实验5 文件应用编程
实验任务1
#task1_1
源码
1 ''' 2 统计文件data1.txt行数(不包括空白行) 3 data1.txt中的空白行包括由空格、Tab键(\t)、换行(\n)构成的空白行 4 ''' 5 6 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/data1.txt', 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as f: 7 data = f.readlines() 8 9 n = 0 10 for line in data: 11 if line.strip() != '': 12 n += 1 13 print(f'data.txt共{n}行')
运行测试截图
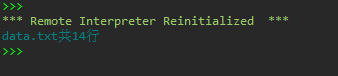
#task1_2
源码
1 ''' 2 统计文件data1.txt行数(不包括空白行) 3 data1.txt中的空白行包括由空格、Tab键(\t)、换行(\n)构成的空白行 4 ''' 5 6 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/data1.txt', 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as f: 7 n = 0 8 for line in f: 9 if line.strip() != '': 10 n += 1 11 print(f'data1.txt共{n}行')
运行测试截图
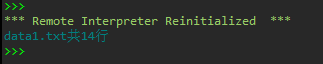
#task1_3
源码
1 ''' 2 统计文件data1.txt行数(不包括空白行) 3 data1.txt中的空白行包括由空格、Tab键(\t)、换行(\n)构成的空白行 4 ''' 5 6 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/data1.txt', 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as f: 7 n = 0 8 for line in f: 9 if not line.isspace(): 10 n += 1 11 print(f'data1.txt共{n}行')
运行测试截图
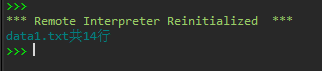
实验任务2
#task2
源码
1 ''' 2 统计数据文件data2.txt中独特行的行数 3 并打印输出独特行 4 ''' 5 6 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/data2.txt', 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as f: 7 data = f.read().split('\n') 8 9 unique_line_lst = [] 10 for line in data: 11 if data.count(line) == 1: 12 unique_line_lst.append(line) 13 14 n = len(unique_line_lst) 15 print(f'data2.tx共{n}行独特行') 16 17 for line in unique_line_lst: 18 print(line)
