前端开发随笔
前端技术栈以 Jinja2 为模板,TailwindCSS 负责样式,而 Alpine.js 则是实现所有客户端交互的“魔法棒”。Alpine.js 允许我们直接在 HTML 中编写组件逻辑,极大地简化了前端开发。
- aimap_fusion.html:三步联动的 AI 融创流程
此页面是项目的核心,它通过三个阶段——解构、构想、呈现——将用户的图片转化为全新的 AI 设计。这背后是一个清晰的状态流转和两次关键的 API 调用。
关键逻辑:fusionApp 组件逻辑
<script>
function fusionApp() {
return {
// --- 状态定义 ---
previewUrl: null, // 用于图片本地预览的 URL
file: null, // 用户上传的文件对象
isLoading: false, // “解析”阶段的加载状态
isGeneratingImage: false, // “生成视觉图”阶段的加载状态
recognitionResult: null, // 第一次 API 调用返回的“元素解构”结果
fusionDesign: null, // 第一次 API 调用返回的“融合构想”结果
generatedImageUrl: null, // 第二次 API 调用返回的最终图片 URL
// --- 方法定义 ---
// 文件处理 (选择或拖拽)
processFile(f) {
this.file = f;
this.previewUrl = URL.createObjectURL(f);
},
// 第一步:开始识别与构想
startRecognition() {
if(!this.file) return;
this.isLoading = true;
const fd = new FormData();
fd.append('file', this.file);
fetch('/api/recognize_costume', {method:'POST', body:fd})
.then(r=>r.json()).then(d=>{
if(d.success){
// 更新状态,触发 UI 变化
this.recognitionResult = d.recognition;
this.fusionDesign = d.fusion_design;
