spring源码-Aware-3.4
一、Aware接口,这个也是spring的拓展之一,为啥要单独拿出来讲呢,因为他相比于BeanFactoryPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor的实用性更加高,并且在具体的业务中也可以灵活使用,主要是能够达到解耦的目的。
二、常用的Aware接口有:第一类:BeanNameAware/BeanClassLoaderAware/BeanFactoryAware。 第二类:EmbeddedValueResolverAware/ResourceLoaderAware/ApplicationEventPublisherAware/MessageSourceAware/ApplicationContextAware。这两类到底有啥区别类,其实没有太大的区别。但是在源码实现中还是存在很大的差别的(后面统一说道)。
三、源码实现:
1、第一类:BeanNameAware/BeanClassLoaderAware/BeanFactoryAware
1)实现方式:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; /** * BeanNameAware/BeanClassLoaderAware/BeanFactoryAware类似 */ public class TestBeanAware implements BeanNameAware{ private String beanName; @Override public void setBeanName(String beanName) { System.out.println(beanName); this.beanName = beanName; } public String getBeanName() { return beanName; } }
2)有啥区别
这里简单说明一下:相对于普通的bean,这里可以获取到beanName/classLoader/beanFactory。是对普通bean的一种增强,然后合理的应用才是关键
3)源码实现部分:
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { public Object run() { AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this.invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; } }, this.getAccessControlContext()); } else { this.invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = this.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName); } try { this.invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable var6) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null, beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", var6); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = this.applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; } private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) { if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware)bean).setBeanName(beanName); } if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware)bean).setBeanClassLoader(this.getBeanClassLoader()); } if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware)bean).setBeanFactory(this); } }
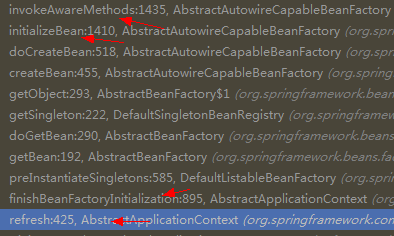
4)何时调用:spring源码-bean之加载-2 的3)点d.3 doCreateBean中的initializeBean()部分开始,所以这个其实是在getBean的时候才会调用。
5)测试的时候发现:在增强容器中refresh方法中finishBeanFactoryInitializationh会完成这部分的调用
2、第二类:EmbeddedValueResolverAware/ResourceLoaderAware/ApplicationEventPublisherAware/MessageSourceAware/ApplicationContextAware
1)实现方式:这里举两个例子EmbeddedValueResolverAware,ApplicationEventPublisherAware
a.EmbeddedValueResolverAware
import org.springframework.context.EmbeddedValueResolverAware; import org.springframework.util.StringValueResolver; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; public class TestEmbeddedValueResolverAware implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware { private StringValueResolver stringValueResolver; @Override public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver stringValueResolver) { this.stringValueResolver = stringValueResolver; } public String getProperties (String name) { String elName = "${"+ name +"}"; return stringValueResolver.resolveStringValue(elName); } @PostConstruct public void test() { System.out.println(getProperties("name")); } }
注意:这里是读取方式配置
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>aware.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean>
aware.properties
name=test
age=25
sex=boy
疑问:和这个有啥关系,看在StringValueResolver可以知道,这里的StringValueResolver指向的是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的内部类PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver,当然具体的实现有不同的方式
private class PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver implements StringValueResolver { private final PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper; private final PlaceholderResolver resolver; public PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver(Properties props) { this.helper = new PropertyPlaceholderHelper(PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.this.placeholderPrefix, PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.this.placeholderSuffix, PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.this.valueSeparator, PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders); this.resolver = PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.this.new PropertyPlaceholderConfigurerResolver(props, (PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurerResolver)null); } public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) throws BeansException { String value = this.helper.replacePlaceholders(strVal, this.resolver); return value.equals(PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.this.nullValue) ? null : value; } }
b.ApplicationEventPublisherAware
