学习笔记——异常&&双链表
一、学习重点
二、学习内容
Question1:
try...catch..finally执行顺序:
finally永远是在最后执行的
public static int test1(){ int i = 10; try { i++; System.out.println("try:" + i); }catch (Exception e){ i--; System.out.println("catch:" + i); }finally { i = 100; System.out.println("finally:" + i); } return i; } public static int test2(){ int i = 10; try { i++; // System.out.println("try:" + i); throw new Exception(); }catch (Exception e){ i--; System.out.println("catch:" + i); }finally { i = 100; System.out.println("finally:" + i); } return i; } // try---finally---return public static int test3(){ int i = 10; try { i++; System.out.println("try:" + i); return i; }catch (Exception e){ i--; System.out.println("catch:" + i); return i; }finally { i = 100; System.out.println("finally:" + i); } } // try...finally...return public static int test4(){ int i = 10; try { i++; System.out.println("try:" + i); return i; }catch (Exception e){ i--; System.out.println("catch:" + i); return i; }finally { i = 100; System.out.println("finally:" + i); return i; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // System.out.println(test1()); // System.out.println(test2()); // System.out.println(test3()); System.out.println(test4()); }
双链表:
class Node { // 数据本身 Integer data; // 上一个结点的地址 Node prev; // 下一个结点的地址 Node next; public Node() { } public Node(Integer data) { this.data = data; } } public class DoubleLinked { // 维护一个头结点,头结点不要动,不存放具体的数据 private Node head = new Node(0); // 返回头结点 public Node getHead() { return head; } // 显示链表(遍历) public void list() { if(head.next == null){ System.out.println("链表为空..."); return; } // 因为头结点,不能动,我们需要一个辅助变量来帮我们遍历 Node temp = head.next; while(true) { // 判断是否走到最后 if(temp == null){ break; } System.out.println(temp.data); // 将指针后移 temp = temp.next; } } // 添加结点到链表最后 // 默认添加的是到链表的最后一个位置 // 找到链表的最后一个结点 // 把这个结点的下一个指向当前结点 // 当前结点的上一个结点指向之前的最后一个结点 public void add(Node node) { // 因为我们头结点不能动,我们 Node temp = head; while(true) { // 找到链表的表尾结点 if(temp.next == null){ break; } // 如果没有找到最后,将temp后移 temp = temp.next; } // 当退出while循环时,temp指针就指向了最后 temp.next = node; node.prev = temp; } // 在指定位置新增 public void add(Node node,int index){ } // 查询指定位置的结点 public