详细介绍:如何在本地部署腾讯混元大模型并连接到 Elasticsearch 进行使用

腾讯混元大模型由腾讯公司全链路自研,在高质量的内容创作、数理逻辑、代码生成、多轮对话、图像与视频生产上性能表现优越,处于业界领先水平。我一直想在我自己的电脑上安装并试用。在本文中,我将详细描述安装过程并连接到 Elasticsearch。
注意:一下展示使用最新的 Elastic Stack 9.2.0。其界面可能和之前的有的版本有所不同。
安装混元大模型
我希望使用 Ollama 来进行安装。很可惜,目前混元大模型还不支持 Ollama 按照。我在国内的网站上搜索了一下,很少有详细介绍如何安装的。腾讯混元-4B(及更小的变体)可以与 Ollama 一起使用,但目前还不能直接开箱即用。你需要使用与 llama.cpp 兼容的 GGUF 量化版本,然后将其包装为自定义 Ollama 模型。
Ollama 使用 llama.cpp 引擎,它支持 GGUF 格式的模型 —— 包括经过转换或已下载为 GGUF 格式的 Hunyuan-4B。
Hugging Face 上已经有一个可直接使用的量化版本:mradermacher/Hunyuan-4B-Instruct-GGUF
详细安装步骤:
步骤 1:安装 Ollama
从 Download Ollama on macOS 下载适用于 macOS、Windows 或 Linux 的 Ollama。
按照安装程序的指引完成安装,安装完成后,在终端运行以下命令进行验证:
ollama --version$ ollama --version
ollama version is 0.12.9步骤 2:下载 GGUF model
从这些版本中选择一个(例如 Q4_K_M,以平衡质量和速度):
mkdir -p ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b
cd ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b
curl -L -O https://huggingface.co/mradermacher/Hunyuan-4B-Instruct-GGUF/resolve/main/Hunyuan-4B-Instruct.Q4_K_M.gguf$ ls .ollama/models/
blobs manifests
$ mkdir -p ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b
$ ls ~/.ollama/models
blobs hunyuan-4b manifests
$ cd ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b
$ curl -L -O https://huggingface.co/mradermacher/Hunyuan-4B-Instruct-GGUF/resolve/main/Hunyuan-4B-Instruct.Q4_K_M.gguf
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 1353 100 1353 0 0 966 0 0:00:01 0:00:01 --:--:-- 966
100 2486M 100 2486M 0 0 5854k 0 0:07:14 0:07:14 --:--:-- 4677k步骤 3 – 创建自定义 Modelfile
在 ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b/Modelfile 中创建以下内容:
FROM ./Hunyuan-4B-Instruct.Q4_K_M.gguf
PARAMETER temperature 0.7
PARAMETER top_p 0.9
PARAMETER num_ctx 4096
TEMPLATE """{{ .System }}
User: {{ .Prompt }}
Assistant:"""
SYSTEM "You are Hunyuan, a helpful Chinese assistant developed by Tencent."$ vi ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b/Modelfile步骤 4 – 在 Ollama 中注册模型
ollama create hunyuan-4b -f ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b/Modelfile$ ollama create hunyuan-4b -f ~/.ollama/models/hunyuan-4b/Modelfile
gathering model components ⠸
gathering model components
copying file sha256:def49bb81ddbecf7c2e3aa557716b915607c6fd3af7e73316c16464321d5da22 100%
parsing GGUF
using existing layer sha256:def49bb81ddbecf7c2e3aa557716b915607c6fd3af7e73316c16464321d5da22
creating new layer sha256:8e48700b8cb5619c3a31e83a13a321070a62ee259d91e1b81b1d2b9eda4a459f
creating new layer sha256:7127d492f5e2ee2a8d4fbfd439094e35f3c13ebc9f07f6e9c9fd64f9cc243f16
creating new layer sha256:dedcbf3159e051675ba89642680de2bbfcac020a3f2c1afde851e27629484659
writing manifest
success步骤 5 – 运行模型
ollama run hunyuan-4b$ ollama run hunyuan-4b
>>> what is Elastic?
1. **Definition:** Elastic refers to the ability of an object or system to change shape or size in response to
external forces without permanent deformation. In simpler terms, it means "bending" or "stretching".
2. **Types of Elasticity:**
* **Elastic (or Young's Modulus):** The property where an object returns to its original shape after the
force is removed.
* **Yield:** When an object deforms permanently even without a constant force applied, it is called yield. A
material that exhibits both elastic and yield properties is called "durable".
3. **Applications of Elasticity in Physics:**
* **Coding (Elastic Database):** Elastic is the name given to the database system by MongoDB.
* **Engineering:** Elasticity is used in designing structures like bridges, buildings, etc., ensuring they
can withstand external forces without permanent deformation.
* **Biology:** Elastic tissues such as muscle and skin are involved in various functions in living organisms.
4. **Elasticity in Software Engineering:** The term "elastic" is often used to describe systems that have the
ability to change their structure or behavior dynamically, adapting to changes in the environment or user input
without a need for complex code modifications.
5. **Elasticity in Physics (Reinforced Elasticity):** A phenomenon where materials undergo multiple rounds of
deformation before returning to their original shape (e.g., rubber bands). This is useful in applications like
car tires, where repeated pressure and release causes small changes in the tire's shape, improving fuel
efficiency.
Okay, let's break down what "Elastic" means.
1. **Core Definition:** In a broad sense, "elasticity" refers to the property of an object or material that can
change its shape or size when subjected to stress (force) and return to its original shape after the stress is
removed.
* Think of stretching a rubber band: it gets longer (deforms), and if you let go, it snaps back to its
original length. That's elastic deformation.
2. **Types in Physics:**
* **Elastic Deformation:** The object returns to its original shape after the force is removed. Examples
include a spring or a metal rod.
* **Yield (or Ductile Deformation):** The object deforms permanently even without constant stress, and
sometimes it will later return to some extent. A material that can undergo both elastic and yield deformation is
called "ductile."
* **Plastic Deformation:** Permanent shape changes that cannot be easily reversed by the removal of stress.
3. **Why Elasticity Matters (Applications):**
* **Engineering & Architecture:** Designing buildings, bridges, and other structures allows for them to
withstand external forces like wind, earthquakes, or traffic loads without collapsing permanently.
* **Biology:** Muscles and skin are elastic tissues that allow movement and flexibility in living
organisms.
* **Physics & Chemistry (Elastic Bands):** Used in demonstrations of elasticity, as mentioned
above.
* **Materials Science:** Understanding how different materials respond to stress helps in selecting the
right material for specific applications.
4. **"Elastic" in Software Development:**
* While not a physical property like in physics or engineering, the term "elastic" is often used
metaphorically in software development:
* An **Elastic Database** (like MongoDB) is designed to scale up and down automatically when the number
of users or data grows. It can handle increased load without requiring manual intervention from developers.
* An **Elastic System** can adapt its behavior or structure dynamically in response to changes, making
it more flexible and resilient than a rigid system.
In summary, "elastic" describes something that can stretch (or compress) and return to its original state. This
property is crucial for many physical systems and also leads to the concept of scalable and adaptable software
architectures.
>>> What is Elasticsearch?
Okay, let's break down what "Elasticsearch" means.
1. **Elastic as a Metaphor:** The name comes from the Greek adjective "ellastos," meaning "to stretch." In the
context of computing, it refers to the ability of software systems to scale and adapt dynamically without
requiring manual intervention or complex code changes.
2. **Core Concept - Scalability & Elasticity:**
* **Scalability (Up-Scaling):** The system can handle a significantly larger number of users or data volume
without performance degradation or crashes. For example, when more people start using a web application, the
database can automatically add more capacity.
* **Elasticity (Auto-Sharding & Rebalancing):** When the load on an Elasticsearch node decreases, it can
remove resources from that node and move them to other nodes with less load. Conversely, if a node becomes
overloaded, it can be assigned new clients or data chunks. This automatic distribution of work keeps the system
balanced and responsive.
3. **Analogy:** Think of your car's engine or brakes being "elastic." If you use more gas (stress), the engine
heats up slightly. When you let off the gas and turn it off, the heat dissipates back to normal (returns to
original state). Similarly, Elasticsearch manages its resources dynamically based on current load.
4. **Why Use Elasticsearch?**
* **High Availability & Fault Tolerance:** It's designed for distributed systems, making it resilient even
if some nodes or data shards fail.
* **Real-time Search and Analytics:** It excels at quickly indexing large amounts of text (like website
content) and retrieving relevant information in near real-time.
* **Distributed Nature:** Data is sharded across many machines, allowing for massive storage and retrieval
capabilities far beyond a single machine's limits.
* **Suitable for Log Data & Large Datasets:** It's commonly used to store and analyze logs from
applications, servers, or IoT devices.
5. **Common Use Cases:**
* **Search Engines (like Solr):** Elasticsearch powers much of Google Search (as part of the search
infrastructure).
* **Log Management & Monitoring:** Storing and analyzing application logs for performance monitoring and
troubleshooting.
* **Data Indexing/Analysis:** As a backend database for applications that need to perform complex queries
or aggregations on large datasets.
* **Real-time Analytics Dashboards.**
In essence, Elasticsearch is a distributed, fault-tolerant search engine designed for high scalability and
elasticity in the context of data indexing, retrieval, and analysis. It's a fundamental technology for modern
data-driven applications.
