【JavaWeb】Maven、Servlet、cookie/session - 教程
5. Maven
Maven是一个强大的项目管理和理解程序,重要用于Java项目的构建、依赖管理和文档生成。以下是Maven的简明概述:
- 核心概念:POM(Project Object Model),它是一个XML文件,包含了项目的配置信息,如依赖、构建目标等。
- 依赖管理:自动处理任务依赖的库,依据中央仓库或自定义仓库下载所需的JAR包,并应对版本冲突。
- 构建生命周期:定义了构建过程的标准阶段,包括验证、编译、测试、打包、集成测试、验证、部署等。
- 插件支持:提供了多种插件来扩展其功能,比如编译代码、创建Javadoc以及运行单元测试等。
- 多模块项目:支持复杂项目的分模块构建,方便大型项目的维护和管理。
Maven凭借提供统一的构建系统、**约定优于配置 **的原则以及强大的依赖管理能力,极大地简化了Java项目的开发流程。
- Maven项目的标准结构:
myproject/├── src/│ ├── main/│ │ ├── java/ ← Java源代码 │ │ └── resources/← 资源档案(如.properties, XML等) │ └── test/└── pom.xml6. Servlet
6.1 Servlet 简介
- Servlet就是sun公司开发动态web的一门技术。
- Sun在这些API中提供一个接口叫做:
Servlet,如果你想研发一个Servlet程序,只需要完成两个小步骤:- 编写一个类,实现
Servlet接口; - 把开发好的Java类部署到web服务器中。
把实现了Servlet接口Java程序叫做Servlet
- 编写一个类,实现
6.2 HelloServlet
Serlvet接口Sun公司有两个默认的实现类:HttpServlet,GenericServlet,如图所示,HttpServlet 继承自 GenericServlet,我们手写一个servlet就需要继承自HttpServlet 。

- 构建一个普通的Maven项目,删掉里面的src目录,在这个项目里面建立Moudel;
这个空的工程就是Maven主工程;
- 关于Maven父子工程的理解:
父工程中会有:
<modules> <module>servlet-01</module> </modules>子项目中会有:
<parent> <groupId>org.example</groupId> <artifactId>javaweb-servlet</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent>父项目中的jar包依赖,子项目可以直接使用,反过来则不可以,这就是继承 。
- Maven环境优化
- 编写一个Servlet代码
- 编写一个普通的类
HelloServlet - 我们实现Servlet接口,这里我们直接继承
HttpServlet类
- 编写一个普通的类
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { System.out.println("hello servlet" ) ; PrintWriterwriter= resp.getWriter( ) ;writer.println("Hello Servlet" ) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req,resp) ; } }- 编写Servlet的映射
为什么需要映射:大家写的是Java程序,但是要通过浏览器访问,而浏览器需连接web服务器,所以我们需要在web服务中注册我们写的Servlet,还需给他一个浏览器能够访问的路径。
<!--注册servlet--> <servlet> <servlet-name>helloservlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sunyiwenlong.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <!--servlet请求路径--> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>helloservlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>- 配置tomcat