}
})
.finally(()=>this.isLoading=false);
},
// 第二步:生成视觉图
generateImage() {
this.isGeneratingImage = true;
// 从上一步的结果中获取用于生成图片的 prompt
const prompt = this.fusionDesign.image_prompt || this.fusionDesign.fusion_design;
fetch('/api/generate_costume_image', {
method:'POST',
headers:{'Content-Type':'application/json'},
body:JSON.stringify({image_prompt:prompt})
})
.then(r=>r.json()).then(d=>{
if(d.success) {
// 更新状态,显示最终生成的图片
this.generatedImageUrl = d.image_url;
}
})
.finally(()=>this.isGeneratingImage=false);
}
}
}
</script>
fusionApp 定义了清晰的状态变量,如 isLoading 和 isGeneratingImage 分别控制两个不同阶段的加载动画,recognitionResult 和 generatedImageUrl 则用于存储 API 返回的数据。当这些状态改变时,HTML 中使用 x-show 或 x-text 指令的元素会自动更新
效果图:

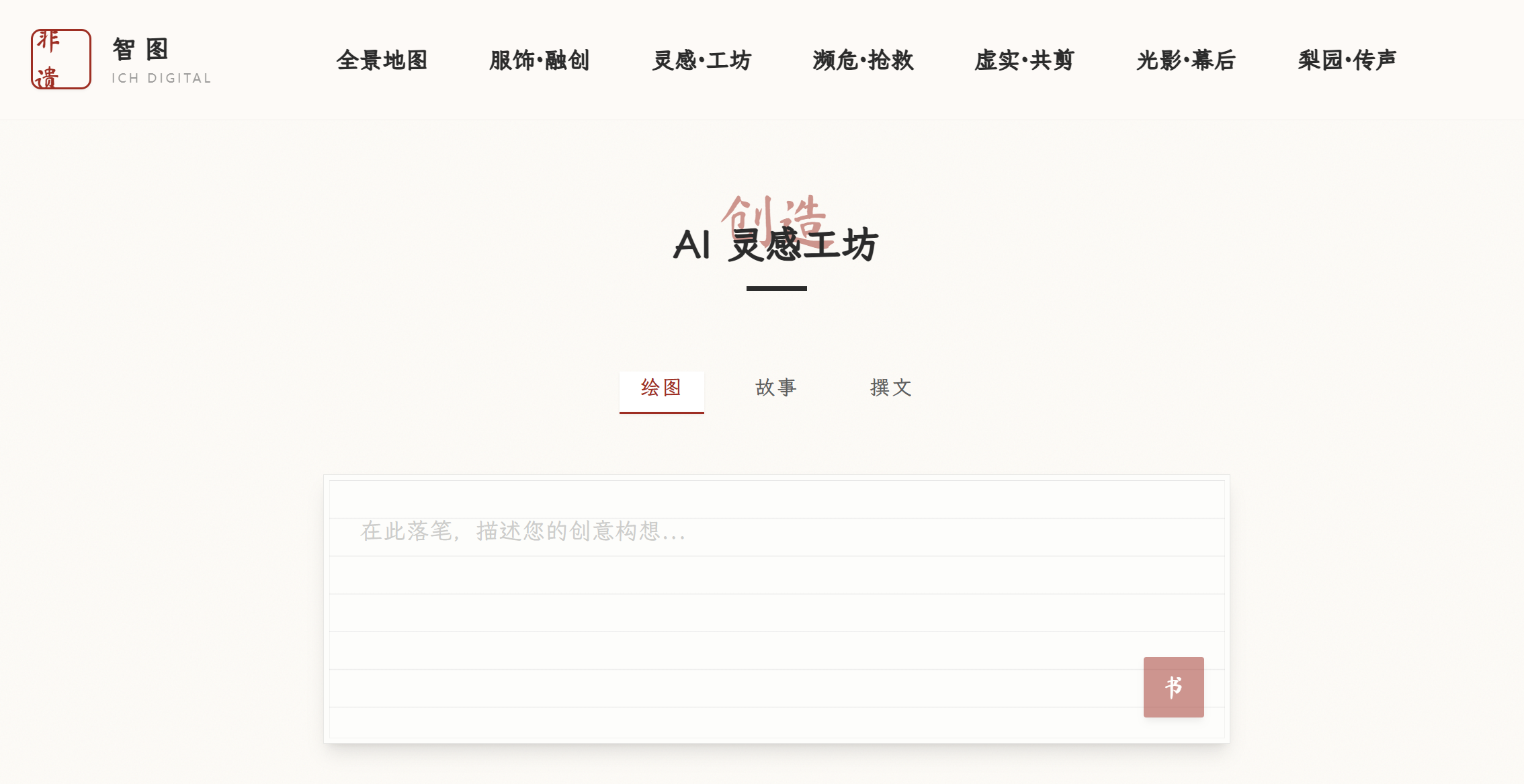
- ai_create.html:灵活的通用 AI 内容工坊
这个页面提供了一个统一的界面来处理绘图、故事和撰文三种不同的 AI 生成任务。它的精妙之处在于用同一个 API 和结果对象,通过 type 状态来区分处理逻辑和展示方式。
关键代码逻辑:
<script>
function createApp() {
return {
// --- 状态定义 ---
type: 'image', // 当前生成类型 ('image', 'story', 'copy')
prompt: '', // 用户输入的文本