>>> 中国最长的河流是哪条河?
中国最长的河流是**长江**。
* **长度:**约6,300公里。这是一条非常长的河流,也是亚洲第一长河。
* **流经地区:**发源于青海省青藏高原的唐古拉山脉各拉丹冬峰西南侧(还有说法认为发源于四川的沱沱河),自西向东流经
青海、西藏、四川、云南、重庆、湖北、湖南、江西、安徽、江苏、上海11个省级行政区,最后注入东海。
* **流域面积:**约94万平方公里。
* **重要性:**
* **经济命脉:**是长江经济带的核心,对促进沿线地区的经济发展至关重要。长江沿岸拥有全国大部分的重要城市和经济
带核心区域。
* **农业灌溉:**提供大量灌溉用水,支撑着沿岸的农业发展。
* **航运价值高:**拥有黄金水道之称,通航里程长,货运量巨大,是中国乃至世界重要的内河运输通道之一(部分河段如
南京到武汉的长江航道已通江)。
* **生态与旅游:**拥有丰富的生物多样性和独特的自然景观,是重要的水电资源和旅游资源。
* **国防意义:**其地理形势对维护国家安全和领土完整具有重要意义。
因此,无论是从长度还是经济、社会等综合角度来看,长江都是中国最重要的河流之一。
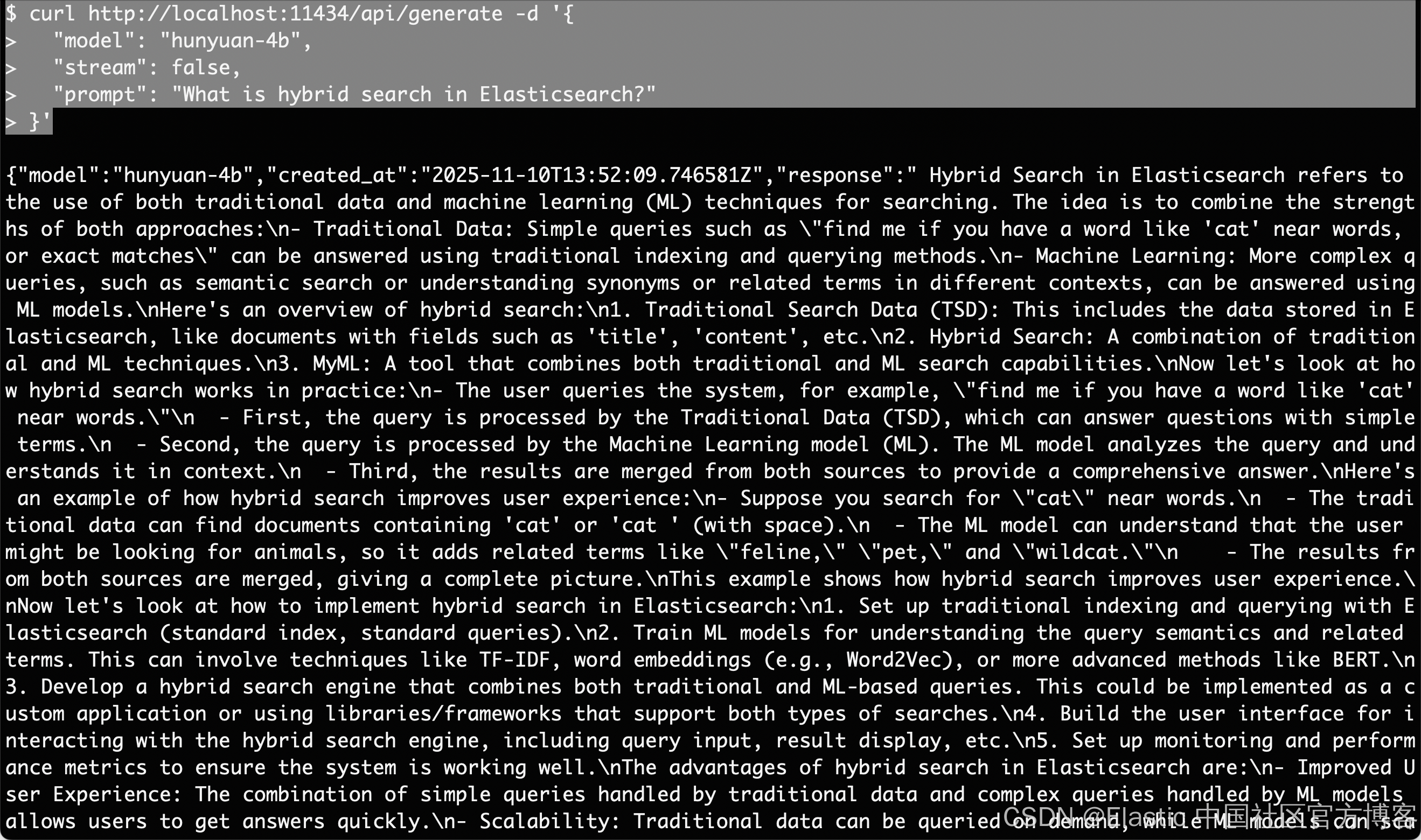
我们可以在另外一个 termninal 中打入如下的命令来进行测试:
curl http://localhost:11434/api/generate -d '{
"model": "hunyuan-4b",
"stream": false,