运行测试截图
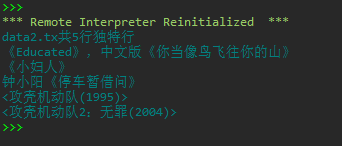
实验任务3
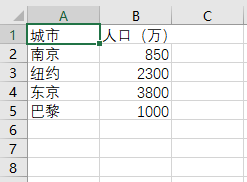
#task3_1
源码
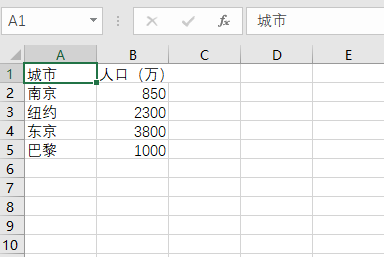
1 ''' 2 把城市、人口信息填入数据文件city1.csv 3 使用python内置的文件操作实现 4 ''' 5 6 title = ['城市', '人口(万)'] 7 info = [['南京','850'], ['纽约', '2300'], ['东京', '3800'], ['巴黎', '1000']] 8 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/city1.csv', 'w', encoding = 'gbk') as f: 9 f.write(','.join(title) + '\n') #写入标题行 10 for item in info: #分行写入info 11 f.write(','.join(item) + '\n')
运行结果截图
#task3_2
源码
1 ''' 2 从文件city1.csv读取城市、人口信息,打印输出到屏幕 3 使用python内置的文件读写操作实现 4 ''' 5 6 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/city1.csv', 'r', encoding = 'gbk') as f: 7 data = f.read() 8 9 print(data.rstrip('\n'))
运行测试截图
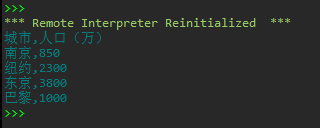
#task3_3
源码
1 ''' 2 从文件city1.csv读取城市、人口信息,将其保存到里列表对象,保存形式诸如: 3 info = [ ['城市', '人口(万)'], 4 ['南京', '850'], 5 ['纽约', '2300'], 6 ['东京', '3800'], 7 ['巴黎', '1000'] ] 8 在屏幕上打印输出列表对象 9 使用python内置的文件读写操作实现 10 ''' 11 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/city1.csv', 'r', encoding = 'gbk') as f: 12 data = f.readlines() 13 14 #打印中间处理结果(供查看) 15 print('data: ') 16 print(data) 17 18 info = [line.strip('\n').split(',') for line in data] 19 print('info: ') 20 print(info)
运行测试截图
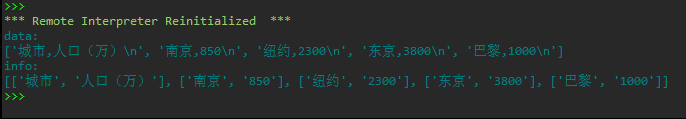
#task3_4
源码