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; public class TestApplicationEventPublisherAware implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware { private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; @Override public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) { this.publisher = applicationEventPublisher; } public ApplicationEventPublisher getPublisher() { return publisher; } public class TestEvent extends ApplicationEvent { private Object object; public TestEvent(Object source, Object object) { super(source); this.object = object; } public Object getObject() { return object; } } @PostConstruct public void test() { publisher.publishEvent(new TestEvent(this, "test")); }
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; public class TestListener implements ApplicationListener<TestApplicationEventPublisherAware.TestEvent>{ @Override public void onApplicationEvent(TestApplicationEventPublisherAware.TestEvent testEvent) { System.out.println("TestEvent is Happen" + testEvent.getObject()); } }
发布,监听的过程相信。在实际业务中很常用吧。这里监听过程后面会讲,这里不细说。
注意:这里用aware的接口方式实现发布,监听过程,会比直接调用的方式更加解耦。
2)重点来了,这玩意在哪里调用的呢。其实我们之前我们忽略了一个重点。
a.先看调用方式
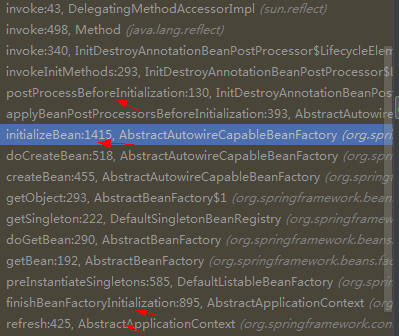
看到postProcessBeforeInitialization应该感到高兴了,因为这不就是实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的前置调用过程吗。
有问题可以参考:spring源码-BeanPostProcessor-3.3
b.疑问:我们并没有手动去实现BeanPostProcessor的接口并且对aware接口做处理啊。
通过debug和查看堆栈信息可以知道方法调用在ApplicationContextAwareProcessor类里面
package org.springframework.context.support; import java.security.AccessControlContext; import java.security.AccessController; import java.security.PrivilegedAction; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.EmbeddedValueResolverAware; import org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware; import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware; import org.springframework.util.StringValueResolver; class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { private final ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext; public ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { AccessControlContext acc = null; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware || bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware || bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)) { acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext(); } if (acc != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { public Object run() { ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.this.invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); return null; } }, acc); } else { this.invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); } return bean; } private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) { if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) { ((EmbeddedValueResolverAware)bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.EmbeddedValueResolver(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory())); } if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) { ((ResourceLoaderAware)bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) { ((ApplicationEventPublisherAware)bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) { ((MessageSourceAware)bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware)bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext); } } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) { return bean; } private static class EmbeddedValueResolver implements StringValueResolver { private final ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory; public EmbeddedValueResolver(ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) { return this.beanFactory.resolveEmbeddedValue(strVal); } } }
c、还有一个问题ApplicationContextAwareProcessor在哪里注册的呢?
通过源码方式查看到在refresh()的this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);中提前准备了ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(this.getClassLoader()); beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver()); beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this)); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this)); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this); if (beanFactory.containsBean("loadTimeWeaver")) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } Object systemEnvironment; if (!beanFactory.containsBean("systemProperties")) { try { systemEnvironment = System.getProperties(); } catch (AccessControlException var4) { systemEnvironment = new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() { protected String getSystemAttribute(String propertyName) { try { return System.getProperty(propertyName); } catch (AccessControlException var3) { if (AbstractApplicationContext.this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { AbstractApplicationContext.this.logger.info("Not allowed to obtain system property [" + propertyName + "]: " + var3.getMessage()); } return null; } } }; } beanFactory.registerSingleton("systemProperties", systemEnvironment); }
四:Aware接口部分就这么多吧,这里没有具体些实现和用法,但是相对于BeanFactoryPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor。Aware在实际应用中会更加常用,这一部分是spring提供出来的拓展,也是必要重要的一个部分。
当然,我这里可能还存在一些纰漏,还请大佬指出来!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号