python 中 跳过表头的实现方式
python 中 跳过表头的实现方式
001、next实现
a、
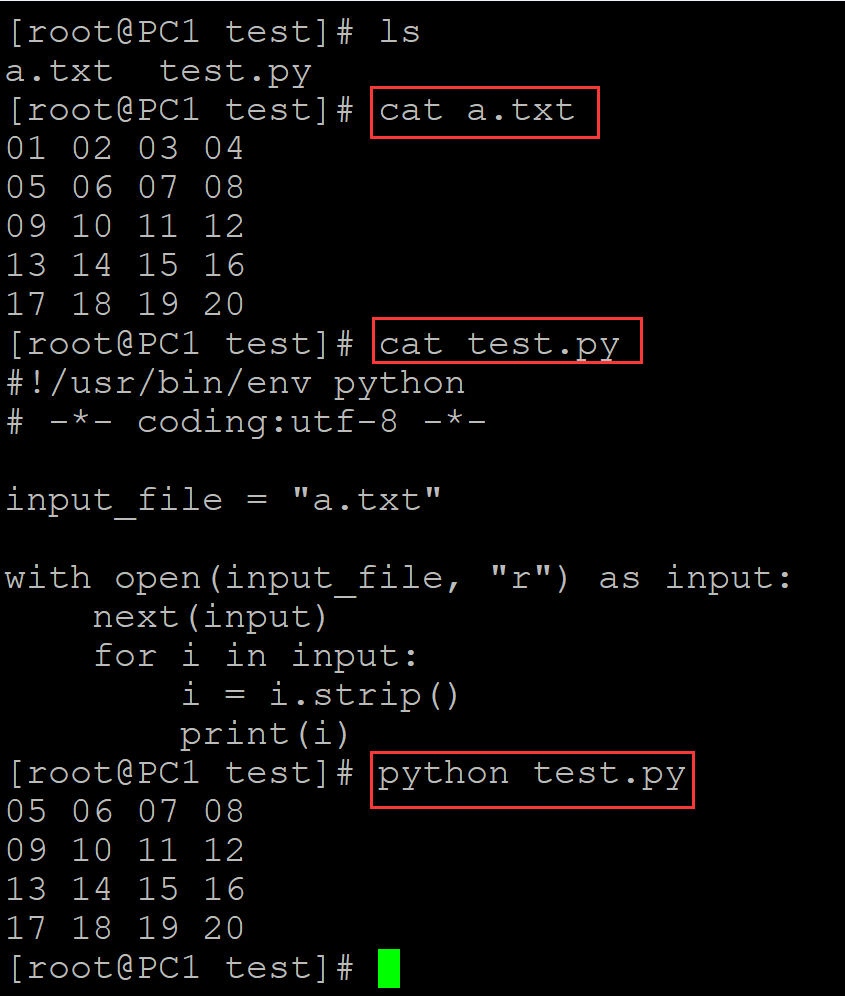
[root@PC1 test]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test]# cat a.txt ## 测试文本,假设第一行是表头 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@PC1 test]# cat test.py ## 测试程序 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- input_file = "a.txt" with open(input_file, "r") as input: next(input) ## 此处跳过第一行 for i in input: i = i.strip() print(i) [root@PC1 test]# python test.py ## 运算 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
b、
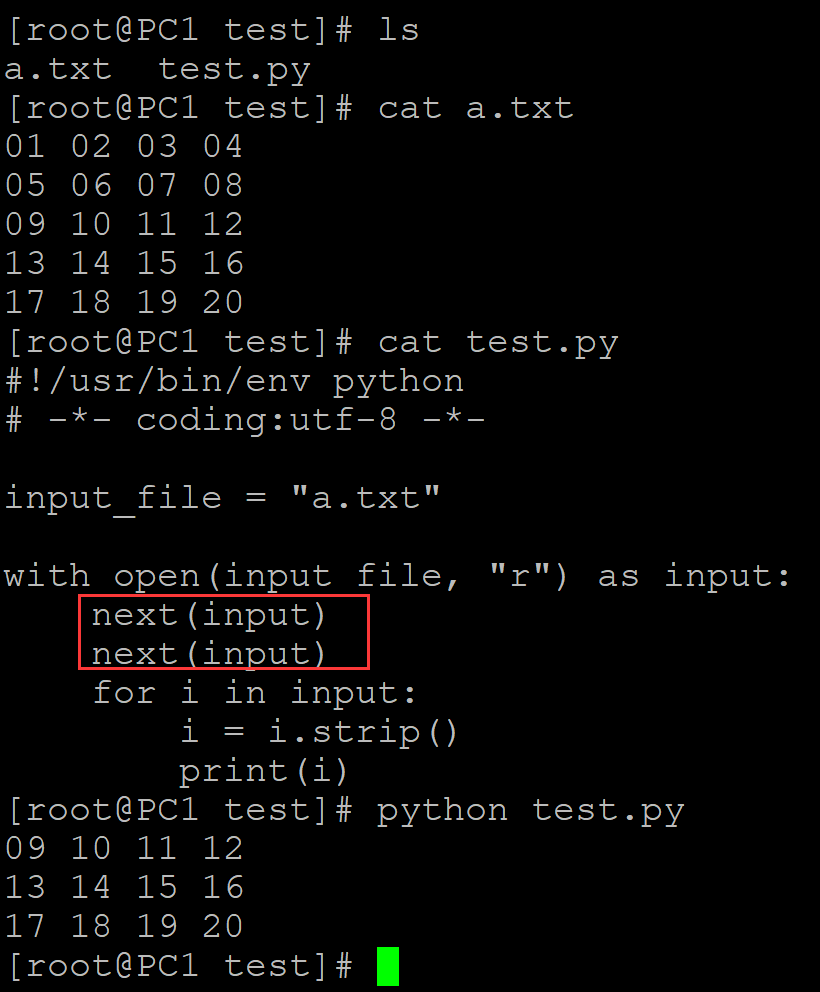