"prompt": "What is hybrid search in Elasticsearch?"
}'
连接到 Elasticsearch
接下来,我们可以参考文章 “Elasticsearch:在 Elastic 中玩转 DeepSeek R1 来实现 RAG 应用” 来连接到 Elasticsearch。首先我们按照该文中描述的那样安装好自己的 Elasticsearch 及 Kibana,并安装好 E5 模型。
创建 Connector
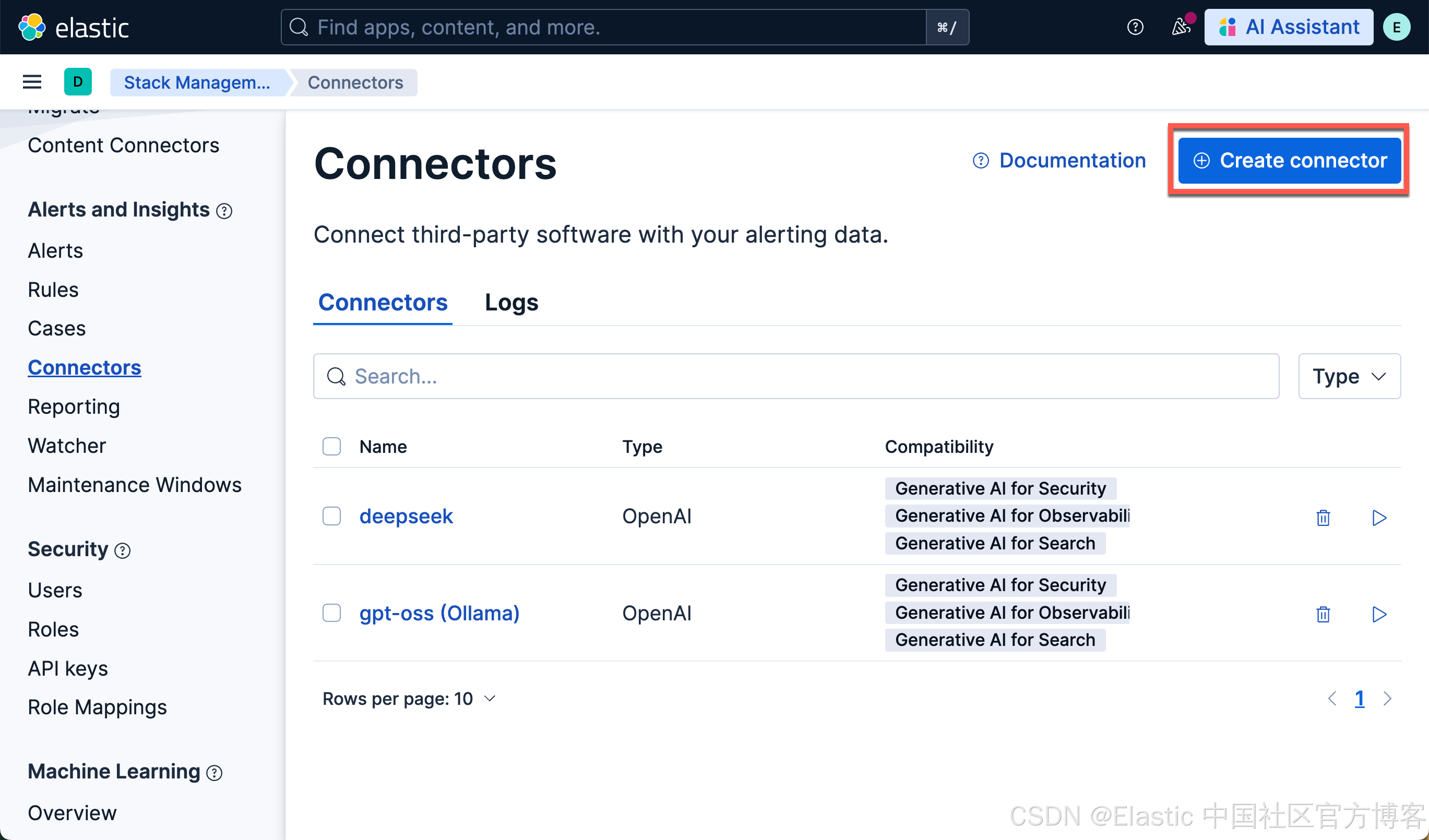
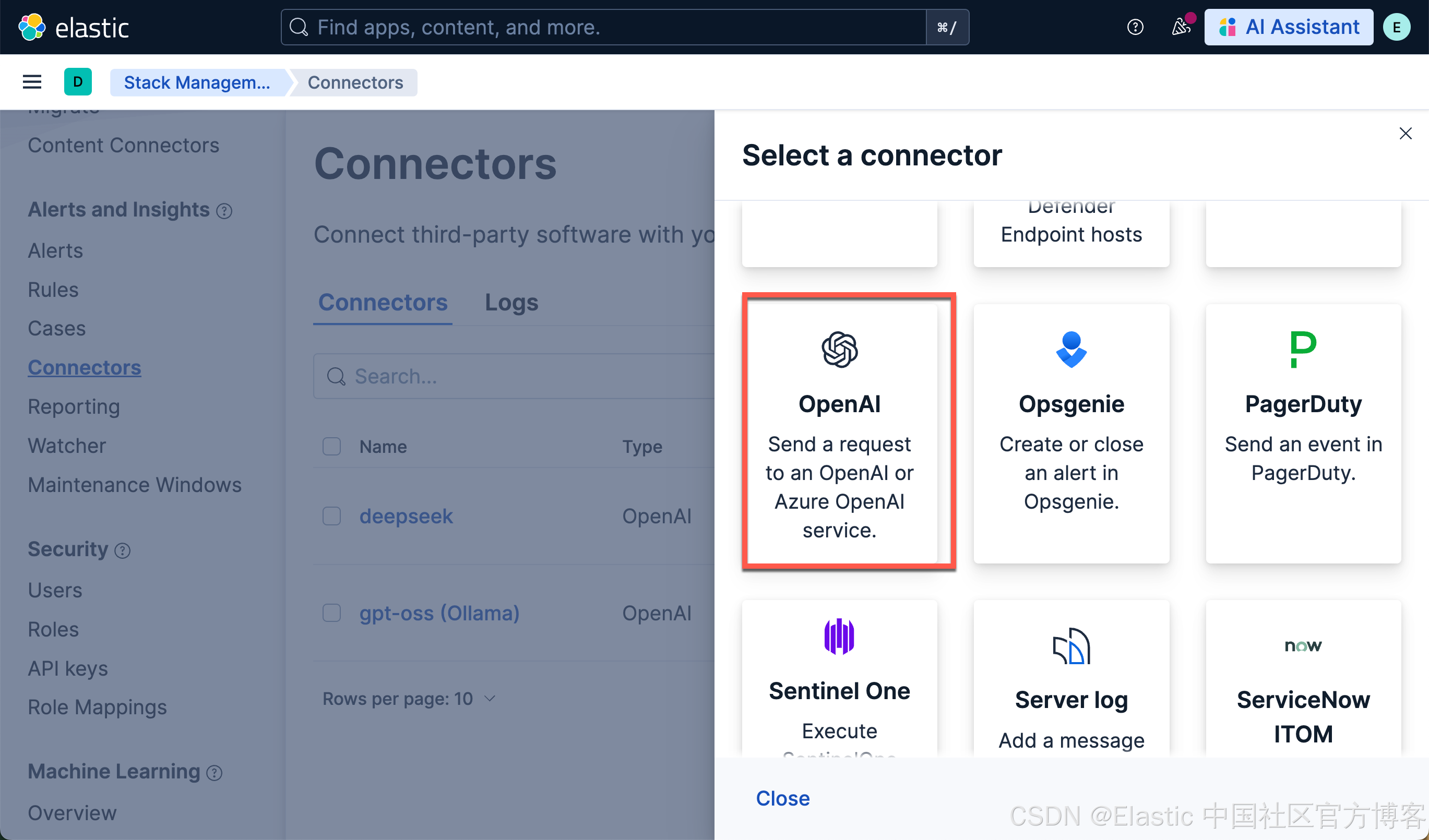