注意:配置项目发布路径就可以了 - 启动测试
6.3 Servlet原理
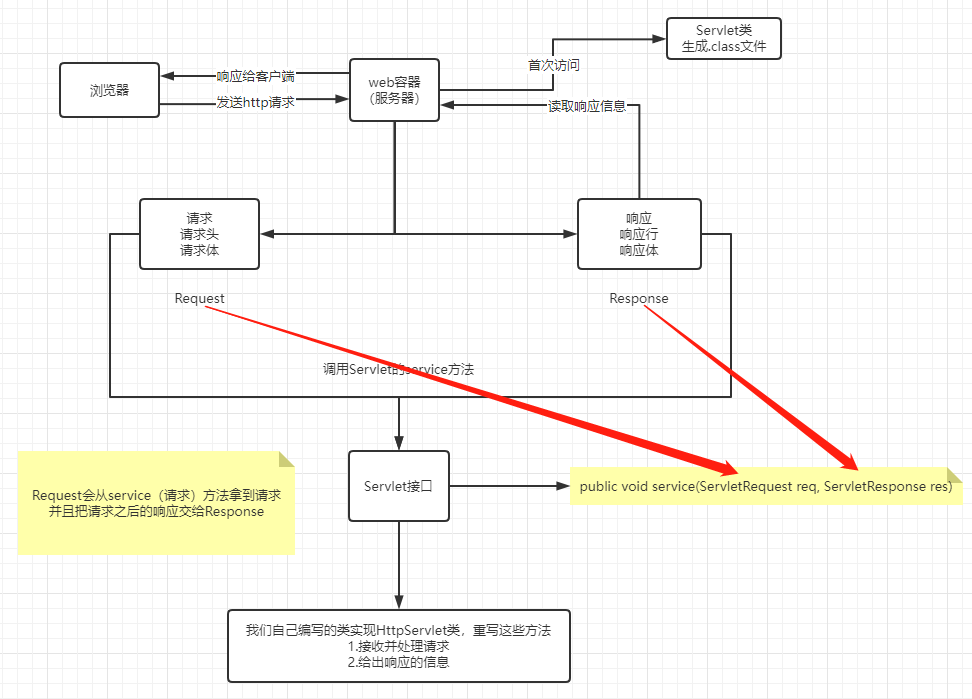
6.4 Mapping( **映射 ** )挑战
<project> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>my-web-app</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <dependencies> <!-- Servlet API --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>4.0.1</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- JSP API --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.3.3</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- Spring MVC 示例 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.3.20</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>mywebapp</finalName> <plugins> <!-- 编译插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- WAR 插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2.3</version> <configuration> <failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>- 一个Servlet可以指定一个映射路径
"/hello"
@WebServlet("/hello" ) public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { // 处理逻辑 } }- 通过一个Servlet能够指定多个映射路径
{"/hello", "/hi", "/greeting"}
@WebServlet({ "/hello" , "/hi" , "/greeting" } ) public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { // 多个路径都能访问到这个 Servlet } }- 通过一个Servlet能够指定通用映射路径
"/user/*"
@WebServlet("/user/*" ) public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { // 所有以 /user/ 开头的请求都会进入该 Servlet } }- 指定一些后缀或者前缀等等…
@WebServlet("*.do" ) public class ActionServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { // 所有以 .do 结尾的请求都进入此 Servlet } }@WebServlet("/api/*" ) public class ApiServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) { // 所有 /api/ 开头的请求进入此 Servlet } }6.5 ServletContext
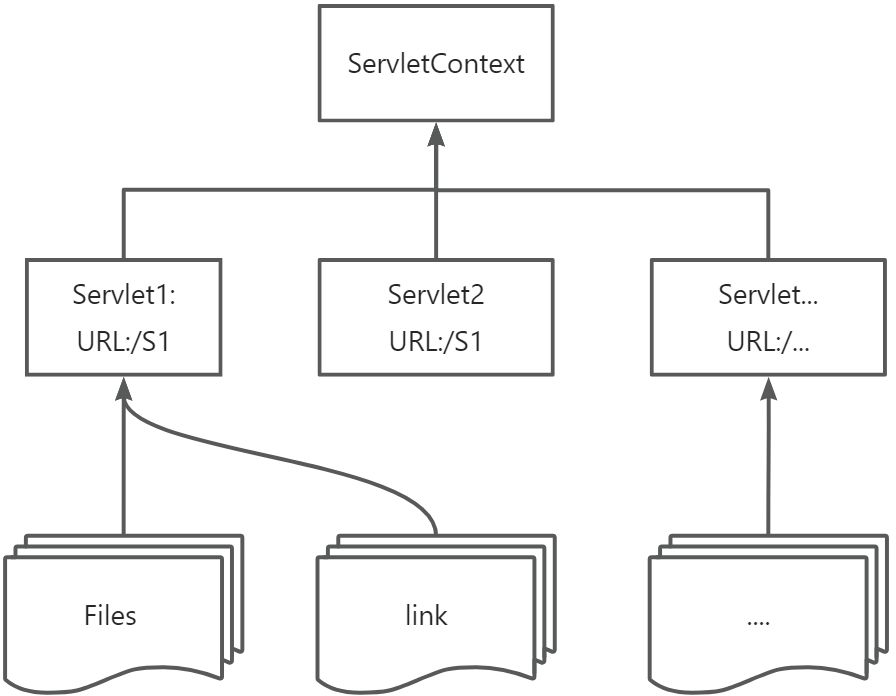
ServletContext 是 Java Web 构建中一个非常核心的接口,属于 Servlet API 的一部分。每个 Web 应用在服务器启动时都会创建一个唯一的 ServletContext 实例。
Q:可以自己手动 new 一个 ServletContext 对象?
