地铁最短路径完整
项目综述
提供一副地铁线路图,计算指定两站之间最短(最少经过站数)乘车路线;输出指定地铁线路的所有站点。以北京地铁为例,地铁线路信息保存在data.txt中,格式如下:
地铁线路总数
线路名1站名1站名2站名3...
线路名2站名1站名2站名3...
线路名3站名1站名2站名3...
1、需求分析
-
支持查询指定地铁线路的所有站点
-
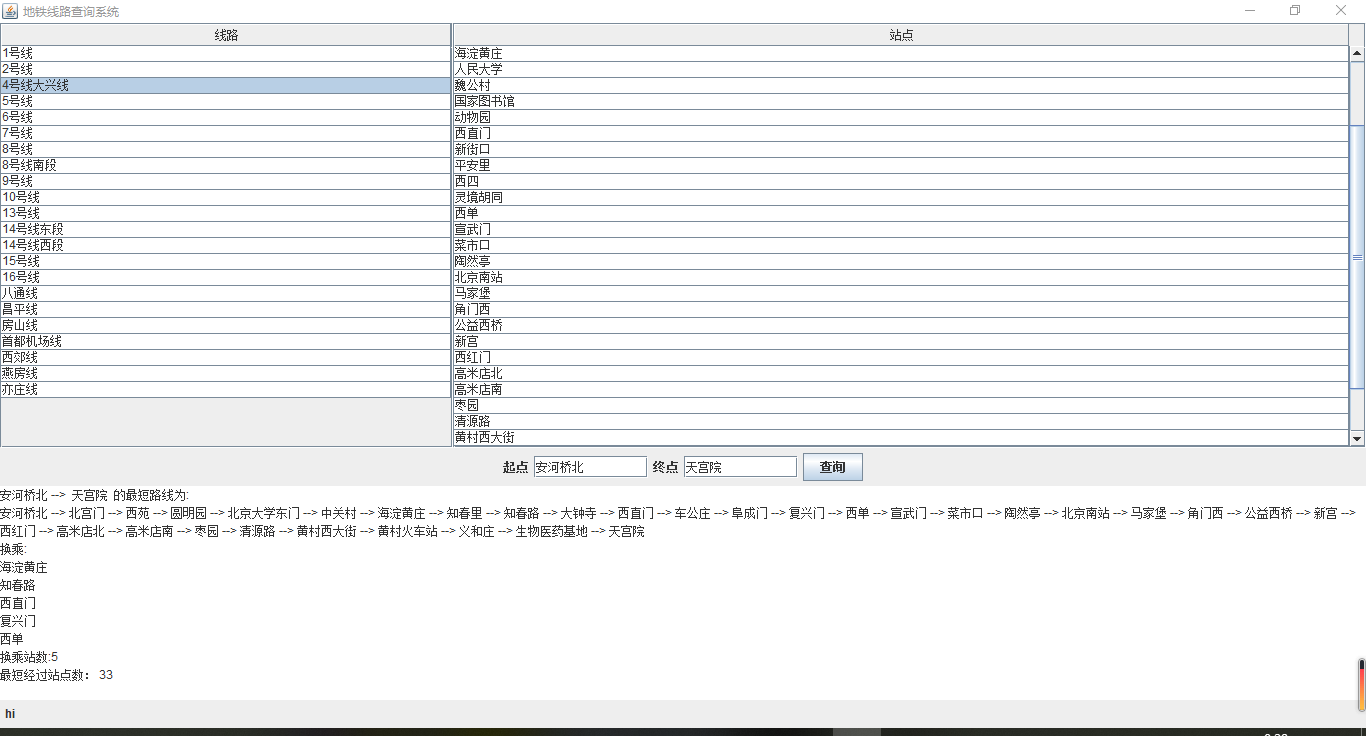
支持查询任意两站之间最短乘车路线,包含经过站名
-
能够输出换乘站点、换乘站数、乘车站数
- 能够在短时间内响应用户,输出信息
2、实现语言
Java
3、实现算法
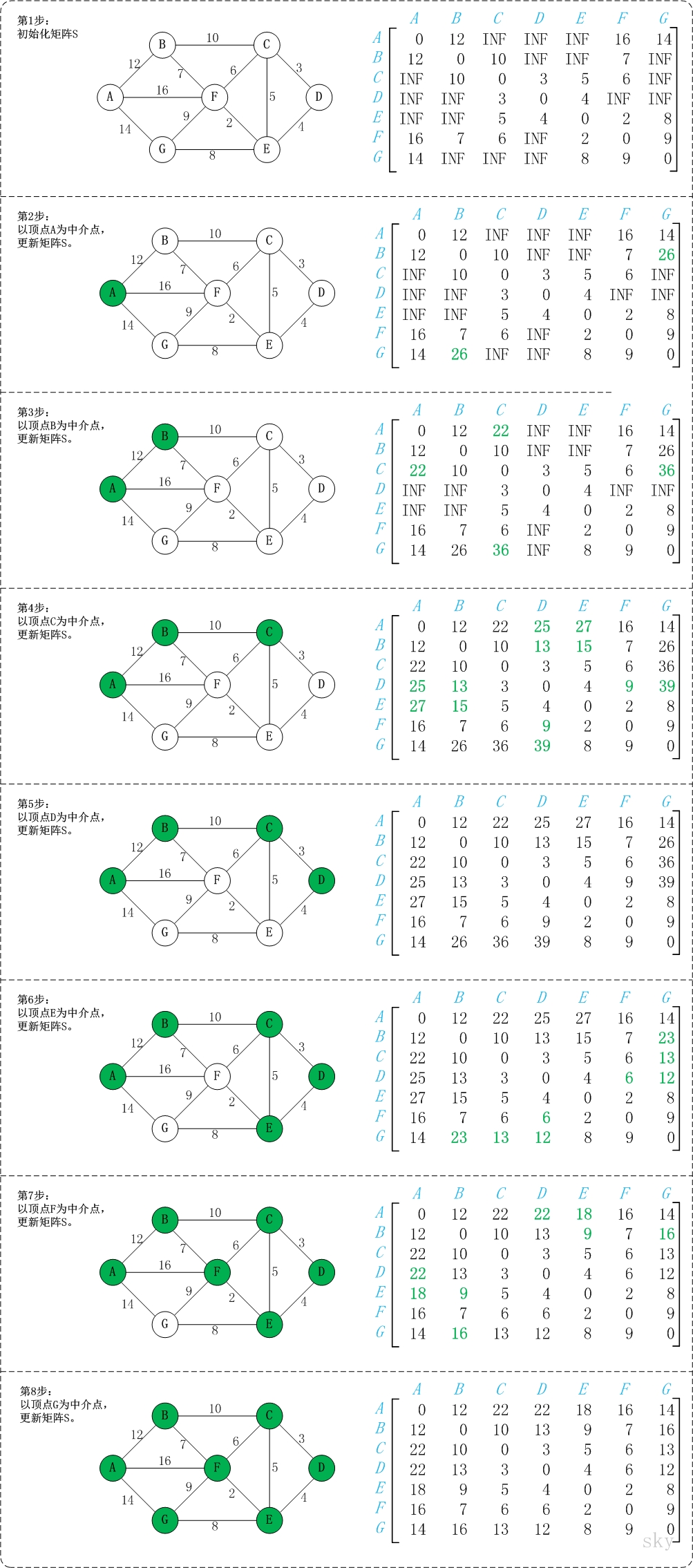
Floyd
算法介绍
弗洛伊德算法定义了两个二维矩阵:
- 矩阵D记录顶点间的最小路径
例如D[0][3]= 10,说明顶点0 到 3 的最短路径为10; - 矩阵P记录顶点间最小路径中的中转点
例如P[0][3]= 1 说明,0 到 3的最短路径轨迹为:0 -> 1 -> 3。
它通过3重循环,k为中转点,v为起点,w为终点,循环比较D[v][w] 和 D[v][k] + D[k][w] 最小值,如果D[v][k] + D[k][w] 为更小值,则把D[v][k] + D[k][w] 覆盖保存在D[v][w]中。
下图能够帮助理解概念。(参考https://blog.csdn.net/jeffleo/article/details/53349825,讲解的很好,很容易理解)
4、类职责划分
- Beanstation