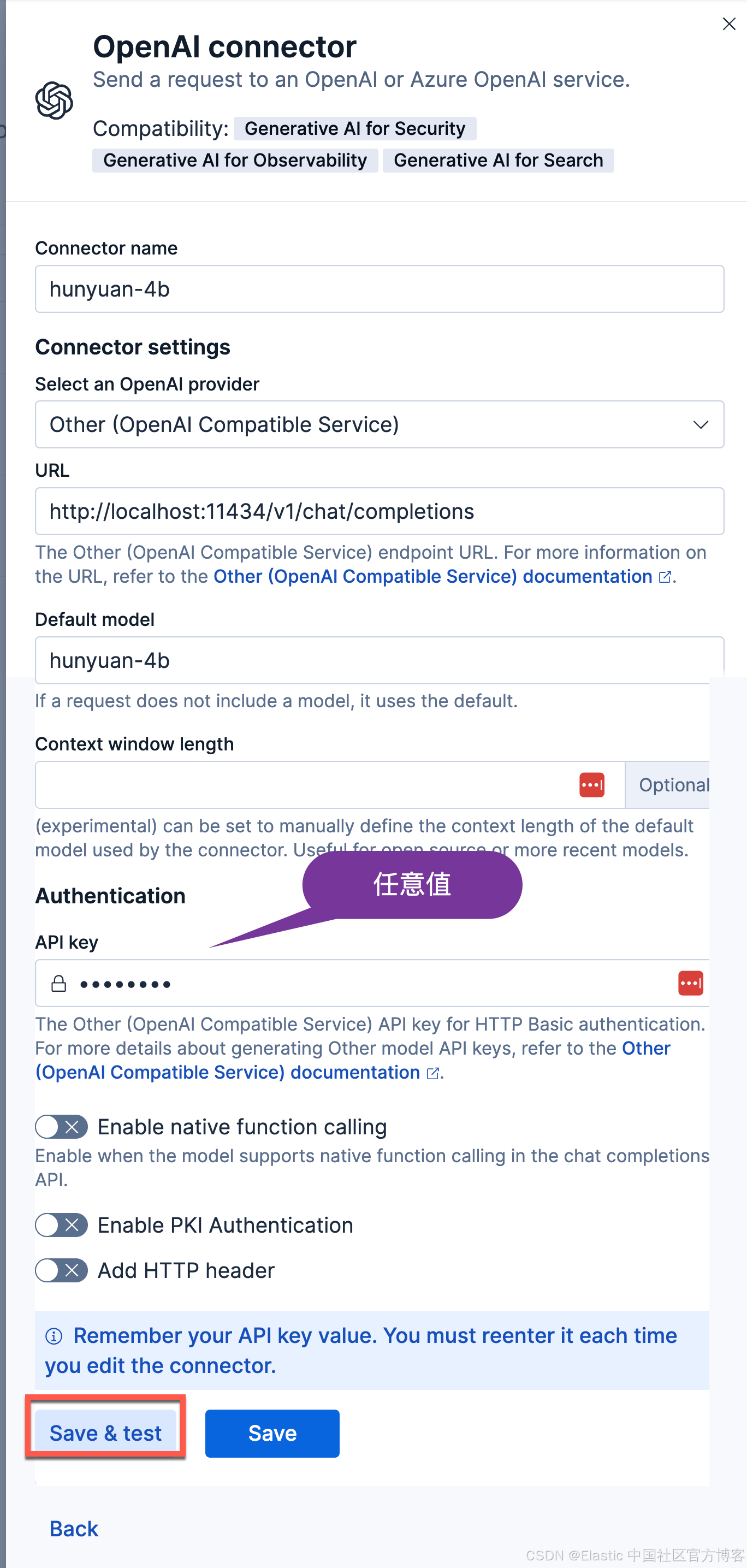
我们按照如下的参数来进行配置:
- Connector name:hunyuan-4b
- 选择 OpenAI provider:other (OpenAI Compatible Service)
- URL:http://localhost:11434/v1/chat/completions
- 调整到你的 ollama 的正确路径。如果你从容器内调用,请记住替换 host.docker.internal 或等效项
- 默认模型:hunyuan-4b
- API 密钥:编造一个,需要输入,但值无关紧要
我们点击上面的 Save & test 按钮:
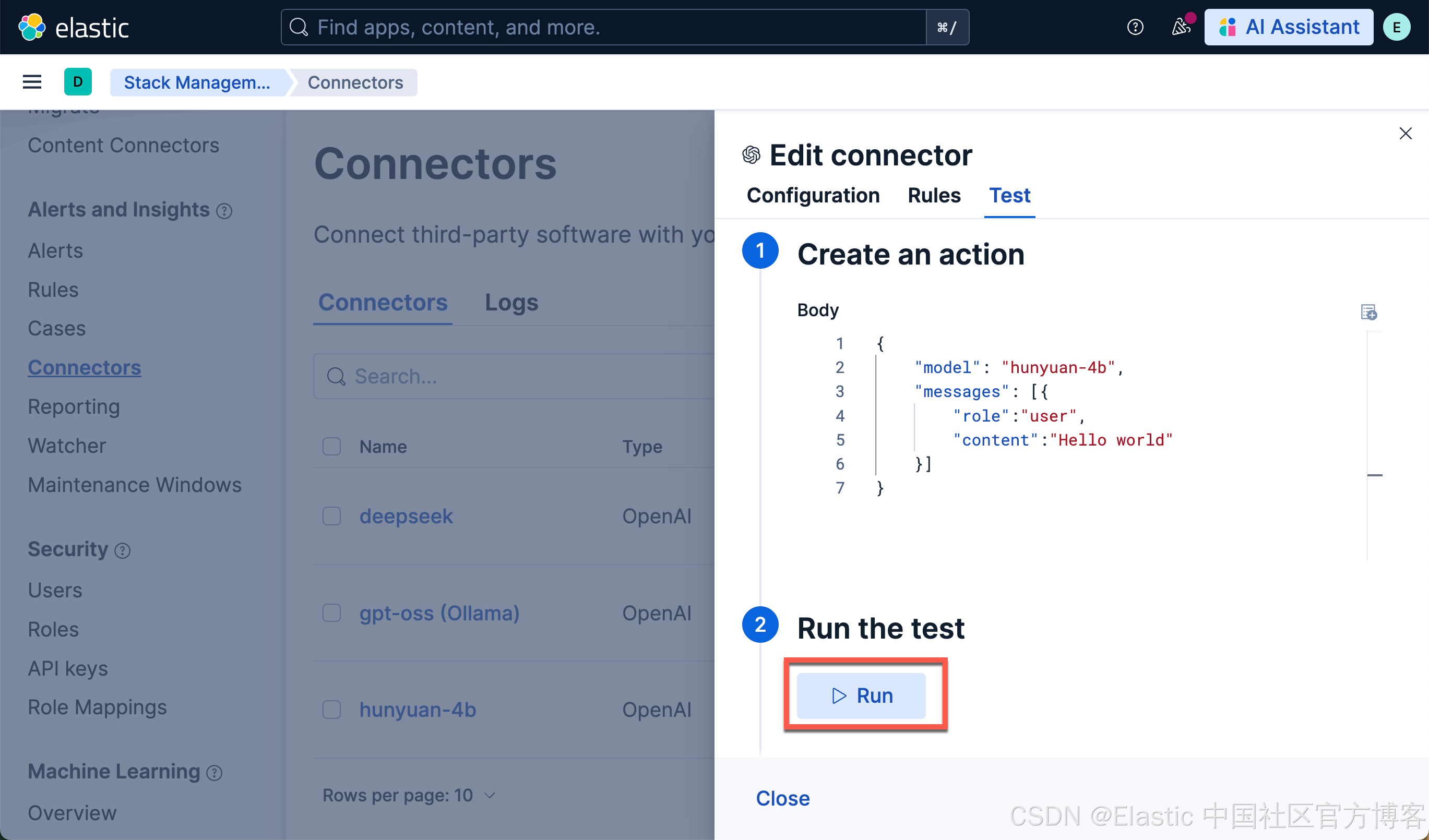
