c语言中存储期概念、自动存储期和静态存储期的对比
存储期可以分为两类:自动存储期和静态存储期。
自动存储期:变量的作用周期在程序块内; 在程序块中使用一般的变量声明模式即可。
静态存储期:变量的作用周期在整个程序期间; 有两种声明方式,1、在程序块外声明; 2、在程序块内使用static关键字
001、自动存储期测试
[root@PC1 test]# ls test.c [root@PC1 test]# cat test.c #include <stdio.h> void fun(void) { int x = 100; // 程序块中定义变量,存储期只在程序块内,结束变量消失 printf("x = %d\n", x++); } int main(void) { int i; for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) { fun(); // 对函数连续调用3次,结果都是100;表明程序存储期只在函数的程序块内 } return 0; } [root@PC1 test]# gcc test.c -o kkk ## 编译 [root@PC1 test]# ls kkk test.c [root@PC1 test]# ./kkk ## 测试 x = 100 x = 100 x = 100
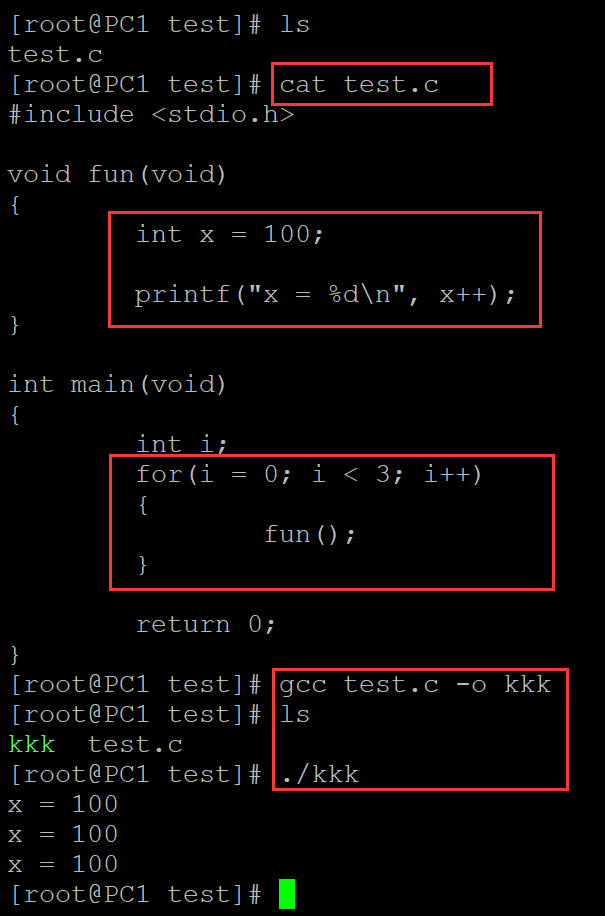
。
002、静态存储期(在程序块内使用关键字static)
[root@PC1 test]# ls test.c [root@PC1 test]# cat test.c ## 测试程序 #include <stdio.h> void fun(void) { static int x = 100; // 定义具有静态存储期的变量 printf("x = %d\n", x++); } int main(void) { int i; for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) // 函数来纳许调用3次,x的值一致在增加,说明x的存储期在整个程序的周期 { fun(); } return 0; } [root@PC1 test]# gcc test.c -o kkk ## 编译 [root@PC1 test]# ls kkk test.c [root@PC1 test]# ./kkk ## 测试 x = 100 x = 101 x = 102
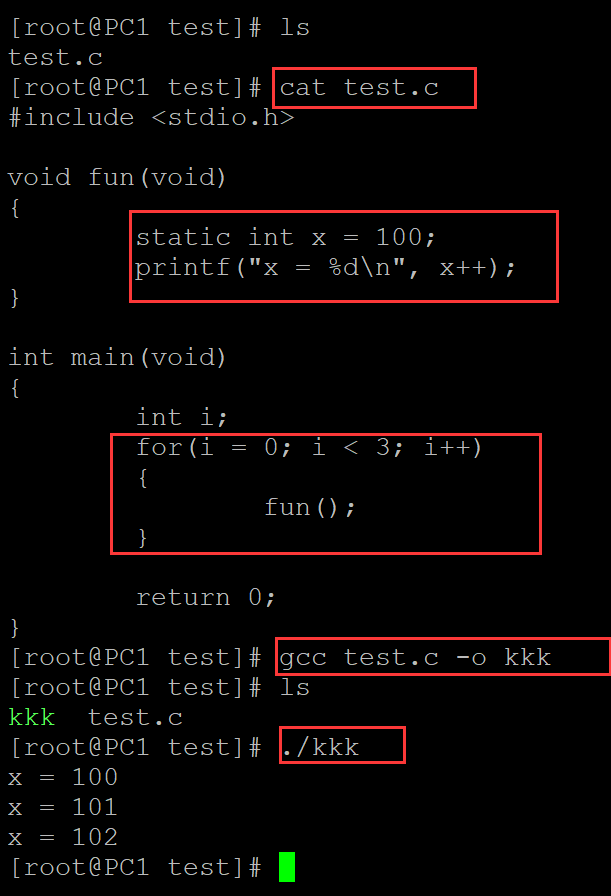
。
003、静态存储期(在程序块外定义变量)
[root@PC1 test]# ls test.c [root@PC1 test]# cat test.c #include <stdio.h> int x = 100; // 在程序块外定义变量具有静态存储期 void fun(void) { printf("x = %d\n", x++); } int main(void) { int i; for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) // 连续调用函数三次 { fun(); } return 0; } [root@PC1 test]# gcc test.c -o kkk ## 编译 [root@PC1 test]# ls kkk test.c [root@PC1 test]# ./kkk ## 测试 x = 100 x = 101 x = 102
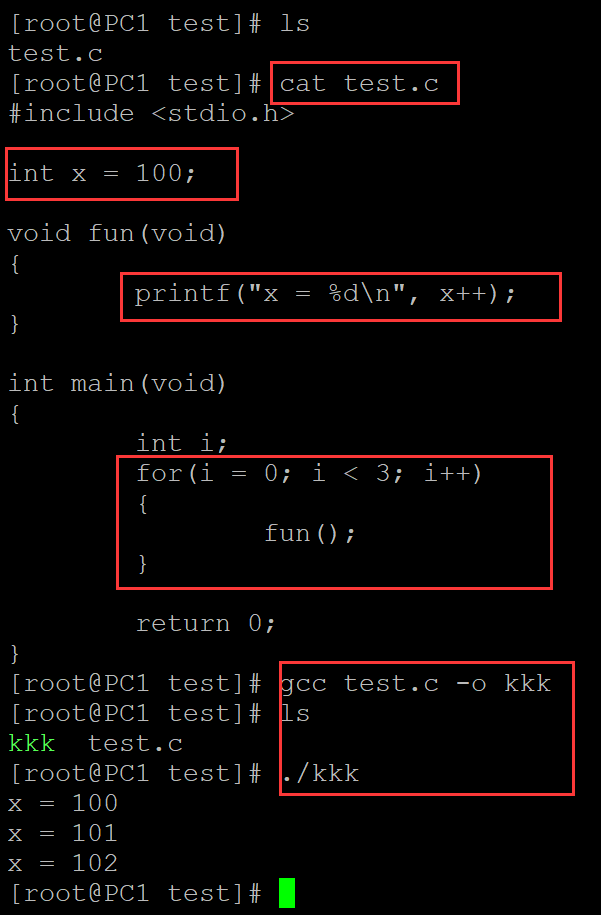
。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号