数据结构与算法——平衡二叉树(AVL树)
二叉排序树存在的问题
一个数列 {1,2,3,4,5,6},创建一颗二叉排序树(BST)

创建完成的树如上图所示,那么它存在的问题有以下几点:
-
左子树全部为空,从形式上看,更像一个单链表
-
插入速度没有影响
-
但查询速度明显降低
因为需要依次比较,不能利用二叉排序树的折半优势。而且每次都还要比较左子树,可能比单链表查询速度还慢。
那么解决这个劣势的方案就是:平衡二叉树(AVL)。
基本介绍
平衡二叉树也叫 平衡二叉搜索树(Self-balancing binary search tree),又被称为 AVL 树,可以保证 查询效率较高。它是解决 二叉排序 可能出现的查询问题。
它的特点:是一颗空树或它的 左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
平衡二叉树的常用实现方法有:
红黑树AVL(算法)替罪羊树Treap伸展树
想了解更多的可以去看 平衡树——维基百科
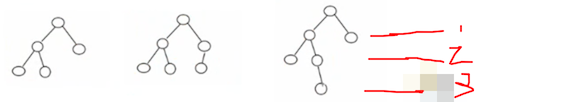
如下所述,哪些是平衡二叉树?
-
是平衡二叉树:
- 左子树高度为 2
- 右子树高度为 1
他们差值为 1
-
也是平衡二叉树
-
不是平衡二叉树
- 左子树高度为 3
- 右子树高度为 1
他们差值为 2,所以不是
单旋转(左旋转)
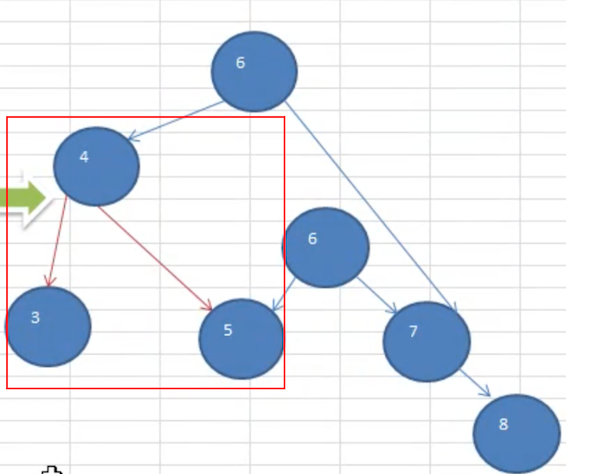
一个数列 4,3,6,5,7,8 ,创建出它对应的平衡二叉树。
思路分析:下图红线部分是调整流程。
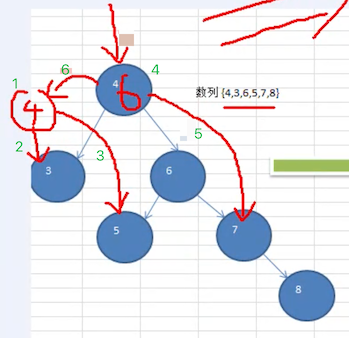
按照规则调整完成之后,形成了下面这样一棵树
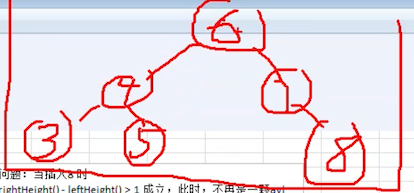
完整流程如下图所示:

如上图,插入 8 时,发现左右子树高度相差大于 1,则进行左旋转:
-
创建一个新的节点
newNode,值等于当前 根节点 的值(上图根节点为 4) -
把新节点的 左子树 设置为当前节点(根节点)的 左子树
newNode.left = this.left -
把新节点的 右子树 设置为当前节点(根节点)的 右子树 的 左子树
newNode.right = this.right.left -
把 当前节点(根节点) 的值换为 右子节点 的值
this.value = this.right.value -
把 当前节点(根节点) 的右子树设置为 右子树的右子树(按上图的话就是 7)
this.right = this.right.right -
把 当前节点(根节点) 的左子树设置为新节点
newNodethis.left = this.newNode
注:左图是调整前,右图是调整后。注意调整前的 6 那个节点,调整之后,没有节点指向他了。也就是说,遍历的时候它是不可达的。那么将会自动的被垃圾回收掉。
树高度计算
前面说过,平衡二叉树是为了解决二叉排序树中可能出现的查找效率问题,那么基本上的代码都可以在之前的二叉排序树上进行优化。那么下面只给出与当前主题相关的代码,最后放出一份完整的代码。
树的高度计算,我们需要得到 3 个高度:
- 这颗树的整体高度
- 左子树的高度
- 右子树的高度
public class AvlTreeTest {
/**
* 树高度测试
*/
@Test
public void heightTest() {
AvlTree tree = new AvlTree();
int[] arr = {4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
tree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
tree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("树高度:" + tree.root.height()); // 4
System.out.println("左树高度:" + tree.root.leftHeight()); // 1
System.out.println("右树高度:" + tree.root.rightHeight()); // 3
}
}
/**
* 排序二叉树
*/
class AvlTree {
Node root;
public Node getRoot() {
return root;
}
}
/**
* 节点
*/
class Node {
/**
* 以当前节点为基础:计算出它包含它子树的所有高度
*
* @return
*/
public int height() {
/*
这里使用了递归:返回了左右子树中,最高的那一个数值。
递归原理:第一个开始统计的时候,一定是一个叶子节点
根据这个逻辑:叶子节点的 Math.max(0,0) = 0 看下面代码
因为当前节点算一层,所以 + 1;
返回到上一层的时候,至少是这样:Math.max(1,0) = 1
然后把自己本身的层 +1。 以此类推,返回到根节点的时候,就拿到了从包含根节点的树的高度
所以这个 +1 是精髓所在
*/
return Math.max(
(left == null ? 0 : left.height()),
(right == null ? 0 : right.height())
) + 1;
}
/**
* 计算左子树的高度
*
* @return
*/
public int leftHeight() {
if (left == null) {
return 0;
}
// 如果从根节点开始的话
// 其实它从中间分开,左侧就有很多的小树
// 所以还是要计算左右树的高度,返回一个最大的值,只不过是开始节点变化了
return left.height();
}
/**
* 计算右子树的高度,与上面的计算左子树同理
*
* @return
*/
public int rightHeight() {
if (right == null) {
return 0;
}