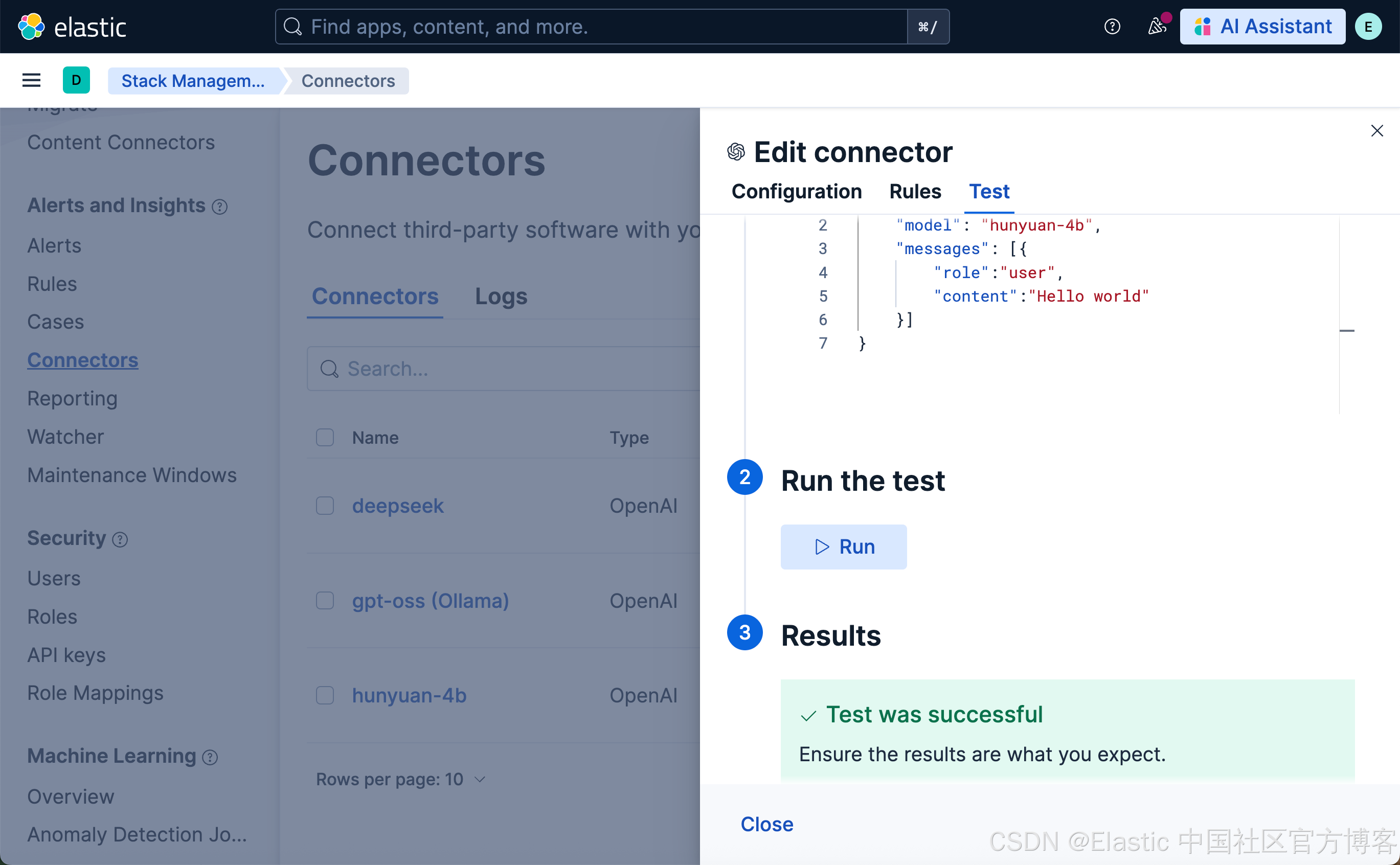
从上面的测试中,我们可以看出来测试是成功的。
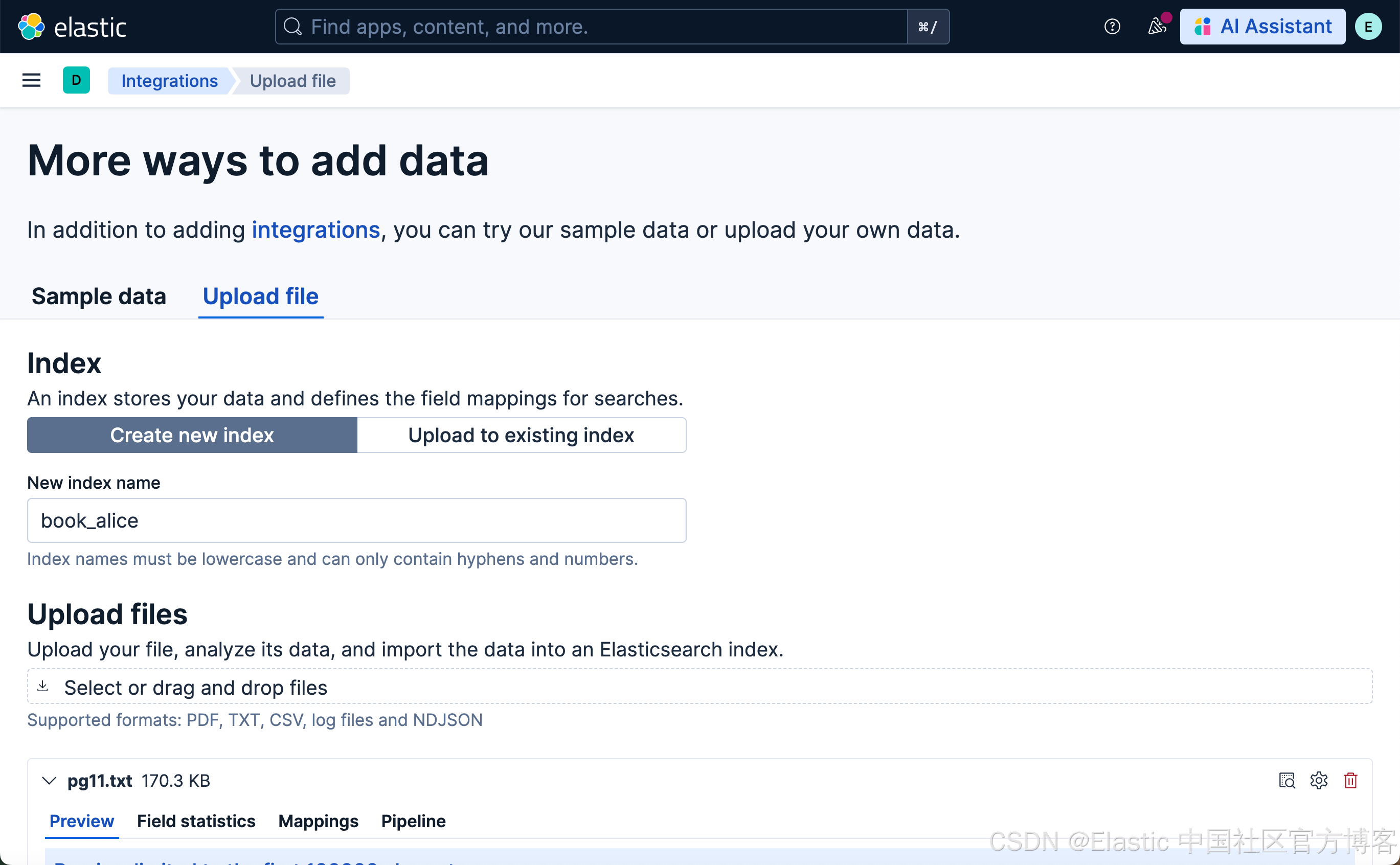
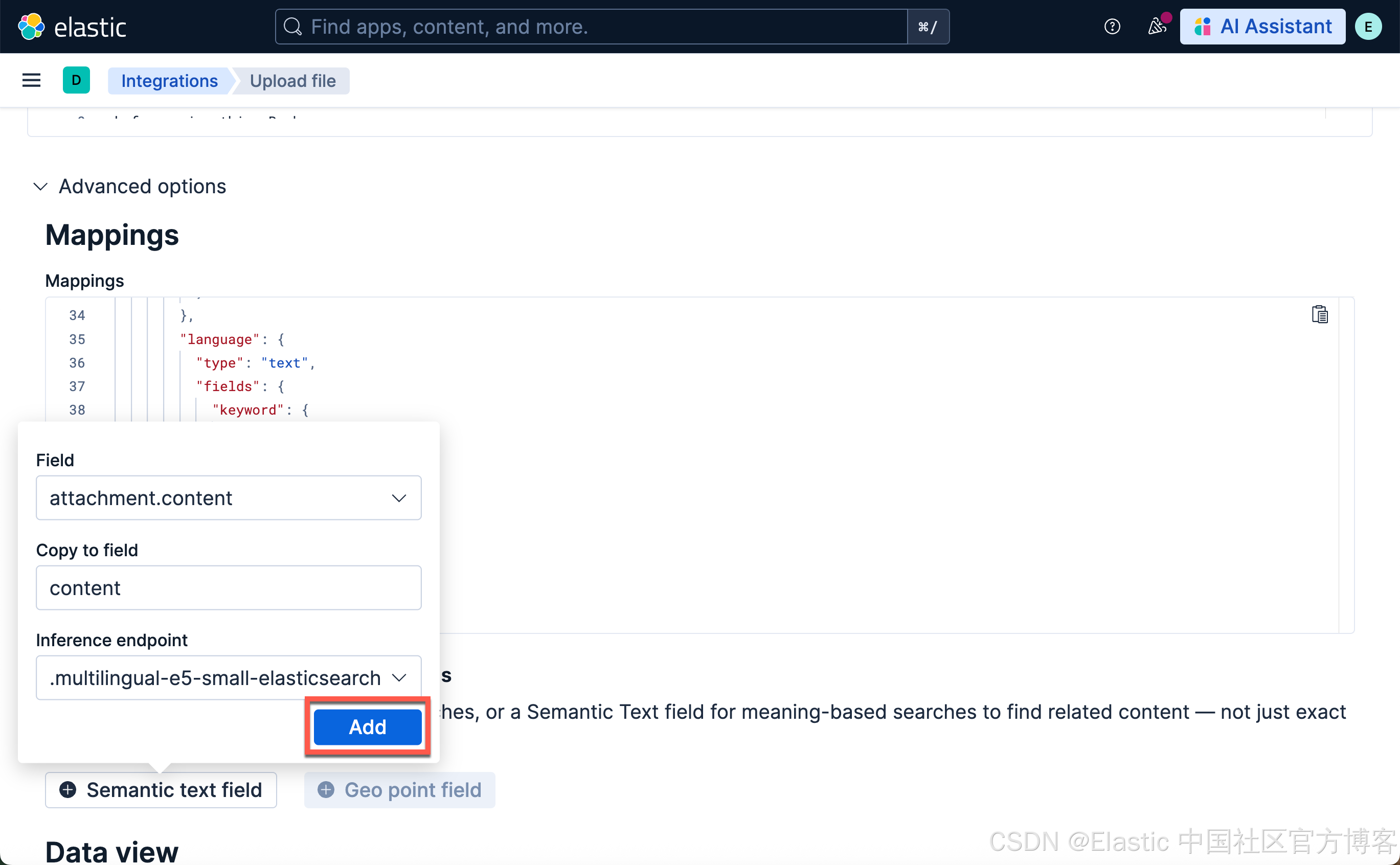
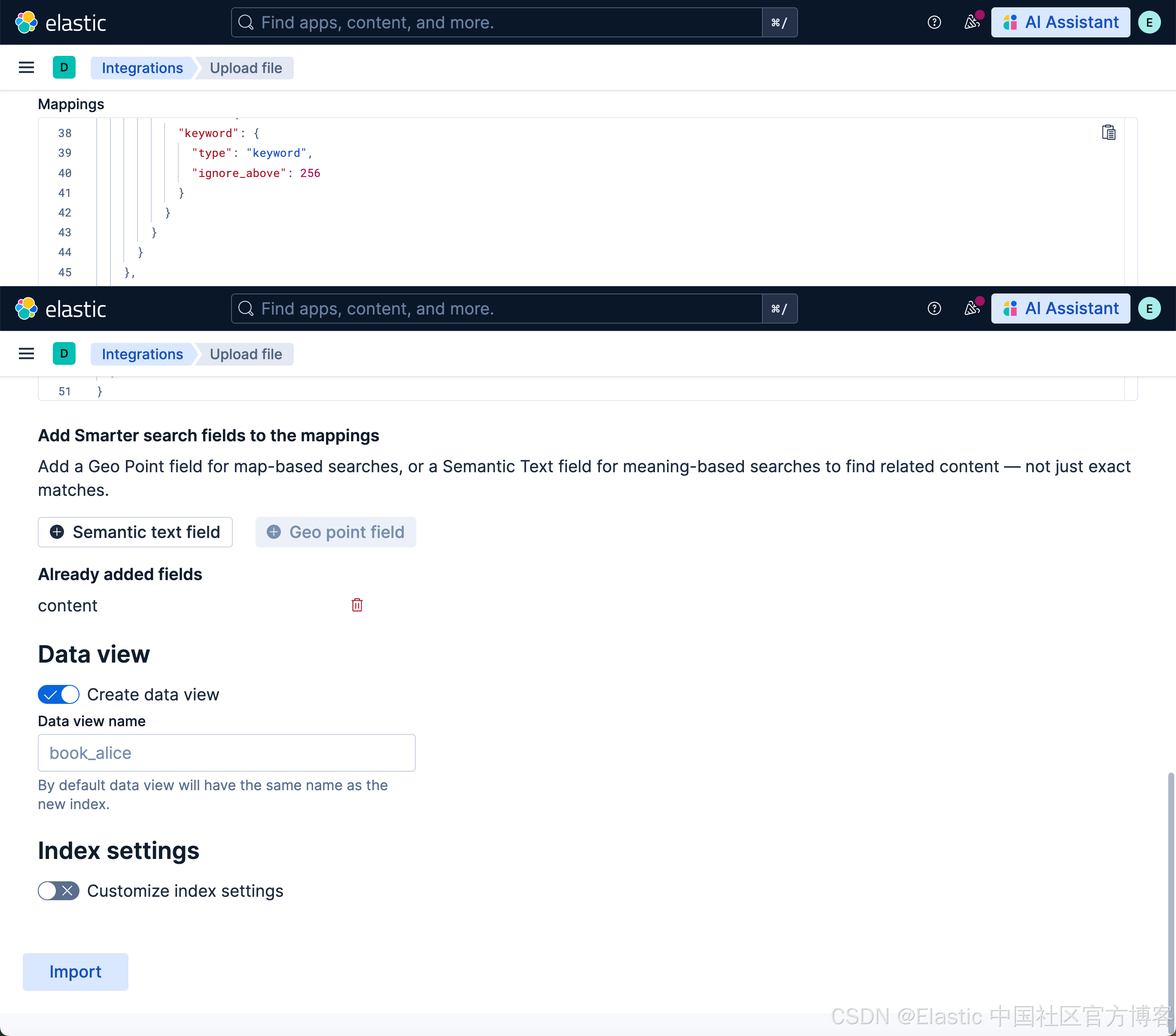
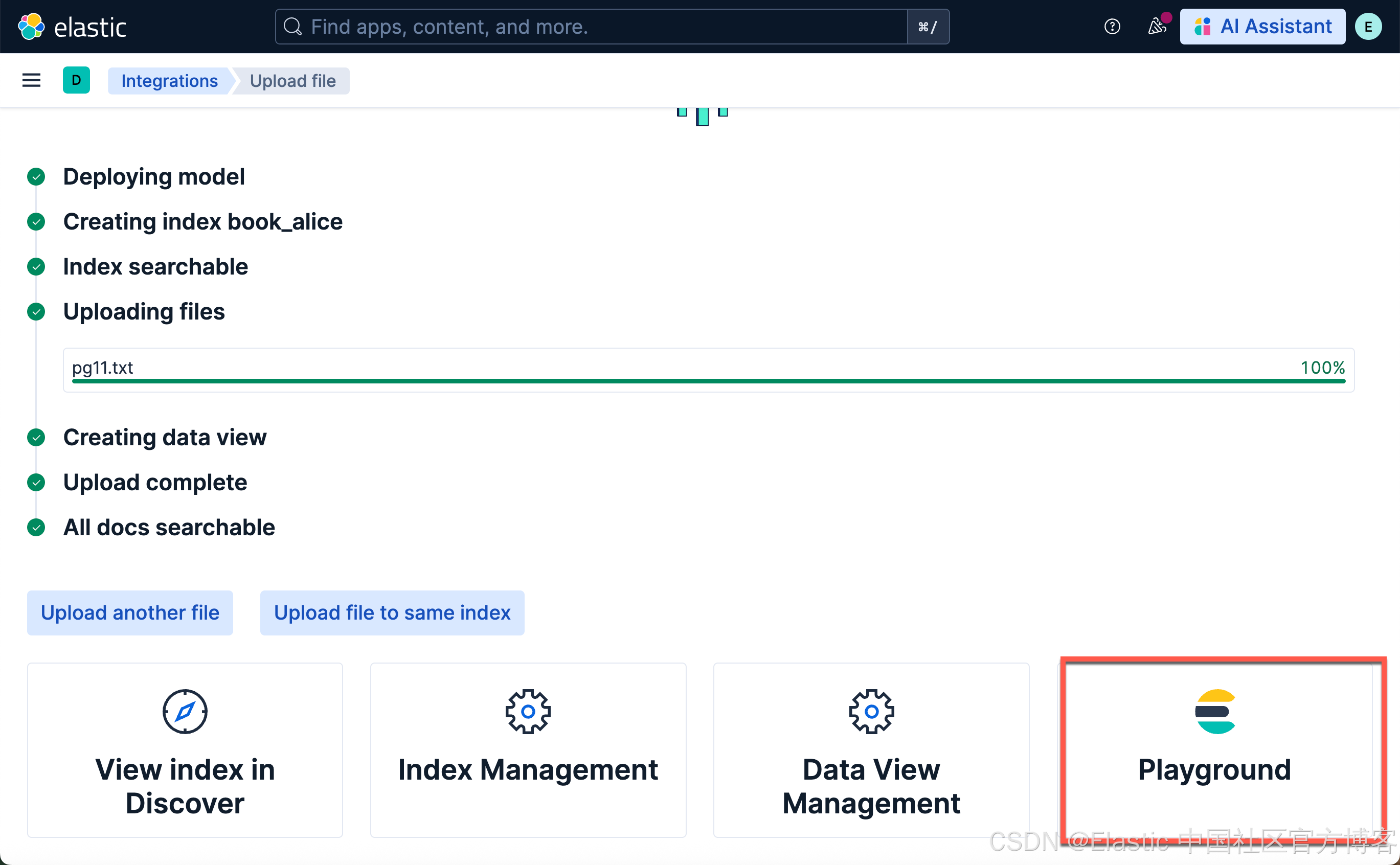
上传文档并在 Playground 中进行测试
我们接下来使用和 “Elasticsearch:在 Elastic 中玩转 DeepSeek R1 来实现 RAG 应用” 文中一样的文档来进行测试。
