1) { System.out.println(courses.get(key).getClassName() + " has no grades yet"); continue; } x = x / y; f = f / y; if (s == 0) { System.out.println(courses.get(key).getClassName() + " " + x); continue; } if (uy == -1) { System.out.println(courses.get(key).getClassName() + " " + f + " " + x); } if (uy != -1) { u = u / uy; System.out.println(courses.get(key).getClassName() + " " + u + " " + f + " " + x); } } } public void classer(Map<String, Class> classes) { Set<String> set = classes.keySet(); String[] arr = set.toArray(new String[0]); Arrays.sort(arr); for (String key : arr) { int temp1 = 0, temp2 = -1; for (Main statistic : Print.newer.list) { if (classes.get(key).students.containsKey(statistic.student.getStudentNum())) { if (temp2 == -1) { temp2 = 0; } temp1 += statistic.score.getAllGrade(); temp2++; } } if (temp2 == -1) { System.out.println(classes.get(key).getClassNum() + " has no grades yet"); continue; } temp1 = temp1 / temp2; System.out.println(classes.get(key).getClassNum() + " " + temp1); } } } public static class error { public String wrong() { return "wrong format"; } public String noexist(String name) { return name + " does not exist"; } public String accmode(String studentNo, String studentName) { return studentNo + " " + studentName + " : access mode mismatch"; } public String coursemoded(String curse) { return curse + " : course type & access mode mismatch"; } } public static class newer { List<String> test = Arrays.asList("必修", "选修", "实验"); List<String> mode = Arrays.asList("考试", "考察", "实验"); String reg = "^([0-9]{8})( )(\\S{1,10})( )(\\S{1,10})( )([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|100)( )([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|100)$"; String reg1 = "^([0-9]{8})( )(\\S{1,10})( )(\\S{1,10})( )([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|10{2})$"; String reg2 = "^(\\S{1,10})( )(必修|选修|实验)( )(考试|考察|实验)$"; String reg3 = "^([0-9]{8})( )(\\S{1,10})( )(\\S{1,10})( )([4-9])( )((([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|100)( ))+)([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|100)$"; String reg4 = "^(\\S{1,10})( )(必修)$"; Map<String, Class> classes = new HashMap<>(); Map<String, Student> students = new HashMap<>(); Map<String, Course> courses = new HashMap<>(); public static List<Main> list = new ArrayList<>(); } output output = new output(); error error = new error(); static newer newer = new newer(); public String print(String str) { String[] s = str.split(" "); if (str.matches(newer.reg)) { if (output.checkStatistic(s)) { return null; } Student student = new