A:不能直接 new 创建 ServletContext
Q:why?
A:ServletContext 是 由 Web 容器(如 Tomcat、Jetty)在启动 Web 应用时自动创建的,它是整个 Web 应用的运行环境对象。
Q:那我们怎么获取它?
A:在 Servlet 、Listener、JSP中获取;
web容器在启动的时候,它会为每个web代码都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象,它代表了当前的web应用。
- 共享信息:在这个Servlet中保存的素材,可以在另一个Servlet中拿到
1. 在 Servlet 中获取 `ServletContext`,将一个数据保存在了`ServletContext`中public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { // this.getInitParameter(); 获取初始化参数(web.xml文件中的初始化参数) // this.getServletConfig(); 获取servlet的配置(web.xml文件中的配置) // this.getServletContext(); 获取servlet上下文 ServletContextcontext= this.getServletContext( ) ; Stringusername= "张三" ;context.setAttribute("username" ,username) ; // 将一个数据保存在了ServletContext中 } }// 在 Listener 中获取getServletContext public class MyListener implements HttpSessionListener { public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) { ServletContextcontext= se.getSession( ).getServletContext( ) ; } }2. 将保存在context的资料响应出来。public class GetServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { ServletContextcontext= this.getServletContext( ) ; Stringusername= (String )context.getAttribute("username" ) ; resp.setContentType("text/html" ) ; resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8" ) ; resp.getWriter( ).println("名字"+username) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req,resp) ; } }3. 设置URL地址映射<!-- // web.xml文件 --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="2.4" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"> <servlet> <servlet-name>helloservlet1</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sunyiwenlong.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>helloservlet1</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet> <servlet-name>getservlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sunyiwenlong.servlet.GetServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>getservlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/getc</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>1. <font style="color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.85);">也可以通过注解配置地址映射 :: Servlet 3.0+ 规范1获取初始化参数
配置web应用中的基本参数
<!-- web.xml资料 --> <!--配置一些web应用一些初始化参数--> <context-param> <param-name>url</param-name> <param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis</param-value> </context-param>- 实现
ServletDemo03的Post和Get的逻辑
public class ServletDemo03 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { String url = this.getInitParameter("url" ) ; resp.getWriter( ).println(url) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }请求转发
配置相关URL映射的地址