private String stationname;//站点名 private List<String> stations=new ArrayList<String>();//某线路中的站点 public String getStationname() { return stationname; } public void setStationname(String stationname) { this.stationname = stationname; } public List<String> getStations() { return stations; } public void setStations(List<String> stations) { this.stations = stations; }
- lineprocess-处理线路和站点信息,建立领接领接,调用floyd-核心算法,见核心代码部分
public lineprocess(List<G> vertices)//初始化领接矩阵函数 public void edg(G start, G stop, int weight)//添加站点之间的边函数 public void floyd(int[][] Graph)//核心,floyd算法 public StringBuffer output(G start, G stop,int[][] sub,List<Beanstation> lines)//查询最短路径并输出函数
- readtxt-读入文本数据
- start-UI入口
- FrmMain-UI页面
5、核心代码
构造线路图
private static final int MAX= 999; private int[][] matirx;//地铁线路图的邻接矩阵 public List<G> vertex;//顶点 public int[][] getMatirx() { return matirx; } //初始化邻接矩阵 public lineprocess(List<G> vertices) { this.vertex = vertices; int size = this.vertex.size(); this.matirx = new int[size][size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if(i==j) this.matirx[i][j]=0; else this.matirx[i][j]=MAX; } } } public void edg(G start, G stop, int a) {//站点间的边边 int i = vertex.indexOf(start); int j = vertex.indexOf(stop); int n = matirx.length; if (i >= 0 && i < n && j >= 0 && j < n&& this.matirx[i][j] == MAX && i != j) { this.matirx[i][j] = a; this.matirx[j][i] = a; } }
- floyd算法-核心
private int[][] D = null;//顶点间的最小路径值矩阵 private int[][] P = null;//对应点的最小路径的前驱点,例如p(1,3) = 2 说明顶点1到顶点3的最小路径要经过2 private int[][][] path = null; private int[] QAQ =null; public