1 ''' 2 把城市、人口信息写入数据文件city1.csv 3 使用python标准模块csv实现 4 ''' 5 6 import csv 7 8 title = ['城市', '人口(万)'] 9 info = [['南京', '850'], ['纽约', '2300'], ['东京', '3800'], ['巴黎', '1000']] 10 11 with open('C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/python实验5/city2.csv', 'w', encoding = 'gbk', newline = '') as f: 12 f_writer = csv.writer(f) #为文件对象f创建一个writer对象 13 f_writer.writerow(title) #通过writer对象的方法writerow()写入一行(标题行) 14 f_writer.writerows(info) #通过writer对象的方法wrierow()写入多行
运行结果截图
![]()
![]()
#task3_5
源码
1 ''' 2 从文件city2.csv读取城市、人口信息,在屏幕上打印输出 3 使用python标准模块csv实现 4 ''' 5 import csv 6 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\city2.csv', 'r', encoding = 'gbk') as f: 7 f_reader = csv.reader(f) #为文件对象f创建一个reader对象 8 for line in f_reader: 9 print(line)
运行测试截图
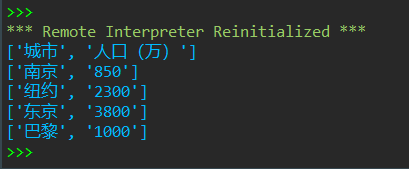
实验任务4
#task4
源码
1 ''' 2 列出当前目录下所以.py文件 3 ''' 4 import os, sys 5 print(os.path.basename(os.getcwd())) 6 7 #将当前路径下所以.py文件名保存到py_file_lst中 8 py_file_lst = [file for file in os.listdir() if file.endswith('.py')] 9 10 #遍历输出 11 for number,file in enumerate(py_file_lst, 1): 12 print(f'{number:-3d}. {file}')
运行测试截图
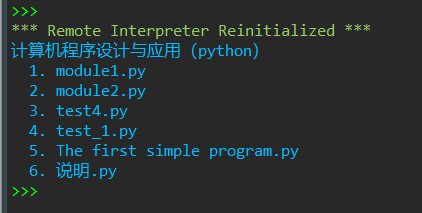
实验任务5
#task5
(源码+运行测试)截图
实验任务6
#task6
源码
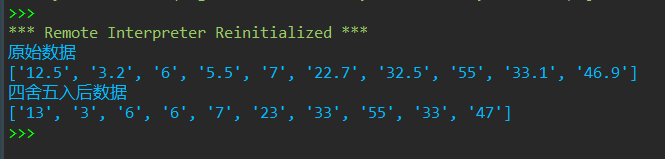
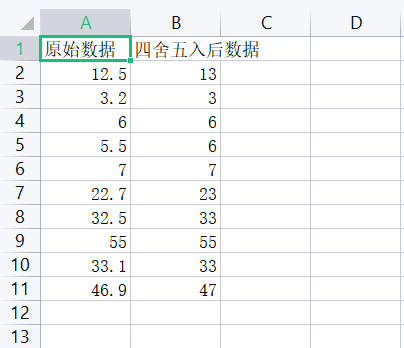
1 import csv 2 info_lst = [] 3 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\data6.csv', 'r', encoding = 'gbk') as f: 4 f_reader = csv.reader(f) 5 info_lst = list(f_reader) 6 7 processed_lst = [] 8 for k in info_lst: 9 if k[0] == '原始数据': 10 processed_lst.append(['四舍五入后数据']) 11 else: 12 processed_data = int(eval(k[0]) + 0.5) 13 small_lst_1 = [] 14 small_lst_1.append(str(processed_data)) 15 processed_lst.append(small_lst_1) 16 17 total_lst = [] 