实验二 栈和队列
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | |
|---|---|
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | |
| 这个作业的目标 | |
| 学号 | |
| 一、 实验目的 |
- 掌握栈的结构特性及其入栈,出栈操作;
- 掌握队列的结构特性及其入队、出队的操作,掌握循环队列的特点及其操作。
二、 实验预习
说明以下概念
- 顺序栈(Sequential stack):栈的顺序存储结构简称为顺序栈;
- 链栈(Chain stack):栈的链式存储结构简称为链栈;
- 循环队列(Circular queue):向量首尾相接,这种意义下向量称为循环向量,并将循环向量中的队列称为循环队列;
- 链队列(Chain queue):队列的链式存储结构简称为链队列;
注:栈是限制仅在表的一端进行插入和删除运算的线性表。
三、 实验内容和要求
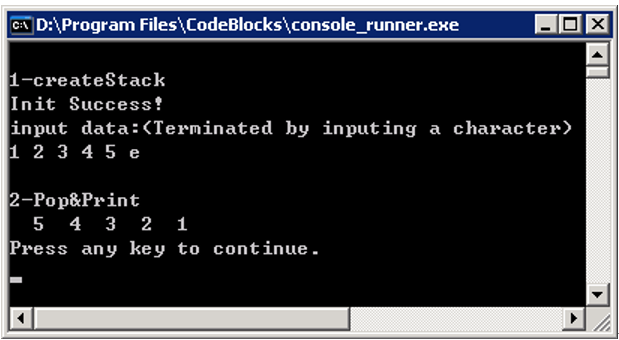
- 阅读下面程序,将函数Push和函数Pop补充完整。要求输入元素序列1 2 3 4 5 e,运行结果如下所示。
![]()
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define ERROR 0
#define OK 1
#define STACK_INT_SIZE 10 /*存储空间初始分配量*/
#define STACKINCREMENT 5 /*存储空间分配增量*/
typedef int ElemType; /*定义元素的类型*/
typedef struct{
ElemType *base;
ElemType *top;
int stacksize; /*当前已分配的存储空间*/
}SqStack;
int InitStack(SqStack *S); /*构造空栈*/
int push(SqStack *S,ElemType e); /*入栈*/
int Pop(SqStack *S,ElemType *e); /*出栈*/
int CreateStack(SqStack *S); /*创建栈*/
void PrintStack(SqStack *S); /*出栈并输出栈中元素*/
int InitStack(SqStack *S){
S->base=(ElemType *)malloc(STACK_INT_SIZE *sizeof(ElemType));
if(!S->base) return ERROR;
S->top=S->base;
S->stacksize=STACK_INT_SIZE;
return OK;
}/*InitStack*/
int Push(SqStack *S,ElemType e){
if(S->top-S->base>=S->stacksize){
S->base=(ElemType*)realloc(S->base,(S->stacksize+STACKINCREMENT)*sizeof(ElemType));
S->top=S->base+S->stacksize;
S->stacksize+=STACKINCREMENT;
}
*S->top++=e;
return 1;
}/*Push*/
int Pop(SqStack *S,ElemType *e){
if(S->top!=S->base) {
*e=*--S->top;
return OK;
}
else
return ERROR;
}/*Pop*/
int CreateStack(SqStack *S){
int e;
if(InitStack(S))
printf("Init Success!\n");
else{
printf("Init Fail!\n");
return ERROR;
}
printf("input data:(Terminated by inputing a character)\n");
while(scanf("%d",&e))
Push(S,e);
return OK;
}/*CreateStack*/
void PrintStack(SqStack *S){
ElemType e;
while(Pop(S,&e))
printf("%3d",e);
}/*Pop_and_Print*/
int main(){
SqStack ss;
printf("\n1-createStack\n");
CreateStack(&ss);
printf("\n2-Pop&Print\n");
PrintStack(&ss);
return 0;
}
算法分析:输入元素序列1 2 3 4 5,为什么输出序列为5 4 3 2 1?体现了栈的什么特性?
- 输入和输出只在栈的一端进行
- 先进后出
- 在第1题的程序中,编写一个十进制转换为二进制的数制转换算法函数(要求利用栈来实现),并验证其正确性。
实现代码:
void PrintStack(SqStack *S){
ElemType e;
while(Pop(S,&e))
printf("%3d",e);
}/*Pop_and_Print*/
void conveshen(SqStack*S){
ElemType n,h;
int m=0,k=0;
InitStack(S);
printf("Inputelement:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n){
m++;
Push(S,n%2);
n=n/2;
}
while(k<m){
k++;
Pop(S,&h);
printf("%d",h);
}
}
int main(){
SqStack S;
conveshen(&S);
printf("\n");
return ERROR;
}
验证:

3、阅读并运行程序,并分析程序功能。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<string.h>
#define M 20
#define elemtype char
typedef struct
{
elemtype stack[M];
int top;
}
stacknode;
void init(stacknode *st);
void push(stacknode *st,elemtype x);
void pop(stacknode *st);
void init(stacknode *st)
{
st->top=0;
}
void push(stacknode *st,elemtype x)
{
if(st->top==M)
printf("the stack is overflow!\n");
else
{
st->top=st->top+1;
st->stack[st->top]=x;
}
}
void pop(stacknode *st)
{
if(st->top>0) st->top--;
else printf(“Stack is Empty!\n”);
}
int main()
{
char s[M];
int i;
stacknode *sp;
printf("create a empty stack!\n");
sp=malloc(sizeof(stacknode));
init(sp);
printf("input a expression:\n");
gets(s);
for(i=0;i<strlen(s);i++)
{
if(s[i]=='(')
push(sp,s[i]);
if(s[i]==')')
pop(sp);
}
if(sp->top==0)
printf("'('match')'!\n");
else
printf("'('not match')'!\n");
return 0;
}
输入:2+((c-d)6-(f-7)a)/6
运行结果:

输入:a-((c-d)*6-(s/3-x)/2
运行结果:

程序的基本功能:
判断所输入多项式的左右括号是否配对。
以下为选做实验:
4. 设计算法,将一个表达式转换为后缀表达式,并按照后缀表达式进行计算,得出表达式得结果。
实现代码:
#define MaxSize 100
#define NUL '\0'
/*运算符栈类型*/
typedef struct{
char data[MaxSize];
int top;
}OP;
/*数值栈类型*/
typedef struct{
float data[MaxSize];
int top;
}ST;
void trans(char exp[], char postexp[])
{
char ch;
int i = 0, j = 0;
OP op;
op.top = -1;//初始化运算符栈
ch = exp[i]; i++;
while (ch != NUL)
{
switch (ch)
{
case '(':
op.top++;
op.data[op.top] = ch;
break;
case ')':
while (op.data[op.top] != '(')
{
postexp[j++] = op.data[op.top--];
}
op.top--;
break;
case '+':
case '-':
while (op.top != -1 && op.data[op.top] != '(')
{
postexp[j++] = op.data[op.top--];
}
op.top++; op.data[op.top] = ch;
break;
case '*':
case '/':
while (op.top != -1 && op.data[op.top] != '(' && (op.data[op.top] == '*' || op.data[op.top] == '/'))
{
postexp[j++] = op.data[op.top--];
}
op.top++;
op.data[op.top] = ch;
break;
case ' ':
break;//过滤掉空格
default:
while (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')
{
postexp[j++] = ch;
ch = exp[i++];
}
i--;
postexp[j++] = '#';
break;
}
ch = exp[i++];
}
while (op.top != -1)
{
postexp[j++] = op.data[op.top--];
}
postexp[j] = NUL;
}
float compvalue(char postexp[])
{
float d=0;
char ch;
int i = 0;
ST st;
st.top = -1;
ch = postexp[i++];
while (ch != NUL)
{
switch (ch)
{
case '+': //从数值栈st退栈两个运算数,相加后进入数值栈st中
st.data[st.top - 1] += st.data[st.top];
st.top--;
break;
case '-': //从数值栈st退栈两个运算数,相减后进入数值栈st中
st.data[st.top - 1] -= st.data[st.top];
st.top--;
break;
case '*': //从数值栈st退栈两个运算数,相乘后进入数值栈st中
st.data[st.top - 1] *= st.data[st.top];
st.top--;
break;
case '/': //从数值栈st退栈两个运算数,相除后进入数值栈st中
if (st.data[st.top] != 0)
st.data[st.top - 1] /= st.data[st.top];
else
{
printf("\n\t除零错误!\n");
exit(0);
}
st.top--;
break;
default:
d = 0; //将数字字符转换成对应的数值存放在d中
while (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') //判定为数字字符
{
d = 10 * d + ch - '0';
ch = postexp[i++];
}
st.top++;
st.data[st.top] = d;
break;
}
ch = postexp[i++];
}
return st.data[st.top];
}
int main()
{
char exp[MaxSize] = { "15*66-89*13+10" };
char postexp[MaxSize];
trans(exp, postexp);
float d = compvalue(postexp);
printf("%f", d);
return 0;
}

