排序算法:heap sort(含heap介绍,python)
heap介绍
binary heap可以被看成是一种接近完成的binary tree。可以分为max-heap和min-heap,max-heap的parent要比children大,min-heap相反。
通常用array A构成的heap中,有两个基本的特性:1. A.length,给出了阵列中的元素个数。2. A.heap-size,给出阵列中在heap中的元素。
这两者的区别是,A.heap-size中的才是在heap里的,A.length的长度可能还包含了其他的很多元素。
这个可以在之后的代码中可以看见。比如有一个list有8个元素,但只有前7个元素在heap里,满足heap的特性,则A.length=8, A.heap-size=7。
heap与array的示意图如下。

一些特性:
-
对于每个节点,要想知道其父与子,有以下关系:
PARENT(i)
return[i/2]
LEFT(i)
return[2i]
RIGHT(i)
return(2i+1)
注意,这里的i是从1开始的,在实际写代码是,一般的list序列都是从0开始,要注意两者之间的不同。这个在之后的代码中会有体现。 -
要把一个A[1...n]转化成heap,在A([n/2]+1...n)中的所有元素都是heap的叶子。
-
保持max-heap特性的操作

这个函数结合build Max heap 是保持整个heap特性的关键。下面讨论具体的实现方法
创建一个max heap
首先要实现从某一个节点开始的max heap
算法如下:

此过程的时间复杂度为o(logn)
在此基础上,建立一个max heap的算法如下:

此过程的时间复杂度为o(nlogn)
heap的priority-queue运算
prority-queue是一种数据结构,它的每一个元素都有一个key值,主要有以下几种运算,其使用heap实现的算法如下。
插入一个元素

此过程的时间复杂度为o(logn)
增加一个元素的值

此过程的时间复杂度为o(logn)
提取最大元素

此过程的时间复杂度为o(logn)
从中可以看到heap的一个重要特性,就是它可以将所有priority-queue运算在时间复杂度lgn内完成。
heap的应用:heap sort
整个过程分为
- 建立heap
- 提取最大值
- 放在序列最后
- 重复指导排序完成
具体算法如下:
![]()
实现
#heap
class heap(object):
def __init__(self,A):
"""
A is a list
"""
# self.list = [0]
self.list = A[:]
# self.list.insert(0,0)
self.heapsize = len(A)
# self.ismaxheap = False
self.build_max_heap()
def __str__(self):
return str(self.list)
def left(self, i):
return 2*(i+1)-1
def right(self, i):
return 2*(i+1)
def parent(self, i):
return (i-1)/2
def insert(self, key):
"""
run time o(logn)
"""
self.heapsize += 1
self.list.append(-float("inf"))
self.increase_key(self.heapsize-1,key)
def increase_key(self,i,key):
"""
run time o(logn)
"""
if key < self.list[i]:
raise ValueError("new key is smaller than current key")
self.list[i] = key
while i>0 and self.list[self.parent(i)] < self.list[i]:
# print("i1="+str(i))
temp = self.list[i]
self.list[i] = self.list[self.parent(i)]
self.list[self.parent(i)] = temp
i = self.parent(i)
# print("i2="+str(i))
def max_heapify(self, i):
"""
run time: o(logn)
the key to maintain the max-heap property
"""
l = self.left(i)
r = self.right(i)
# i_m = i
# largest = 0
# print("l="+str(l)+" r="+str(r))
# print(self.heapsize)
largest = i
if l < self.heapsize:
if self.list[l] > self.list[i]:
largest = l
# print("r="+str(r)+" largest="+str(largest))
if r < self.heapsize:
if self.list[r] > self.list[largest]:
largest = r
# print("largest="+str(largest))
if largest != i:
temp = self.list[i]
self.list[i] = self.list[largest]
self.list[largest] = temp
self.max_heapify(largest)
def build_max_heap(self):
"""
run time: o(nlogn)
"""
# print(self.heapsize//2)
for i in range(self.heapsize//2-1,-1,-1):
# print(i)
self.max_heapify(i)
# self.ismaxheap = True
def extract_max(self):
"""
build a maxheap and return the max value of it(the first element)
also pop the first element out of the heap
run time o(logn)
"""
if self.heapsize < 1:
raise ValueError("heap underflow")
# if self.ismaxheap == False:
# self.build_max_heap()
maxele = self.list[0]
self.list[0] = self.list[self.heapsize-1]
self.list[self.heapsize-1] = maxele
self.heapsize -= 1
self.max_heapify(0)
return maxele
def heap_sort(self):
"""
using recurrence to impelete, can also use for loop
"""
if self.heapsize == 1:
return self.list
self.build_max_heap()
temp = self.list[0]
self.list[0] = self.list[self.heapsize-1]
self.list[self.heapsize-1] = temp
self.heapsize -= 1
self.heap_sort()
A = [3,4,5,7,1,4,9]
heap1 = heap(A)
print(heap1)
heap1.insert(2)
print(heap1)
print(heap1.heapsize)
maxele = heap1.extract_max()
print(maxele)
print(heap1)
print(heap1.heapsize)
heap1.increase_key(3,10)
print(heap1)
print(heap1.heapsize)
heap1.heap_sort()
print(heap1)
print(heap1.heapsize)

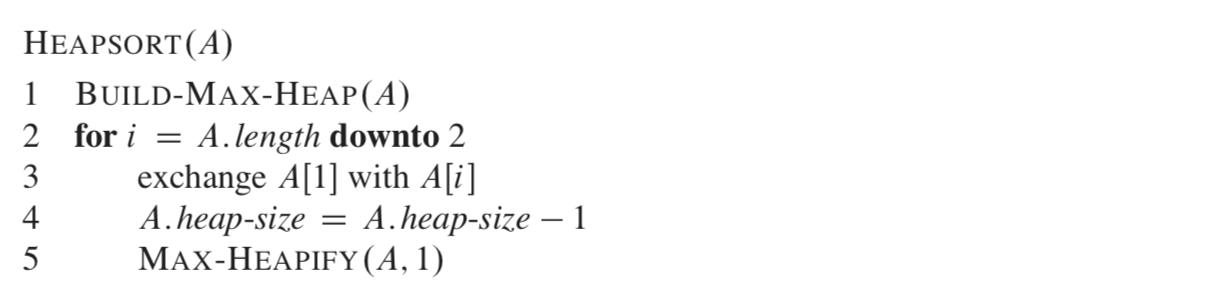

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号