python 中 if __name__ == "__main__": main() 的作用
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() 语句的作用
001、
[root@PC1 test]# ls script.py test.py [root@PC1 test]# cat script.py ## 测试程序script.py #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- def add(x, y): return x + y print("This will be printed when imported.") if __name__ == "__main__": ## 直接运行python脚本时,"__name__"变量会被定义未"__main__" print("Running main function") print(add(2, 3)) [root@PC1 test]# python script.py ## 测试,执行了if语句下的内容 This will be printed when imported. Running main function 5
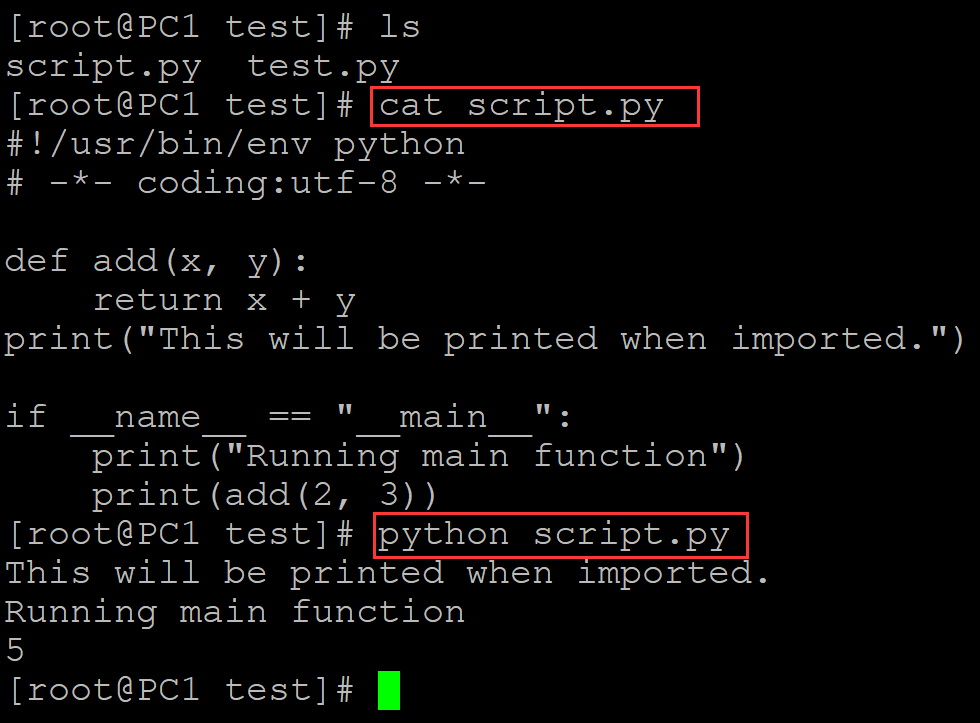
。
002、
[root@PC1 test]# ls script.py test.py [root@PC1 test]# cat script.py ## 测试脚本1 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- def add(x, y): return x + y print("This will be printed when imported.") if __name__ == "__main__": print("Running main function") print(add(2, 3)) [root@PC1 test]# cat test.py ## 测试脚本2 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import script result = script.add(10, 20) print(result) [root@PC1 test]# python test.py ## 执行测试脚本2,此时script被用作模块 This will be printed when imported. 30
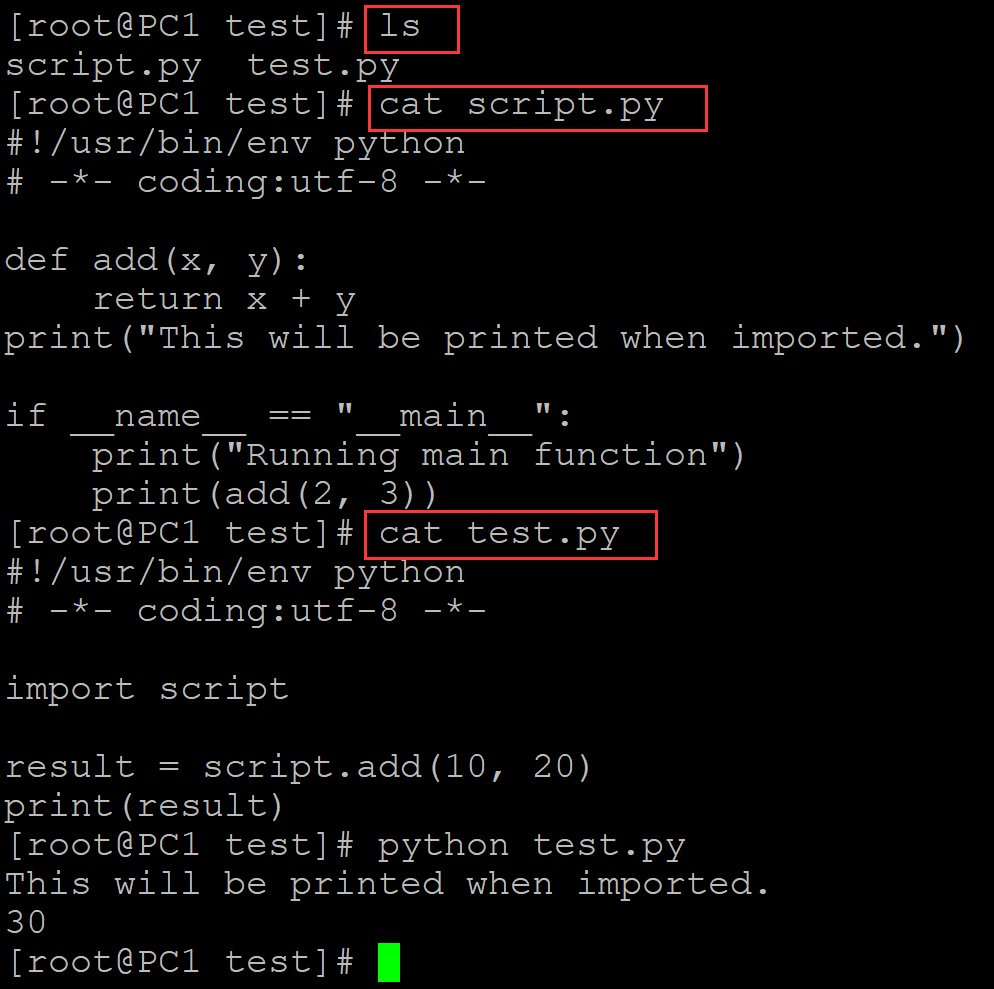
。
这样写的目的是:
01:既可以把这个脚本当作主程序运行,直接运行python脚本。
02:又可以当作模块导入而不自动执行主程序部分, 当脚本当作模块导入时,使用import时,即当把脚本当作模块使用时,调用模块时,__name__变量的内容为 脚本的名称。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号