18 i = 0 19 while i < len(info_lst): 20 small_lst_2 = [] 21 small_lst_2.append(info_lst[i][0]) 22 small_lst_2.append(processed_lst[i][0]) 23 total_lst.append(small_lst_2) 24 i += 1 25 26 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\data6_processed.csv', 'w', encoding = 'utf-8', newline = '') as f: 27 writer = csv.writer(f) 28 writer.writerows(total_lst) 29 30 print(info_lst[0][0]) 31 original_datas_lst = [i[0] for i in info_lst[1:]] 32 print(original_datas_lst) 33 34 print(processed_lst[0][0]) 35 processed_datas_lst = [k[0] for k in processed_lst[1:]] 36 print(processed_datas_lst)
运行测试截图
实验任务7
#task7
源码
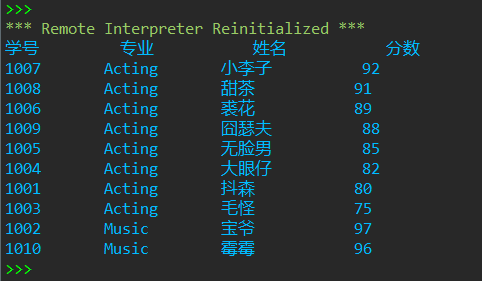
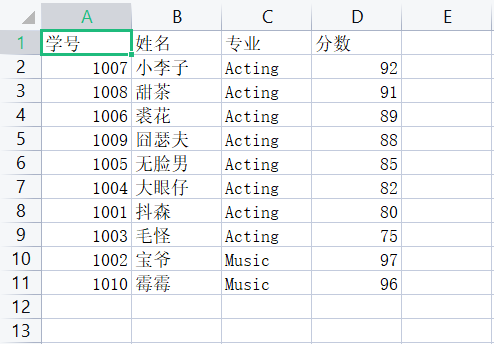
1 import csv 2 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\data7.csv', 'r', encoding='gbk') as f: 3 f_reader = csv.reader(f) 4 info_lst = list(f_reader) 5 6 info_lst2 = [] 7 for i in info_lst: 8 info_lst2.append(tuple(i)) 9 10 processed_lst1 = sorted(info_lst2[1:], key = lambda x:(x[2], - int(x[3]))) 11 12 processed_lst2 = [info_lst[0]] 13 for i in processed_lst1: 14 processed_lst2.append(list(i)) 15 16 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\data7_processed.csv', 'w', encoding='gbk', newline="") as f: 17 writer = csv.writer(f) 18 writer.writerows(processed_lst2) 19 20 for number,name,major,grade in processed_lst2: 21 print(f'{number:10s} {major:12s} {name:12s} {grade:10s}')
运行测试截图
实验任务8
#task8
源码