// web.xml文件 // 请求sd4<servlet> <servlet-name>gp</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sunyiwenlong.servlet.ServletDemo03</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>gp</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/gp</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet> <servlet-name>sd4</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sunyiwenlong.servlet.ServletDemo04</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>sd4</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/sd4</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>/sd4请求 找到ServletDemo04,ServletDemo04逻辑块中进行请求 转发到/gp,到/gp的页面,/gp找到ServletDemo03。
// 请求/sd4找到ServletDemo04,ServletDemo04进行请求转发到/gp,到/gp的页面 // (浏览器路径是sd4的路径,页面拿到的是/gp的资料) public class ServletDemo04 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { ServletContextcontext= this.getServletContext( ) ; System.out.println("进入了demo04" ) ; // RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = context.getRequestDispatcher("/gp");// 转发的路径 // requestDispatcher.forward(req,resp);// 调用forward请求转发context.getRequestDispatcher("/gp" ).forward(req,resp) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }- 读取资源文件
Properties
- 在
src/main/java目录下新建properties - 在
src/main/resources目录下新建properties - 最后都被打包到了同一个路径下:
target/classes,大家俗称这个路径为classpath。
- 构建一个文件流,读取
properties
public class ServletDemo05 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { InputStreamstream= this.getServletContext( ).getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/CLASSES/db.properties" ) ; Propertiesproperties= new Properties( ) ;properties.load(stream) ; Stringusername=properties.getProperty("username" ) ; Stringpassword=properties.getProperty("password" ) ; resp.getWriter( ).println(username+":"+password) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }- 用例图解析:
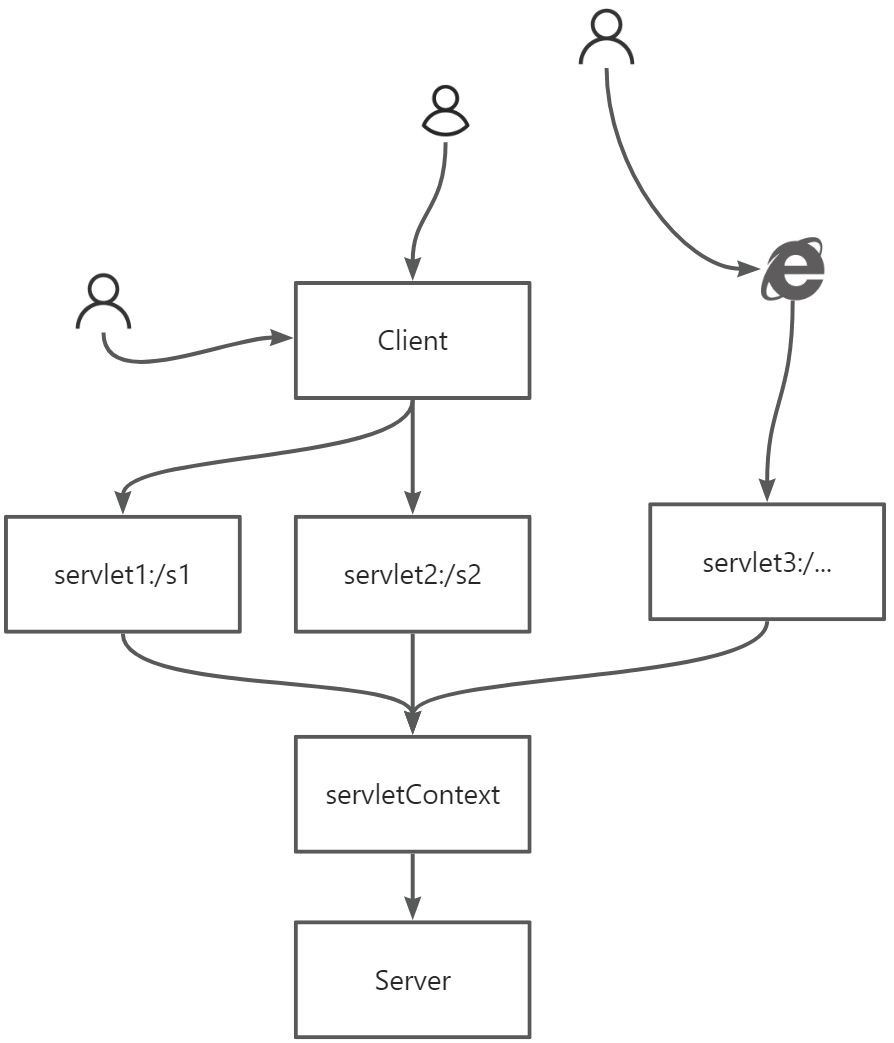
在一个Web应用中,客户端通过请求与服务器上的多个Servlet交互,ServletContext提供一个全局的数据共享空间。就是在其中扮演的角色
重点理解:
ServletContext是所有Servlet都能访问的全局上下文,用于在应用范围内共享资料;而HttpSession则是针对单个用户的会话管理,用于保存用户相关的临时素材。
6.6 HttpServletResponse
web服务器接收到客户端的http请求,针对这个请求,分别创建一个代表请求的HttpServletRequest对象,代表响应的一个HttpServletResponse ;
- 如果要获取客户端请求过来的参数:找
HttpServletRequest - 如果要给客户端响应一些信息:找
HttpServletResponse
- 负责向浏览器发送数据的手段
public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream( ) throws IOException ; public PrintWriter getWriter( ) throws IOException ;- 响应的状态码
public static final int SC_CONTINUE = 100 ; /** * Status code (200) indicating the request succeeded normally. */ public static final int SC_OK = 200 ; /** * Status code (302) indicating that the resource has temporarily * moved to another location, but that future references should * still use the original URI to access the resource. * * This definition is being retained for backwards compatibility. * SC_FOUND is now the preferred definition. */ public static final int SC_MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302 ; /** * Status code (302) indicating that the resource reside * temporarily under a different URI. Since the redirection might * be altered on occasion, the client should continue to use the * Request-URI for future requests.