return right.height();
}
}
测试输出
3
4
5
6
7
8
树高度:4
左树高度:1
右树高度:3
旋转
说下旋转的时机:也就是什么时机采取做旋转的操作?
当然是:当 右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1 时,才执行左旋转。
这里就得到一些信息:
-
每次添加完一个节点后,就需要检查树的高度
-
满足
右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1,那么一定满足下面的条件:①左子树高度为 1
②右子树高度为 3
也就是符合这张图
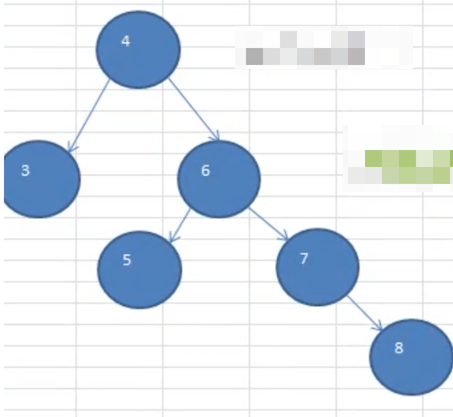
也正是有如上的信息逻辑,在实现旋转的时候,只要按照思路分析写就可以了,不需要进行边界判定了。
class Node {
/**
* 添加节点:按照排序二叉树的要求添加
*
* @param node
*/
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 如果添加的值小于当前节点,则往左走
if (node.value < value) {
// 左节点为空,则直接挂在上面
if (left == null) {
left = node;
} else {
// 否则继续往下查找
left.add(node);
}
} else {
// 往右走
if (right == null) {
right = node;
} else {
right.add(node);
}
}
// 旋转的时候有以下规则
// 每添加一个节点之后:检查树的高度是否平衡
// 如果右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1,则左旋转
// 也就是说:每次旋转的层只涉及到 4 层(对照笔记上的图示理解)
if (rightHeight() - leftHeight() > 1) {
leftRotate();
}
}
/**
* 以当前节点为根节点,进行左旋转
*/
public void leftRotate() {
// 1. 创建一个新的节点 newNode,值等于当前 根节点 的值
Node newNode = new Node(value);
// 2. 把 新节点的 左子树 设置为当前节点的左子树
newNode.left = left;
// 3. 把 新节点的 右子树 设置为当前节点的 右子树的左子树
newNode.right = right.left;
// 4. 把 当前节点的值,替换为 右子树 节点的子
value = right.value;
// 5. 把 当前节点 的 右节点 设置为 右子树的右子树
right = right.right;
// 6. 把 当前节点 的 左节点 设置为 新节点
left = newNode;
}
}
测试
/**
* 左旋转测试
*/
@Test
public void leftRotatedTest() {
AvlTree tree = new AvlTree();
int[] arr = {4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
tree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
tree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("树高度:" + tree.root.height()); // 3
System.out.println("左树高度:" + tree.root.leftHeight()); // 2
System.out.println("右树高度:" + tree.root.rightHeight()); // 2
}
测试输出
3
4
5
6
7
8
树高度:3
左树高度:2
右树高度:2
看完代码之后,它的旋转其实就是,将 root 节点,往下沉到了,root.right 节点下面。
看着上图,是否有想过,貌似根本就可以不用前面讲解的 6 个步骤来旋转:
- 不用创建新节点
- 直接将 node 节点下沉
- 更改 node 的 right 节点为 right.left
- 更改 right.left = node
其实就已经完成了旋转。但是你仔细想一想,旋转逻辑是写在 node 里面的, avgTree 中的引用如何改变?除非把旋转逻辑移动到 avgTree 中去,就可以省略掉新建节点的步骤来完成。
右旋转
弄懂了左旋转,对于右旋转其实就很好理解了:
- 左旋转:
右 - 左 > 1,把右边的往左边旋转一层 - 右旋转:
左 - 右 > 1,把左边的往右边旋转一层
他们其实是反着来的,那么右旋转的思路如下:
-
创建一个新的节点
newNode,值等于当前 根节点 的值(以 4 创建) -
把新节点的 右子树 设置为当前节点(根节点)的 右子树
newNode.right = right -
把新节点的 左子树 设置为当前节点(根节点)的 左子树的右子树
newNode.left = left.right -
把 当前节点(根节点) 的值换为 左子节点 的值
value = left.value -
把 当前节点 (根节点)的左子树设置为 左子树的左子树
left = left.left -
把 当前节点 的右子树设置为新节点
right = newNode
上述步骤就是对下图的描述:查看图示更清楚

class Node {
/**
* 添加节点:按照排序二叉树的要求添加
*
* @param node
*/
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 如果添加的值小于当前节点,则往左走
if (node.value < value) {
// 左节点为空,则直接挂在上面
if (left == null) {
left = node;
} else {