loading: false, // 加载状态
result: null, // 存储 API 返回的完整结果对象
// --- 方法定义 ---
submit() {
this.loading = true;
this.result = null;
fetch('/api/ai/generate', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json'},
// 将 prompt 和 type 一同发送给后端
body: JSON.stringify({prompt: this.prompt, generation_type: this.type})
})
.then(r=>r.json())
.then(d=>{
if(d.success) {
// 直接将返回的 JSON 对象赋给 result
this.result = d;
}
})
.finally(()=>this.loading=false);
}
}
}
</script>
submit 方法将用户的 prompt 和当前的 type 一起打包发送到统一的 /api/ai/generate 接口。后端可以根据 generation_type 字段来决定调用哪个 AI 模型
效果图:
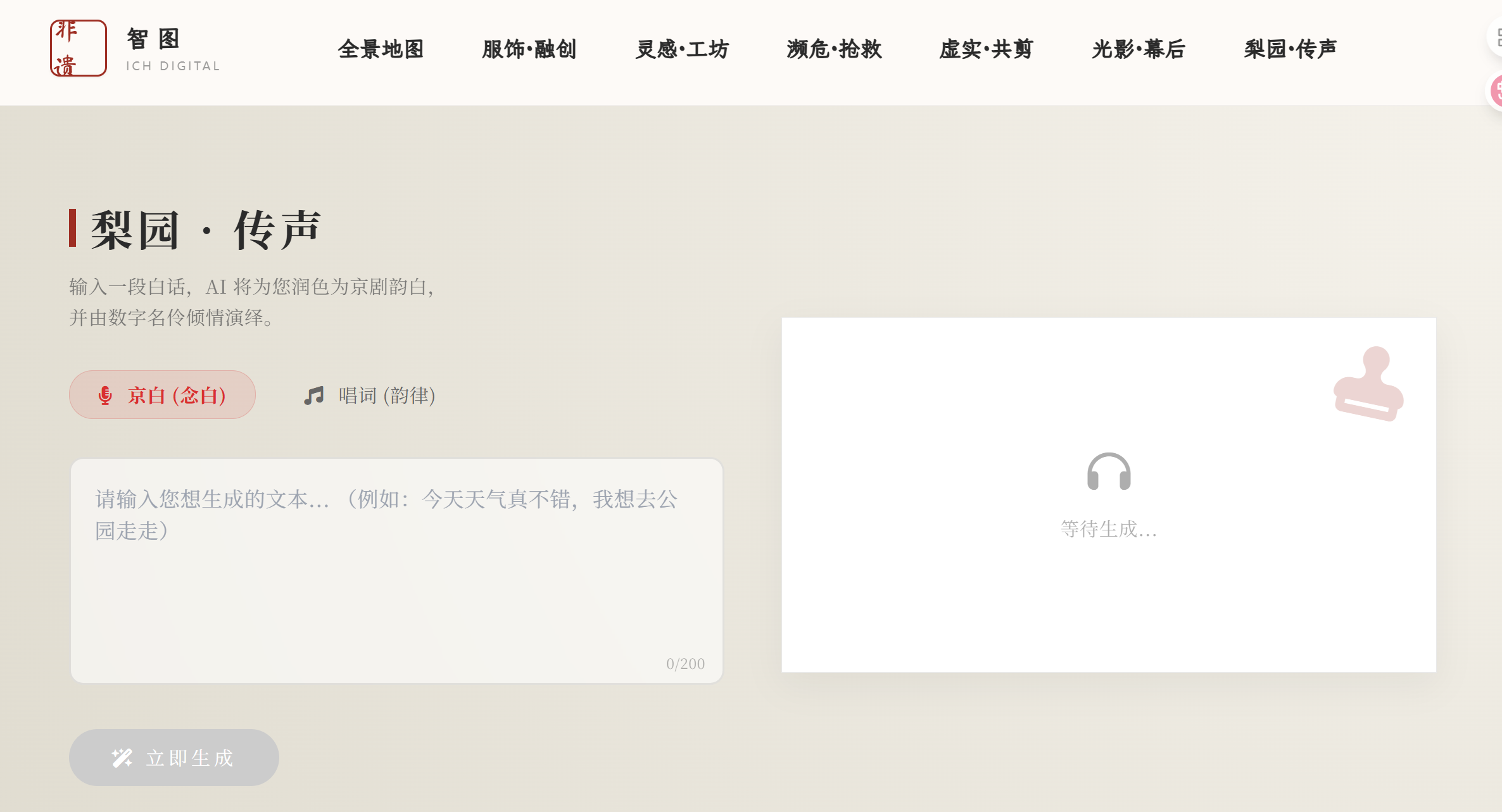
- jingju_synthesis.html:融合 AI 与音频播放
此页面实现了从文本到京剧韵白音频的转换,并内置了播放器。代码的重点在于 API 调用、音频元素 (
关键代码逻辑:
<script>
function jingjuApp() {
return {
// --- 状态定义 ---
inputText: '', // 用户输入的原文
resultText: '', // AI 润色后的京剧文本
audioUrl: '', // 生成的音频文件 URL
style: 'jingju_nianbai',// 'jingju_nianbai' 或 'jingju_changci'
isPlaying: false, // 是否正在播放
loading: false,
// --- 方法定义 ---
generateAudio() {
// ... 省略非核心代码 ...