(HTTP/1.1) To represent the * status code (302), it is recommended to use this variable. */ public static final int SC_FOUND = 302 ; /** * Status code (304) indicating that a conditional GET operation * found that the resource was available and not modified. */ public static final int SC_NOT_MODIFIED = 304 ; /** * Status code (404) indicating that the requested resource is not * available. */ public static final int SC_NOT_FOUND = 404 ; /** * Status code (500) indicating an error inside the HTTP server * which prevented it from fulfilling the request. */ public static final int SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500 ; /** * Status code (502) indicating that the HTTP server received an * invalid response from a server it consulted when acting as a * proxy or gateway. */ public static final int SC_BAD_GATEWAY = 502 ; // ...常见应用
- 向浏览器输出消息的
- 下载文件 实现方式
public class FileServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { // 1.要获取下载文件的路径 :\转义字符 StringrealPath= "E:\\dev\\StudyProjects\\javaweb-servlet\\response\\src\\main\\resources\\大乔.jpg" ; // 2.下载的文件名是啥? Stringfilename=realPath.substring(realPath.lastIndexOf("\\" ) + 1 ) ; // 3.设置想办法让浏览器能够支持下载我们需要的东西 resp.setHeader("Content-disposition" ,"attachment;filename="+ URLEncoder.encode(filename,"utf-8" ) ) ; // 4.获取下载文件的输入流 FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(realPath) ; // 5.创建缓冲区 int len = 0 ; byte[]buffer= new byte[1024] ; // 每次读取的长度 // 6.获取OutputStream对象 ServletOutputStream out = resp.getOutputStream( ) ; // 7.将FileOutputStream流写入到bufer缓冲区 while ((len = in.read(buffer) )> 0 ){ // 每次读取的长度大于0的情况下,就写出去 out.write(buffer,0 ,len) ; // 写出字节,从0写到len } // 8.使用OutputStream将缓冲区中的资料输出到客户端! in.close( ) ; out.close( ) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }- 验证码功能 实现方式
public class ImageServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { // 让浏览器3秒刷新一次 resp.setHeader("refresh" , "3" ) ; // 在内存中创建一个图片 BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(80 , 20 , BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB ) ; // 宽、高、颜色 // 得到图片 Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D ) image.getGraphics( ) ; // 得到一只2D的笔 // 设置图片的背景颜色 g.setColor(Color.white) ; g.fillRect(0 , 0 , 80 , 20 ) ; // 填充颜色 // 换个背景颜色 g.setColor(Color.BLUE ) ; // 设置字体样式:粗体,20 g.setFont( new Font( null ,Font.BOLD ,20 ) ) ; // 画一个字符串(给图片写素材) g.drawString(makeNum( ) ,0 ,20 ) ; // 告诉浏览器,这个请求用图片的方式打开 resp.setContentType("image/jpeg" ) ; // 网站存在缓存,不让浏览器缓存 resp.setDateHeader("expires" ,-1 ) ; resp.setHeader("Cache-Control" ,"no-cache" ) ; resp.setHeader("Pragma" ,"no-cache" ) ; // 把图片写给浏览器 boolean write = ImageIO.write(image, "jpg" ,resp.getOutputStream( ) ) ; } // 