4、python基本知识点及字符串常用方法
查看变量内存地址 id(变量名)
ni = 123
n2 = 123
ni和n2肯定是用的两份内存,但是python对于数字在-5~257之间的数字共用一份地址,范围可以修改
name = ‘李璐’
for i in name:
print(i) //将会打印出李璐
print(bytes(i,encoding='utf-8')) //把utf-8编码的字符转换成字节流
--恢复内容开始---
name1 = "wupeiqi" name2 = name1
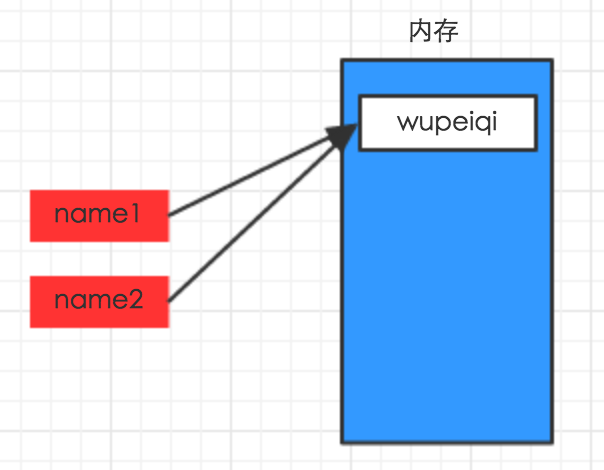
---恢复内容结束---
pycharm工具使用ctrl + / 可以批量注释
1、查看对象的类,或对象所具备的功能
temp = ‘ssss’
dir(temp) 可以字符串类所有该功能
help(temp) 或者help(type(temp))可以详细接受每种功能
class str(basestring):
"""
str(object='') -> string
Return a nice string representation of the object.
If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
"""
def capitalize(self):
""" 首字母变大写 """
def center(self, width, fillchar=None):
""" 内容居中,width:总长度;fillchar:空白处填充内容,默认无 """
def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 子序列个数 """
def decode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
""" 解码 """
def encode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
""" 编码,针对unicode """
def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None):
""" 是否以 xxx 结束 """
def expandtabs(self, tabsize=None):
""" 将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 """
‘hello\t999’ -> ‘hello 999’
def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 寻找子序列位置,如果没找到,返回 -1 """
def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format
""" 字符串格式化,动态参数,将函数式编程时细说 """
'hello {0},age {1}'.format('alex',19) -> hello alex,age 19
def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 子序列位置,如果没找到,报错 """
def isalnum(self):
""" 是否是字母和数字 """
def isalpha(self):
""" 是否是字母 """
def isdigit(self):
""" 是否是数字 """
def islower(self):
""" 是否小写 """
def isspace(self):
是否是空格
def istitle(self):
是否是标题(单词首字母是不是都大写)
def isupper(self):
是否大写
def join(self, iterable):
""" 连接 """
b是列表或者元组 a.join(b) -> 把列表 b中每个元素用a连接起来
def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None):
""" 内容左对齐,右侧填充 """
def lower(self):
""" 变小写 """
def lstrip(self, chars=None):
""" 移除左侧空白 """
def partition(self, sep):
""" 分割,前,中,后三部分 """
"""
S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)(元组)
def replace(self, old, new, count=None):
""" 替换 """
"""count表示从左往右替换多少个
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> string
def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
"""从右往左找
S.rfind(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
"""
def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None):
"""
S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> string
Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
"""
return ""
def rpartition(self, sep):
"""
S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
"""
S.rsplit([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings
从左边开始分割
def rstrip(self, chars=None):
"""把右边空白移除
S.rstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode
def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
""" 分割, maxsplit最多分割几次 """
"""
S.split([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings
def splitlines(self, keepends=False):
""" 根据换行分割 """
"""
S.splitlines(keepends=False) -> list of strings
def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None):
""" 是否已摸个字符或者字符串起始 """
"""
S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
def strip(self, chars=None):
""" 移除两段空白 """
"""
S.strip([chars]) -> string or unicode
def swapcase(self):
""" 大写变小写,小写变大写 """
def title(self):
"""
字符串”变成标题
“the sheool” -> 'The School'
def translate(self, table, deletechars=None):
"""
转换,需要先做一个对应表,最后一个表示删除字符集合
intab = "aeiou"
outtab = "12345"
trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab)
str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
print str.translate(trantab, 'xm')
"""
def upper(self):
"""
S.upper() -> string
Return a copy of the string S converted to uppercase.
"""
return ""
def zfill(self, width):
"""方法返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。"""
"""
S.zfill(width) -> string
Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
"""
return ""
def _formatter_field_name_split(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def _formatter_parser(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __contains__(self, y):
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass
def __eq__(self, y):
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __format__(self, format_spec):
"""
S.__format__(format_spec) -> string
Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec.
"""
return ""
def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y):
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getslice__(self, i, j):
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __ge__(self, y):
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y):
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __hash__(self):
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __init__(self, string=''): # known special case of str.__init__
"""
str(object='') -> string
Return a nice string representation of the object.
If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __len__(self):
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y):
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y):
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, n):
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y):
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self):
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, n):
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass
def __sizeof__(self):
""" S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """
pass
def __str__(self):
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号