Node getNode(int index) { // for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) { // // } return null; } // 修改一个结点的内容 public void update(Node node,Node newNode) { // 判断是否为空 if(head.next == null){ System.out.println("链表为空..."); return; } // 找到要修改的结点,根据data找 // 定义一个辅助变量 Node temp = head.next; boolean flag = false; while(true) { if(temp == null) { break; // 已经找完一遍了,没找到 } if(temp.data == node.data){ flag = true; break; } temp = temp.next; } // 根据flag判断是否找到要修改的结点 if(flag) { // 改变这个结点的内容 temp.data = newNode.data; }else { System.out.println("没有找到" + node.data + "结点..."); } } // 从双向链表中删除一个结点 // 1.对于双向链表,我们先要找到要删除的这个结点 // 2.找到后,直接删除 public void del(Integer data){ // 判断是否为空 if(head.next == null){ System.out.println("链表为空..."); return; } // 找到要修改的结点,根据data找 // 定义一个辅助变量 Node temp = head.next; boolean flag = false; while(true) { if(temp == null) { break; // 已经找完一遍了,没找到 } if(temp.data == data){ flag = true; break; } temp = temp.next; } if(flag) { //找到了 // 删除 // temp.next = temp.next.next; temp.prev.next = temp.next; // 这里我们写的有点问题? // 如果是最后一个结点, if(temp.next != null){ temp.next.prev = temp.prev; } }else { System.out.println("没有找到" + data + "结点..."); } } public static void main(String[] args) { DoubleLinked doubleLinked = new DoubleLinked(); doubleLinked.add(new Node(1)); doubleLinked.add(new Node(2)); doubleLinked.add(new Node(3)); doubleLinked.add(new Node(4)); // doubleLinked.update(new Node(5),new Node(30)); doubleLinked.del(4); doubleLinked.list(); // System.out.println(doubleLinked.getHead()); } }
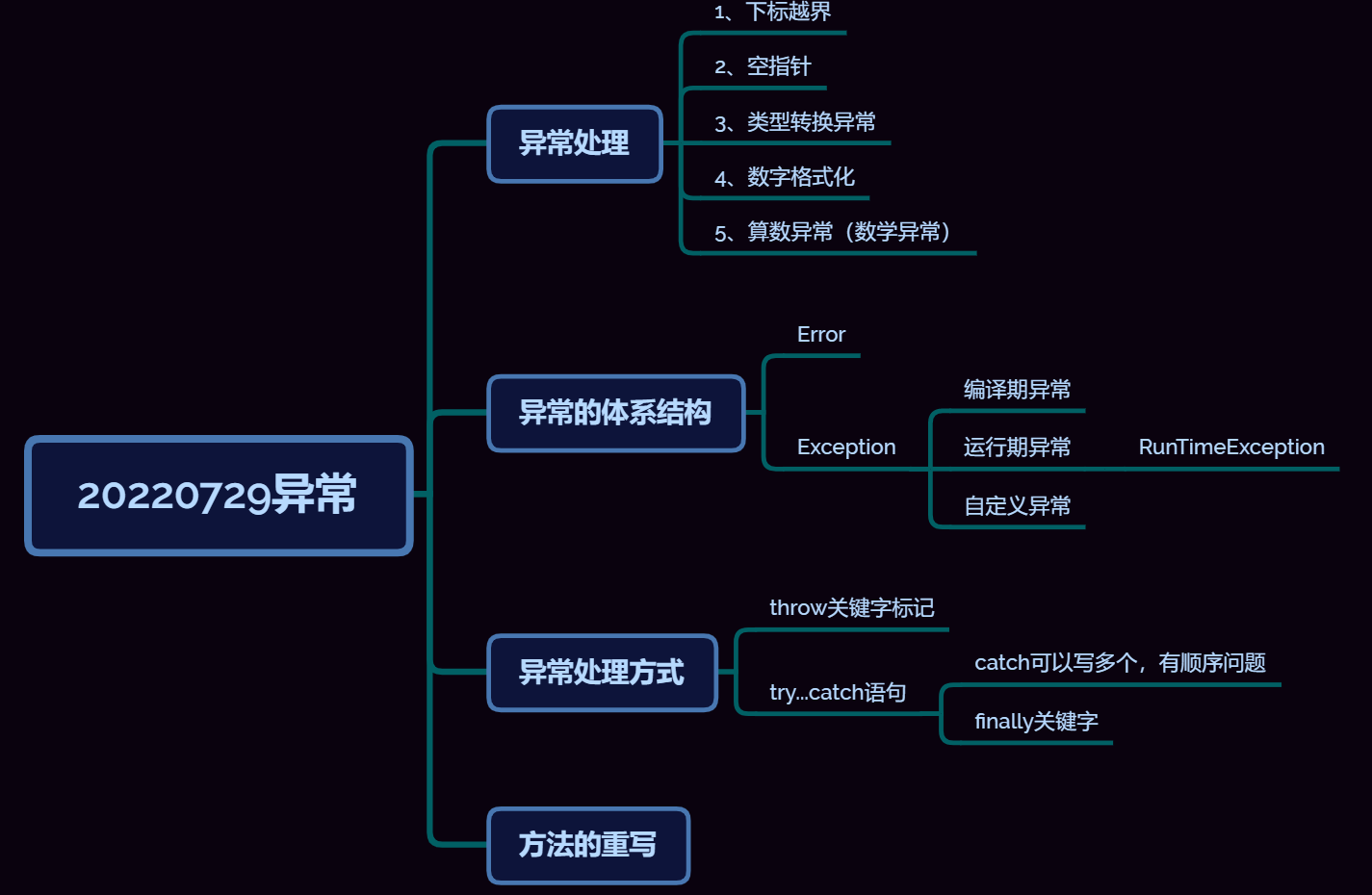
三、笔记内容
异常处理
1、下标越界
2、空指针
3、类型转换异常
4、数字格式化
5、算数异常(数学异常)
编程界:
1、除数为0
2、IO流,没有关闭
3、停电
当一个程序抛异常,抛异常后面的语句不再执行,类似于return的功能,终止方法的执行
public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 0; // double num3 = 0; System.out.println(num1/num2);// by zero // System.out.println(num1/num3);//Infinity 无穷大 System.out.println("我很重要"); }
异常的继承体系结构
最顶级的Throwable:错误,异常
Error:正常情况下,不太可能出现的。绝大多数Error都会导致程序处于非正常状态下,很难恢复
外力的作用下,不考虑。
Error是Throwable的子类。它是在Java程序处理范围之外的
Exception:Java语言中,将程序执行中发生的不正常的情况称之为异常
编译期异常:写代码的时候,抛异常。如果编译期不解决,会编译不通过
运行期异常:RunTimeException,运行时会抛异常,平时没事
自定义异常:Java中的异常机制,结合实际业务。
怎么自定义异常?
