C++ 二叉搜索树 - 教程
1.概念
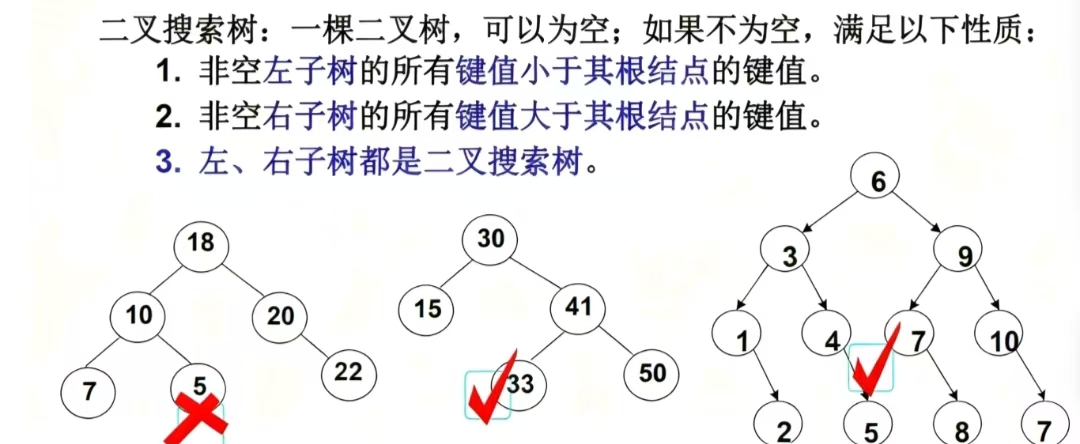
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树或者二叉查找树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值,若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值,它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树。
2.特点
1. 有序性:这是最核心的特点。对BST进行中序遍历(左-根-右),能得到一个严格递增(无重复值时)的有序序列,如同按顺序翻阅一本排好序的字典。
2. 查找高效:类似“二分查找”逻辑,每次比较可排除一半子树。若树平衡,查找、插入、删除操作时间复杂度为O(log n);若失衡(如退化为链表),则降为O(n)。
3. 结构约束:每个节点的左子树仅存储更小的值,右子树仅存储更大的值,不存在值相等的节点(通常定义,也有允许重复值的变体,需额外约定存储位置)。
3.二叉树的操作
3.1 二叉树的查找
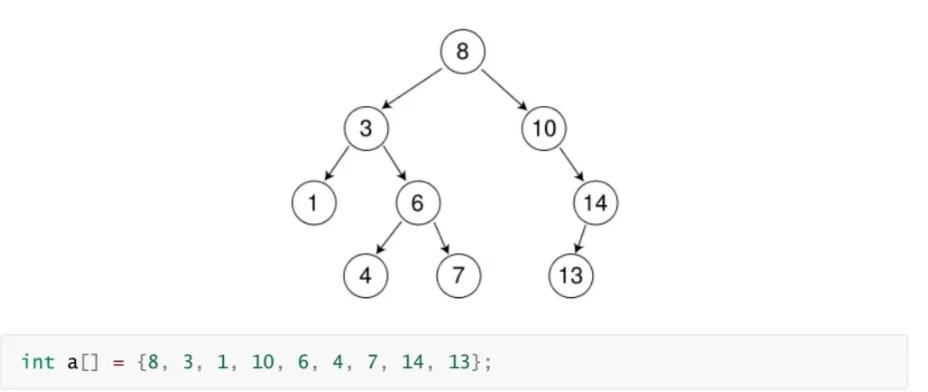
1、从根开始比较,查找,比根大则往右边走查找,比根小则往左边走查找。
2、最多查找高度次,走到到空,还没找到,这个值不存在。
3.2二叉树的插入
1. 树为空,则直接新增节点,赋值给root指针。
2. 树不空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点。
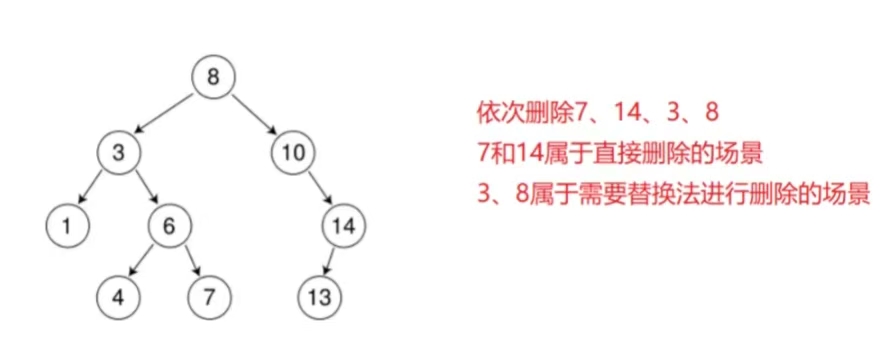
3.3 二叉树的删除
首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回, 否则要删除的结点可能分下面四种情况:
1. 要删除的结点无孩子结点
2. 要删除的结点只有左孩子结点
3. 要删除的结点只有右孩子结点
4. 要删除的结点有左、右孩子结点
看起来有待删除节点有4中情况,实际情况1可以与情况2或者3合并起来,因此真正的删除过程如下:
情况2:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除节点的左孩子结点--直接删除
情况3:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点--直接删除
情况4:在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题--替换法删除
4.二叉搜索树的模拟实现
4.1 节点的实现
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode* _left;//左节点指针
BSTreeNode* _right;//右节点指针
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
}; 4.2 查找的实现
bool find(const K& key)
{
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}查找逻辑是从根节点开始查找。如果查找值比当前值大时,往右走;查找值比当前值小时,往左走;否则就是相等,即找到了。
4.3 插入的实现
bool insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new node(key);
return true;
}
node* partent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;//不允许重复
}
}
cur = new node(key);
if (partent->_key < key)
{
partent->_right = cur;
}
else if (partent->_key > key)
{
partent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}如果是空树,就直接创建一个新的节点,不是的话就从根节点开始比较,小就往左走,大就往右走,同时要记录父节点的指针,找到合适的位置,创建节点,建立链接。
4.4 删除的实现
bool erase(const K& key)
{
node* partent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else//找到了
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左为空
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (partent->_right == cur)
{
partent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
partent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//右为空
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (partent->_right == cur)
{
partent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
partent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
