1.盒子模型
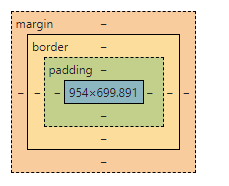
1.1 什么时盒子模型?
![]()
margin:外边距
padding:内边距
border:边框
1.2 边框
1. 边框的粗细
2. 边框的样式
3. 边框的颜色
#box{
/*boder: 粗细 ,样式, 颜色*/
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid cadetblue;
margin: auto;
}
1.3圆角边框
<!--左上 右上 右下 左下 顺时针方向 -->
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
margin: 0;
background: aqua;
border-radius: 50px 50px 0px 0px;
}
2.浮动
2.1 标准文档流
![]()
块级元素:独占一行
h1~h6 p div 列表
行内元素: 不独占一行
span a img strong
行内元素可以被包含在块级元素中,反之,则不可以
2.2 display
<!--
block 块元素
inline 行内元素
inline-block 是块元素,但是可以内联,在一行
none 隐藏
-->
3.定位
3.1 相对定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--相对定位
相对于自己原来的位置进行偏移
-->
<style>
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 25px;
}
#father{
border: 1px solid #666666;
padding: 0;
}
#first{
border: 1px solid red;
position: relative; /*相对定位*/
left: 20px;
}
#second{
border: 1px solid orange;
position: relative;
right: 20px;
}
#third{
border: 1px solid skyblue;
position: relative;
top: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div id="first">第一个盒子</div>
<div id="second">第二个盒子</div>
<div id="third">第三个盒子</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
相对定位:position:relative
相对于原来的位置,进行指定的偏移: top,left,bottom,right
3.2 绝对定位: position:absolute
定位:基于XXX定位,上下左右~
1.没有父级元素定位的前提下,相对于浏览器定位
2.假设父级元素存在定位,我们通常会相对于父级元素进行偏移
3.在父级元素范围内移动
3.3 固定定位: position:fixed



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号