// 否则继续往下查找
left.add(node);
}
} else {
// 往右走
if (right == null) {
right = node;
} else {
right.add(node);
}
}
// 旋转的时候有以下规则
// 每添加一个节点之后:检查树的高度是否平衡
// 如果右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1,则左旋转
// 也就是说:每次旋转的层只涉及到 4 层(对照笔记上的图示理解)
if (rightHeight() - leftHeight() > 1) {
leftRotate();
return;
}
if (leftHeight() - rightHeight() > 1) {
rightRotate();
}
}
/**
* 以当前节点为根节点,进行右旋转
*/
public void rightRotate() {
// 1. 创建一个新的节点 newNode,值等于当前 根节点 的值
Node newNode = new Node(value);
// 2. 把 新节点的 右子树 设置为当前节点的右子树
newNode.right = right;
// 3. 把 新节点的 左子树 设置为当前节点的 左子树的右子树
newNode.left = left.right;
// 4. 把 当前节点的值,替换为 左子树 节点的子
value = left.value;
// 5. 把 当前节点 的 左节点 设置为 左子树的左子树
left = left.left;
// 6. 把 当前节点 的 右节点 设置为 新节点
right = newNode;
}
}
测试
/**
* 右旋转测试
*/
@Test
public void rightRotatedTest() {
AvlTree tree = new AvlTree();
int[] arr = {10, 12, 8, 9, 7, 6};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
tree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
tree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("树高度:" + tree.root.height()); // 3
System.out.println("左树高度:" + tree.root.leftHeight()); // 2
System.out.println("右树高度:" + tree.root.rightHeight()); // 2
System.out.println("当前根节点:" + tree.root); // 8
}
测试输出
6
7
8
9
10
12
树高度:3
左树高度:2
右树高度:2
当前根节点:Node{value=8}
双旋转
在前面的例子中,使用单旋转(即一次旋转)就可以将非平衡二叉树转换为平衡二叉树。
但是在某些情况下,就无法做到。比如下面这两组数列
int[] arr ={10,11,7,6,8,9}
int[] arr ={2,1,6,5,7,3}
运行上面的代码测试可以发现并未生效
/**
* 不能通过单旋转解决的场景
*/
@Test
public void notLeftOrRightRotatedTest() {
AvlTree tree = new AvlTree();
int[] arr = {10, 11, 7, 6, 8, 9};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
tree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
tree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("树高度:" + tree.root.height()); // 4
System.out.println("左树高度:" + tree.root.leftHeight()); // 1
System.out.println("右树高度:" + tree.root.rightHeight()); // 3
System.out.println("当前根节点:" + tree.root); // 7
}
测试输出
6
7
8
9
10
11
树高度:4
左树高度:1
右树高度:3
当前根节点:Node{value=7}
为什么会出现这种情况呢?看下图

左侧这个树满足 leftHeight - rightHeight > 1 ,也就是满足右旋转,旋转之后,树结构变化了。但是还是一个非平衡二叉树。
它的主要原因是:root 左子树的 左子树高度 小于 右子树的高度。即:节点 7 的左子树高度小于右子树的高度。
解决办法:
- 先将 7 这个节点作为 root 节点,进行左旋转
- 再将原始的 root 节点进行右旋转
过程示意图如下:

其实可以参考下前面两个单旋转的图例,它有这样一个特点:
- 右旋转:
- root 的 left 左子树高度 大于 右子树高度
- 右旋转的时候,会将
left.right旋转到right.left节点上
- 左旋转:
- root 的 right 右子树高度 大于 左子树高度
- 左旋转的时候,会将
right.left旋转到left.right上。
如果不满足这个要求,在第二个操作的时候,就会导致 2 层的高度被旋转到 1 层的节点下面,导致不平衡了。
那么解决代码如下:
在 Node 类的 add 方法中进行双节点逻辑的执行。
/**
* 添加节点:按照排序二叉树的要求添加
*
* @param node
*/
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 如果添加的值小于当前节点,则往左走
if (node.value < value) {