void floyd(int[][] Graph) { int vexnum = Graph.length;//顶点数 this.D = Graph;//初始化D矩阵 this.P = new int[vexnum][vexnum]; this.QAQ = new int[vexnum]; this.path = new int[vexnum][vexnum][]; //初始化P矩阵 for (int v = 0; v < vexnum; v++) { QAQ[v] = -1; for (int w = 0; w < vexnum; w++) P[v][w] =-1; } //这里是弗洛伊德算法的核心部分 //k为中间点 for (int k = 0; k < vexnum; k++) { //v为起点 for (int v = 0; v < vexnum; v++) { //w为终点 for (int w = 0; w < vexnum; w++) { if (D[v][w] > D[v][k] + D[k][w]) { D[v][w] = D[v][k] + D[k][w];//更新最小路径 P[v][w] = k;//更新最小路径中间顶点 } } } } //v->w的路径 for (int v = 0; v < vexnum; v++) { int[] lenth = new int[1];//经过的点数 for (int w = 0; w < vexnum; w++) { lenth[0] = 0; //起点为v QAQ[lenth[0]++] = v; resultpath(P, v, w, QAQ, lenth);// 更新QAQ path[v][w] = new int[lenth[0]]; for (int s = 0; s < lenth[0]; s++) path[v][w][s] = QAQ[s]; } } } // 输出v到w的路径 private void resultpath(int[][] P, int v, int w, int[] QAQ, int[] lenth) { if (v == w) return ; if (P[v][w] == -1) QAQ[lenth[0]++] = w; else { resultpath(P, v, P[v][w], QAQ, lenth); resultpath(P, P[v][w], w, QAQ, lenth); } }
- 读取数据
public class readtxt { public List<Beanstation> txt(String data) throws IOException{ List<Beanstation> lines=new ArrayList<Beanstation>();//存取所有线路 String fg=" ";//空格是分隔符 File file=new File(data); InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)); BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(read); String Line1 = null; //读文件 while((Line1 = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){ // 字符串分隔 Beanstation station=new