深入理解TCP协议及其源代码
一、TCP简介
1. TCP的概念
传输控制协议(TCP,Transmission Control Protocol)是一种面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的传输层通信协议。应用层向TCP层发送用于网间传输的、用8位字节表示的数据流,然后TCP把数据流分区成适当长度的报文段(MTU)。之后TCP把结果包传给IP层,由它来通过网络将包传送给接收端实体的TCP层。TCP为了保证不发生丢包,就给每个包一个序号,同时序号也保证了传送到接收端实体的包的按序接收。然后接收端实体对已成功收到的包发回一个相应的确认(ACK);如果发送端实体在合理的往返时延(RTT)内未收到确认,那么对应的数据包就被假设为已丢失将会被进行重传。TCP用一个校验和函数来检验数据是否有错误;在发送和接收时都要计算校验和。
2.TCP三次握手过程
所谓三次握手(Three-Way Handshake)即建立TCP连接,是指建立一个TCP连接时,需要客户端和服务端总共发送3个包以确认连接的建立。在socket编程中,这一过程由客户端执行connect来触发,整个流程如下图所示:
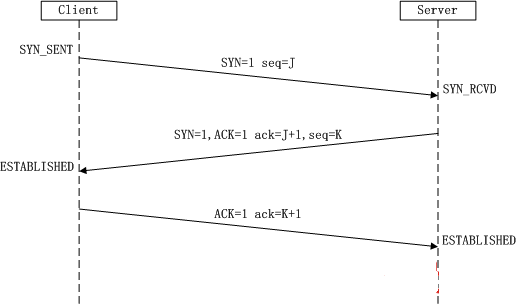
(1)第一次握手:Client将标志位SYN置为1,随机产生一个值seq=J,并将该数据包发送给Server,Client进入SYN_SENT状态,等待Server确认。
(2)第二次握手:Server收到数据包后由标志位SYN=1知道Client请求建立连接,Server将标志位SYN和ACK都置为1,ack (number )=J+1,随机产生一个值seq=K,并将该数据包发送给Client以确认连接请求,Server进入SYN_RCVD状态。
(3)第三次握手:Client收到确认后,检查ack是否为J+1,ACK是否为1,如果正确则将标志位ACK置为1,ack=K+1,并将该数据包发送给Server,Server检查ack是否为K+1,ACK是否为1,如果正确则连接建立成功,Client和Server进入ESTABLISHED状态,完成三次握手,随后Client与Server之间可以开始传输数据了。
以上是我们熟知的TCP的三次握手的过程,我们可以通过wireshark等工具来验证次过程,而我们主要想研究的是在底层socket的API层面上,TCP的三次握手到底调用了哪些API以及具体的过程到底是怎么样的。根据我们的分析,由于客户端主动发起连接,因此结合底层API我们分析出客户端和服务器端的连接过程如图所示:
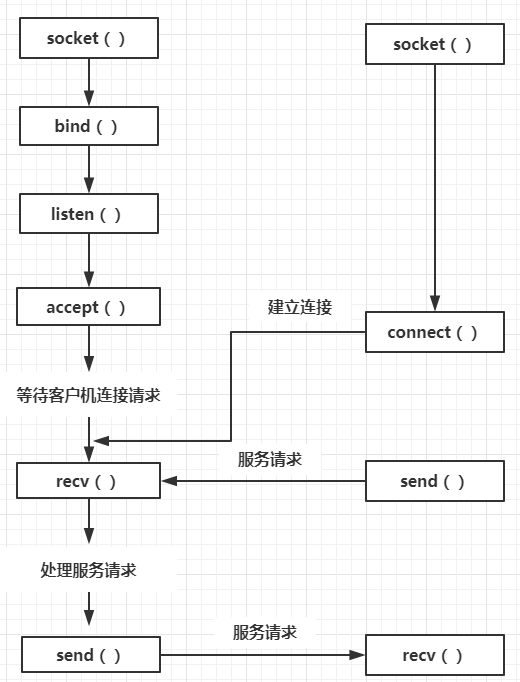
TCP协议的双方分为主动打开和被动打开,从三次握手的角度讲,主动发起握手的一方属于主动打开;被动接受握手的一方属于被动打开。客户端属于主动打开,服务器端属于被动打开。API分为两类,一类客户端和服务器端都可以调用;另一类API独属于客户端或者服务器端。
客户端和服务器端都可以调用的API:socket(), bind(), send/write(),write()/recv(),close()
独属于客户端和服务器端的API:客户端:connect(),服务器端:listen(),accept()
按照先启动server再启动client的顺序,在我们启动server端并完成server socket的建立后,按序执行了bind和listen,他们分别完成了将socket绑定到某一端口和设置此socket能够处理的请求排队的最大长度的工作。
完成上述操作后执行accept,它会一致阻塞直到有客户端的socket发起连接。启动client后,同样在先完成socket的建立后我们执行了connect这个阻塞函数,它发起和server的主动连接,连接成功后返回。也就是说,三次握手的具体过程发生在accept和connect之间。
二、跟踪分析TCP协议
1.首先客户端发送SYN报文
tcp_v4_connect函数
int tcp_v4_connect(struct sock *sk, struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len)
{
struct sockaddr_in *usin = (struct sockaddr_in *)uaddr;
struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