生成随机数 private String makeNum( ) { Randomrandom= new Random( ) ; String num =random.nextInt(9999999 ) + "" ; // 随机数,最大七位,[0,9999999) StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer( ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 7 - num.length( ) ; i++ ) { // 不足七位,则添加0 sb.append("0" ) ; } num = sb.toString( )+num; // 不足七位,在随机数前面添加0 return num; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }- 实现 请求重定向
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { /*resp.setHeader("Location","/response_war/image"); resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);*/ resp.sendRedirect("/response_war/image" ) ; // 重定向相当于上面两行代码 } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }6.7 HttpServletRequest
HttpServletRequest代表客户端的请求,用户依据Http协议访问服务器,HTTP请求中的所有信息会被封装到HttpServletRequest ,通过这个 HttpServletRequest的办法,获得客户端的所有信息。
- 获取前端传递的参数
getParameter(String name)| 获取指定名称的请求参数值(GET 或 POST 表单)
Stringusername=request.getParameter("username" ) ; Stringpassword=request.getParameter("password" ) ;getParameterValues(String name)| 用于获取多个值的参数(如多选框)
String[]hobbies=request.getParameterValues("hobby" ) ; if (hobbies!= null ) { for (String hobby :hobbies) { System.out.println("兴趣爱好:" + hobby) ; } }getParameterMap()| 返回所有参数的 Map 形式,键为参数名,值为字符串数组(适合处理复杂表单)
Map< String , String[]>parameterMap=request.getParameterMap( ) ; for (Map.Entry< String , String[]> entry :parameterMap.entrySet( ) ) { //使用foreach语句循环应用 System.out.println(entry.getKey( ) + " = " + Arrays.toString(entry.getValue( ) ) ) ; }getInputStream()/getReader()| 适用于接收 JSON、XML 等原始请求体内容(常用于前后端分离工程)
StringBuilderjsonBody= new StringBuilder( ) ; BufferedReaderreader=request.getReader( ) ; String line; while ((line =reader.readLine( ) ) != null ) {jsonBody.append(line) ; } System.out.println("接收到的JSON:" +jsonBody.toString( ) ) ;注意:你需要使用 JSON 解析库(如 Jackson、Gson)来解析这个字符串。
- 获取路径参数(RESTful 风格) :
request.getPathInfo()
@WebServlet("/user/*" ) public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequestrequest, HttpServletResponseresponse) { StringpathInfo=request.getPathInfo( ) ; // 如:/user/123 → 返回 "/123" if (pathInfo!= null &&pathInfo.length( ) > 1 ) { StringuserId=pathInfo.substring(1 ) ; // 去掉开头斜杠 System.out.println("用户ID:" +userId) ; } } }- 完整代码如下:
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequestrequest, HttpServletResponseresponse) throws ServletException , IOException { // 获取普通参数 Stringusername=request.getParameter("username" ) ; Stringpassword=request.getParameter("password" ) ; // 获取多选参数 String[]hobbies=request.getParameterValues("hobby" ) ; // 获取所有参数(Map) Map< String , String[]>parameterMap=request.getParameterMap( ) ; // 输出参数 System.out.println("用户名:" +username) ; System.out.println("密码:" +password) ; if (hobbies!= null ) { for (String hobby :hobbies) { System.out.println("兴趣:" + hobby) ; } } // 处理 JSON 数据(如果需要) if ("application/json".equals(request.getContentType( ) ) ) { BufferedReaderreader=request.getReader( ) ; StringBuilder json = new StringBuilder( ) ; String line; while ((line =reader.readLine( ) ) != null ) { json.append(line) ; } System.out.println("JSON 内容:" + json) ; } }- 请求 转发