1 print('hamlet.txt粗略统计:') 2 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\hamlet.txt', 'r', encoding= 'gbk') as f: 3 line_number = len(f.readlines()) 4 print(f'行数: {line_number}') 5 6 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\hamlet.txt', 'r', encoding= 'gbk') as f: 7 contents = f.read() 8 word_number = len(contents.split()) 9 print(f'单词数: {word_number}') 10 character_number = len(contents) 11 print(f'字符数: {character_number}') 12 spacing_number = contents.count(' ') 13 print(f'空格数: {spacing_number}') 14 15 import csv 16 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\hamlet_with_line_number.txt', 'w', encoding= 'gbk', newline="") as f: 17 i = 0 18 contents_lst = contents.splitlines() 19 processed_lst = [] 20 while i < len(contents_lst): 21 processed_lst.append(f'{i+1} {contents_lst[i]}') 22 i += 1 23 processed_contents = '\n'.join(processed_lst) 24 f.write(processed_contents)
运行测试截图
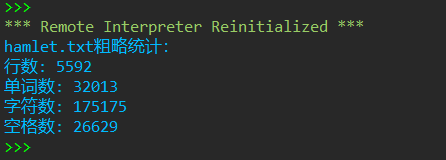
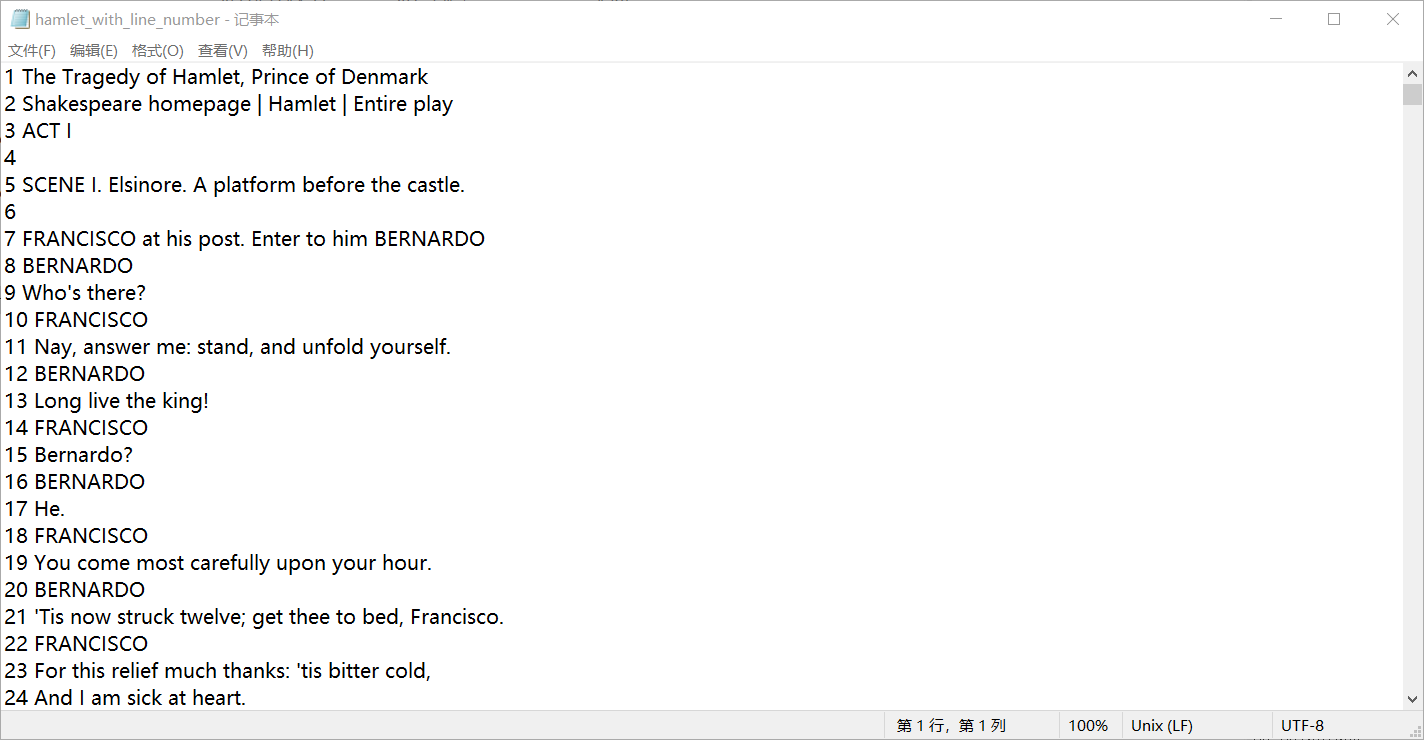
实验任务9
#task9
源码
1 def is_valid(id_number): 2 if len(id_number) != 18: 3 return False 4 else: 5 number_set = {str(i) for i in range(0,10)} #定义数字集合 6 id_set = {str(i) for i in range(0,10)} #定义数字+X的集合 7 id_set.add('X') 8 front_id_number = id_number[0:17] 9 #以下判断所给号码前十七位与最后一位是否分别符合要求身份证要求 10 if set(id_number[0:17]) <= number_set and id_number[17] in id_set: 11 return True 12 else: 13 return False 14 15 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\data9_id.txt', 'r') as f: 16 datas = f.readlines() 17 data_lst = [] 18 for i in datas: 19 t = i.strip('\n').split(',') 20 data_lst.append(t) #取出信息,组成列表 21 22 valid_id_info_lst = [] 23 for i in