__be16 orig_sport, orig_dport;
__be32 daddr, nexthop;
struct flowi4 *fl4;
struct rtable *rt;
int err;
struct ip_options_rcu *inet_opt;
struct inet_timewait_death_row *tcp_death_row = &sock_net(sk)->ipv4.tcp_death_row;
return -EINVAL;
return -EAFNOSUPPORT;
inet_opt = rcu_dereference_protected(inet->inet_opt,
lockdep_sock_is_held(sk));
if (inet_opt && inet_opt->opt.srr) {
if (!daddr)
return -EINVAL;
nexthop = inet_opt->opt.faddr;
}
orig_dport = usin->sin_port;
fl4 = &inet->cork.fl.u.ip4;
rt = ip_route_connect(fl4, nexthop, inet->inet_saddr,
RT_CONN_FLAGS(sk), sk->sk_bound_dev_if,
IPPROTO_TCP,
orig_sport, orig_dport, sk);
if (IS_ERR(rt)) {
err = PTR_ERR(rt);
if (err == -ENETUNREACH)
IP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), IPSTATS_MIB_OUTNOROUTES);
return err;
}
ip_rt_put(rt);
return -ENETUNREACH;
}
daddr = fl4->daddr;
inet->inet_saddr = fl4->saddr;
sk_rcv_saddr_set(sk, inet->inet_saddr);
/* Reset inherited state */
tp->rx_opt.ts_recent = 0;
tp->rx_opt.ts_recent_stamp = 0;
if (likely(!tp->repair))
tp->write_seq = 0;
}
sk_daddr_set(sk, daddr);
if (inet_opt)
inet_csk(sk)->icsk_ext_hdr_len = inet_opt->opt.optlen;
* However we set state to SYN-SENT and not releasing socket
* lock select source port, enter ourselves into the hash tables and
* complete initialization after this.
*/
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_SYN_SENT);
err = inet_hash_connect(tcp_death_row, sk);
if (err)
goto failure;
inet->inet_sport, inet->inet_dport, sk);
if (IS_ERR(rt)) {
err = PTR_ERR(rt);
rt = NULL;
goto failure;
}
/* OK, now commit destination to socket. */
sk->sk_gso_type = SKB_GSO_TCPV4;
sk_setup_caps(sk, &rt->dst);
rt = NULL;
if (!tp->write_seq)
tp->write_seq = secure_tcp_seq(inet->inet_saddr,
inet->inet_daddr,
inet->inet_sport,
usin->sin_port);
tp->tsoffset = secure_tcp_ts_off(sock_net(sk),
inet->inet_saddr,
inet->inet_daddr);
}
return err;
if (err)
goto failure;
goto failure;
/*
* This unhashes the socket and releases the local port,
* if necessary.