Instructions:
You are an assistant for question-answering tasks using relevant text passages from the book Alice in wonderland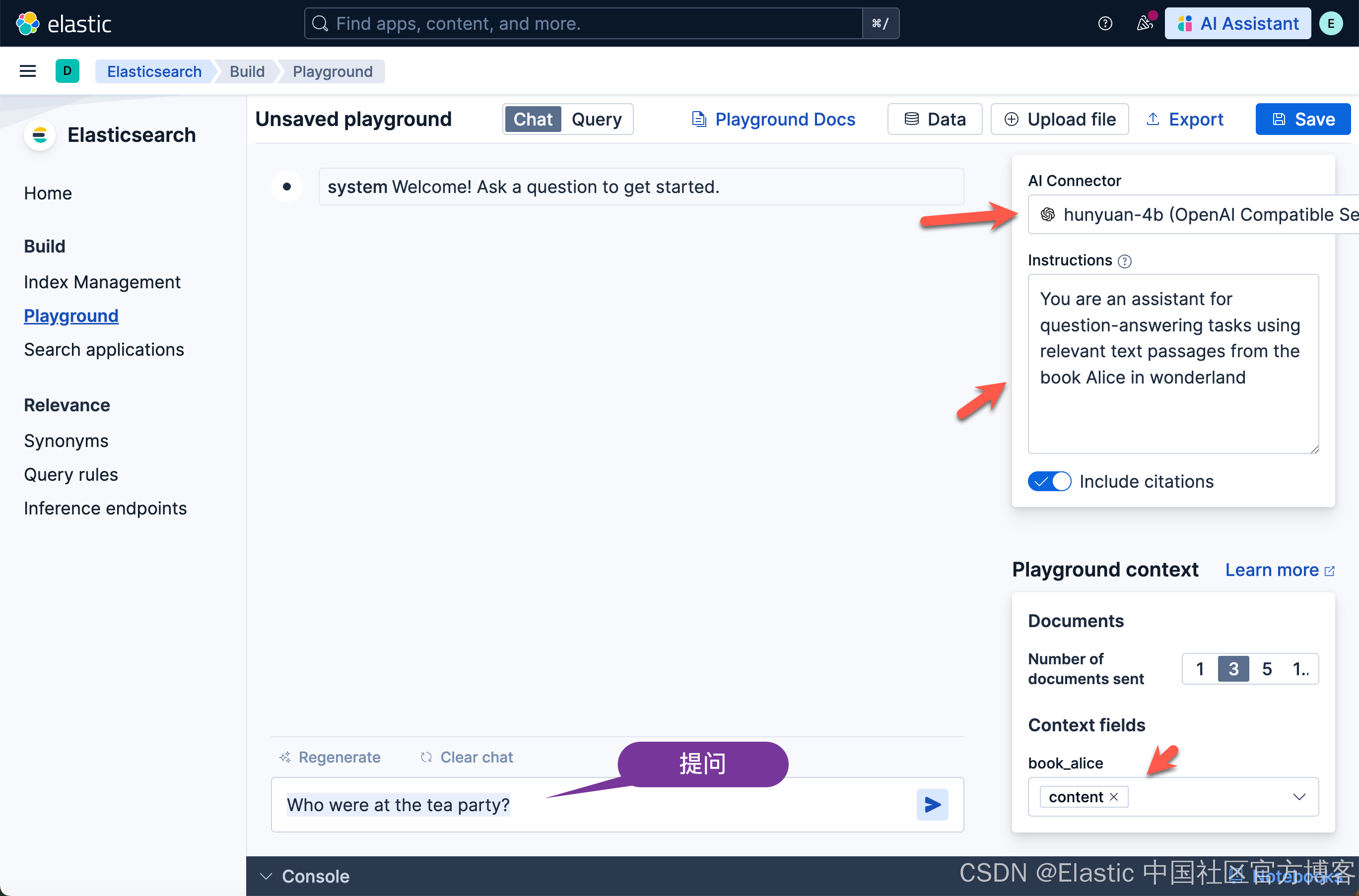
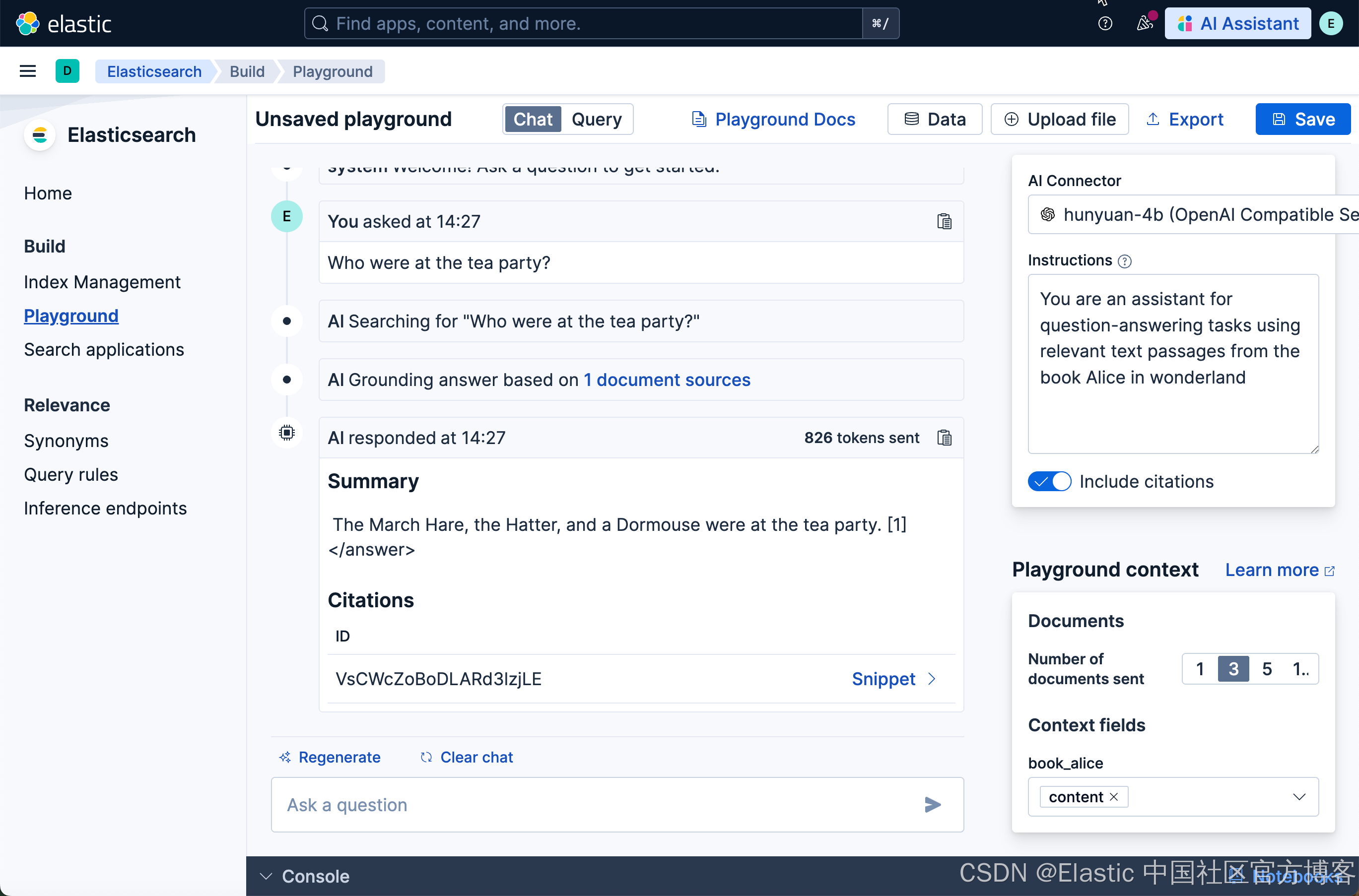
很有意思,混元模型的反应速度比我想象的要快。至少比我上次使用 DeepSeek R1 要快很多。我们尝试使用中文来进行提问:
谁出现在茶会上?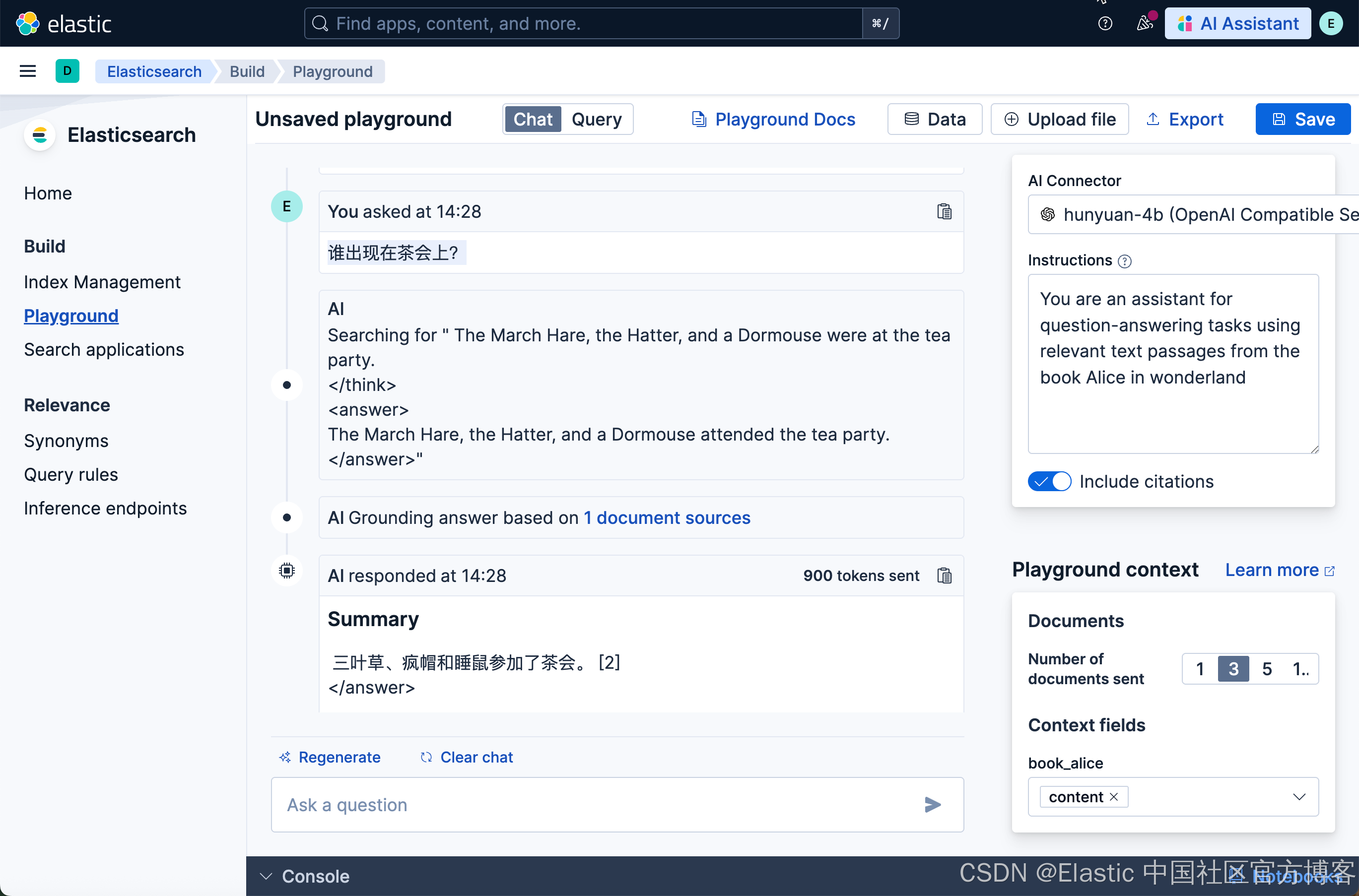