this.loading = true;
const audio = this.$refs.audioPlayer; // 通过 x-ref 获取 audio 元素
audio.pause();
fetch('/api/jingju', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json'},
body: JSON.stringify({ text: this.inputText, prompt_style: this.style })
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.ok) {
this.resultText = data.jingju_text;
this.audioUrl = data.wav_url;
audio.src = this.audioUrl; // 设置音频源
audio.load();
audio.play().then(() => {
this.isPlaying = true; // 播放成功后更新状态
});
}
})
.finally(() => { this.loading = false; });
},
togglePlay() {
const audio = this.$refs.audioPlayer;
if (this.isPlaying) {
audio.pause();
} else {
if (this.audioUrl) audio.play();
}
// isPlaying 状态会通过 audio 元素的 @play 和 @ended 事件自动更新
}
}
}
</script>
通过在
效果图:
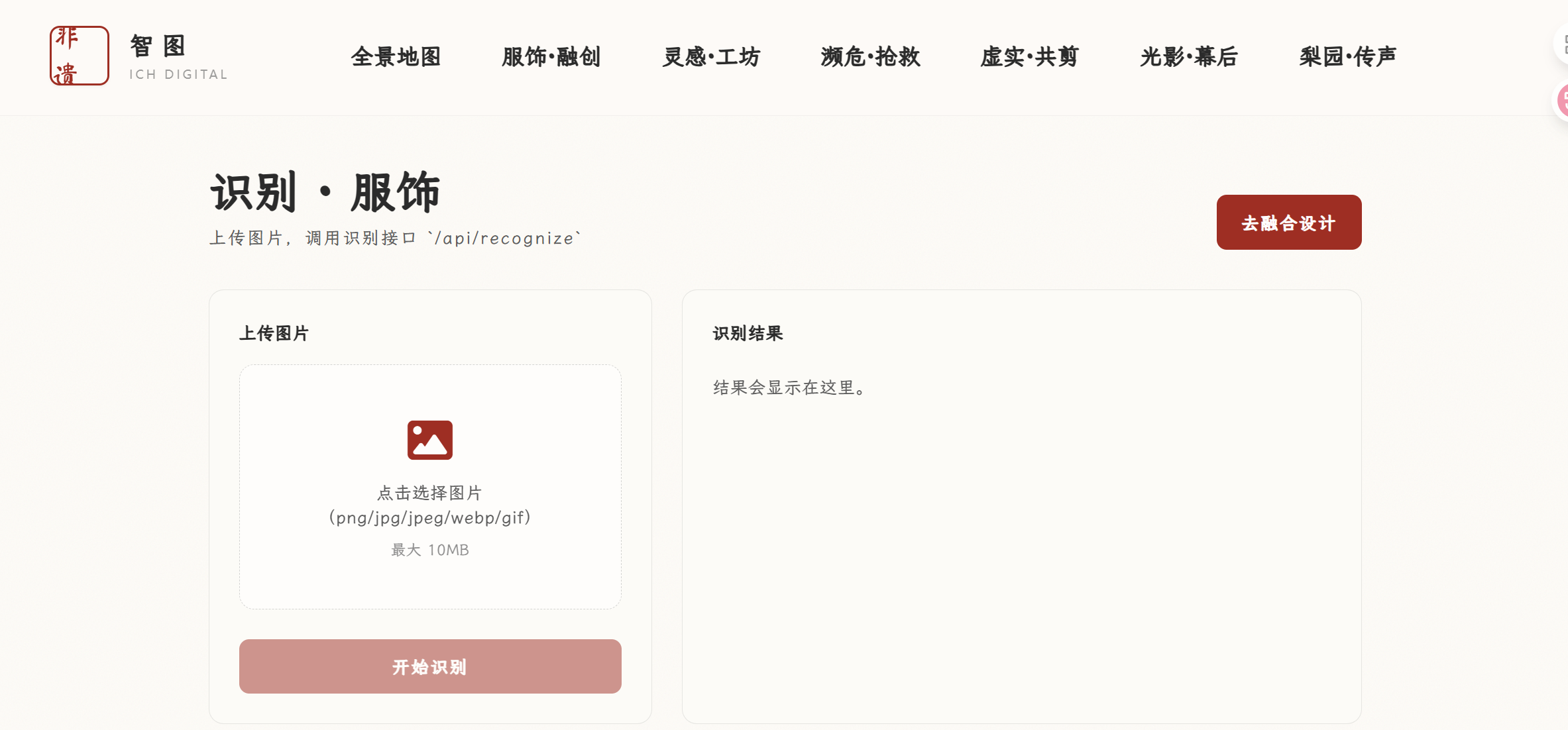
- recognize.html:纯粹的 API 测试与展示
这个页面功能最直接:上传图片,调用 API,然后将返回的原始 JSON 数据完整显示。在主项目中没有展示,测试效果良好
关键代码逻辑:
<script>
function recognizeApp() {
return {
// ... 状态定义: file, previewUrl, loading, error ...
raw: null, // 用于存储完整的 API 响应 JSON
async submit() {
this.error = "";
this.raw = null;
if (!this.file) return;
this.loading = true;
try {
const form = new FormData();
form.append("file", this.file);
const resp = await fetch("/api/recognize", { method: "POST", body: form });
const data = await resp.json().catch(() => ({})); // 防止 JSON 解析失败
if (!resp.ok || !data.success) {
this.error = (data && data.error) ? data.error : `请求失败 (HTTP ${resp.status})`;
return;
}
this.raw = data; // 将整个成功响应赋给 raw
} catch (e) {
this.error = String(e);
} finally {
this.loading = false;
}
},
// ...
}
}
</script>
结果直接存储在 raw 状态中。HTML 中使用
将其格式化后优雅地展示出来效果图:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号