*/
tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE);
ip_rt_put(rt);
sk->sk_route_caps = 0;
inet->inet_dport = 0;
return err;
2.另一头服务端accept等待连接请求
inet_csk_accept函数
/* * This will accept the next outstanding connection. */ struct sock *inet_csk_accept(struct sock *sk, int flags, int *err, bool kern) { struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk); struct request_sock_queue *queue = &icsk->icsk_accept_queue; struct request_sock *req; struct sock *newsk; int error; lock_sock(sk); /* We need to make sure that this socket is listening, * and that it has something pending. */ error = -EINVAL; if (sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN) goto out_err; /* Find already established connection */ if (reqsk_queue_empty(queue)) { long timeo = sock_rcvtimeo(sk, flags & O_NONBLOCK); /* If this is a non blocking socket don't sleep */ error = -EAGAIN; if (!timeo) goto out_err; error = inet_csk_wait_for_connect(sk, timeo); if (error) goto out_err; } req = reqsk_queue_remove(queue, sk); newsk = req->sk; if (sk->sk_protocol == IPPROTO_TCP && tcp_rsk(req)->tfo_listener) { spin_lock_bh(&queue->fastopenq.lock); if (tcp_rsk(req)->tfo_listener) { /* We are still waiting for the final ACK from 3WHS * so can't free req now. Instead, we set req->sk to * NULL to signify that the child socket is taken * so reqsk_fastopen_remove() will free the req * when 3WHS finishes (or is aborted). */ req->sk = NULL; req = NULL; } spin_unlock_bh(&queue->fastopenq.lock); } out: release_sock(sk); if (req) reqsk_put(req); return newsk; out_err: newsk = NULL; req = NULL; *err = error; goto out; }
inet_csk_wait_for_connect函数
/* * Wait for an incoming connection, avoid race conditions. This must be called * with the socket locked. */ static int inet_csk_wait_for_connect(struct sock *sk, long timeo) { struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk); DEFINE_WAIT(wait); int err; /* * True wake-one mechanism for incoming connections: only * one process gets woken up, not the 'whole herd'. * Since we do not 'race & poll' for established sockets * anymore, the common case will execute the loop only once. * * Subtle issue: "add_wait_queue_exclusive()" will be added * after any current non-exclusive waiters, and we know that * it