1、所有的异常必须是Throwable的子类(大材小用,没必要)
2、如果要定义一个编译期异常,需要继承Exception类
3、如果要定义一个运行期异常,需要继承RunTimeException类
public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 0; //处理异常 try { //有可能抛出异常的代码放到try语句块里 System.out.println(num1/num2);// by zero } catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("除数不能为零"); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("我很重要"); }
编译期异常
public class MyException extends Exception { public MyException(String message) { super(message); } }
运行期异常
public class MyRuntimeException extends RuntimeException { public MyRuntimeException(String message) { super(message); } }
错误码和异常信息
public class ServiceException extends RuntimeException { //错误码 private Integer code; //异常信息 private String message; public ServiceException() { } public ServiceException(Integer code, String message) { this.code = code; this.message = message; } public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } @Override public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } }
try...catch
在一个语句块中,如果使用throw抛出一个编译期异常,就必须在方法的声明处使用throws关键字来标记异常
还有一种处理方式,就是try...catch
我们为什么要手动抛异常
因为要配合全局异常处理机制来解决
public static void fun(int i, int j) throws MyException { if (j==0){ throw new MyException("除数不能为0"); } System.out.println(i/j); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { fun(1,0); } catch (MyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
throw语句时可以当作方法的返回值的
在一个有返回值的方法中,如果有条件分支,一定要保证每种条件下都有条件异常
开发中大部分情况下,使用的都是运行期异常!!!
public static String show(String str){ if (!Objects.isNull(str)){ return str.concat("hello"); } // throw new RuntimeException("参数不能为空"); throw new ServiceException(101,"账号不能为空"); } public static void main(String[] args) { show(null); // show("null"); }
异常链
一个异常被抛出去之后会继续被调用这个方法的方法捕获被抛出,异常会扩散
只要说解决异常,处理异常,捕获 就是try...catch
class A{ public void a(){ throw new ServiceException(201,"业务异常..."); } } class B{ public void b(){ A aa= new A(); try { aa.a(); }catch (Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("B方法的语句"); } } class C{ public void c(){ B bb= new B(); bb.b(); } } public class Ch05 { public static void main(String[] args) { C c = new C(); c.c(); } }
如果一个方法没有捕获一个编译期异常,该方法必须使用throws异常
throws并不是真正的解决了异常,只是把异常抛给了下一级调用者
service层,干脏活和累活的
面试题:
throws和throw区别
throws出现在方法的声明处,抛出多个异常,用逗号隔开
public void show() throws MyException,RuntimeException,NullPointerException{ } public void info() throws MyException { show(); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { new Ch06().info(); } catch (MyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
finally:关键字
finally用来创建在try代码块后面执行的代码块
无论是否方法异常,finally代码块中的代码一定会执行,一般finally中的finally
try...catch...finally
try...finally
public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 0; String str = null; //处理异常 try { //有可能抛出异常的代码放到try语句块里 System.out.println(num1/num2); System.out.println(str.length()); } catch (ArithmeticException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println("finally..."); } }
catch可以写多个,有顺序问题。
先写小的,再写大的
int num1 = 10; int num2 = 0; try { System.out.println(num1 / num2); // 开发角度来说,应该写指定的。 } catch (ArithmeticException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("除数不能为0"); } catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("未知错误"); } }
方法的重写
4.重写的方法不能抛出比被重写方法更大的异常类型
interface Inter01 { void show() throws Exception; } public class Ch09 implements Inter01 { @Override public void show() throws NullPointerException { } }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号