}
else//左右都不为空
{
node* partent = cur;//找替代节点
node* leftmax = cur->_left;
while (leftmax->_right)//找最右节点
{
partent = leftmax;
leftmax = leftmax->_right;
}
swap(leftmax->_key, cur->_key);
if (partent->_left == leftmax)
{
partent->_left = leftmax->_left;
}
else
{
partent->_right = leftmax->_left;
}
cur = leftmax;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}删除的比较复杂,一段一段拿出来分析
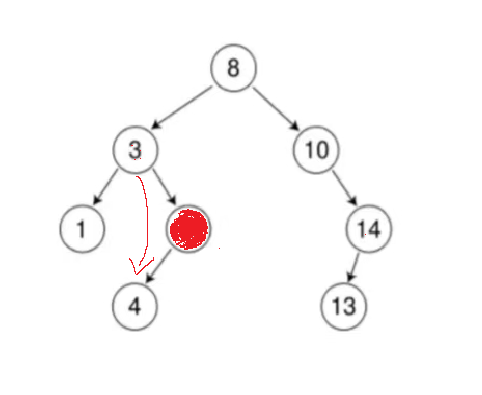
分析要删除的节点左,右节点为空的情况:
红色的节点表示要删除的节点。
node* partent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else//找到了
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左为空
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (partent->_right == cur)
{
partent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
partent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//右为空
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (partent->_right == cur)
{
partent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
partent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
}这时候cur已经指向了要删除的节点,如果被删除的节点左边的节点为空的话,只需要把它的判断它在父节点的左边还是右边,在左边。让父节点的左指针指向它的右节点,在右边就让父节点的右指针指向它的右节点。
ps:要注意如果要删除的节点是根节点,那么父节点就是空节点,调用会报错,所以要先判断是否为根节点。
分析都不为空的情况:
else//左右都不为空
{
node* partent = cur;//找替代节点
node* leftmax = cur->_left;
while (leftmax->_right)//找最右节点
{
partent = leftmax;
leftmax = leftmax->_right;
}
swap(leftmax->_key, cur->_key);
if (partent->_left == leftmax)
{
partent->_left = leftmax->_left;
}
else
{
partent->_right = leftmax->_left;
}
cur = leftmax;
}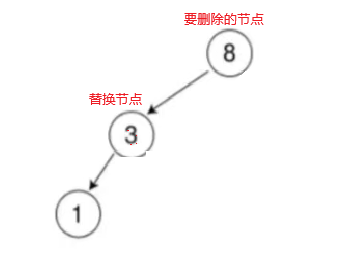
首先要找代替节点,可以找左子树的最右节点或者右子树的最左节点,代码中找的是左子树的最右节点,找到替代节点后交换两个节点的值,这个时候不能直观的认为替换的节点虽然是左子树的最右节点但是并不一定它一定在父节点的右边,还要判断,并且父节点不能一上来就置为空,如果是上图的情况就会出问题。
4.5 二叉搜索树的遍历
void _inorder(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_inorder(root->_right);
}这里实现的是中序遍历。
5.二叉搜索树的模拟实现(递归版)
5.1 查找的实现
bool _findr(node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _findr(root->_left,key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _findr(root->_right,key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}递归查找逻辑是如果当前根的值小于目标值,递归至右树查找;如果当前根的值大于目标值,递归至左树查找;否则就是找到了,返回true。
5.2 插入的实现
bool _insertr(node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _insertr(root->_right,key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _insertr(root->_left,key);
}
else return false;
}如果是空树,就直接创建一个新的节点,不是的话就从根节点开始比较,小就递归到左数去比较,大就递归到右数去比较,找到合适的位置,创建节点,建立链接,如果遇到一样的就返回错误。
4.4 删除的实现
bool _eraser(node* &root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _eraser(root->_left,key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _eraser(root->_right,key);
