pwnable.kr memcpy之write up
1 // compiled with : gcc -o memcpy memcpy.c -m32 -lm 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <signal.h> 6 #include <unistd.h> 7 #include <sys/mman.h> 8 #include <math.h> 9 10 unsigned long long rdtsc(){ 11 asm("rdtsc"); 12 } 13 14 char* slow_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){ 15 int i; 16 for (i=0; i<len; i++) { 17 dest[i] = src[i]; 18 } 19 return dest; 20 } 21 22 char* fast_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){ 23 size_t i; 24 // 64-byte block fast copy 25 if(len >= 64){ 26 i = len / 64; 27 len &= (64-1); 28 while(i-- > 0){ 29 __asm__ __volatile__ ( 30 "movdqa (%0), %%xmm0\n" 31 "movdqa 16(%0), %%xmm1\n" 32 "movdqa 32(%0), %%xmm2\n" 33 "movdqa 48(%0), %%xmm3\n" 34 "movntps %%xmm0, (%1)\n" 35 "movntps %%xmm1, 16(%1)\n" 36 "movntps %%xmm2, 32(%1)\n" 37 "movntps %%xmm3, 48(%1)\n" 38 ::"r"(src),"r"(dest):"memory"); 39 dest += 64; 40 src += 64; 41 } 42 } 43 44 // byte-to-byte slow copy 45 if(len) slow_memcpy(dest, src, len); 46 return dest; 47 } 48 49 int main(void){ 50 51 setvbuf(stdout, 0, _IONBF, 0); 52 setvbuf(stdin, 0, _IOLBF, 0); 53 54 printf("Hey, I have a boring assignment for CS class.. :(\n"); 55 printf("The assignment is simple.\n"); 56 57 printf("-----------------------------------------------------\n"); 58 printf("- What is the best implementation of memcpy? -\n"); 59 printf("- 1. implement your own slow/fast version of memcpy -\n"); 60 printf("- 2. compare them with various size of data -\n"); 61 printf("- 3. conclude your experiment and submit report -\n"); 62 printf("-----------------------------------------------------\n"); 63 64 printf("This time, just help me out with my experiment and get flag\n"); 65 printf("No fancy hacking, I promise :D\n"); 66 67 unsigned long long t1, t2; 68 int e; 69 char* src; 70 char* dest; 71 unsigned int low, high; 72 unsigned int size; 73 // allocate memory 74 char* cache1 = mmap(0, 0x4000, 7, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0); 75 char* cache2 = mmap(0, 0x4000, 7, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0); 76 src = mmap(0, 0x2000, 7, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0); 77 78 size_t sizes[10]; 79 int i=0; 80 81 // setup experiment parameters 82 for(e=4; e<14; e++){ // 2^13 = 8K 83 low = pow(2,e-1); 84 high = pow(2,e); 85 printf("specify the memcpy amount between %d ~ %d : ", low, high); 86 scanf("%d", &size); 87 if( size < low || size > high ){ 88 printf("don't mess with the experiment.\n"); 89 exit(0); 90 } 91 sizes[i++] = size; 92 } 93 94 sleep(1); 95 printf("ok, lets run the experiment with your configuration\n"); 96 sleep(1); 97 98 // run experiment 99 for(i=0; i<10; i++){ 100 size = sizes[i]; 101 printf("experiment %d : memcpy with buffer size %d\n", i+1, size); 102 dest = malloc( size ); 103 104 memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect 105 t1 = rdtsc(); 106 slow_memcpy(dest, src, size); // byte-to-byte memcpy 107 t2 = rdtsc(); 108 printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1); 109 110 memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect 111 t1 = rdtsc(); 112 fast_memcpy(dest, src, size); // block-to-block memcpy 113 t2 = rdtsc(); 114 printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1); 115 printf("\n"); 116 } 117 118 printf("thanks for helping my experiment!\n"); 119 printf("flag : ----- erased in this source code -----\n"); 120 return 0; 121 }
分析源码:
size_t sizes[10]; int i=0; // setup experiment parameters for(e=4; e<14; e++){ // 2^13 = 8K low = pow(2,e-1); high = pow(2,e); printf("specify the memcpy amount between %d ~ %d : ", low, high); scanf("%d", &size); if( size < low || size > high ){ printf("don't mess with the experiment.\n"); exit(0); } sizes[i++] = size; }
从上代码中分析得到,需要输入2的n次幂和2的n+1次幂之间
// run experiment for(i=0; i<10; i++){ size = sizes[i]; printf("experiment %d : memcpy with buffer size %d\n", i+1, size); dest = malloc( size );
这段代码分析得到,输入size后malloc分配空间,分配的空间大小就是我们输入的size大小。
memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect t1 = rdtsc(); slow_memcpy(dest, src, size); // byte-to-byte memcpy t2 = rdtsc(); printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1); memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect t1 = rdtsc(); fast_memcpy(dest, src, size); // block-to-block memcpy t2 = rdtsc(); printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1); printf("\n"); }
分配空间后,分别用slow_memcpy和fast_memcpy两种方式,对堆块内的数据向另外一个内存地址拷贝,并比较二者时间。那么分析一下slow_memcpy和fast_memcpy:
char* slow_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){ int i; for (i=0; i<len; i++) { dest[i] = src[i]; } return dest; }
char* fast_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){
size_t i;
// 64-byte block fast copy
if(len >= 64){
i = len / 64;
len &= (64-1);
while(i-- > 0){
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"movdqa (%0), %%xmm0\n"
"movdqa 16(%0), %%xmm1\n"
"movdqa 32(%0), %%xmm2\n"
"movdqa 48(%0), %%xmm3\n"
"movntps %%xmm0, (%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm1, 16(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm2, 32(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm3, 48(%1)\n"
::"r"(src),"r"(dest):"memory");
dest += 64;
src += 64;
}
}
slow_memcpy是循环赋值,fast_memcpy是用asm汇编指令movdqa进行拷贝。拷贝结束后输入flag。
根据提示生成可执行程序,然后执行程序看一下:
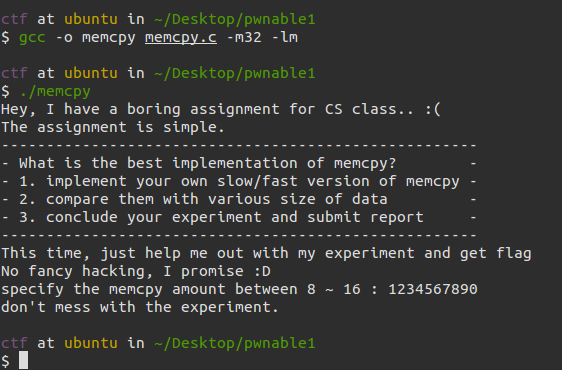
那么我们运行程序来看一下:
随便输入发现出错了:
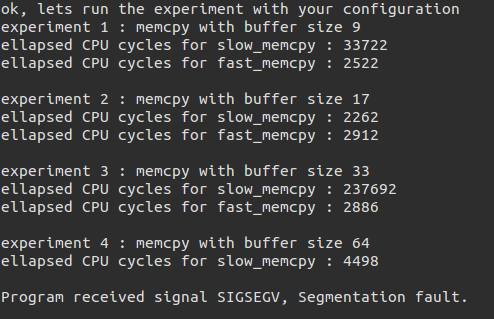
我们用gdb来看,发现了出错的位置:

出错的位置,也就是movntps的执行出了问题,百度了一下movntps的用法:
movntps m128,XMM
m128 <== XMM 直接把XMM中的值送入m128,不经过cache,必须对齐16字节。再参考别人的wp:
malloc分配的堆块大小是以8字节对其的。
假设用户申请的堆块大小是a的话,malloc(a)分配的堆块大小为 8*(int((a+4)/8)+1)。
因此假设第一个malloc分配地址是16字节对齐的,则每次请求大小为16字节对齐的数据块即可成功运行结束。可以用脚本来算一下:
# coidng = utf-8 while(1): a = raw_input() a = int(a) if ((a+4)%16>=9) or ((a+4)%16==0): print a," is true" else: print a," is false"
根据脚本算出来的数,我们输入得到flag:
memcpy@ubuntu:~$ ls memcpy.c readme memcpy@ubuntu:~$ cat readme the compiled binary of "memcpy.c" source code (with real flag) will be executed under memcpy_pwn privilege if you connect to port 9022. execute the binary by connecting to daemon(nc 0 9022). memcpy@ubuntu:~$ nc o 9022 nc: getaddrinfo: Name or service not known memcpy@ubuntu:~$ nc 0 9022 Hey, I have a boring assignment for CS class.. :( The assignment is simple. ----------------------------------------------------- - What is the best implementation of memcpy? - - 1. implement your own slow/fast version of memcpy - - 2. compare them with various size of data - - 3. conclude your experiment and submit report - ----------------------------------------------------- This time, just help me out with my experiment and get flag No fancy hacking, I promise :D specify the memcpy amount between 8 ~ 16 : 9 specify the memcpy amount between 16 ~ 32 : 21 specify the memcpy amount between 32 ~ 64 : 40 specify the memcpy amount between 64 ~ 128 : 70 specify the memcpy amount between 128 ~ 256 : 135 specify the memcpy amount between 256 ~ 512 : 265 specify the memcpy amount between 512 ~ 1024 : 520 specify the memcpy amount between 1024 ~ 2048 : 1030 specify the memcpy amount between 2048 ~ 4096 : 2055 specify the memcpy amount between 4096 ~ 8192 : 5210 ok, lets run the experiment with your configuration experiment 1 : memcpy with buffer size 9 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 1497 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 438 experiment 2 : memcpy with buffer size 21 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 384 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 411 experiment 3 : memcpy with buffer size 40 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 636 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 672 experiment 4 : memcpy with buffer size 70 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 1134 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 288 experiment 5 : memcpy with buffer size 135 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 1938 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 237 experiment 6 : memcpy with buffer size 265 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 3633 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 291 experiment 7 : memcpy with buffer size 520 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 7287 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 342 experiment 8 : memcpy with buffer size 1030 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 13860 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 441 experiment 9 : memcpy with buffer size 2055 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 27561 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 984 experiment 10 : memcpy with buffer size 5210 ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 72930 ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 2628 thanks for helping my experiment! flag : 1_w4nn4_br34K_th3_m3m0ry_4lignm3nt




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号