5. 假设以带头结点的循环链表表示队列,并且只设一个指针指向队尾结点(不设队头指针),试编写相应的置空队列、入队列、出队列的算法。
实现代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ERROR 0
#define OK 1
#define OVERFLOW 0
typedef int qelemType;
typedef struct queue
{
qelemType data;
struct queue *next;
}queue,*linkqueue;
typedef struct
{
linkqueue rear;
int length;
}sqqueue;
void initQueue(sqqueue &queue)//置空队列
{
queue.rear=(linkqueue)malloc(sizeof(queue));
queue.rear->next=queue.rear;
}
int emptyQueue(sqqueue &queue)//判队列是否为空
{
if(queue.rear->next==queue.rear)
return OK;
else
return 0;
}
int enqueue(sqqueue &queue,qelemType e)
{
linkqueue p;
p=(linkqueue)malloc(sizeof(queue));
if(!p)
return OVERFLOW;
p->data=e;
p->next=queue.rear->next;
queue.rear->next=p;
queue.rear=p;
return OK;
}
int delqueue(sqqueue &queue,qelemType &e)
{
linkqueue p;
if(queue.rear->next==queue.rear)
return ERROR;//若队列为空返回0
p=queue.rear->next->next;//循环链表队列队尾指针下一结点(也即头结点)的下一结点(即队头指针)
e=p->data;
queue.rear->next->next=p->next;
free(p);
//delete(p);//free函数与delete函数均可使用
return OK;
}
int main()
{
sqqueue queue2;
qelemType num;
initQueue(queue2);
if(emptyQueue(queue2))
printf("该队列目前为空!\n");
else
printf("该队列不为空!\n");
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++)
if(enqueue(queue2,i))
printf("元素%d成功入列!\n",i);
printf("\n\n");
for(int j=1;j<=9;j++)
if(delqueue(queue2,num))
printf("元素%d成功出列!\n",num);
if(emptyQueue(queue2))
printf("该队列目前为空!\n");
else
printf("该队列不为空!\n");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

四、 实验小结
本实验以栈和队列的内容为基础,利用C++软件对其相关的应用和推广进行算法实现,从而加深我们对栈和队列的理解。我们先对数据结构的栈和队列进行基础性学习,了解相关的伪代码,为后面的的算法实现奠定基础。在充分学习了栈和队列的内容后,我们对所给的代码进行初步的学习和认识,以此方便我们下一步地编码。为了代码更好地实现,我们充分地利用网络及书籍等各种资源,并进行认真学习,对每部分代码模块的内容有了一定地了解后尝试编码。
五、 评语




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号