}
else
{
node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
node* leftmax = root->_left;
while (leftmax->right)
{
leftmax = leftmax->_right;
}
swap(root->_key, leftmax->_key);
return _eraser(root->_left, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}分析要删除的节点左,右节点为空的情况:
使用指针引用,在递归中,root存储的左或右指针的引用,当找到要删除的值时,直接改变指针的指向即可。
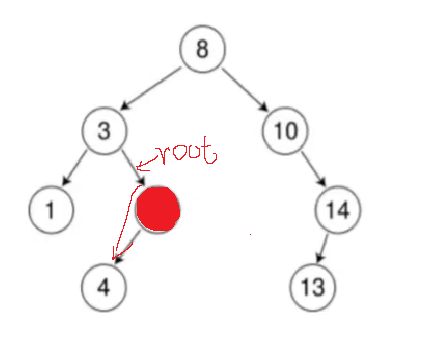
当递归到root为要删除的节点时,因为我们使用了指针引用,所以这个时候root是节点3的右指针引用,我们直接改变节点3的右指针的指向,指向为4即可。
分析都不为空的情况:
找到左子树的最右节点,交换两个数的值,在递归中去删除,因为交换了之后,左子树的最右节点的位置的右一定是空的。
4.5 析构函数
void destory(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
destory(root->_left);
destory(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}由于二叉搜索树的节点是通过new创建在堆上的,所以在销毁二叉搜索树时需要递归地释放每个节点的内存。这里采用后序遍历的方式,先释放左右子树,再释放根节点。
4.6 拷贝构造和赋值重载
node* copy(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
node*copyroot = new node(root->_key, root->_value);
copyroot->_left=copy(root->_left);
copyroot->_right=copy(root->_right);
return copyroot;
}
BSTree& operator=(BSTree t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
} 拷贝构造运行前序遍历,先拷贝根节点再拷贝左右节点,赋值重载直接使用swap函数。
6.模拟实现的两个版本的完整代码
template
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode* _left;//左节点指针
BSTreeNode* _right;//右节点指针
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
template
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
BSTree(const BSTree& t)
{
_root = copy(t._root);
}
BSTree& operator=(BSTree t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
destory(_root);
}
bool find(const K& key)
{
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new node(key);
return true;
}
node* partent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;//不允许重复
}
}
cur = new node(key);
if (partent->_key < key)
{
partent->_right = cur;
}
else if (partent->_key > key)
{
partent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
node* partent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
partent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else//找到了
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左为空
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (partent->_right == cur)
{
partent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
partent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//右为空
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (partent->_right == cur)
{
partent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
