React Hooks方法
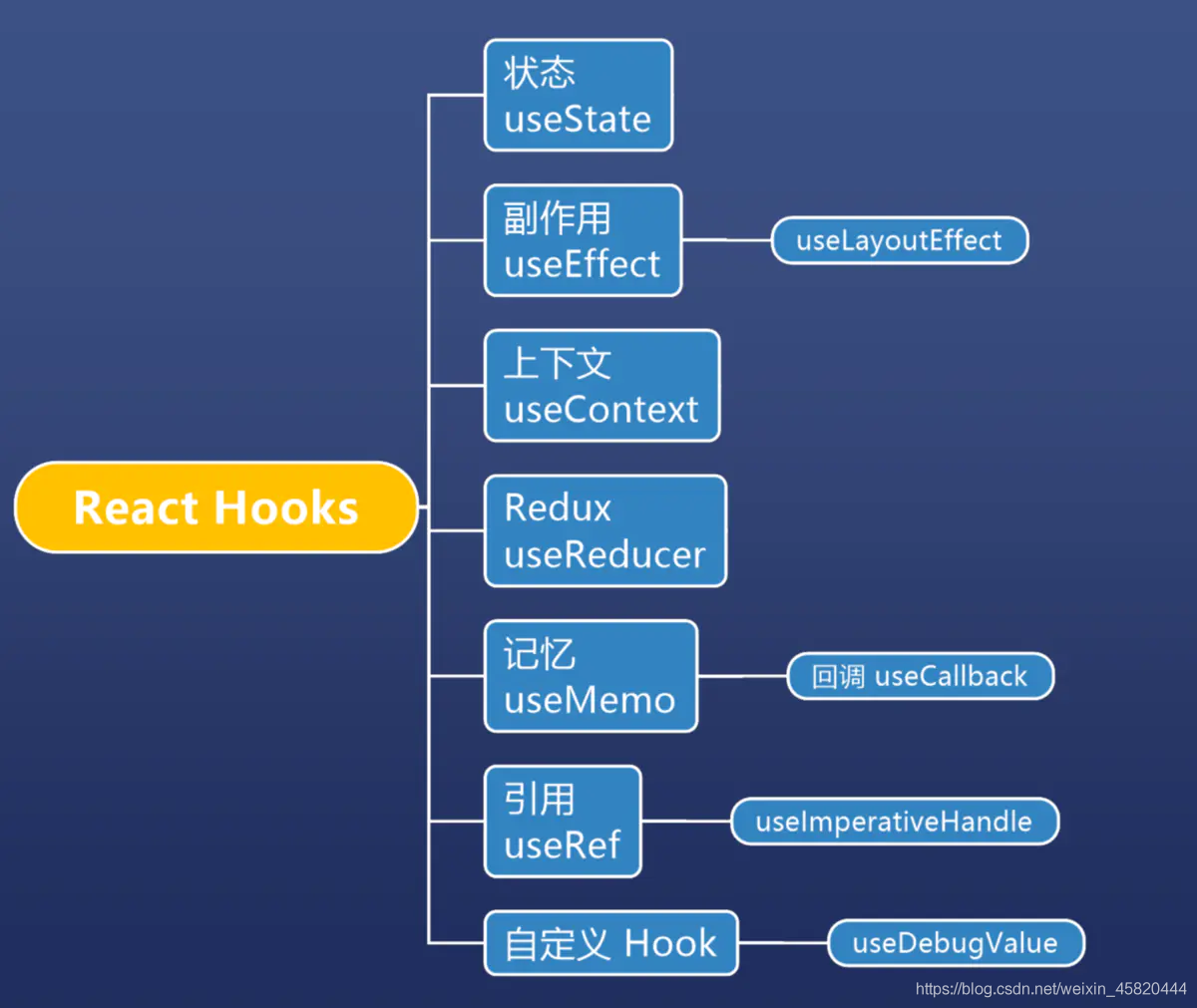
1.useState
import React, { useState } from "react";
/*
目标:
掌握useState的使用
作用:实现响应式数据的
用法:引入,useState构造响应式数据
const [val,修改val的函数]=useState(val的初始值)
注意点:
1.hook都必须是以use开头的
2.必须在函数的最顶层使用
*/
export default function App() {
const [user, setUser] = React.useState({ name: "Jack", age: 18 });
const onClick = () => {
//setUser不可以局部更新,如果只改变其中一个,那么整个数据都会被覆盖
// setUser({
// name: 'Frank'
// })
setUser({
...user, //拷贝之前的所有属性
name: "Frank", //这里的name覆盖之前的name
});
};
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>{user.name}</h1>
<h2>{user.age}</h2>
<button onClick={onClick}>Click</button>
</div>
);
}
注意事项:
地址要进行改变
setState(obj) 如果obj地址不变,那么React就认为数据没有变化,不会更新视图
2.useEffect
// 副作用hook用来处理一些React之外的事件 //但是其实EffectHook最常见的使用场景是模拟生命周期 // 用法:当useEffect依赖的数据发生变化,就会调用回调函数 // useEffect(回调函数,[依赖的数据]) import React, { useEffect, useState } from "react"; export default function EffectHook() { const [val, setVal] = useState(0); // 当前这个用法,模拟了componentDidUpdated这个生命周期 // useEffect(() => { // console.log(1); // }, [val]); // setInterval(() => { // setVal(val + 1); // }, 1000); // 使用useEffect模拟componentDidMount // useEffect(() => { // //该回调函数会在第一次渲染的时候调用一次 // console.log(3); // }, []); useEffect(() => { // 在回调函数里面返回一个函数 return () => { console.log("卸载"); }; }, []); return <div></div>; }
3.useContext
import React, { useState, createContext, useContext } from "react";
/*
目标:
学会使用useContext 使用context进行多级组件传递数据
用法:
1.createContext
2.Provider
3.useContext
const data=useContext(MyContext)
data为 Provider给的value的值
MyContext为在第一步创建的context的变量
*/
// 1.创建一个context
const MyContext = createContext();
export default function ContextStudy() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(5);
const add = () => {
setCount(count + 1);
};
// 2.需要一个Provider
return (
<MyContext.Provider value={{ count, add }}>
<Parent></Parent>
</MyContext.Provider>
);
}
function Parent() {
return <Child></Child>;
}
function Child() {
const data = useContext(MyContext);
console.log(data);
return (
<div>
<h3>孙子</h3>
<p>{data.count}</p>