[root@PC1 test]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@PC1 test]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- input_file = "a.txt" with open(input_file, "r") as input: next(input) next(input) ## 连续使用两个next表示跳过两行 for i in input: i = i.strip() print(i) [root@PC1 test]# python test.py 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
。
002、利用readline函数实现
a、
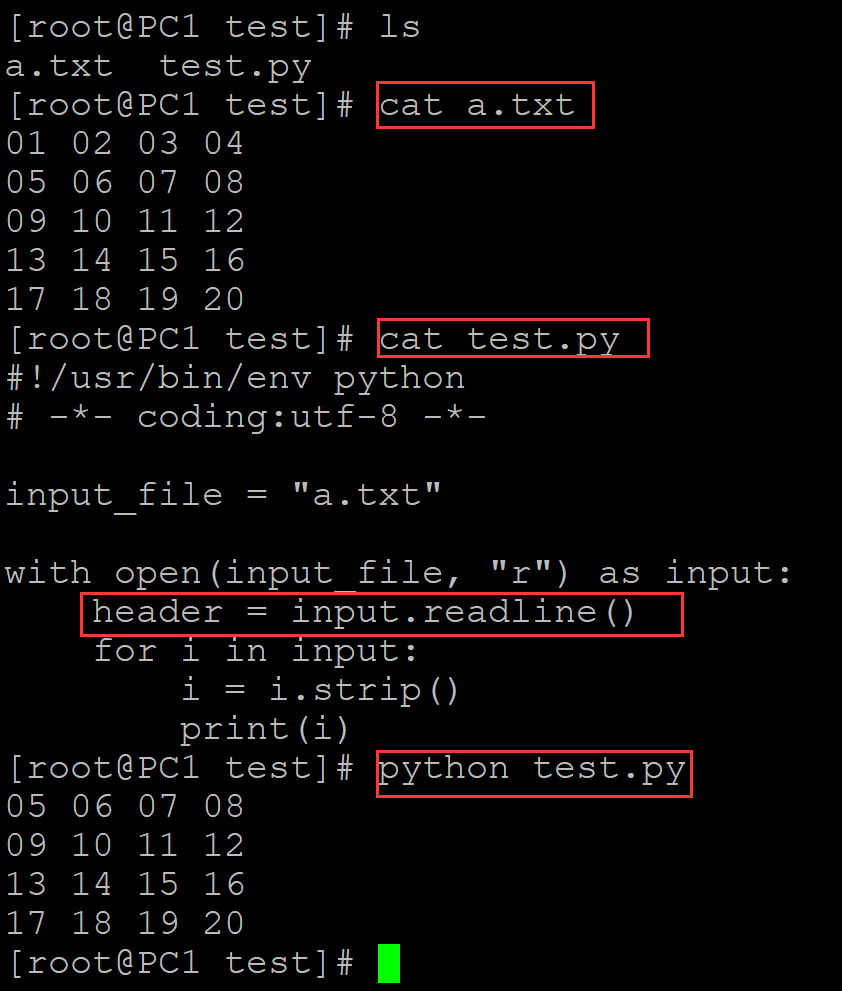
[root@PC1 test]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test]# cat a.txt ## 测试文本 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@PC1 test]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- input_file = "a.txt" with open(input_file, "r") as input: header = input.readline() ## 利用readline()函数跳过第一行 for i in input: i = i.strip() print(i) [root@PC1 test]# python test.py 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
。
b、
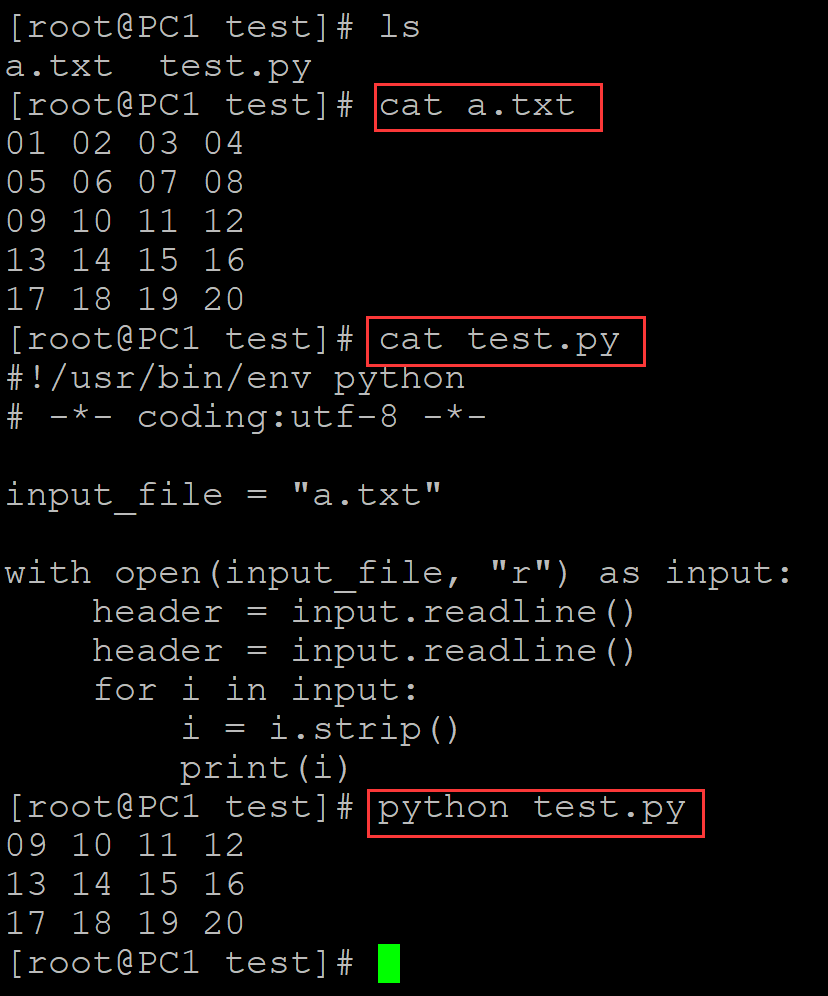
[root@PC1 test]# ls a.txt test.py [root@PC1 test]# cat a.txt 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@PC1 test]# cat test.py #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- input_file = "a.txt" with open(input_file, "r") as input: header = input.readline() header = input.readline() ## 连续跳过表头 for i in input: i = i.strip() print(i) [root@PC1 test]# python test.py 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号