// 左节点为空,则直接挂在上面
if (left == null) {
left = node;
} else {
// 否则继续往下查找
left.add(node);
}
} else {
// 往右走
if (right == null) {
right = node;
} else {
right.add(node);
}
}
// 旋转的时候有以下规则
// 每添加一个节点之后:检查树的高度是否平衡
// 如果右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1,则左旋转
// 也就是说:每次旋转的层只涉及到 4 层(对照笔记上的图示理解)
// 小旋转的时候:只涉及到 3 层,旋转的时候,最多操作了当前节点和左右节点,所以不会导致 NPE 问题,这一点一定要明白
if (rightHeight() - leftHeight() > 1) {
// 当 右节点的:左子树高度 大于 右子树的高度时,将 right 节点进行 右旋转
if (right != null && right.leftHeight() > right.rightHeight()) {
right.rightRotate();
}
leftRotate();
return;
}
if (leftHeight() - rightHeight() > 1) {
// 当 左节点的:右子树高度 大于 左子树的高度时,将 left 节点进行左旋转
if (left != null && left.rightHeight() > left.leftHeight()) {
left.leftRotate();
}
rightRotate();
}
}
测试代码
/**
* 添加双旋转之后,之前测试不能旋转的数列进行测试
*/
@Test
public void doubleRotatedTest() {
AvlTree tree = new AvlTree();
int[] arr = {10, 11, 7, 6, 8, 9};
// int[] arr ={2,1,6,5,7,3}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
tree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
tree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("树高度:" + tree.root.height());
System.out.println("左树高度:" + tree.root.leftHeight());
System.out.println("右树高度:" + tree.root.rightHeight());
System.out.println("当前根节点:" + tree.root);
}
输出信息
6
7
8
9
10
11
树高度:3
左树高度:2
右树高度:2
当前根节点:Node{value=8}
1
2
3
5
6
7
树高度:3
左树高度:2
右树高度:2
当前根节点:Node{value=5}
完整代码
public class AVLTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int[] arr = {4,3,6,5,7,8};
//int[] arr = { 10, 12, 8, 9, 7, 6 };
int[] arr = {10, 11, 7, 6, 8, 9};
//创建一个 AVLTree对象
AVLTree avlTree = new AVLTree();
//添加结点
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
avlTree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
//遍历
System.out.println("中序遍历");
avlTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("在平衡处理~~");
System.out.println("树的高度=" + avlTree.getRoot().height()); //3
System.out.println("树的左子树高度=" + avlTree.getRoot().leftHeight()); // 2
System.out.println("树的右子树高度=" + avlTree.getRoot().rightHeight()); // 2
System.out.println("当前的根结点=" + avlTree.getRoot());//8
}
}
// 创建AVLTree
class AVLTree {
private Node root;
public Node getRoot() {
return root;
}
// 查找要删除的结点
public Node search(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.search(value);
}
}
// 查找父结点
public Node searchParent(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.searchParent(value);
}
}
// 编写方法:
// 1. 返回的 以node 为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点的值
// 2. 删除node 为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点
/**
* @param node 传入的结点(当做二叉排序树的根结点)
* @return 返回的 以node 为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点的值