will always _stay_ after any new non-exclusive waiters * because all non-exclusive waiters are added at the * beginning of the wait-queue. As such, it's ok to "drop" * our exclusiveness temporarily when we get woken up without * having to remove and re-insert us on the wait queue. */ for (;;) { prepare_to_wait_exclusive(sk_sleep(sk), &wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); release_sock(sk); if (reqsk_queue_empty(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue)) timeo = schedule_timeout(timeo); sched_annotate_sleep(); lock_sock(sk); err = 0; if (!reqsk_queue_empty(&icsk->icsk_accept_queue)) break; err = -EINVAL; if (sk->sk_state != TCP_LISTEN) break; err = sock_intr_errno(timeo); if (signal_pending(current)) break; err = -EAGAIN; if (!timeo) break; } finish_wait(sk_sleep(sk), &wait); return err; }
3.三次握手中携带SYN/ACK的TCP头数据的发送和接收TCP/IP协议栈初始化
inet_init函数
static __net_init int inet_init_net(struct net *net) { /* * Set defaults for local port range */ seqlock_init(&net->ipv4.ip_local_ports.lock); net->ipv4.ip_local_ports.range[0] = 32768; net->ipv4.ip_local_ports.range[1] = 60999; seqlock_init(&net->ipv4.ping_group_range.lock); /* * Sane defaults - nobody may create ping sockets. * Boot scripts should set this to distro-specific group. */ net->ipv4.ping_group_range.range[0] = make_kgid(&init_user_ns, 1); net->ipv4.ping_group_range.range[1] = make_kgid(&init_user_ns, 0); /* Default values for sysctl-controlled parameters. * We set them here, in case sysctl is not compiled. */ net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_default_ttl = IPDEFTTL; net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_fwd_update_priority = 1; net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_dynaddr = 0; net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_early_demux = 1; net->ipv4.sysctl_udp_early_demux = 1; net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_early_demux = 1; #ifdef CONFIG_SYSCTL net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_prot_sock = PROT_SOCK; #endif /* Some igmp sysctl, whose values are always used */ net->ipv4.sysctl_igmp_max_memberships = 20; net->ipv4.sysctl_igmp_max_msf = 10; /* IGMP reports for link-local multicast groups are enabled by default */ net->ipv4.sysctl_igmp_llm_reports = 1; net->ipv4.sysctl_igmp_qrv = 2; return 0; }