前端:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html> <head> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br> 密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br> 爱好: <input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="代码"> 代码 <input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="唱歌"> 唱歌 <input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="女孩"> 女孩 <input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="电影"> 电影 <br> <input type="submit" name="提交"> </form> </body> </html>后端:
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doPost(req, resp) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { // 处理请求中文乱码(后期行使用过滤器来解决) req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8" ) ; resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8" ) ; Stringusername= req.getParameter("username" ) ; // 用户 Stringpassword= req.getParameter("password" ) ; // 密码 String[]hobbys= req.getParameterValues("hobbys" ) ; // 爱好 System.out.println(username) ; System.out.println(password) ; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbys) ) ; // 这里的 / 代表当前的web应用,所以不需要再加上/request_war这个上下文路径了,否则会出现404错误 转发 req.getRequestDispatcher("/success.jsp" ).forward(req,resp) ; } }web.xml
<servlet> <servlet-name>login</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sunyiwenlong.request.LoginServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>login</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/login</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>该 web.xml 配置定义了一个名为 login 的Servlet及其URL映射,对应的Java代码构建了基本的登录处理逻辑,包括获取请求参数和返回响应
面试题:请你聊聊重定向和转发的区别?
相同点:页面都会搭建跳转
不同点:
请求转发的时候,URL地址栏不会产生变化。
- 适合服务器内部跳转 。
- 状态码:
307(临时重定向)RequestDispatcher.forward()
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequestrequest, HttpServletResponseresponse) throws ServletException , IOException { // 设置属性request.setAttribute("message" , "这是转发时携带的消息" ) ; // 获取 RequestDispatcher 并转发 RequestDispatcherdispatcher=request.getRequestDispatcher("/target.jsp" ) ;dispatcher.forward(request,response) ; }重定向时候,URL地址栏会发生变化。
- 跳转到外部网站。
- 状态码:302 ,301(永久重定向)
HttpServletResponse.sendRedirect()
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequestrequest, HttpServletResponseresponse) throws IOException { // 重定向到另一个路径response.sendRedirect("http://example.com" ) ; // 也可以是相对路径:"/myapp/target.jsp" }7. cookie/session
7.1 会话
无状态的会话:用户打开一个浏览器,点击了很多超链接,访问多个web资源,关闭浏览器,这个过程能够称之为会话。
有状态的会话:一个用户打开一个浏览器,访问某些资源(网站),下次再来访问该资源(网站),我们会知道该用户曾经来过,称之为有状态会话;
一个网站,怎么证明你来过?