<button onClick={data.add}>++</button>
</div>
)
}
4.useReducer
import React, { useReducer, useState } from "react";
/*
目标:
掌握 ReducerHook
作用: 解决 useState 在处理数据比较复杂的时候的使用问题
[数据,处理数据的委托] = useReducer(处理函数,数据初始值)
*/
function useCount() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
// const add1 = () => {
// setCount(count + 1);
// };
// const add2 = () => {
// setCount(count - 1);
// };
// const add3 = () => {
// setCount(count + 5);
// };
// function add({ type, pyload }) {
// if (type == "add1") {
// setCount(count + 1);
// } else if (type === "add2") {
// setCount(count - 1);
// }
// }
// return [count, add];
}
const reducer = (state, action) => {
console.log(action);
//判断action的type进行处理
switch (action.type) {
case "add1":
state++;
break;
case "add2":
state--;
break;
case "add3":
state += action.pyload;
break;
}
return state;
};
export default function ReducerHook() {
const [count, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, 0);
return (
<div>
<div>ReducerHook</div>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: "add1", pyload: 10 })}>++</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: "add2" })}>++</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: "add3", pyload: 5 })}>++</button>
</div>
);
}
5.useRef
import React, { useEffect, useRef } from "react";
export default function RefHook() {
const btn = useRef();
const sp = useRef();
// console.log(btn);
// 在componentDidMount后获取
useEffect(() => {
console.log(btn.current);
console.log(sp.current);
}, []);
return (
<div>
<button ref={btn}>Button</button>
<span ref={sp}>你好</span>
</div>
);
}
6.自定义Hook
import React, { useState } from "react";
/*
目标:
自定义Hook
把自己处理数据的过程变成一个hook
要求:
hook都要以use开头
好处:
1.代码简洁,方便书写和维护
2.逻辑会更加独立
*/
function useCount() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const onClick = () => {
setCount(count + 1);
};
return [count, onClick];
}
export default function CusHook() {
const [a, b] = useCount();
return (
<div>
<h1>CusHook</h1>
<p>{a}</p>
<button onClick={b}>++</button>
</div>
);
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号