4.服务端接收客户端发来的SYN,发送SYN+ACK
tcp_v4_do_rcv函数
* The socket must have it's spinlock held when we get * here, unless it is a TCP_LISTEN socket. * * We have a potential double-lock case here, so even when * doing backlog processing we use the BH locking scheme. * This is because we cannot sleep with the original spinlock * held. */ int tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) { struct sock *rsk; if (sk->sk_state == TCP_ESTABLISHED) { /* Fast path */ struct dst_entry *dst = sk->sk_rx_dst; sock_rps_save_rxhash(sk, skb); sk_mark_napi_id(sk, skb); if (dst) { if (inet_sk(sk)->rx_dst_ifindex != skb->skb_iif || !dst->ops->check(dst, 0)) { dst_release(dst); sk->sk_rx_dst = NULL; } } tcp_rcv_established(sk, skb); return 0; } if (tcp_checksum_complete(skb)) goto csum_err; if (sk->sk_state == TCP_LISTEN) { struct sock *nsk = tcp_v4_cookie_check(sk, skb); if (!nsk) goto discard; if (nsk != sk) { if (tcp_child_process(sk, nsk, skb)) { rsk = nsk; goto reset; } return 0; } } else sock_rps_save_rxhash(sk, skb); if (tcp_rcv_state_process(sk, skb)) { rsk = sk; goto reset; } return 0; reset: tcp_v4_send_reset(rsk, skb); discard: kfree_skb(skb); /* Be careful here. If this function gets more complicated and * gcc suffers from register pressure on the x86, sk (in %ebx) * might be destroyed here. This current version compiles correctly, * but you have been warned. */ return 0; csum_err: TCP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_CSUMERRORS); TCP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_INERRS); goto discard; }
5 客户端收到服务端的SYN+ACK,发送ACK
tcp_rcv_synsent_state_proces函数
static int tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, const struct tcphdr *th, unsigned int len) { .. tcp_send_ack(sk); ... }
下面在MenuOS中验证三次握手过程
cd LinuxKernel cd linux-5.0.1 gdb file ./vmlinux target remote:1234 #设置断点 b __sys_socket b __sys_bind b __sys_connect b __sys_listen b __sys_accept4
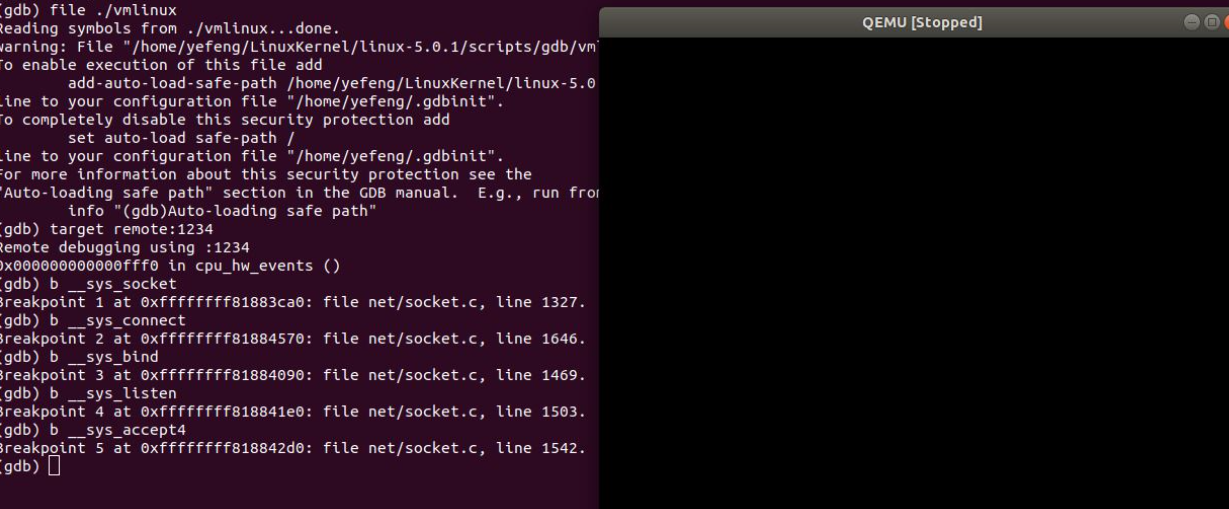
然后一直按c,直到完成一次replyhi/hello的过程
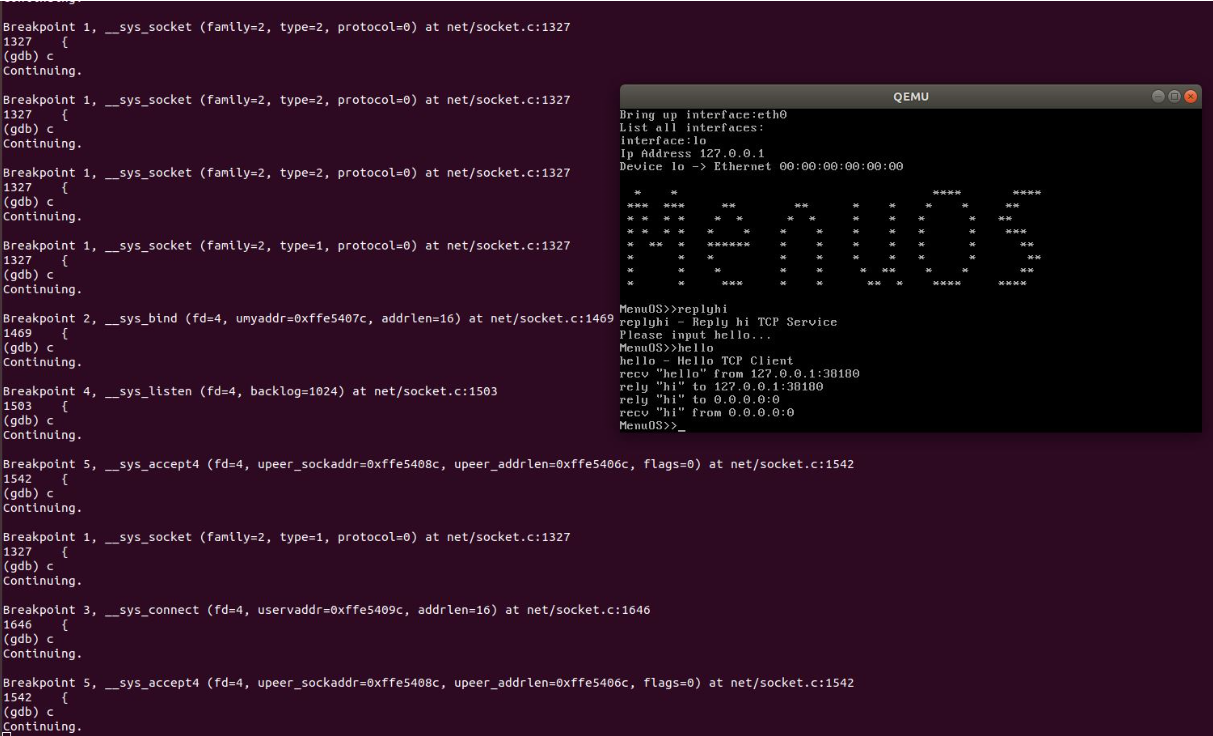
从上图中可以看到,捕捉到的断点序列为1,2,4,5,1,3分别对应着socket,bind,listen,accept,socket,connect。至此已经验证了我们之前分析的TCP三次握手在底层API上的实现过程。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号