- 服务端给客户端一个信件,客户端下次访问服务端带上信件就允许了;cookie(客户端)
- 服务器登记你来过了,下次你来的时候我来匹配你;session(服务端)
7.2 保存会话的两种技术
cookie:客户端技术,(响应、请求)session:服务端技术,利用该技术,可以保存用户的会话信息?我们可以把信息或者数据放在Session中。
用户登录 ↓ 服务器创建 Session 并保存用户信息 ↓ 服务器生成 JSESSIONID 并写入 Cookie ↓ 客户端保存 Cookie ↓ 后续请求携带 Cookie 到服务器 ↓ 服务器根据 JSESSIONID 找到对应的 Session ↓ 继续处理用户逻辑7.3 Cookie
- 从请求中拿到cookie
- 服务器响应给客户端cookie
Cookie[]cookies= req.getCookies( ) ; // 获得cookiecookie.getName( ) ; // 获得cookie中的keycookie.getValue( ) ; // 获得cookie中的value new Cookie("lastLoginTime" ,System.currentTimeMills( )+"" ) ; // 新建一个cookiecookie.setMaxAge(24*60*60 ) ; // 设置cookie的有效期,单位:秒 resp.addCookie(cookie) ; // 响应给客户端一个cookieQ:cookie:一般会保存在本地的用户目录下appdata,一个网站cookie是否存在上限!聊聊细节问题
- 一个Cookie只能保存一个信息;
- 一个web站点可能给浏览器发送多个cookie,最多存放20个cookie;
- Cookie大小有限制4kb
- 300个cookie浏览器上限
删除cookie
- 不设置有效期,关闭浏览器,自动失效
- 设置有效期时间为 0
编码解码,怎么解决中文乱码问题
URLEncoder.encode("张三" ,"UTF-8" ) URLDecoder.decode("张三" ,"UTF-8" )保存上一次登录时间** 达成方式 **
// 保存用户上一次访问的时间 public class CookieDemo01 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { // 服务器告诉你,你来的时间,把这个时间封装成一个信息,你下次带来,我就知道你上次来的时间 // 解决中文乱码 req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8" ) ; resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8" ) ; PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter( ) ; // Cookie,服务器端从客户端获取cookie Cookie[]cookies= req.getCookies( ) ; // 数组,说明cookie可以有多个 // 判断cookie是否 if (cookies!= null ) { out.write(:"就是"你上一次登录的时间 ) ; for ( int i = 0 ; i <cookies.length; i++ ) { // 获取cookie的名字 if (cookies[i].getName( ).equals("lastLoginTime" ) ) { // 获取cookie的值 long l = Long.parseLong(cookies[i].getValue( ) ) ; Date date = new Date(l) ; out.write(date.toLocaleString( ) ) ; } } } else { out.write("你是第一次登录!" ) ; } Cookiecookie= new Cookie("lastLoginTime" , System.currentTimeMillis( ) + "" ) ;cookie.setMaxAge(24*60*60 ) ; // 设置cookie的有效期为一天,单位是:秒 resp.addCookie(cookie) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }7.4 Session (重点)
什么是Session:
- 服务器会给每一个用户(浏览器)创建一个Seesion对象。
- 一个session独占一个浏览器,只要浏览器没有关闭,这个session就存在。
- 通过用户登录之后,整个网站它都能够访问。(保存用户的信息;也行保存购物车的信息)
Session和cookie的区别
- Cookie是把用户的内容写给用户的浏览器,浏览器保存(可以保存多个)保存在
客户端; - Session把用户的数据写到用户独占
Session中,服务器端保存(保存重要的信息,减少服务器资源的浪费) - Session对象由服务(
sevice)创建;
使用场景
- 保存一个登录用户的信息;
- 购物车信息;
- 在整个网站中时常会运用的数据,我们将它保存在 Session 中;
会话自动过期
<!--设置session默认的失效时间--> <session-config> <!--15分钟后session自动失效,以分钟为单位--> <session-timeout>15</session-timeout> </session-config>Session的采用
public class SessionDemo01 extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { // 解决中文乱码 req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ) ; resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ) ; resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8" ) ; // 得到Session HttpSessionsession= req.getSession( ) ; // 给session中存东西session.setAttribute("name" , "张三" ) ; // 获取session的id StringsessionId=session.getId( ) ; // 判断session是不是新创建 if (session.isNew( ) ) { resp.getWriter( ).write("session创建成功,ID:" +sessionId) ; } else { resp.getWriter( ).write("session已经存在了,ID:" +sessionId) ; } // session创建的时候做了什么事情 /*Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID", sessionId); resp.addCookie(cookie);*/ //------------------ // 从session中获取数据 String name = (String )session.getAttribute("name" ) ; //------------------ // 从session中删除指定name的数据session.removeAttribute("name" ) ; // 手动注销sessionsession.invalidate( ) ; } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException , IOException { this.doGet(req, resp) ; } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号