*/
public int delRightTreeMin(Node node) {
Node target = node;
// 循环的查找左子节点,就会找到最小值
while (target.left != null) {
target = target.left;
}
// 这时 target就指向了最小结点
// 删除最小结点
delNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
// 删除结点
public void delNode(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
// 1.需求先去找到要删除的结点 targetNode
Node targetNode = search(value);
// 如果没有找到要删除的结点
if (targetNode == null) {
return;
}
// 如果我们发现当前这颗二叉排序树只有一个结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
root = null;
return;
}
// 去找到targetNode的父结点
Node parent = searchParent(value);
// 如果要删除的结点是叶子结点
if (targetNode.left == null && targetNode.right == null) {
// 判断targetNode 是父结点的左子结点,还是右子结点
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) { // 是左子结点
parent.left = null;
} else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) {// 是由子结点
parent.right = null;
}
} else if (targetNode.left != null && targetNode.right != null) { // 删除有两颗子树的节点
int minVal = delRightTreeMin(targetNode.right);
targetNode.value = minVal;
} else { // 删除只有一颗子树的结点
// 如果要删除的结点有左子结点
if (targetNode.left != null) {
if (parent != null) {
// 如果 targetNode 是 parent 的左子结点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = targetNode.left;
} else { // targetNode 是 parent 的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.left;
}
} else {
root = targetNode.left;
}
} else { // 如果要删除的结点有右子结点
if (parent != null) {
// 如果 targetNode 是 parent 的左子结点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = targetNode.right;
} else { // 如果 targetNode 是 parent 的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.right;
}
} else {
root = targetNode.right;
}
}
}
}
}
// 添加结点的方法
public void add(Node node) {
if (root == null) {
root = node;// 如果root为空则直接让root指向node
} else {
root.add(node);
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (root != null) {
root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉排序树为空,不能遍历");
}
}
}
// 创建Node结点
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
/**
* 以当前节点为基础:计算出它包含它子树的所有高度
*
* @return
*/
public int height() {
/*
这里使用了递归:返回了左右子树中,最高的那一个数值。
递归原理:第一个开始统计的时候,一定是一个叶子节点
根据这个逻辑:叶子节点的 Math.max(0,0) = 0 看下面代码
因为当前节点算一层,所以 + 1;
返回到上一层的时候,至少是这样:Math.max(1,0) = 1
然后把自己本身的层 +1。 以此类推,返回到根节点的时候,就拿到了从包含根节点的树的高度
所以这个 +1 是精髓所在
*/
return Math.max(
(left == null ? 0 : left.height()),
(right == null ? 0 : right.height())
) + 1;
}
/**
* 计算左子树的高度
*
* @return
*/
public int leftHeight() {
if (left == null) {
return 0;
}
// 如果从根节点开始的话
// 其实它从中间分开,左侧就有很多的小树
// 所以还是要计算左右树的高度,返回一个最大的值,只不过是开始节点变化了
return left.height();
}
/**
* 计算右子树的高度,与上面的计算左子树同理
*
* @return
*/
public int rightHeight() {