Student(s[1], s[0]); newer.students.put(s[0], student); String classNum = s[0].substring(0, 6); if (!newer.classes.containsKey(classNum)) { Class aClass = new Class(classNum); newer.classes.put(classNum, aClass); newer.classes.get(classNum).students = new HashMap<>(); } newer.classes.get(classNum).students.put(s[0], student); if (!newer.courses.containsKey(s[2])) { return error.noexist(s[2]); } if (newer.courses.get(s[2]).getClassMode() != 1) { return error.accmode(s[0], s[1]); } int finalGrade = Integer.parseInt(s[4]); int usualGrade = Integer.parseInt(s[3]); Main statistic = new Main(student, newer.courses.get(s[2]), new Score(finalGrade, usualGrade)); Print.newer.list.add(statistic); return null; } if (str.matches(newer.reg1)) { if (output.checkStatistic(s)) { return null; } Student student = new Student(s[1], s[0]); newer.students.put(s[0], student); String classNum = s[0].substring(0, 6); if (!newer.classes.containsKey(classNum)) { Class aClass = new Class(classNum); newer.classes.put(classNum, aClass); newer.classes.get(classNum).students = new HashMap<>(); } newer.classes.get(classNum).addStudent(student); if (newer.courses.get(s[2]) == null) { return error.noexist(s[2]); } if (newer.courses.get(s[2]).getClassMode() != 2) { return error.accmode(s[0], s[1]); } int finalGrade = Integer.parseInt(s[3]); Main statistic = new Main(student, newer.courses.get(s[2]), new Score(finalGrade)); Print.newer.list.add(statistic); return null; } if (str.matches(newer.reg2)) { int i = newer.test.indexOf(s[1]) + 1; int j = newer.mode.indexOf(s[2]) + 1; if (i == 1 && j != 1) { return error.coursemoded(s[0]); } if (i == 3 && j != 3) { return error.coursemoded(s[0]); } if (i != 3 && j == 3) { return error.coursemoded(s[0]); } if (newer.courses.get(s[0]) != null) { return null; } Course course = new Course(s[0], i, j); newer.courses.put(s[0], course); return null; } if (str.matches(newer.reg3)) { if (output.checkStatistic(s)) { return null; } Student student = new Student(s[1], s[0]); newer.students.put(s[0], student); String classNum = s[0].substring(0, 6); if (newer.classes.get(classNum) == null) { Class aClass = new Class(classNum); newer.classes.put(classNum, aClass); newer.classes.get(classNum).students = new HashMap<>(); } newer.classes.get(classNum).addStudent(student); if (newer.courses.get(s[2]) == null) { return error.noexist(s[2]); } if (newer.courses.get(s[2]).getClassMode() != 3) { return error.accmode(s[0], s[1]); } int usualNum = Integer.parseInt(s[3]); if (s.length - 4 != usualNum) { return error.accmode(s[0], s[1]); } List<Integer> usualGrades = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= usualNum; i++) { usualGrades.add(Integer.parseInt(s[3 + i])); } Main statistic = new Main(student, newer.courses.get(s[2]), new Score(usualGrades)); Print.newer.list.add(statistic); return null; } if (str.matches(newer.reg4)) { int i = 1; int j = 1; if (newer.courses.get(s[0]) != null) { return null; } Course course = new Course(s[0], i, j); newer.courses.put(s[0], course); return null; } return error.wrong(); } } }
7-4 判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数:
从键盘输入两个日期,格式如:2022-06-18。判断两个日期的先后,并输出它们之间间隔的天数、周数(不足一周按0计算)。
预备知识:通过查询Java API文档,了解Scanner类中nextLine()等方法、String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法的用法,了解LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。
import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String startTime = sc.next(); String endTime = sc.next(); print(startTime, endTime); } public static void print(String startTime, String endTime) { String[] starttime = startTime.split("-"); String[] endtime = endTime.split("-"); int startyear = Integer.parseInt(starttime[0]); int startmonth = Integer.parseInt(starttime[1]); int startday = Integer.parseInt(starttime[2]); int endyear = Integer.parseInt(endtime[0]); int endmonth = Integer.parseInt(endtime[1]); int endday = Integer.parseInt(endtime[2]); LocalDate Time1 = LocalDate.of(startyear, startmonth, startday); LocalDate Time2 = LocalDate.of(endyear, endmonth, endday); if (Time1.isBefore(Time2)) { System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更早"); int day = (int) ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(Time1, Time2); System.out.println("两个日期间隔" + Math.abs(day) + "天"); System.out.print("两个日期间隔" + Math.abs(day / 7) + "周"); } else { System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更晚"); int day = (int) ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(Time1, Time2); System.out.println("两个日期间隔" + Math.abs(day) + "天"); System.out.print("两个日期间隔" + Math.abs(day / 7) + "周"); } } }
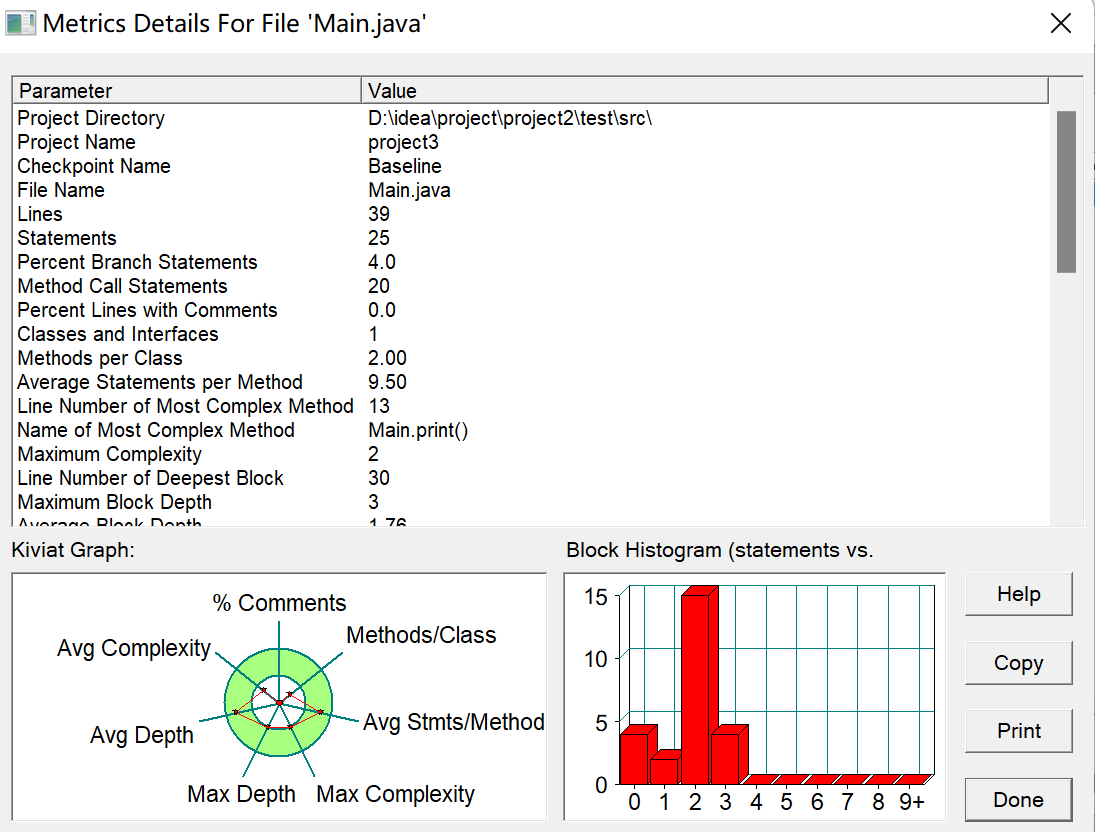
这道题算的上是对前面时间类用法的改进,与前面的时间类题目相似,将输入的时间格式转换成LocalDate时间日期对象,再用时间按日期对象中的isBefor方法对两个日期进行判断谁前世谁后,通过
ChronoUnit.DAYS.between来操作时间日期对象,得到两个日期之间相隔的天数。这道题目还是考察的对日期类的使用以及一些方法的使用;
总结:
通过前三次JavaPTA的作业,熟悉了新学到的Java语法和各种常用的方法。从第一次作业较为基础的知识点应用(像if else条件语句、一维数组等等),到第二次作业更为复杂的类的使用,再到第三次作业规范的类的创建(即一个类包含若干属性和若干方法),三次作业逐步引导我从面向对象程序设计的思维过渡到面向对象的程序设计思维。目前,我认为自己在Java方法的运用中仍存在不足,对其运用的具体场景和条件以及具体的内部原理了解不够透彻,仍需要进一步学习和实践。除此之外,我对于多个类的程序设计仍比较陌生,需要更进一步的学习。另外,自己在编程过程中需要养成更好的习惯,首先要习惯用面向对象的思维去思考问题、设计算法;其次,代码的书写要规范、美观、简略,这也方便自己查找错误,避免了很多不必要的麻烦。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号