Beanstation(); String route=""; String tmp[] = Line1.split(fg); route=tmp[0]; station.setStationname(route); List<String> stations=new ArrayList<>();//站点集合 for(String s:tmp) stations.add(s); stations.remove(0); station.setStations(stations); lines.add(station);//在该线路中加站点 } return lines; } }
代码详见https://github.com/31803160/subway
6、测试用例
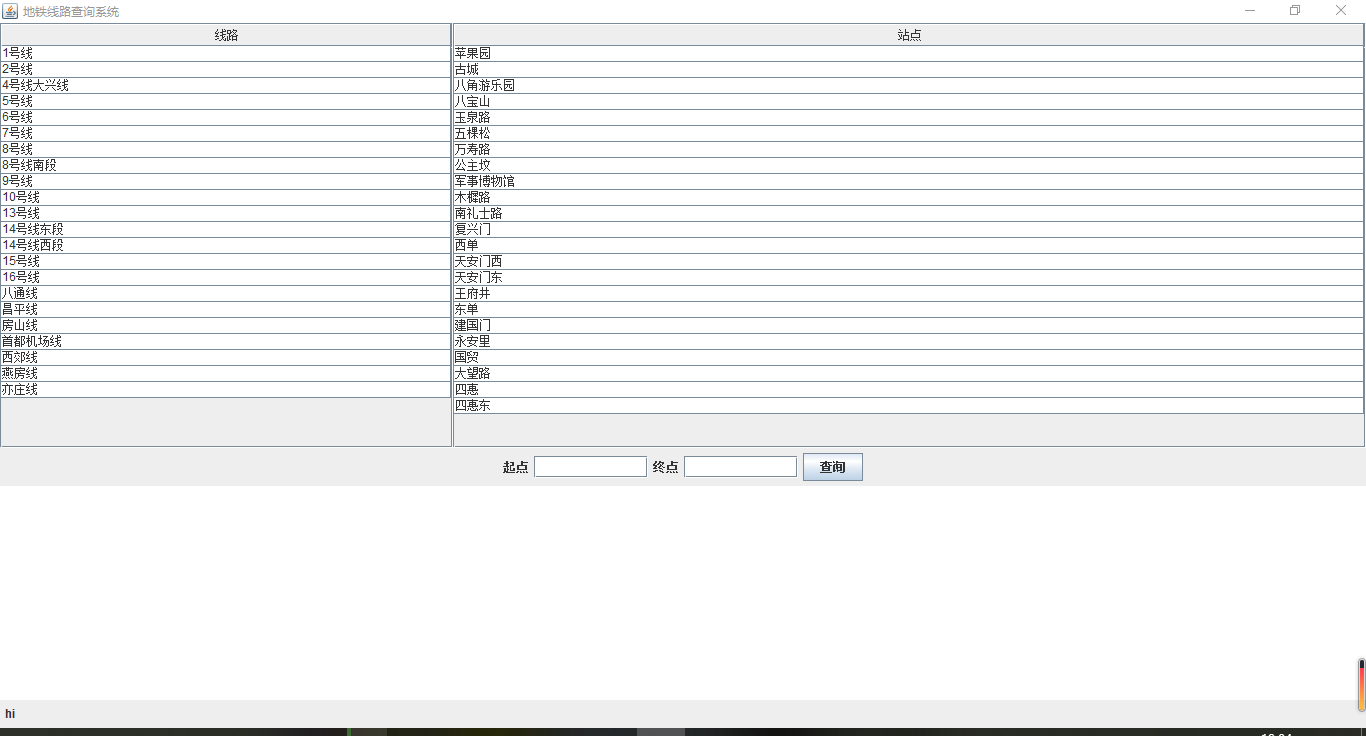
- 初始页面(默认显示1号线站点)
![]()
- 查看某路线中的所有站点
![]()
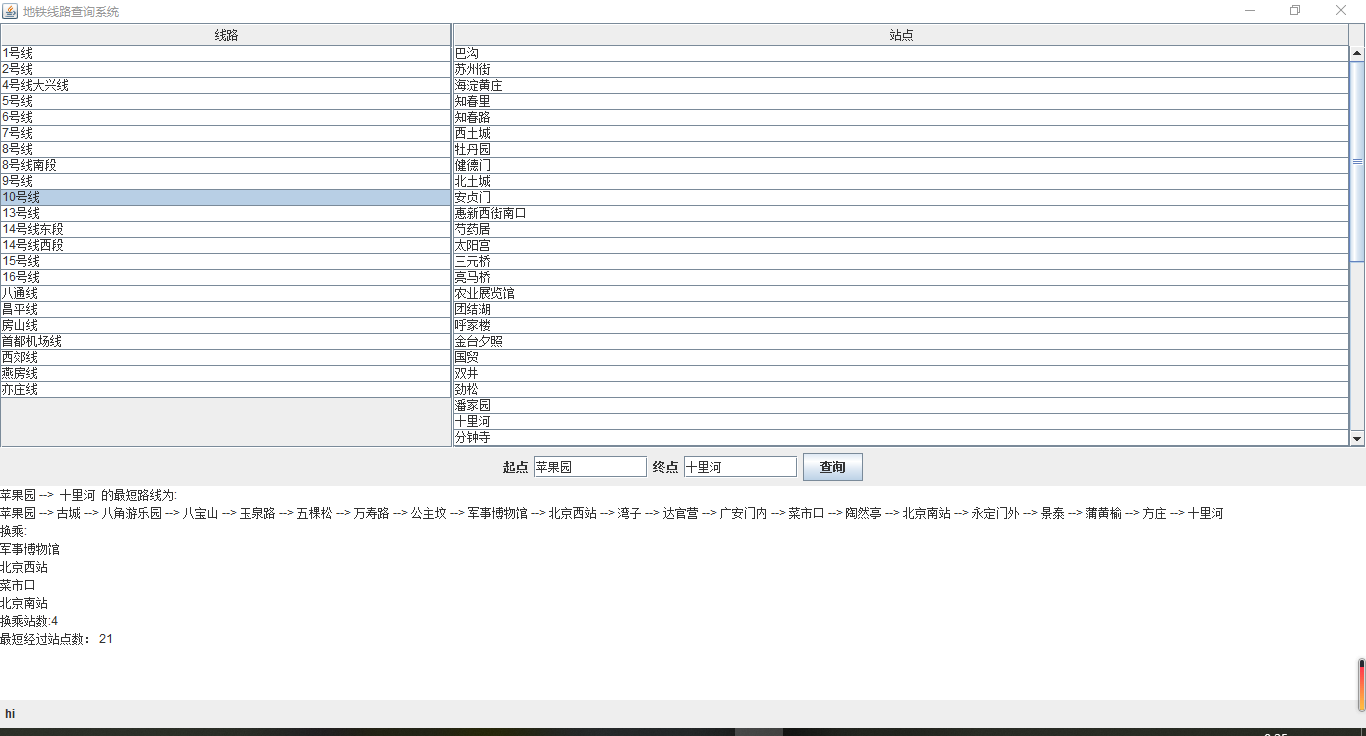
- 任意两点线路查询
![]()
![]()
- 同一条线
![]()
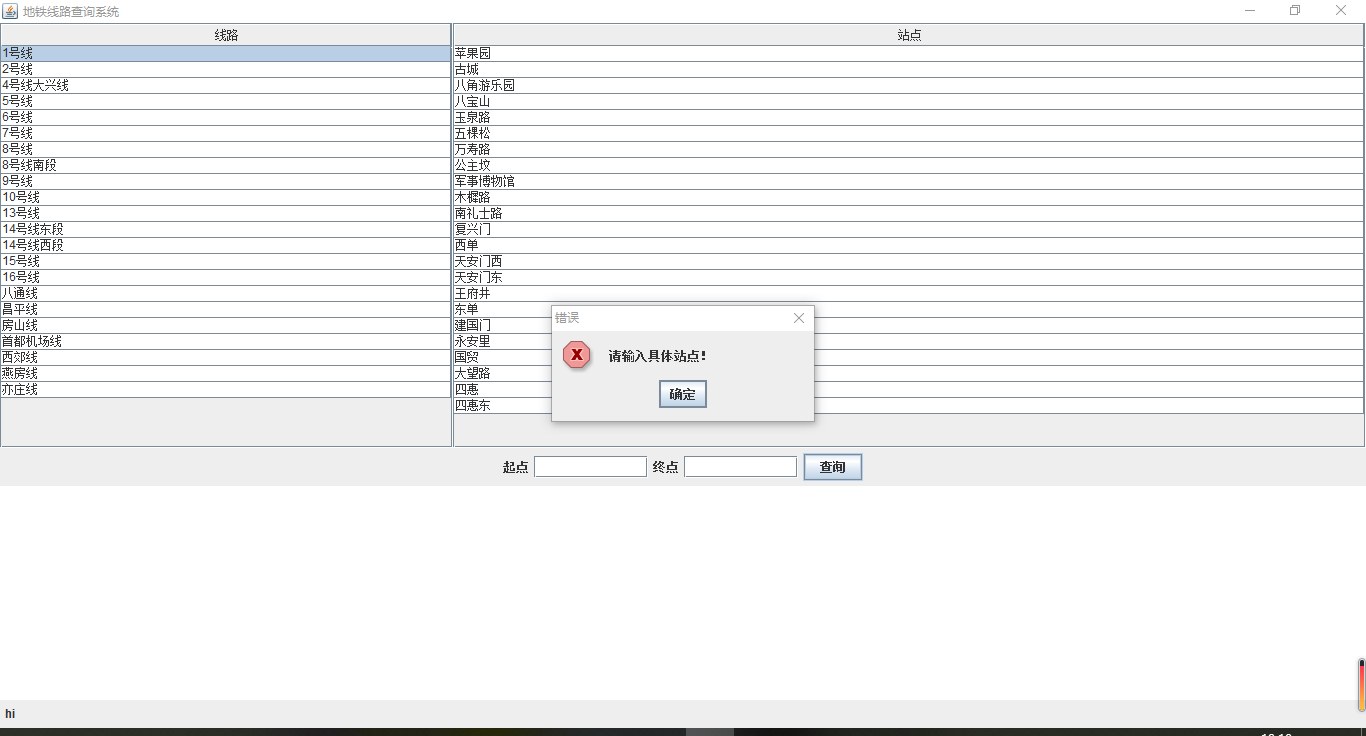
- 输入为空
![]()
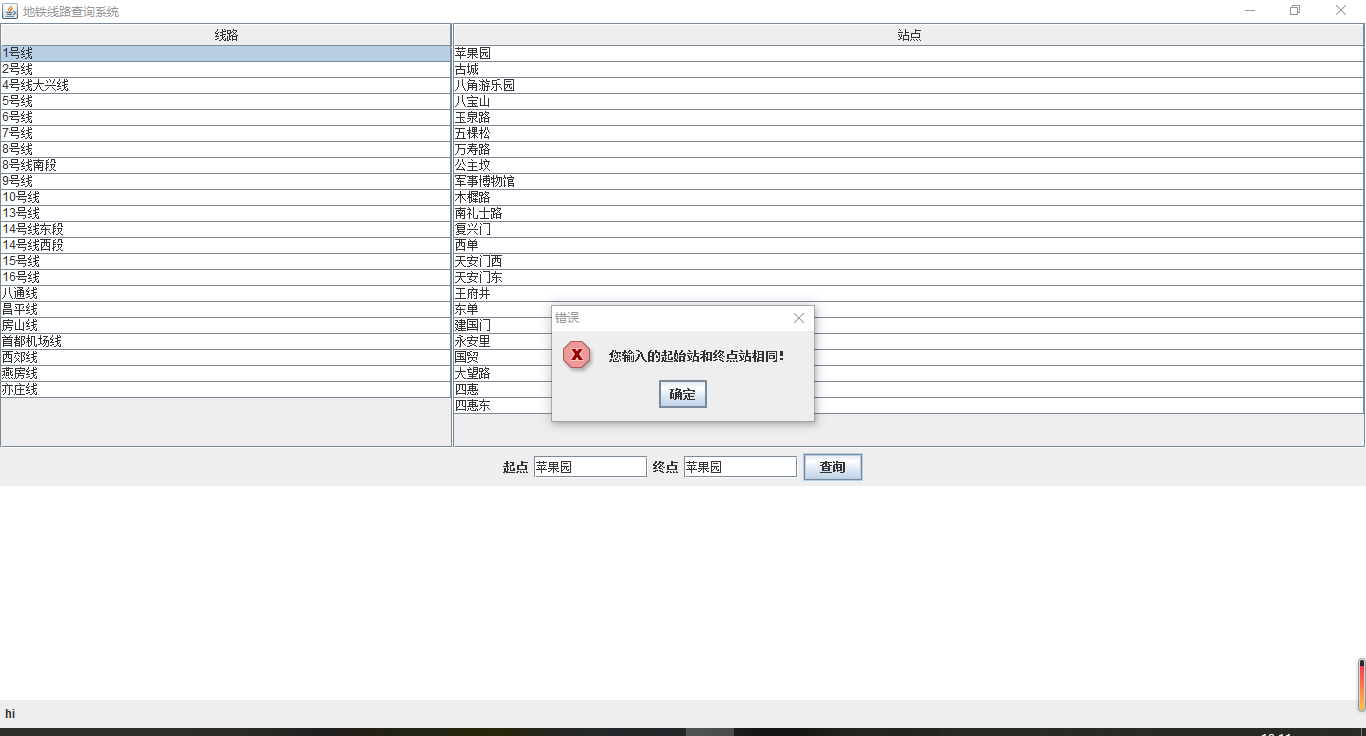
- 起点终点相同
![]()
- 输入站点不存在
![]()
7、个人总结
了解了写一个小项目的大致流程以及如何呈现在博客上。
学习了Floyd算法,CSDN上有很多讲解的很好的博客非常值得学习。
认清自己,适当放弃。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号