data_lst[1:]: 24 if is_valid(i[1]) == True: 25 valid_id_info_lst.append(i) #得到符合条件的信息列表 26 27 import datetime 28 def age_calculate(a,b,c): #定义实时年龄计算函数 29 now = datetime.datetime.now() 30 birth = datetime.datetime(int(a),int(b),int(c)) 31 days = now - birth 32 return days.days//365 33 34 info_lst = [] 35 i = 0 36 while i < len(valid_id_info_lst): 37 born_day_info = valid_id_info_lst[i][1][6:14] #得到一整个出生日期 38 born_day_info_lst = [born_day_info[0:4],born_day_info[4:6],born_day_info[6:8]] #切片得出生年、月、日 39 born_day_info_modified = "-".join(born_day_info_lst) #得到用-连接起来的出生日期 40 41 info_small_lst = [] #准备组建最终信息组(最后转为元组形式) 42 info_small_lst.append(valid_id_info_lst[i][0]) #得到信息组第一号信息:姓名 43 info_small_lst.append(born_day_info_modified) #得到信息组第二号信息:用-连接起来的出生日期 44 #以下得到信息组第三号信息:实时年龄 45 info_small_lst.append(age_calculate(born_day_info[0:4],born_day_info[4:6],born_day_info[6:8])) 46 info_lst.append(tuple(info_small_lst)) 47 i += 1 48 49 sorted_info_lst = sorted(info_lst, key = lambda x:(-x[2])) #按年龄排序 50 51 print('姓名,出生日期,年龄') #开始打印所需的信息 52 for i in sorted_info_lst: 53 print(f'{i[0]},{i[1]},{i[2]}')
运行测试截图
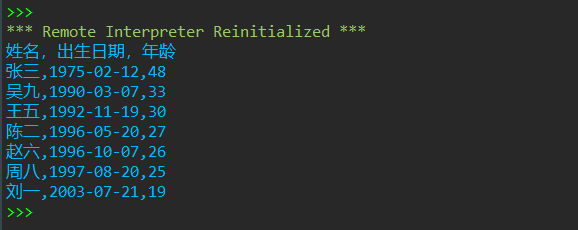
实验任务10
#task10_1
源码
1 import os 2 from datetime import datetime 3 now = datetime.now() 4 time_str = now.strftime("%Y%m%d") 5 file_name = f'{time_str}.txt' 6 7 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\data10_stu.txt', 'r') as f: 8 datas = f.readlines() 9 10 import random 11 def call_roll_and_save(n): 12 call_lst = random.choices(datas, k = n) 13 for i in call_lst: 14 print(i) 15 with open(f'D:\实验5数据文件\{file_name}','w')as f: 16 f.writelines(call_lst) 17 18 n = int(input('输入随机抽点人数:')) 19 call_roll_and_save(n)