文章有哪些章节?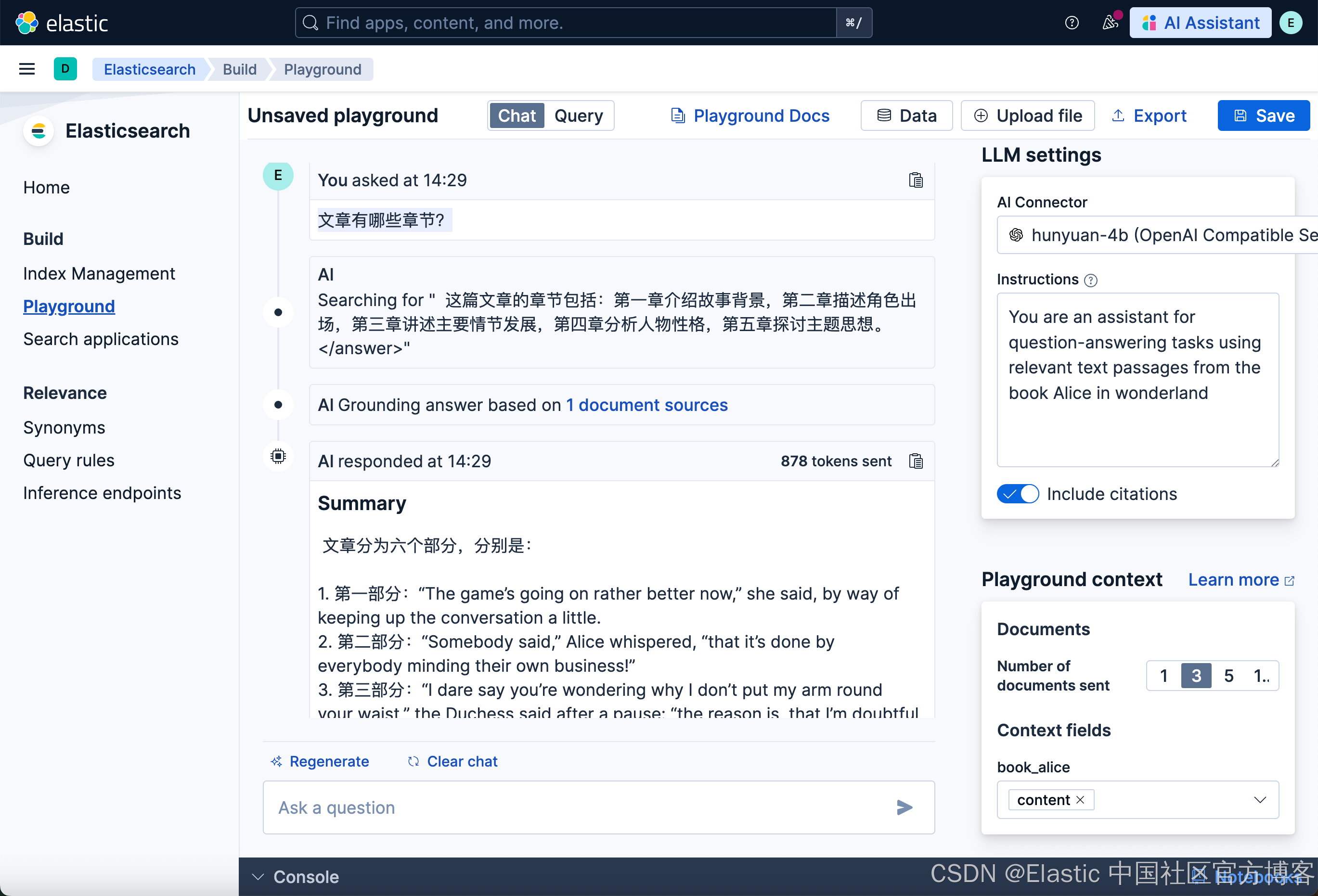
如果你想使用代码来完成查询的话,那么请按照如下的步骤:
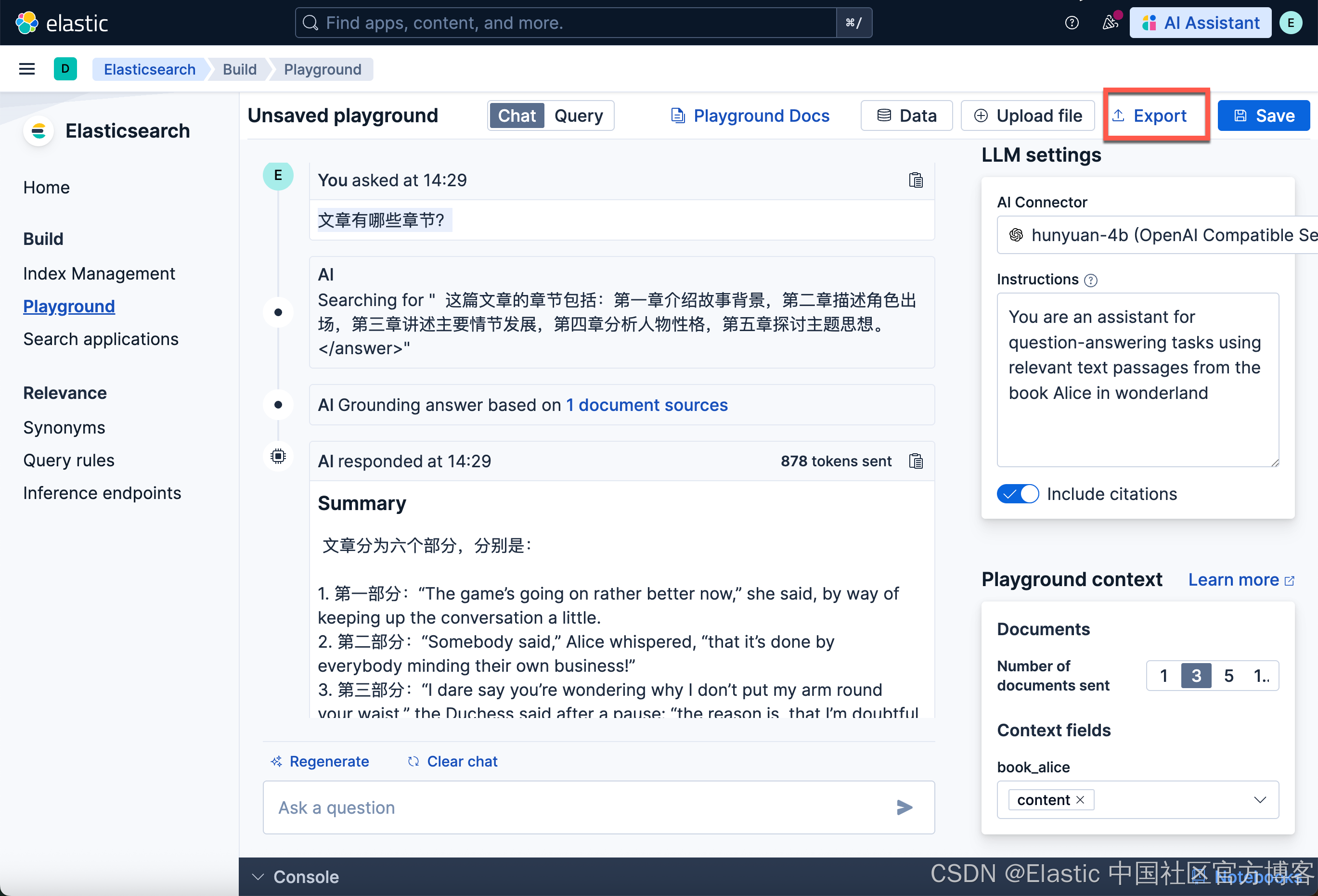
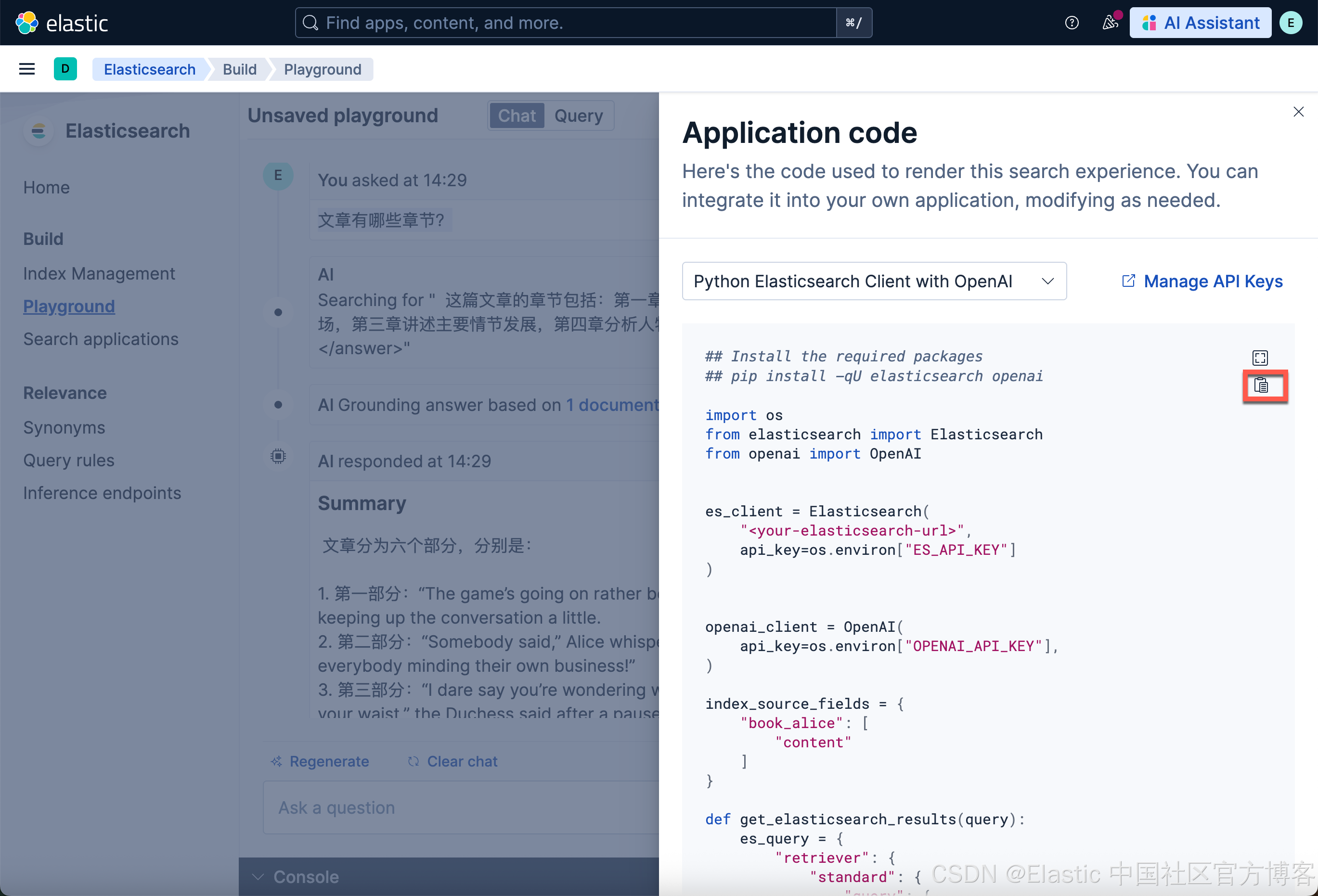
我们可以点击上面的拷贝图标,并做相应的修改 即可。具体的操作步骤,请详细参阅我之前的文章 “Elasticsearch:在 Elastic 中玩转 DeepSeek R1 来实现 RAG 应用”。
好了,今天的分享就到这里。祝大家学习愉快!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号