if (right == null) {
return 0;
}
return right.height();
}
//左旋转方法
private void leftRotate() {
//创建新的结点,以当前根结点的值
Node newNode = new Node(value);
//把新的结点的左子树设置成当前结点的左子树
newNode.left = left;
//把新的结点的右子树设置成带你过去结点的右子树的左子树
newNode.right = right.left;
//把当前结点的值替换成右子结点的值
value = right.value;
//把当前结点的右子树设置成当前结点右子树的右子树
right = right.right;
//把当前结点的左子树(左子结点)设置成新的结点
left = newNode;
}
//右旋转
private void rightRotate() {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.right = right;
newNode.left = left.right;
value = left.value;
left = left.left;
right = newNode;
}
// 查找要删除的结点
/**
* @param value 希望删除的结点的值
* @return 如果找到返回该结点,否则返回null
*/
public Node search(int value) {
if (value == this.value) { // 找到就是该结点
return this;
} else if (value < this.value) {// 如果查找的值小于当前结点,向左子树递归查找
// 如果左子结点为空
if (this.left == null) {
return null;
}
return this.left.search(value);
} else { // 如果查找的值不小于当前结点,向右子树递归查找
if (this.right == null) {
return null;
}
return this.right.search(value);
}
}
// 查找要删除结点的父结点
/**
* @param value 要找到的结点的值
* @return 返回的是要删除的结点的父结点,如果没有就返回null
*/
public Node searchParent(int value) {
// 如果当前结点就是要删除的结点的父结点,就返回
if ((this.left != null && this.left.value == value) || (this.right != null && this.right.value == value)) {
return this;
} else {
// 如果查找的值小于当前结点的值, 并且当前结点的左子结点不为空
if (value < this.value && this.left != null) {
return this.left.searchParent(value); // 向左子树递归查找
} else if (value >= this.value && this.right != null) {
return this.right.searchParent(value); // 向右子树递归查找
} else {
return null; // 没有找到父结点
}
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [value=" + value + "]";
}
// 添加结点的方法
// 递归的形式添加结点,注意需要满足二叉排序树的要求
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 判断传入的结点的值,和当前子树的根结点的值关系
if (node.value < this.value) {
// 如果当前结点左子结点为null
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = node;
} else {
// 递归的向左子树添加
this.left.add(node);
}
} else { // 添加的结点的值大于 当前结点的值
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
// 递归的向右子树添加
this.right.add(node);
}
}
// 旋转的时候有以下规则
// 每添加一个节点之后:检查树的高度是否平衡
// 如果右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1,则左旋转
// 也就是说:每次旋转的层只涉及到 4 层(对照笔记上的图示理解)
// 小旋转的时候:只涉及到 3 层,旋转的时候,最多操作了当前节点和左右节点,所以不会导致 NPE 问题,这一点一定要明白
if (rightHeight() - leftHeight() > 1) {
// 当 右节点的:左子树高度 大于 右子树的高度时,将 right 节点进行 右旋转
if (right != null && right.leftHeight() > right.rightHeight()) {
right.rightRotate();
}
leftRotate();
return;
}
if (leftHeight() - rightHeight() > 1) {
// 当 左节点的:右子树高度 大于 左子树的高度时,将 left 节点进行左旋转
if (left != null && left.rightHeight() > left.leftHeight()) {
left.leftRotate();
}
rightRotate();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号