partent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
}
else//左右都不为空
{
node* partent = cur;//找替代节点
node* leftmax = cur->_left;
while (leftmax->_right)//找最右节点
{
partent = leftmax;
leftmax = leftmax->_right;
}
swap(leftmax->_key, cur->_key);
if (partent->_left == leftmax)
{
partent->_left = leftmax->_left;
}
else
{
partent->_right = leftmax->_left;
}
cur = leftmax;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void inorder()
{
_inorder(_root);
}
void findr(const K& key)
{
return _findr(_root, key);
}
void insertr(const K& key)
{
return _insertr(_root, key);
}
void eraser(const K& key)
{
return _eraser(_root, key);
}
private:
node* copy(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
node* copyroot = new node(root->_key);
copyroot->_left=copy(root->_left);
copyroot->_right=copy(root->_right);
return copyroot;
}
void destory(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
destory(root->_left);
destory(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
bool _findr(node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _findr(root->_left,key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _findr(root->_right,key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
bool _insertr(node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _insertr(root->_right,key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _insertr(root->_left,key);
}
else return false;
}
bool _eraser(node* &root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _eraser(root->_left,key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _eraser(root->_right,key);
}
else
{
node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
node* leftmax = root->_left;
while (leftmax->right)
{
leftmax = leftmax->_right;
}
swap(root->_key, leftmax->_key);
return _eraser(root->_left, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
void _inorder(node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_inorder(root->_right);
}
node* _root;
}; 7.二叉树的应用场景
1.key模型:用“唯一标识”锁定目标,一个key对应一个确定的实体/数据,身份证号 → 个人信息,图书ISBN码 → 书籍详情。
2.key_value模型:用“键值对”映射现实关系,学生学号(key)→ 成绩(value),商品条形码(key)→ 价格(value)。
7.1 二叉搜索树小结
插入和删除操作都必须先查找,查找效率代表了二叉搜索树中各个操作的性能。
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二
叉搜索树的深度的函数,即结点越深,则比较次数越多。
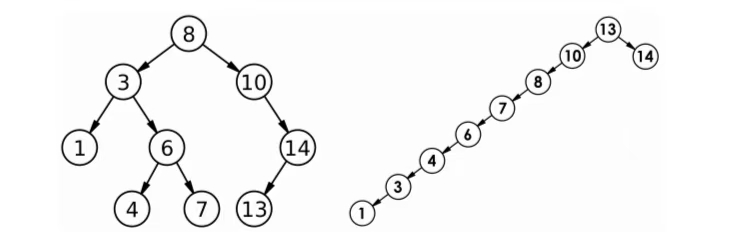
但对于同一个关键码集合,如果各关键码插入的次序不同,可能得到不同结构的二叉搜索树:
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树(或者接近完全二叉树)效率为logN。
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树(或者类似单支)效率为N。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号