运行测试截图

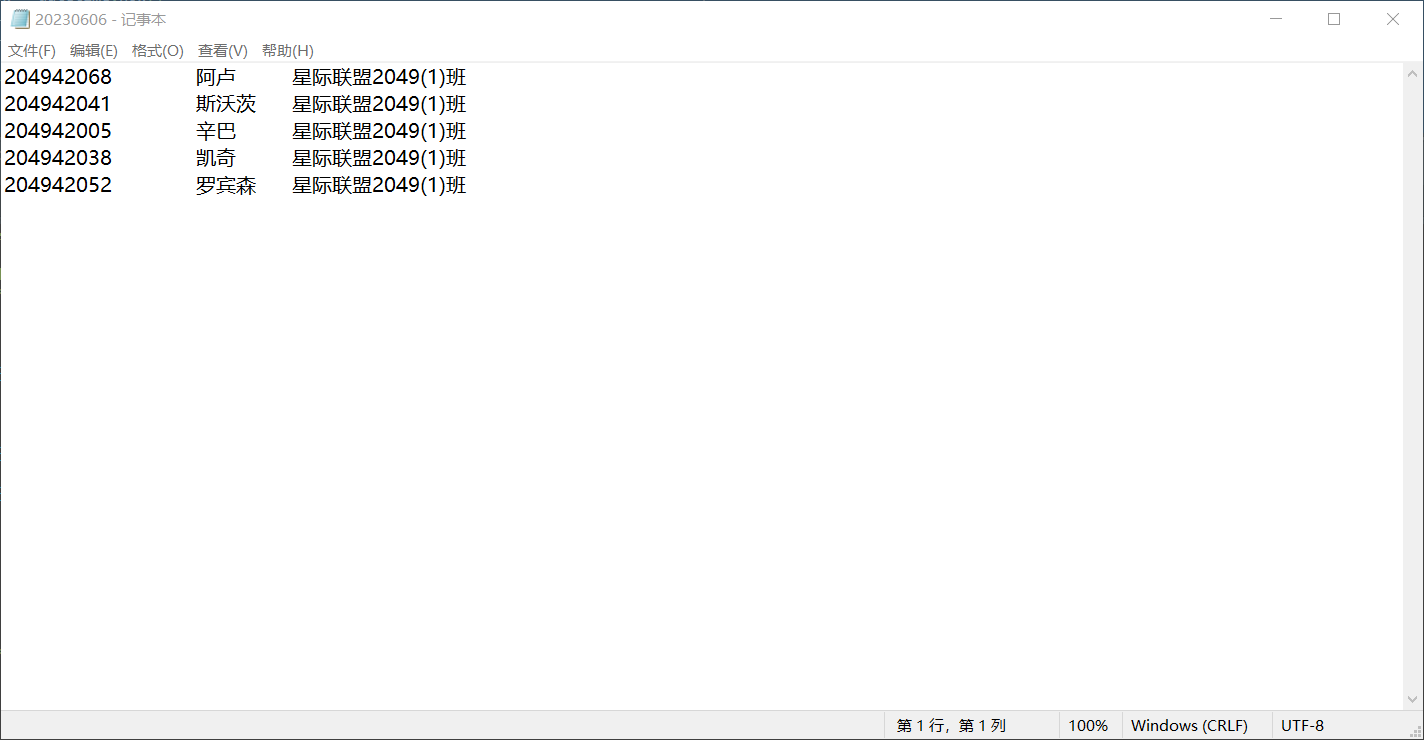
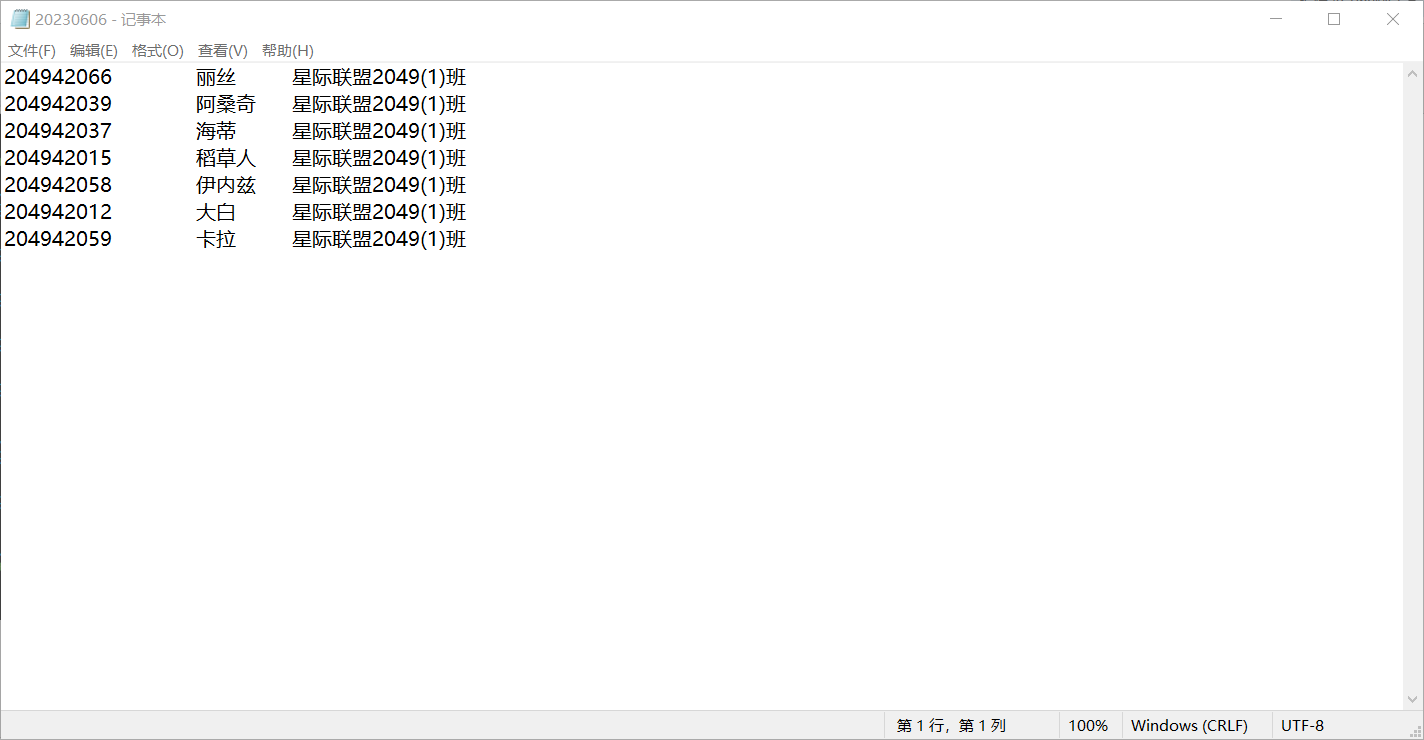
#task10_2
源码
1 import os 2 from datetime import datetime 3 now = datetime.now() 4 time_str = now.strftime("%Y%m%d") #将当天日期赋值给变量time_str 5 file_name = f'{time_str}.txt' 6 7 with open('D:\实验5数据文件\data10_stu.txt', 'r') as f: 8 datas = f.readlines() #提取数据 9 10 import random 11 import copy 12 call_lst = [] 13 total_lst = [] 14 modified_datas = copy.deepcopy(datas) #深拷贝数据,使原有数据不因为后续操作而被修改,方便查看原始数据 15 with open(f'D:\实验5数据文件\{file_name}','w')as f: #事先创建一个空的记事本,后续都是在原基础上添加内容 16 f.writelines(call_lst) 17 def continue_call_roll_and_save(n): 18 while n != 0: 19 call_lst = [] 20 while len(call_lst) < n: 21 index = random.randint(0,len(modified_datas) -1) #指定随机索引在规定范围内 22 call_roll_info = modified_datas[index] #利用随机索引取出对应数据 23 modified_datas.remove(modified_datas[index]) #在深拷贝的内容中,删除对应项数据,避免取出数据重复 24 if call_roll_info not in call_lst: #判断取得数据是否与前面的数据重复,若重复,则不输出或计入输出数据汇总表 25 print(call_roll_info) 26 call_lst.append(call_roll_info) #临时存储单次点明对应的被点明者数据 27 total_lst.append(call_roll_info) #存储所有被点明者数据 28 n = int(input('输入随机抽点人数:')) 29 with open(f'D:\实验5数据文件\{file_name}','a')as f: 30 f.writelines(total_lst) #将所有被点明者数据写入记事本并保存 31 32 print('{:*^40}'.format('抽点开始')) 33 n = int(input('输入随机抽点人数:')) 34 continue_call_roll_and_save(n) 35 print('{:*^40}'.format('抽点结束'))
运行测试截图





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号